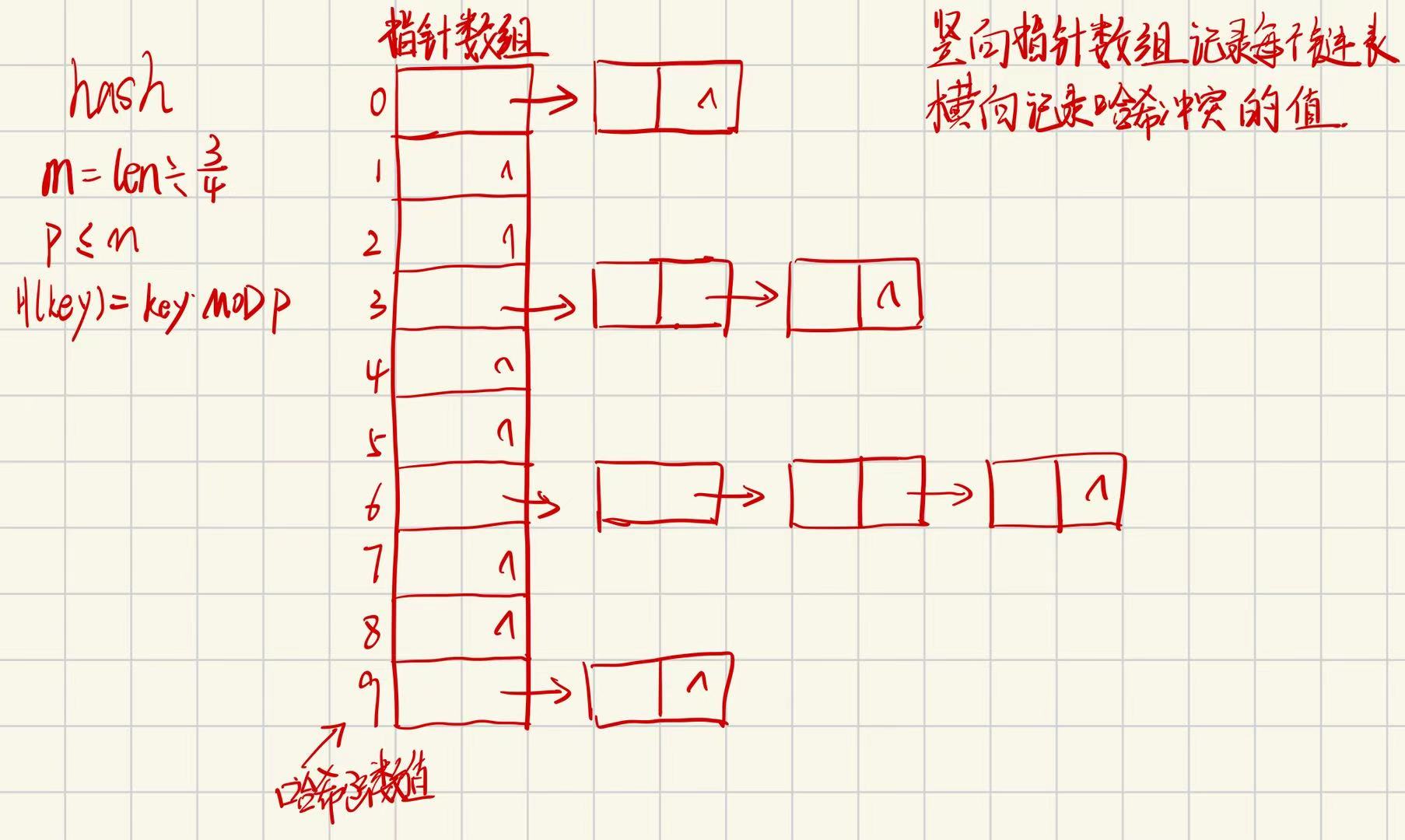
哈希表
概念
存放记录数组,主要实现查找的功能
哈希函数
取关键字被某个不大于散列表表长m的数p除后所得的余数为散列地址
H(key)=key MOD p , p≤mm为数组长度除以3/4 即m=len*4/3
p为小于等于m的最小素数
哈希冲突
将所有哈希函数值相同的记录存储在同一线性表
图示
哈希表代码相关函数
链表的结构
//链表结构
typedef struct node
{
union
{
int len;
int data;
};
struct node *next;
}node,*node_ptr;节点创建
node_ptr link_create(int n)
函数功能:创建头节点和其他节点
参数:n决定创建头节点还是其他节点
返回值:创建节点地址
node_ptr p=(node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(p==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//创建成功
if(n==0)
{
p->len=0;
}
else if(n==1)
{
p->data=0;
}
p->next=NULL;
return p;素数判定
int prime(int m)
函数功能:求出小于m的最大素数
参数:m 哈希表长度
返回值:p 最大素数
外循环遍历小于m的数,内循环遍历整除,当不能整除即为找到素数
for(int i=m;i>2;i--)
{
int conut=0;
for(int j=2;j<sqrt(i);j++)
{
if(i%j==0)
conut++;
}
if(conut==0)
return i;
}插入到哈希表
void insert_head(int key,node_ptr hash[],int m)
函数功能:将数值通过哈希函数确定位置后插入到哈希表内
参数:数值,哈希表,哈希表长度
返回值:无
//哈希函数
int p=prime(m);
int sub=key%p;
//将key插入到hash[sub]
node_ptr head=hash[sub];
//创建新节点
node_ptr s=link_create(1);
s->data=key;
//头插
s->next=head->next;
head->next=s;
//长度自增
head->len++;哈希表遍历
void hash_show(node_ptr hash[],int m)
函数功能:遍历哈希表的值
参数:哈希表,哈希表长度
返回值:无
void hash_show(node_ptr hash[],int m)
{
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
printf("%d::",i);
node_ptr p=hash[i]->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%-4d",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}哈希表查找
void seach(int key,node_ptr hash[],int m)
函数功能:哈希表的查找值
参数:值,哈希表,哈希表长度
返回值:无
通过哈希函数确实查找元素所在的行,再遍历行链表
void seach(int key,node_ptr hash[],int m)
{
int p=prime(m);
//哈希函数
int sub=key%p;
node_ptr pa=hash[sub]->next;
while(pa!=NULL)
{
if(pa->data==key)
{
printf("查找元素存在\n");
return ;
}
pa=pa->next;
}
printf("查找元素不存在\n");
}完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
//链表结构
typedef struct node
{
union
{
int len;
int data;
};
struct node *next;
}node,*node_ptr;
//节点创建
node_ptr link_create(int n)
{
node_ptr p=(node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(p==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//创建成功
if(n==0)
{
p->len=0;
}
else if(n==1)
{
p->data=0;
}
p->next=NULL;
return p;
}
//素数判定函数
int prime(int m)
{
for(int i=m;i>2;i--)
{
int conut=0;
for(int j=2;j<sqrt(i);j++)
{
if(i%j==0)
{
conut++;
}
}
if(conut==0)
return i;
}
}
//插入到哈希表
void insert_head(int key,node_ptr hash[],int m)
{
//哈希函数
int p=prime(m);
int sub=key%p;
//将key插入到hash[sub]
node_ptr head=hash[sub];
//创建新节点
node_ptr s=link_create(1);
s->data=key;
//头插
s->next=head->next;
head->next=s;
//长度自增
head->len++;
}
void hash_show(node_ptr hash[],int m)
{
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
printf("%d::",i);
node_ptr p=hash[i]->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%-4d",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
void seach(int key,node_ptr hash[],int m)
{
int p=prime(m);
//哈希函数
int sub=key%p;
node_ptr pa=hash[sub]->next;
while(pa!=NULL)
{
if(pa->data==key)
{
printf("查找元素存在\n");
return ;
}
pa=pa->next;
}
printf("查找元素不存在\n");
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建数组
int arr[]={25,51,8,22,26,67,11,16,54,41};
//创建一个哈希表
int len=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int m=len*4/3;
//先创建一个指针数组记录头节点的地址
node_ptr hash[m];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
hash[i]=link_create(0);
}
//再创建链表,将数组元素放入哈希表内
for (int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
//插入元素
insert_head(arr[i],hash,m);
}
//遍历哈希表
hash_show(hash,m);
//哈希查找
printf("请输入key值");
int key;
scanf("%d",&key);
seach(key,hash,m);
return 0;
}树
二叉树的性质
1.在非空二叉树的第i层上,至多有2^(i-1)个结点(i>=1)
【1,2^(i-1)】
2.在深度为K的二叉树上总结点最多有(2^k)-1个结点(k>=1)
二叉树:[k,(2^k)-1]
完全二叉树:[2^(k-1), (2^k)-1]
3.在任意一棵二叉树中,叶子结点的数目比度数为2的结点的数目多1
总节点=树杈数+1

二叉树代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node
{
char data;
struct node *lchild;
struct node *rchild;
}node,*node_ptr;
//节点创建
node_ptr node_create()
{
node_ptr p=(node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(NULL==p)
return NULL;
//初始化
p->data=0;
p->lchild=NULL;
p->rchild=NULL;
}
//二叉树的创建
node_ptr tree_create()
{
char e;
printf("请输入字符\n");
scanf(" %c",&e);
if('#'==e)
return NULL;
//创建节点
node_ptr tree=node_create();
tree->data=e;
//左孩子节点
tree->lchild=tree_create();
//右孩子节点
tree->rchild=tree_create();
return tree;
}
void first_out(node_ptr tree)
{
if(tree==NULL)
return ;
//根左右
printf("%c",tree->data); //根
first_out(tree->lchild); //左
first_out(tree->rchild); //右
}
void temp_out(node_ptr tree)
{
if(tree==NULL)
return ;
//左根右
first_out(tree->lchild); //左
printf("%c",tree->data); //根
first_out(tree->rchild); //右
}
void last_out(node_ptr tree)
{
if(tree==NULL)
return ;
//左右根
first_out(tree->lchild); //左
first_out(tree->rchild); //右
printf("%c",tree->data); //根
}
void count(node_ptr tree,int *n0,int *n1,int *n2)
{
if(tree==NULL)
return ;
//左右
count(tree->lchild,n0,n1,n2); //左
count(tree->rchild,n0,n1,n2); //右
if(tree->lchild==NULL &&tree->rchild==NULL )
++*n0;
else if(tree->lchild!=NULL&& tree->rchild!=NULL )
++*n2;
else
++*n1;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
node_ptr tree=tree_create();
//打印二叉树
//先序便利
first_out(tree);
putchar(10);
//中序
temp_out(tree);
putchar(10);
//后序
last_out(tree);
putchar(10);
//计算
int n0=0,n1=0,n2=0;
count(tree,&n0,&n1,&n2);
printf("n0=%d n1=%d n2=%d\n",n0,n1,n2);
return 0;
}