文章目录
- 一、结构体的基本概念
-
- 1.1结构体的声明
- [1.2 结构体变量的创建](#1.2 结构体变量的创建)
-
- [1.2.1 在结构体声明同时创建](#1.2.1 在结构体声明同时创建)
- [1.2.2 在main函数中创建](#1.2.2 在main函数中创建)
- [1.3 结构体变量的初始化](#1.3 结构体变量的初始化)
-
- [1.3.1 按照默认顺序](#1.3.1 按照默认顺序)
- [1.3.2 指定成员初始化](#1.3.2 指定成员初始化)
- [1.4 结构体成员访问](#1.4 结构体成员访问)
- 二、结构体的代码示例
-
- [1. 结构体数组](#1. 结构体数组)
- [2. 结构体作为函数参数](#2. 结构体作为函数参数)
- [3. 结构体嵌套](#3. 结构体嵌套)
一、结构体的基本概念
C语言已经提供了内置类型,如char,short,float,double等,这些内置类型无法描述一个复杂的对象。因此C语言提供了结构体这种自定义的数据类型。它允许我们将不同类型的数据组合在一起,形成一个新的自定义数据类型。这一特性极大地增强了 C 语言处理复杂数据的能力,在实际编程中有着广泛的应用。
1.1结构体的声明
结构体使用关键字 struct 来定义
例如,想要描述一个学生:
c
struct student
{
char name[20]; // 名字
int age; //年龄
double height; //身高
double weight; //体重
char id[16] //学号
};//分号不可以少结构体是一些值的集合 ,这些值称为成员变量。结构体中的每个成员可以是不同的数据类型,如标量,数组,指针甚至是其他结构体。
1.2 结构体变量的创建
1.2.1 在结构体声明同时创建
c
struct student
{
char name[20];
int age;
double height ;
double weight;
char id[16]
} s1,s2;结构体声明时,创建变量是可选选项。此时创建的s1,s2是全局变量。
1.2.2 在main函数中创建
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct student
{
char name[20];
int age;
double height;
double weight;
char id[16]
};
int main( )
{
struct student s3;
struct student s4;
return 0;
}此时创建的变量是局部变量。
1.3 结构体变量的初始化
1.3.1 按照默认顺序
c
struct student s3 = {"daisy",20,170,50,"2410"};如果结构体成员变量中包含结构体:
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct S
{
char c;
int n;
};
struct A
{
struct S s;
int* p;
char arr[10];
};
int main()
{
struct A a = { {'1',1},NULL,"hhhh"};
}1.3.2 指定成员初始化
c
struct student s3 = {.age = 30,.weight=60,.name="Rare",.height=180,.id="2410"};1.4 结构体成员访问
使用操作符.可以访问结构体中的成员
例如:打印结构体成员:
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct student
{
char name[20]; // 名字
int age; //年龄
double height; //身高
double weight; //体重
char id[16]; //学号
};
int main()
{
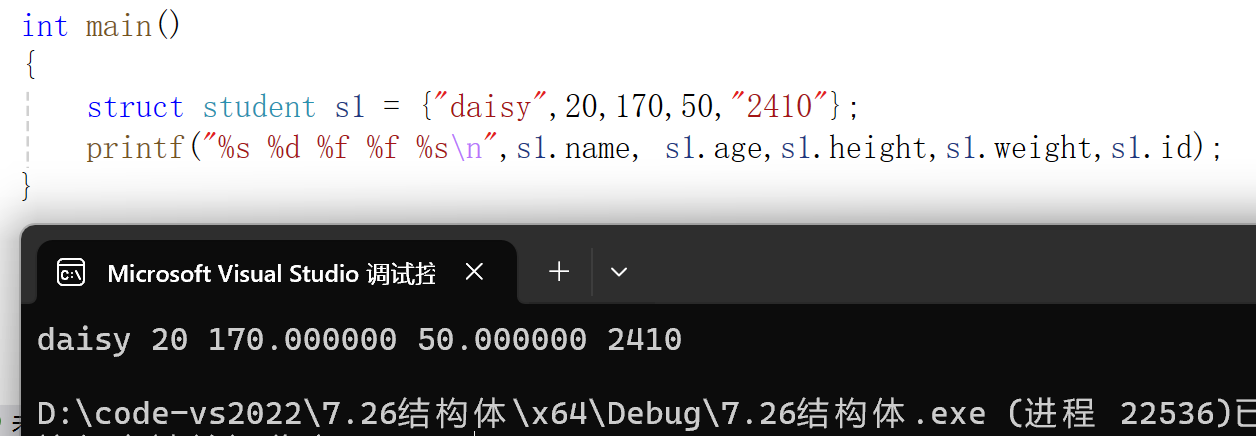
struct student s1 = {"daisy",20,170,50,"2410"};
printf("%s %d %f %f %s\n",s1.name, s1.age,s1.height,s1.weight,s1.id);
}
如果结构体变量是指针类型,则需要使用"->"运算符来访问成员,格式为:
c
结构体指针->成员名例如:
c
struct Student *p = &stu1;
p->age = 19; // 等价于(*p).age = 19二、结构体的代码示例
1. 结构体数组
结构体数组是由多个相同结构体类型的变量组成的数组。
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct Book {
char title[50];
char author[30];
float price;
};
int main() {
// 定义并初始化结构体数组
struct Book books[3] = {
{"C语言程序设计", "谭浩强", 39.8},
{"数据结构", "严蔚敏", 45.0},
{"计算机网络", "谢希仁", 42.5}
};
// 遍历结构体数组并输出信息
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("第%d本书:\n", i + 1);
printf("书名:%s\n", books[i].title);
printf("作者:%s\n", books[i].author);
printf("价格:%.1f\n\n", books[i].price);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
第1本书:
书名:C语言程序设计
作者:谭浩强
价格:39.8
第2本书:
书名:数据结构
作者:严蔚敏
价格:45.0
第3本书:
书名:计算机网络
作者:谢希仁
价格:42.52. 结构体作为函数参数
结构体可以作为函数的参数进行传递,既可以传递结构体变量本身(值传递),也可以传递结构体指针(地址传递)。
- 值传递:函数接收的是结构体变量的一个副本,在函数内部对结构体成员的修改不会影响原变量。
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
// 值传递结构体参数
void printPoint(struct Point p) {
printf("点的坐标:(%d, %d)\n", p.x, p.y);
p.x = 10; // 修改副本的成员,不影响原变量
p.y = 20;
}
int main() {
struct Point p = {3, 4};
printPoint(p);
printf("原变量坐标:(%d, %d)\n", p.x, p.y); // 原变量未被修改
return 0;
}运行结果:
点的坐标:(3, 4)
原变量坐标:(3, 4)- 地址传递:函数接收的是结构体变量的地址,通过指针可以访问和修改原结构体变量的成员。
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
// 地址传递结构体参数
void modifyPoint(struct Point *p) {
p->x = 10; // 修改原变量的成员
p->y = 20;
}
int main() {
struct Point p = {3, 4};
modifyPoint(&p);
printf("修改后坐标:(%d, %d)\n", p.x, p.y); // 原变量被修改
return 0;
}运行结果:
修改后坐标:(10, 20)3. 结构体嵌套
结构体的成员可以是另一个结构体,这就是结构体的嵌套。
c
#include <stdio.h>
// 定义日期结构体
struct Date {
int year;
int month;
int day;
};
// 定义学生结构体,其中包含Date类型的成员
struct Student {
char name[20];
struct Date birthday;
float score;
};
int main() {
// 初始化嵌套结构体变量
struct Student stu = {
"Bob",
{2003, 5, 15},
92.0
};
// 访问嵌套结构体的成员
printf("姓名:%s\n", stu.name);
printf("生日:%d年%d月%d日\n", stu.birthday.year, stu.birthday.month, stu.birthday.day);
printf("成绩:%.1f\n", stu.score);
return 0;
}运行结果:
姓名:Bob
生日:2003年5月15日
成绩:92.0