给个一键三联吧
1. 栈的定义
栈是限定仅在一端 (称为栈顶,Top)进行插入(入栈)和删除(出栈)操作的线性表。
操作原则 :最后插入的元素最先被删除,即后进先出(LIFO)。
术语:
- 栈顶(Top):允许操作(插入/删除)的一端。
- 栈底(Bottom):固定不动、不允许操作的另一端。
- 空栈(Empty Stack):栈中无元素的状态
2.通过C语言来实现
2.1栈支持以下核心操作:
- 入栈(Push):在栈顶插入新元素,栈大小增加。
- 出栈(Pop):删除栈顶元素,栈大小减少。
- 取栈顶(Top/Peek):获取栈顶元素值,不修改栈结构。
- 判空(IsEmpty):检查栈是否为空。
- 初始化(Init)与销毁(Destroy):创建空栈或释放栈内存。
2.2具体代码如下:
首先要有以下的格式分类:
c
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define STDatatype int
struct Stack
{
STDatatype* a;
int top;//栈顶
int capacity;//栈的容量
};
typedef struct Stack st;
//栈的初始化和销毁
void StackInit(st* pst);
void StackDestroy(st* pst);
//入栈和出栈
void StackPop(st* pst);
void StackPush(st* pst, STDatatype date);这一块代码是栈的头文件,我们给出接口,接下来我们要尝试在stack.c里面实现这些代码,即这些头文件的接口具体如何实现
c
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(st* pst)
{
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestroy(st* pst)
{
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
void StackPop(st* pst)
{
assert(pst);//断言是否为空指针
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
//直接减一就ok
}
void StackPush(st* pst, STDatatype date)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int NewCapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * pst->capacity;
STDatatype* tmp = (STDatatype*)realloc(pst->a, NewCapacity*sizeof(STDatatype));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(1);
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = NewCapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = date;
pst->top++;
}
bool StackEmpty(st* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;//capacity 可能开辟了变大了
}//为空就返回真值
STDatatype StackTop(st* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(st* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
//top 其实就是有效的数量。
}我们通过编写依次完成了这些代码的编写。
我们接下来测试这些代码是否正常源代码如下:
c
#include"stack.h"
void test1(st* pst)
{
StackInit(pst);
int ret = StackEmpty(pst);
printf("%d\n", ret);
StackPush(pst, 1);
StackPush(pst, 2);
StackPush(pst, 3);
StackPush(pst, 4);
printf("%d\n", StackSize(pst));
while (pst->top)
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(pst));
StackPop(pst);
}
printf("\n");
printf("%d", StackSize(pst));
StackDestroy(pst);
}
int main()
{
st s1;
test1(&s1);
return 0;
}打印结果如下:
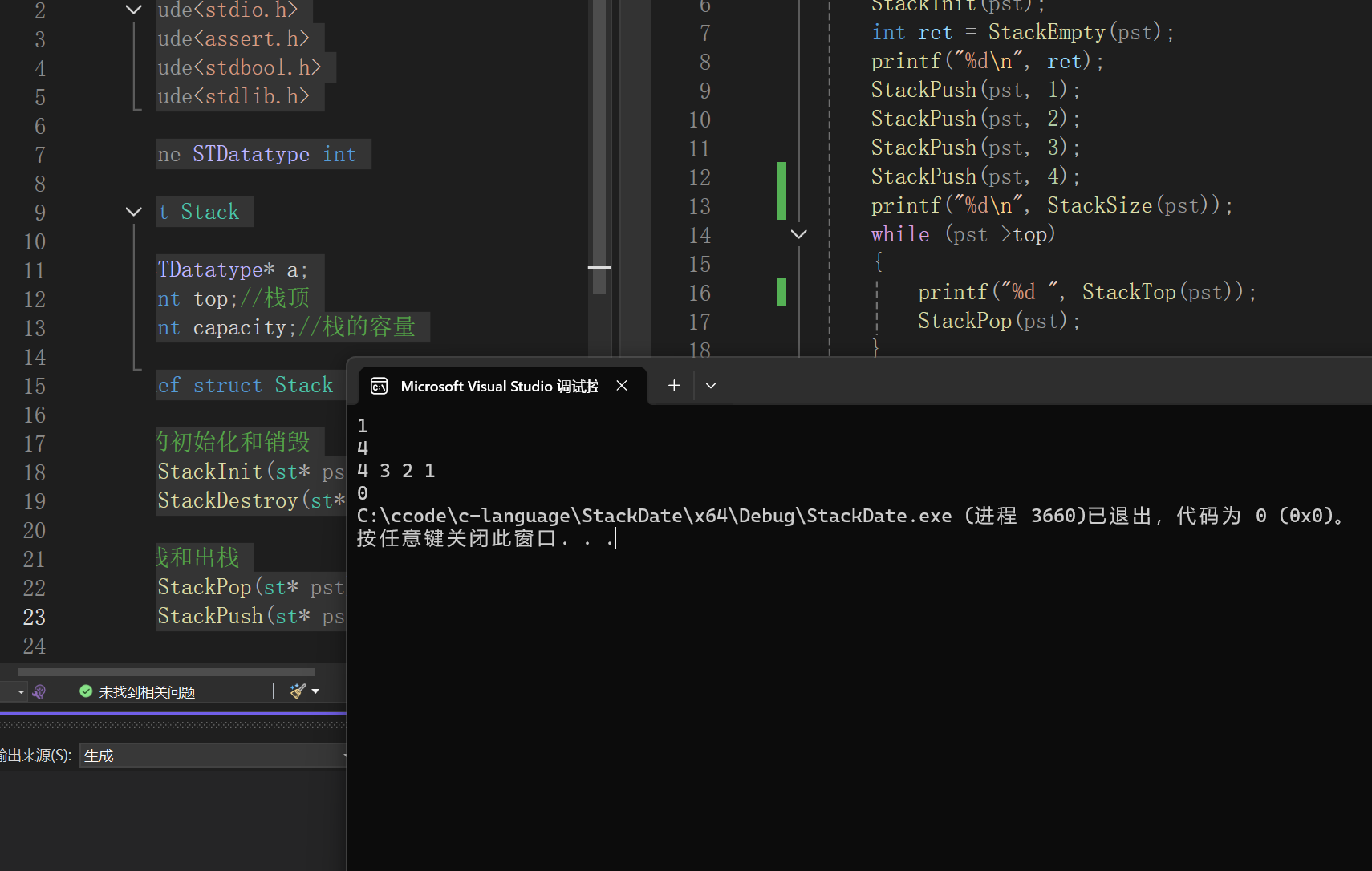
这样我们就完成了C语言代码实现的栈
3.总结
栈的本质是操作受限的线性表,通过LIFO原则和单端操作特性,高效支持特定场景(如函数调用、递归)。其实现需关注边界条件(空/满栈)和存储方式(顺序/链式)的选择,以平衡性能与内存需求。