文章目录
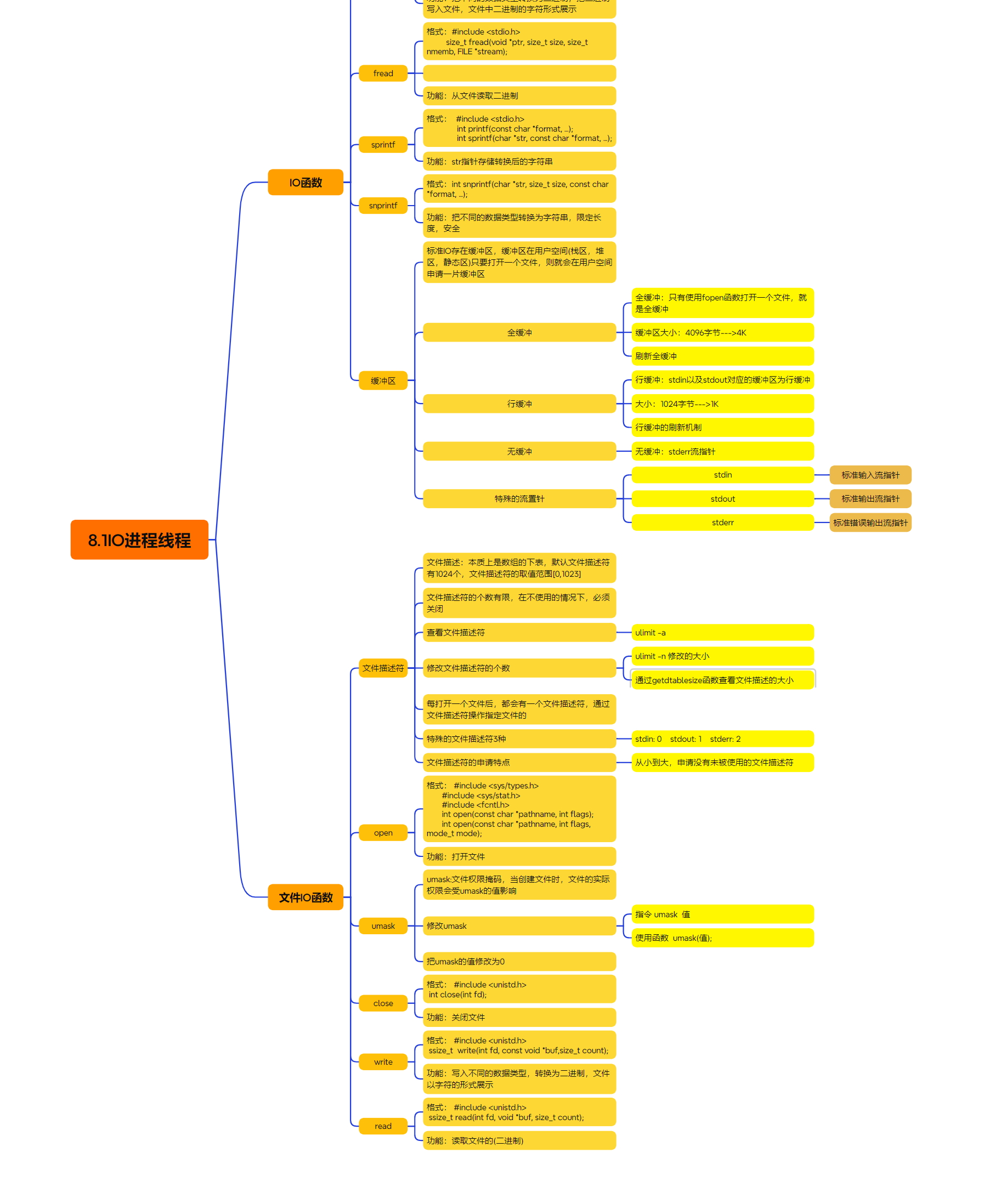
一、思维导图
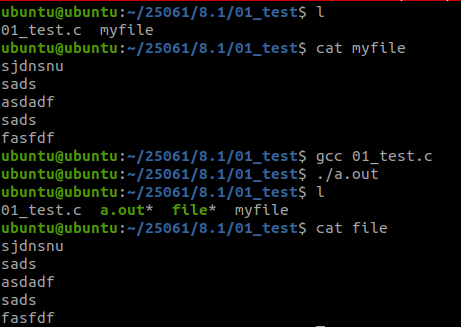
二、使用文件IO函数,实现文件的拷贝
myhead.h
c
#ifndef __MYHEAD_H__
#define __MYHEAD_H__
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define ERR_MSG(msg) do{perror(msg);printf("%d\n",__LINE__);return -1;}while(0)
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#endif代码
c
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//文件IO实现文件拷贝
umask(0);
//打开要下载的文件
int fd_r=open("./myfile",O_RDONLY);
if(fd_r==-1)
{
ERR_MSG("open fd_r error");
}
//打开要下载到的文件
int fd_w=open("./file",O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC,0774);
if(fd_w==-1)
{
ERR_MSG("open fd_w error");
}
//读取下载文件的内容
char buf[128]="";
if(-1==read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf)))
{
ERR_MSG("read error");
}
//将读取到的内容下载
if(-1==write(fd_w,buf,strlen(buf)))
{
ERR_MSG("write error");
}
//关闭文件
close(fd_r);
close(fd_w);
return 0;
}现象
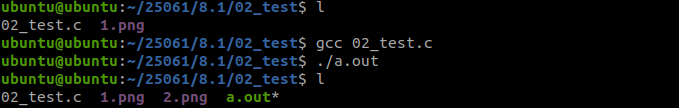
三、使用标准IO函数,实现图片的拷贝
代码
c
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp_1=fopen("./1.png","r");
if(fp_1==NULL)
{
ERR_MSG("fopen myfile_1 error");
return -1;
}
char arr[4096];
FILE *fp_2=fopen("./2.png","w");
if(fp_2==NULL)
{
ERR_MSG("fopen myfile_2 error");
return -1;
}
ssize_t size;
while((size=fread(arr,1,4096,fp_1))>0)
{
fwrite(arr,1,4096,fp_2);
}
fclose(fp_1);
fclose(fp_2);
return 0;
}现象
四、使用文件IO函数,计算文件的大小
代码
c
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//文件IO实现文件拷贝
umask(0);
//打开文件
int fd_r=open("./myfile",O_RDONLY);
if(fd_r==-1)
{
ERR_MSG("open fd_r error");
}
//读取文件的内容并计算长度
char buf[128]="";
int size;
while(1)
{
ssize_t set=read(fd_r,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(set==-1)
{
ERR_MSG("read error");
}
else if(set==0)
{
printf("The end of the file has been reached\n");
break;
}
size+=strlen(buf);
}
printf("%d\n",size);
//关闭文件
close(fd_r);
return 0;
}现象
The end of the file has been reached
32
五、牛客网刷题