概述
ReplicaManager 是 Kafka Broker 中最核心的组件之一,负责管理分区副本的完整生命周期,包括副本同步、ISR 管理、高水位更新、日志追加等关键功能。它是 Kafka 数据一致性和高可用性的基石。本文将结合源码深入解析 ReplicaManager 的设计原理和实现机制。
1. ReplicaManager 架构概览
1.1 整体架构

1.2 启动初始化
ReplicaManager 在启动时会初始化各种核心组件和定时任务:
scss
def startup(): Unit = {
scheduler.schedule("isr-expiration", () => maybeShrinkIsr(), 0L, config.replicaLagTimeMaxMs / 2) // ISR 过期检查
scheduler.schedule("shutdown-idle-replica-alter-log-dirs-thread", () => shutdownIdleReplicaAlterLogDirsThread(), 0L, 10000L) // 空闲线程清理
logDirFailureHandler = new LogDirFailureHandler("LogDirFailureHandler") // 日志目录故障处理器
logDirFailureHandler.start()
addPartitionsToTxnManager.foreach(_.start()) // 事务管理器启动
remoteLogManager.foreach(rlm => rlm.setDelayedOperationPurgatory(delayedRemoteListOffsetsPurgatory)) // 远程日志管理器配置
}源码位置 : ReplicaManager.scala:392-402
核心功能:
- 定时任务调度管理(ISR 检查、故障处理)
- 组件协调启动(日志管理器、事务管理器)
- 故障检测和恢复机制初始化
- 延迟操作管理器配置
2. 副本状态管理
2.1 Leader/Follower 状态转换
ReplicaManager 处理来自 Controller 的 LeaderAndIsr 请求,实现副本角色转换:
kotlin
def becomeLeaderOrFollower(correlationId: Int,
leaderAndIsrRequest: LeaderAndIsrRequest,
onLeadershipChange: (Iterable[Partition], Iterable[Partition]) => Unit): LeaderAndIsrResponse = {
replicaStateChangeLock synchronized {
val controllerId = leaderAndIsrRequest.controllerId
val requestPartitionStates = leaderAndIsrRequest.partitionStates.asScala
// 验证 Controller 纪元,防止过期请求
if (leaderAndIsrRequest.controllerEpoch < controllerEpoch) {
stateChangeLogger.warn(s"Ignoring LeaderAndIsr request from controller $controllerId")
leaderAndIsrRequest.getErrorResponse(Errors.STALE_CONTROLLER_EPOCH.exception)
} else {
// 处理状态转换逻辑...
}
}
}源码位置 : ReplicaManager.scala:2048-2060
核心功能:
- Controller 纪元验证,防止过期请求
- 分区角色转换协调
- 状态变更日志记录
- 并发安全的状态转换
2.2 成为 Leader 的处理流程
当 Broker 需要成为某些分区的 Leader 时,执行以下处理流程:
dart
private def makeLeaders(controllerId: Int,
controllerEpoch: Int,
partitionStates: Map[Partition, LeaderAndIsrRequest.PartitionState],
correlationId: Int,
responseMap: mutable.Map[TopicPartition, Errors],
highWatermarkCheckpoints: LazyOffsetCheckpoints,
topicIds: Map[String, Uuid]): Set[Partition] = {
val partitionsToMakeLeader: mutable.Set[Partition] = mutable.Set()
try {
partitionStates.foreachEntry { (partition, partitionState) =>
try {
if (partition.makeLeader(partitionState, highWatermarkCheckpoints, topicIds(partitionState.topicName))) {
partitionsToMakeLeader += partition // 成功转换为 Leader
}
} catch {
case e: KafkaStorageException =>
stateChangeLogger.error(s"Skipped the become-leader state change due to storage error")
markPartitionOffline(partition.topicPartition) // 标记分区离线
}
}
partitionsToMakeLeader
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
partitionStates.keys.foreach { partition =>
stateChangeLogger.error(s"Error while processing LeaderAndIsr request for partition ${partition.topicPartition}", e)
}
throw e
}
}源码位置 : ReplicaManager.scala:2308-2320
核心功能:
- 停止分区的 Fetcher 线程(如果之前是 Follower)
- 更新分区元数据缓存
- 将分区添加到 Leader 分区集合
- 异常处理和分区离线标记
2.3 成为 Follower 的处理流程
当 Broker 需要成为某些分区的 Follower 时,执行以下处理流程:
dart
private def makeFollowers(controllerId: Int,
controllerEpoch: Int,
partitionStates: Map[Partition, LeaderAndIsrRequest.PartitionState],
correlationId: Int,
responseMap: mutable.Map[TopicPartition, Errors],
highWatermarkCheckpoints: LazyOffsetCheckpoints,
topicIds: Map[String, Uuid]): Set[Partition] = {
val partitionsToMakeFollower: mutable.Set[Partition] = mutable.Set()
try {
partitionStates.foreachEntry { (partition, partitionState) =>
val newLeaderBrokerId = partitionState.leader
try {
if (metadataCache.hasAliveBroker(newLeaderBrokerId)) {
if (partition.makeFollower(partitionState, highWatermarkCheckpoints, topicIds(partitionState.topicName))) {
partitionsToMakeFollower += partition // 成功转换为 Follower
}
} else {
stateChangeLogger.error(s"Cannot become follower since the new leader $newLeaderBrokerId is unavailable")
// 即使 Leader 不可用也要创建本地副本,确保高水位被包含在检查点文件中
partition.createLogIfNotExists(isNew = false, isFutureReplica = false,
highWatermarkCheckpoints, topicIds(partitionState.topicName))
}
} catch {
case e: KafkaStorageException =>
stateChangeLogger.error(s"Skipped the become-follower state change due to storage error")
}
}
partitionsToMakeFollower
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
stateChangeLogger.error(s"Error while processing LeaderAndIsr request", e)
throw e
}
}源码位置 : ReplicaManager.scala:2406-2430
核心功能:
- 验证新 Leader 的可用性
- 更新 Leader 信息并启动 Fetcher
- 创建本地日志副本
- 异常处理和状态恢复
状态转换流程图:

3. ISR 同步副本集合管理
3.1 ISR 核心概念
3.1.1 ISR 定义与作用
ISR(In-Sync Replicas,同步副本集合)是 Kafka 保证数据一致性和可用性的核心机制:
- 定义: 与 Leader 副本保持同步的副本集合
- 组成: Leader 副本 + 所有跟上进度的 Follower 副本
- 作用: 只有 ISR 中的副本才有资格被选举为新的 Leader

3.1.2 ISR 核心机制
1. 数据一致性保证
scss
if (allIsrReplicasAcknowledged(message)) {
updateHighWatermark(); // 更新高水位
makeMessageVisibleToConsumers(); // 消息对消费者可见
}核心功能:
- 只有当消息被所有 ISR 副本确认后,才会更新高水位
- 消费者只能看到高水位之前的消息,确保读取的数据不会丢失
2. Leader 选举基础
ini
Set<Integer> eligibleLeaders = currentIsr; // 只有 ISR 中的副本才能成为新 Leader
int newLeader = selectLeaderFromIsr(eligibleLeaders); // 确保新 Leader 拥有最新的已提交数据3. 动态可用性平衡
scss
if (replicaLagTime > maxLagTime) {
removeFromIsr(replicaId); // 移除滞后副本
} else if (replicaCaughtUp) {
addToIsr(replicaId); // 添加同步副本
}核心功能:
- 通过动态调整 ISR 成员,在一致性和可用性之间取得平衡
- 适应网络和性能变化
3.1.3 ISR 与其他概念的关系
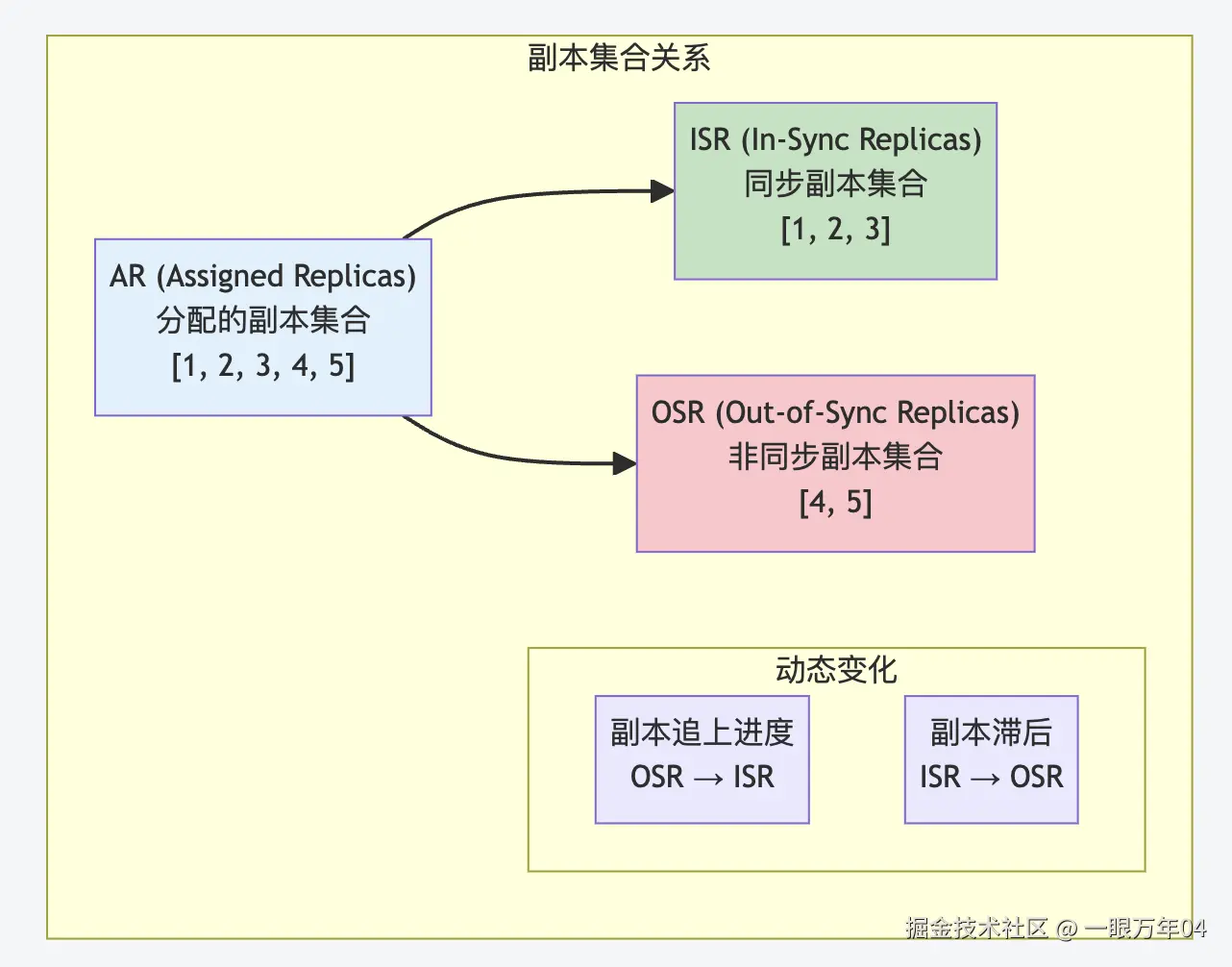
ISR vs AR(Assigned Replicas)
ISR vs 高水位的关系
csharp
long calculateHighWatermark() {
long minLeo = leaderLeo;
for (int replicaId : currentIsr) {
if (replicaId != leaderId) {
minLeo = Math.min(minLeo, getReplicaLeo(replicaId)); // 取所有 ISR 副本的最小 LEO
}
}
return minLeo; // HW = min(所有 ISR 副本的 LEO)
}核心功能:
- 高水位计算依赖于 ISR 集合
- 确保只有被所有 ISR 副本确认的消息才对消费者可见
4. Leader 纪元机制
4.1 Leader 纪元概念
Leader 纪元是 Controller 为每个分区的每任 Leader 分配的单调递增标识符,用于解决分布式系统中的"脑裂"问题和数据一致性问题。

4.2 核心功能
1. 防止数据不一致
scss
leaderLog.assignEpochStartOffset(partitionState.leaderEpoch, leaderEpochStartOffset) // 在成为 Leader 时,分配新的纪元起始偏移量源码位置 : Partition.scala:793
2. 解决"僵尸 Leader"问题
java
private def checkCurrentLeaderEpoch(remoteLeaderEpochOpt: Optional[Integer]): Errors = {
if (!remoteLeaderEpochOpt.isPresent) {
Errors.NONE
} else {
val remoteLeaderEpoch = remoteLeaderEpochOpt.get
val localLeaderEpoch = leaderEpoch
if (localLeaderEpoch > remoteLeaderEpoch)
Errors.FENCED_LEADER_EPOCH // 拒绝过期纪元的请求
else if (localLeaderEpoch < remoteLeaderEpoch)
Errors.UNKNOWN_LEADER_EPOCH // 本地纪元过期
else
Errors.NONE
}
}核心功能:
- 检查 Leader 纪元,防止过期的 Leader 继续服务
- 通过纪元比较实现分布式锁机制
3. 指导副本截断
kotlin
public class LeaderEpochTruncation {
// Follower 根据新 Leader 的纪元信息决定截断位置
// 确保只截断未提交的数据,保留已提交的数据
}核心功能:
- Leader 纪元帮助 Follower 确定正确的截断点
- 避免在 Leader 切换时丢失已提交的数据
4.3 存储和管理
Leader 纪元通过 LeaderEpochFileCache 进行存储和管理:
java
public final class LeaderEpochFileCache {
private final NavigableMap<Integer, EpochEntry> epochs = new TreeMap<>(); // 维护 (epoch -> startOffset) 的映射
public void assign(int epoch, long startOffset) {
EpochEntry entry = new EpochEntry(epoch, startOffset);
if (assign(entry)) {
log.debug("Appended new epoch entry {}. Cache now contains {} entries.", entry, epochs.size());
writeToFile(); // 持久化到磁盘
}
}
public OptionalInt epochForOffset(long offset) {
// 返回包含该偏移量的纪元
// 用于副本同步时的一致性检查
}
}源码位置 : LeaderEpochFileCache.java
核心功能:
- Leader 纪元缓存管理
- 纪元到偏移量的映射维护
- 持久化存储到磁盘
- 副本同步时的一致性检查
Leader 纪元在故障恢复中的作用:

3.2 ISR 动态管理
3.2.1 成员资格判断
ISR 成员资格的判断需要同时考虑高水位和 Leader 纪元:
kotlin
private def isFollowerInSync(followerReplica: Replica): Boolean = {
leaderLogIfLocal.exists { leaderLog =>
val followerEndOffset = followerReplica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffset
followerEndOffset >= leaderLog.highWatermark && // 条件1:Follower LEO >= Leader HW
leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt.exists(followerEndOffset >= _) // 条件2:Follower LEO >= 当前 Leader 纪元的起始偏移量
}
}
private def isFollowerOutOfSync(replicaId: Int, leaderEndOffset: Long,
currentTimeMs: Long, maxLagMs: Long): Boolean = {
getReplica(replicaId) match {
case Some(followerReplica) =>
val followerState = followerReplica.stateSnapshot
val timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs = currentTimeMs - followerState.lastCaughtUpTimeMs
timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs > maxLagMs // 关键条件:超过最大滞后时间
case None =>
true // 副本不存在,视为不同步
}
}源码位置 : Partition.scala
核心功能:
- 基本同步要求:Follower LEO >= Leader HW
- 纪元一致性要求:Follower LEO >= Leader Epoch 起始偏移量
- 时间滞后检查:副本滞后时间不超过配置阈值
Leader 纪元在 ISR 判断中的重要性:
条件2(leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt.exists(followerEndOffset >= _))确保:
- Follower 的数据至少包含当前 Leader 纪元的起始点
- 防止包含过期纪元数据的副本被错误地认为是同步的
- 在 Leader 切换后,只有真正跟上新 Leader 的副本才能加入 ISR
实际场景示例:

这个机制防止了以下问题:
- 数据不一致:确保副本包含当前纪元的完整数据
- 脑裂恢复:旧 Leader 恢复时必须先同步新纪元的数据
- 一致性保证:只有真正同步的副本才能参与 ISR
ISR 变化的触发条件:
-
加入 ISR 的条件
- Follower LEO >= Leader HW
- Follower LEO >= Leader Epoch 起始偏移量
- 副本处于活跃状态
-
移出 ISR 的条件
- 副本滞后时间 >
replica.lag.time.max.ms - 副本离线或不可达
- 副本发生存储异常
- 副本滞后时间 >
3.1.6 ISR 配置参数详解
关键配置参数:
ini
# ISR 管理的核心配置
replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000
# 说明:副本最大滞后时间,超过此时间的副本会被移出 ISR
# 影响:较小的值提高一致性但可能影响可用性;较大的值相反
min.insync.replicas=2
# 说明:最小同步副本数,ISR 副本数必须 >= 此值才能接受写入
# 影响:提高数据安全性,但可能在副本故障时影响可用性
unclean.leader.election.enable=false
# 说明:是否允许非 ISR 副本成为 Leader
# 影响:false 保证数据一致性,true 提高可用性但可能丢失数据
replica.fetch.wait.max.ms=500
# 说明:Follower 拉取数据的最大等待时间
# 影响:影响副本同步的实时性和 ISR 成员资格配置示例和影响分析:

3.3 ISR 扩展机制
3.3.1 扩展条件和流程
ISR 扩展是将符合条件的 Follower 副本添加到 ISR 集合中的过程:
scss
def maybeExpandIsr(followerReplica: Replica, followerFetchTimeMs: Long): Boolean = {
val needsIsrUpdate = !partitionState.isInflight && inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
needsExpandIsr(followerReplica) // 检查是否需要扩展
}
if (needsIsrUpdate) {
val alterIsrUpdateOpt = inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
partitionState match {
case currentState: CommittedPartitionState if needsExpandIsr(followerReplica) =>
Some(prepareIsrExpand(currentState, followerReplica.brokerId)) // 准备扩展 ISR
case _ =>
None
}
}
alterIsrUpdateOpt.foreach(submitAlterPartition) // 提交 AlterPartition 请求
}
}
private def needsExpandIsr(followerReplica: Replica): Boolean = {
canAddReplicaToIsr(followerReplica.brokerId) && isFollowerInSync(followerReplica) // 检查副本是否可以加入 ISR 且已同步
}
private def isFollowerInSync(followerReplica: Replica): Boolean = {
leaderLogIfLocal.exists { leaderLog =>
val followerEndOffset = followerReplica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffset
followerEndOffset >= leaderLog.highWatermark && leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt.exists(followerEndOffset >= _) // 同步条件检查
}
}源码位置 : Partition.scala:1022-1036
核心功能:
- 检查副本是否满足加入 ISR 的条件
- 准备 ISR 扩展操作
- 提交 AlterPartition 请求到 Controller
- 线程安全的状态更新
3.2.2 ISR 扩展的实际场景
场景1:新副本启动并追上进度

场景2:网络恢复后副本重新同步
scss
if (followerReplica.logEndOffset >= leaderLog.highWatermark &&
followerReplica.logEndOffset >= leaderEpochStartOffset) {
prepareIsrExpand(currentState, followerReplica.brokerId); // 满足扩展条件,准备加入 ISR
}核心功能:
- Follower 重新连接到 Leader
- 快速追赶落后的数据
- 满足同步条件后自动加入 ISR
3.4 ISR 收缩机制
3.4.1 收缩触发条件
ReplicaManager 定期检查并收缩 ISR:
scss
private def maybeShrinkIsr(): Unit = {
trace("Evaluating ISR list of partitions to see which replicas can be removed from the ISR")
allPartitions.forEach { (topicPartition, _) =>
onlinePartition(topicPartition).foreach(_.maybeShrinkIsr()) // 为非离线分区收缩 ISR
}
}源码位置 : ReplicaManager.scala:2544-2551
分区级别的 ISR 收缩检查:
scss
def maybeShrinkIsr(): Unit = {
def needsIsrUpdate: Boolean = {
!partitionState.isInflight && inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
needsShrinkIsr() // 检查是否需要收缩
}
}
if (needsIsrUpdate) {
val alterIsrUpdateOpt = inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
leaderLogIfLocal.flatMap { leaderLog =>
val outOfSyncReplicaIds = getOutOfSyncReplicas(replicaLagTimeMaxMs) // 获取不同步的副本
partitionState match {
case currentState: CommittedPartitionState if outOfSyncReplicaIds.nonEmpty =>
val outOfSyncReplicaLog = outOfSyncReplicaIds.map { replicaId =>
val replicaStateSnapshot = getReplica(replicaId).map(_.stateSnapshot)
val logEndOffsetMessage = replicaStateSnapshot.map(_.logEndOffset.toString).getOrElse("unknown")
val lastCaughtUpTimeMessage = replicaStateSnapshot.map(_.lastCaughtUpTimeMs.toString).getOrElse("unknown")
s"(brokerId: $replicaId, endOffset: $logEndOffsetMessage, lastCaughtUpTimeMs: $lastCaughtUpTimeMessage)"
}.mkString(" ")
info(s"Shrinking ISR from ${currentState.isr.mkString(",")} to " +
s"${(currentState.isr -- outOfSyncReplicaIds).mkString(",")}") // 记录 ISR 收缩日志
Some(prepareIsrShrink(currentState, outOfSyncReplicaIds)) // 准备收缩 ISR
case _ => None
}
}
}
alterIsrUpdateOpt.foreach(submitAlterPartition) // 提交 AlterPartition 请求
}
}源码位置 : Partition.scala:1231-1260
核心功能:
- 检查是否有不同步的副本需要移出 ISR
- 记录详细的收缩日志信息
- 准备并提交 ISR 收缩请求
- 线程安全的状态更新
3.5 ISR 管理流程图

3.6 ISR 故障场景分析
3.6.1 常见故障场景
场景1:网络分区导致的 ISR 收缩

场景2:副本性能问题导致的滞后
scss
// 副本滞后的常见原因
public class ReplicaLagCauses {
// 1. 磁盘 I/O 性能问题
if (diskIOLatency > threshold) {
// 磁盘写入慢,导致副本跟不上
}
// 2. 网络带宽不足
if (networkThroughput < requiredBandwidth) {
// 网络传输慢,Fetch 请求延迟
}
// 3. GC 停顿时间过长
if (gcPauseTime > maxAcceptablePause) {
// JVM GC 导致副本处理暂停
}
// 4. CPU 资源不足
if (cpuUsage > 90) {
// CPU 负载高,影响副本同步处理
}
}场景3:Broker 故障恢复

3.6.2 ISR 监控和告警
关键监控指标:
ini
# 1. ISR 大小监控
kafka.cluster:type=Partition,name=InSyncReplicasCount,topic=*,partition=*
# 2. ISR 变化频率
kafka.server:type=ReplicaManager,name=IsrExpandsPerSec
kafka.server:type=ReplicaManager,name=IsrShrinksPerSec
# 3. 副本不足的分区数
kafka.server:type=ReplicaManager,name=UnderReplicatedPartitions
# 4. 离线分区数
kafka.controller:type=KafkaController,name=OfflinePartitionsCount告警规则示例:
yaml
# ISR 相关告警配置
alerts:
- alert: ISRShrinkageHigh
expr: rate(kafka_server_replicamanager_isrshrinkspersec[5m]) > 0.1
for: 2m
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "ISR 收缩频率过高"
description: "ISR 收缩频率 {{ $value }} 超过阈值,可能存在副本同步问题"
- alert: UnderReplicatedPartitions
expr: kafka_server_replicamanager_underreplicatedpartitions > 0
for: 1m
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "存在副本不足的分区"
description: "{{ $value }} 个分区的副本数不足,存在数据丢失风险"
- alert: MinISRViolation
expr: kafka_cluster_partition_insyncreplicascount < 2
for: 30s
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "分区 ISR 副本数低于最小要求"
description: "分区 {{ $labels.topic }}-{{ $labels.partition }} ISR 副本数为 {{ $value }}"3.7 ISR 最佳实践
3.7.1 配置优化建议
生产环境推荐配置:
ini
# 平衡一致性和可用性
min.insync.replicas=2
replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000
unclean.leader.election.enable=false
# 网络和性能优化
replica.fetch.wait.max.ms=500
replica.fetch.max.bytes=1048576
replica.socket.timeout.ms=30000
# 监控和调试
replica.high.watermark.checkpoint.interval.ms=5000
log.flush.interval.messages=10000不同场景的配置策略:
-
高一致性场景(金融、支付)
inimin.insync.replicas=3 replica.lag.time.max.ms=10000 unclean.leader.election.enable=false acks=all -
高可用性场景(日志收集)
inimin.insync.replicas=1 replica.lag.time.max.ms=60000 unclean.leader.election.enable=true acks=1 -
平衡场景(一般业务)
inimin.insync.replicas=2 replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000 unclean.leader.election.enable=false acks=all
4. 高水位管理
4.1 高水位概念
4.1.1 高水位定义
高水位(High Watermark,简称 HW)是分区中已被所有 ISR 副本同步的最大偏移量,是保证数据一致性和可见性的核心机制。 
4.1.2 核心作用
1. 数据可见性控制
- 只有高水位之前的消息对消费者可见
- 确保消费者不会读到可能丢失的数据
2. 一致性保证
- 所有 ISR 副本都已确认的数据才能被消费
- 防止在 Leader 切换时数据不一致
3. 故障恢复基准
- Leader 故障时,新 Leader 从高水位开始提供服务
- 确保已提交的数据不会丢失
4.1.3 高水位 vs LEO
arduino
// LEO(Log End Offset):日志结束偏移量
// - 表示日志中下一条消息将要写入的偏移量
// - 每个副本都有自己的 LEO
// - LEO 总是 >= HW
// HW(High Watermark):高水位
// - 表示已被所有 ISR 副本确认的最大偏移量
// - 整个分区只有一个 HW(由 Leader 维护)
// - HW = min(所有 ISR 副本的 LEO)核心功能:
- LEO 表示副本的最新写入位置
- HW 表示已确认的安全读取位置
- 两者配合实现数据一致性保证
关系示例:
ini
Leader: [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9] LEO=10
Follower-1: [0][1][2][3][4][5][6][7] LEO=8
Follower-2: [0][1][2][3][4][5] LEO=6
High Watermark = min(10, 8, 6) = 6
消费者只能看到 offset 0-5 的消息4.2 高水位更新机制
高水位的更新是一个精心设计的过程,确保数据一致性:
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/cluster/Partition.scala:1152-1195
scala
// 检查并可能增加 Leader 的高水位
private def maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog: UnifiedLog, currentTimeMs: Long = time.milliseconds): Boolean = {
if (isUnderMinIsr) {
trace(s"Not increasing HWM because partition is under min ISR(ISR=${partitionState.isr}")
return false
}
// maybeIncrementLeaderHW 在热路径中,以下代码避免不必要的集合生成
val leaderLogEndOffset = leaderLog.logEndOffsetMetadata
var newHighWatermark = leaderLogEndOffset
// 遍历所有远程副本,找到最小的 LEO 作为新的高水位
remoteReplicasMap.forEach { (_, replica) =>
val replicaState = replica.stateSnapshot
def shouldWaitForReplicaToJoinIsr: Boolean = {
replicaState.isCaughtUp(leaderLogEndOffset.messageOffset, currentTimeMs, replicaLagTimeMaxMs) &&
isReplicaIsrEligible(replica.brokerId)
}
// 只考虑 ISR 中的副本或者即将加入 ISR 的副本
if (partitionState.isr.contains(replica.brokerId) || shouldWaitForReplicaToJoinIsr) {
val replicaLogEndOffset = replicaState.logEndOffsetMetadata
newHighWatermark = newHighWatermark.min(replicaLogEndOffset)
}
}
// 尝试更新高水位
leaderLog.maybeIncrementHighWatermark(newHighWatermark).toScala match {
case Some(oldHighWatermark) =>
debug(s"High watermark updated from $oldHighWatermark to $newHighWatermark")
true
case None =>
if (isTraceEnabled) {
val replicaInfo = remoteReplicas.map(replica => (replica.brokerId, replica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffsetMetadata)).toSet
val localLogInfo = (localBrokerId, localLogOrException.logEndOffsetMetadata)
trace(s"Skipping update high watermark since new hw $newHighWatermark is not larger than old value. " +
s"All current LEOs are ${(replicaInfo + localLogInfo).map(logEndOffsetString)}")
}
false
}
}4.3 高水位更新的触发时机
高水位的更新有多个触发时机,确保及时反映副本同步状态:
4.3.1 主要触发场景
-
Follower 拉取数据后
ini// 当 Follower 更新 LEO 时,可能触发 HW 更新 val leaderHWIncremented = if (prevFollowerEndOffset != replica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffset) { inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) { leaderLogIfLocal.exists(leaderLog => maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog, followerFetchTimeMs)) } } else { false } -
ISR 变化时
c// ISR 扩展或收缩后,需要重新计算 HW leaderLogIfLocal.exists(log => maybeIncrementLeaderHW(log)) -
Leader 写入新数据后
scss// Leader 追加新消息后,检查是否可以提升 HW partition.appendRecordsToLeader(records, origin, requiredAcks, requestLocal) // 内部会调用 maybeIncrementLeaderHW
4.3.2 高水位计算算法
kotlin
// 高水位计算的核心逻辑
private def maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog: UnifiedLog, currentTimeMs: Long): Boolean = {
// 1. 检查是否满足最小 ISR 要求
if (isUnderMinIsr) {
trace(s"Not increasing HWM because partition is under min ISR(ISR=${partitionState.isr}")
return false
}
// 2. 从 Leader LEO 开始
val leaderLogEndOffset = leaderLog.logEndOffsetMetadata
var newHighWatermark = leaderLogEndOffset
// 3. 遍历所有远程副本,找到最小的 LEO
remoteReplicasMap.forEach { (_, replica) =>
val replicaState = replica.stateSnapshot
// 只考虑 ISR 中的副本或即将加入 ISR 的副本
if (partitionState.isr.contains(replica.brokerId) || shouldWaitForReplicaToJoinIsr) {
val replicaLogEndOffset = replicaState.logEndOffsetMetadata
newHighWatermark = newHighWatermark.min(replicaLogEndOffset) // 取最小值
}
}
// 4. 尝试更新高水位
leaderLog.maybeIncrementHighWatermark(newHighWatermark)
}4.3.3 高水位更新的约束条件
更新条件:
- 新 HW > 当前 HW:只能向前推进,不能回退
- 满足最小 ISR:ISR 副本数 >= min.insync.replicas
- 副本同步状态:只考虑 ISR 中的副本或即将加入的副本
特殊情况处理:
scss
// 等待副本加入 ISR 的条件
def shouldWaitForReplicaToJoinIsr: Boolean = {
replicaState.isCaughtUp(leaderLogEndOffset.messageOffset, currentTimeMs, replicaLagTimeMaxMs) &&
isReplicaIsrEligible(replica.brokerId)
}4.4 高水位检查点管理
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:2560-2582
arduino
// 将所有分区的高水位值刷新到高水位文件
def checkpointHighWatermarks(): Unit = {
def putHw(logDirToCheckpoints: mutable.AnyRefMap[String, mutable.AnyRefMap[TopicPartition, JLong]],
log: UnifiedLog): Unit = {
val checkpoints = logDirToCheckpoints.getOrElseUpdate(log.parentDir,
new mutable.AnyRefMap[TopicPartition, JLong]())
checkpoints.put(log.topicPartition, log.highWatermark)
}
val logDirToHws = new mutable.AnyRefMap[String, mutable.AnyRefMap[TopicPartition, JLong]](
allPartitions.size)
// 收集所有在线分区的高水位
onlinePartitionsIterator.foreach { partition =>
partition.log.foreach(putHw(logDirToHws, _))
partition.futureLog.foreach(putHw(logDirToHws, _))
}
// 写入检查点文件
for ((logDir, hws) <- logDirToHws) {
try highWatermarkCheckpoints.get(logDir).foreach(_.write(hws.asJava))
catch {
case e: KafkaStorageException =>
error(s"Error while writing to highwatermark file in directory $logDir", e)
}
}
}高水位更新流程:

4.5 高水位在不同场景下的行为
4.5.1 正常生产消费场景

4.5.2 Leader 故障切换场景

4.5.3 ISR 收缩场景

4.6 高水位相关的重要配置
4.6.1 关键配置参数
ini
# 最小同步副本数 - 影响高水位计算
min.insync.replicas=2
# 副本滞后时间 - 影响 ISR 成员资格
replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000
# 高水位检查点间隔 - 影响持久化频率
replica.high.watermark.checkpoint.interval.ms=5000
# 不干净的 Leader 选举 - 影响数据一致性
unclean.leader.election.enable=false4.6.2 配置对高水位的影响
min.insync.replicas 的影响:
kotlin
// 当 ISR 副本数 < min.insync.replicas 时
if (isUnderMinIsr) {
// 不更新高水位,保护数据安全
trace(s"Not increasing HWM because partition is under min ISR")
return false
}
java
// 副本超时会被移出 ISR,影响高水位计算
val timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs = currentTimeMs - followerState.lastCaughtUpTimeMs
if (timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs > maxLagMs) {
// 副本被标记为不同步,将从 ISR 中移除
// 高水位计算将不再考虑此副本
}4.7 高水位监控和故障排查
4.7.1 关键监控指标
csharp
# 查看分区的高水位信息
kafka-log-dirs.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --json
# 查看消费者组的消费进度(相对于高水位)
kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group my-group
# 监控 ISR 变化(影响高水位计算)
kafka.cluster:type=Partition,name=InSyncReplicasCount,topic=*,partition=*4.7.2 常见问题和解决方案
问题1:高水位长时间不更新
perl
# 可能原因:
# 1. Follower 同步滞后
# 2. ISR 副本数不足
# 3. 网络分区
# 排查步骤:
# 1. 检查 ISR 状态
kafka-topics.sh --describe --topic my-topic
# 2. 检查副本滞后情况
kafka-replica-verification.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic-white-list my-topic问题2:消费者看不到最新消息
bash
# 原因:消息还未达到高水位
# 解决:检查副本同步状态,确保 ISR 副本正常同步5. 日志追加:生产者消息的处理流程
5.1 日志追加的核心流程
ReplicaManager 处理生产者消息的追加是其最重要的功能之一:
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:1426-1503
scss
// 将消息追加到本地副本日志
private def appendToLocalLog(internalTopicsAllowed: Boolean,
origin: AppendOrigin,
entriesPerPartition: Map[TopicIdPartition, MemoryRecords],
requiredAcks: Short,
requestLocal: RequestLocal,
verificationGuards: Map[TopicPartition, VerificationGuard]):
Map[TopicIdPartition, LogAppendResult] = {
val traceEnabled = isTraceEnabled
def processFailedRecord(topicIdPartition: TopicIdPartition, t: Throwable) = {
val logStartOffset = onlinePartition(topicIdPartition.topicPartition()).map(_.logStartOffset).getOrElse(-1L)
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicIdPartition.topic).failedProduceRequestRate.mark()
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.failedProduceRequestRate.mark()
// 处理各种异常情况...
}
entriesPerPartition.map { case (topicIdPartition, records) =>
// 拒绝追加到内部主题(如果不允许)
if (Topic.isInternal(topicIdPartition.topic) && !internalTopicsAllowed) {
(topicIdPartition, LogAppendResult(
LogAppendInfo.UNKNOWN_LOG_APPEND_INFO,
Some(new InvalidTopicException(s"Cannot append to internal topic ${topicIdPartition.topic}")),
hasCustomErrorMessage = false))
} else {
try {
val partition = getPartitionOrException(topicIdPartition)
val info = partition.appendRecordsToLeader(records, origin, requiredAcks, requestLocal,
verificationGuards.getOrElse(topicIdPartition.topicPartition(), VerificationGuard.SENTINEL))
val numAppendedMessages = info.numMessages
// 更新成功追加的字节数和消息数统计
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicIdPartition.topic).bytesInRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.bytesInRate.mark(records.sizeInBytes)
brokerTopicStats.topicStats(topicIdPartition.topic).messagesInRate.mark(numAppendedMessages)
brokerTopicStats.allTopicsStats.messagesInRate.mark(numAppendedMessages)
if (traceEnabled)
trace(s"${records.sizeInBytes} written to log $topicIdPartition beginning at offset " +
s"${info.firstOffset} and ending at offset ${info.lastOffset}")
(topicIdPartition, LogAppendResult(info, exception = None, hasCustomErrorMessage = false))
} catch {
case e: KafkaStorageException =>
processFailedRecord(topicIdPartition, e)
(topicIdPartition, LogAppendResult(LogAppendInfo.unknownLogAppendInfoWithLogStartOffset(logStartOffset),
Some(e), hasCustomErrorMessage = false))
// 处理其他异常...
}
}
}
}5.2 生产者请求的完整处理
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:684-706
less
// 生产者消息追加的主入口
def appendRecordsToLocalLog(timeout: Long,
requiredAcks: Short,
internalTopicsAllowed: Boolean,
origin: AppendOrigin,
entriesPerPartition: Map[TopicIdPartition, MemoryRecords],
requestLocal: RequestLocal = RequestLocal.noCaching,
actionQueue: ActionQueue = this.defaultActionQueue,
verificationGuards: Map[TopicPartition, VerificationGuard] = Map.empty
): Map[TopicIdPartition, LogAppendResult] = {
val startTimeMs = time.milliseconds
// 追加到本地日志
val localProduceResultsWithTopicId = appendToLocalLog(
internalTopicsAllowed = internalTopicsAllowed,
origin,
entriesPerPartition,
requiredAcks,
requestLocal,
verificationGuards.toMap
)
debug("Produce to local log in %d ms".format(time.milliseconds - startTimeMs))
// 添加完成清理操作到队列
addCompletePurgatoryAction(actionQueue, localProduceResultsWithTopicId)
localProduceResultsWithTopicId
}5.3 日志追加流程图

6. 副本同步:Follower 的数据拉取机制
6.1 Follower 拉取处理
ReplicaManager 还负责处理 Follower 的拉取请求:
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/cluster/Partition.scala:940-955
scss
// 更新 Follower 副本状态并检查高水位
def updateFollowerFetchState(followerId: Int,
followerFetchOffsetMetadata: LogOffsetMetadata,
followerStartOffset: Long,
followerFetchTimeMs: Long,
leaderEndOffset: Long): Boolean = {
getReplica(followerId) match {
case Some(followerReplica) =>
val prevFollowerEndOffset = followerReplica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffset
followerReplica.updateFetchState(followerFetchOffsetMetadata, followerStartOffset, followerFetchTimeMs, leaderEndOffset)
// 检查分区的 HW 是否可以增加,因为副本可能已经在 ISR 中且其 LEO 刚刚增加
val leaderHWIncremented = if (prevFollowerEndOffset != replica.stateSnapshot.logEndOffset) {
// Leader 日志可能被 ReplicaAlterLogDirsThread 更新,所以以下方法必须在 leaderIsrUpdateLock 锁中
// 以防止向无效日志添加新的 hw
inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
leaderLogIfLocal.exists(leaderLog => maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog, followerFetchTimeMs))
}
} else {
false
}
// 一些延迟操作可能在 HW 或 LW 改变后被解除阻塞
if (leaderLWIncremented || leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
leaderHWIncremented
case None =>
false
}
}6.2 副本同步状态检查
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/cluster/Partition.scala:1297-1307
ini
// 获取不同步的副本集合
def getOutOfSyncReplicas(maxLagMs: Long): Set[Int] = {
val current = partitionState
if (!current.isInflight) {
val candidateReplicaIds = current.isr - localBrokerId
val currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds()
val leaderEndOffset = localLogOrException.logEndOffset
candidateReplicaIds.filter(replicaId => isFollowerOutOfSync(replicaId, leaderEndOffset, currentTimeMs, maxLagMs))
} else {
Set.empty
}
}
// 判断 Follower 是否不同步
private def isFollowerOutOfSync(replicaId: Int, leaderEndOffset: Long, currentTimeMs: Long, maxLagMs: Long): Boolean = {
getReplica(replicaId) match {
case Some(followerReplica) =>
val followerState = followerReplica.stateSnapshot
val timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs = math.max(0L, currentTimeMs - followerState.lastCaughtUpTimeMs)
timeSinceLastCaughtUpMs > maxLagMs
case None =>
true
}
}7. 分区管理:在线/离线状态处理
7.1 分区状态管理
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:2584-2592
scss
// 标记分区为离线状态
def markPartitionOffline(tp: TopicPartition): Unit = replicaStateChangeLock synchronized {
allPartitions.get(tp) match {
case HostedPartition.Online(partition) =>
allPartitions.put(tp, HostedPartition.Offline(Some(partition)))
partition.markOffline()
case _ =>
allPartitions.put(tp, HostedPartition.Offline(None))
}
}7.2 分区创建和获取
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:2752-2770
sql
// 获取或创建分区
private[kafka] def getOrCreatePartition(tp: TopicPartition,
delta: TopicsDelta,
topicId: Uuid): Option[(Partition, Boolean)] = {
getPartition(tp) match {
case HostedPartition.Offline(offlinePartition) =>
if (offlinePartition.flatMap(p => p.topicId).contains(topicId)) {
stateChangeLogger.warn(s"Unable to bring up new local leader $tp " +
s"with topic id $topicId because it resides in an offline log " +
"directory.")
None
} else {
stateChangeLogger.info(s"Creating new partition $tp with topic id " + s"$topicId." +
s"A topic with the same name but different id exists but it resides in an offline log " +
s"directory.")
val partition = Partition(new TopicIdPartition(topicId, tp), time, this)
allPartitions.put(tp, HostedPartition.Online(partition))
Some((partition, true))
}
case HostedPartition.Online(partition) =>
if (partition.topicId.contains(topicId)) {
Some((partition, false))
} else {
// 主题 ID 不匹配,可能是主题被删除并重新创建
stateChangeLogger.info(s"Deleting partition $tp with topic id ${partition.topicId} " +
s"since a partition with the same name but different topic id $topicId needs to be created.")
partition.delete()
val newPartition = Partition(new TopicIdPartition(topicId, tp), time, this)
allPartitions.put(tp, HostedPartition.Online(newPartition))
Some((newPartition, true))
}
case HostedPartition.None =>
val partition = Partition(new TopicIdPartition(topicId, tp), time, this)
allPartitions.put(tp, HostedPartition.Online(partition))
Some((partition, true))
}
}8. 性能优化和监控
8.1 关键性能指标
ReplicaManager 提供了丰富的监控指标:
源码位置: core/src/main/scala/kafka/server/ReplicaManager.scala:367-371
ini
// ISR 相关指标
val isrExpandRate: Meter = metricsGroup.newMeter(IsrExpandsPerSecMetricName, "expands", TimeUnit.SECONDS)
val isrShrinkRate: Meter = metricsGroup.newMeter(IsrShrinksPerSecMetricName, "shrinks", TimeUnit.SECONDS)
val failedIsrUpdatesRate: Meter = metricsGroup.newMeter(FailedIsrUpdatesPerSecMetricName, "failedUpdates", TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// 副本不足的分区数量
def underReplicatedPartitionCount: Int = leaderPartitionsIterator.count(_.isUnderReplicated)8.2 配置优化建议
ini
# 副本管理相关配置
replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000 # 副本最大滞后时间
replica.fetch.max.bytes=1048576 # 副本拉取最大字节数
replica.fetch.wait.max.ms=500 # 副本拉取最大等待时间
replica.high.watermark.checkpoint.interval.ms=5000 # 高水位检查点间隔
# ISR 管理配置
min.insync.replicas=2 # 最小同步副本数
unclean.leader.election.enable=false # 禁用不干净的 Leader 选举
# 性能调优配置
num.replica.fetchers=1 # 副本拉取线程数
replica.fetch.backoff.ms=1000 # 副本拉取退避时间9. 故障处理和恢复机制
9.1 日志目录故障处理
ReplicaManager 内置了完善的故障处理机制:
scss
// 日志目录故障处理器
logDirFailureHandler = new LogDirFailureHandler("LogDirFailureHandler")
logDirFailureHandler.start()9.2 副本恢复流程

总结
ReplicaManager 是 Kafka 副本管理的核心引擎,其设计体现了分布式系统的核心原则:
核心优势:
- 数据一致性:通过 ISR 和高水位机制确保强一致性
- 高可用性:支持动态的 Leader/Follower 切换和故障恢复
- 性能优化:高效的日志追加和副本同步机制
- 监控完善:丰富的指标体系支持运维监控
设计精髓:
- 状态机管理:清晰的分区状态转换和副本状态管理
- 异步处理:大量使用异步操作提升性能
- 故障容错:完善的故障检测和恢复机制
- 可扩展性:支持大规模分区和副本的管理
ReplicaManager 的实现展现了 Kafka 在数据一致性、高可用性和高性能方面的精心设计,是理解 Kafka 核心机制的重要组件。