一,Dijkstra算法说明
1.举例说明
我们之前的prim和kruskal都是求最小生成树的n-1条边
而现在迪杰斯特拉是求单源点到其他顶点的最短距离
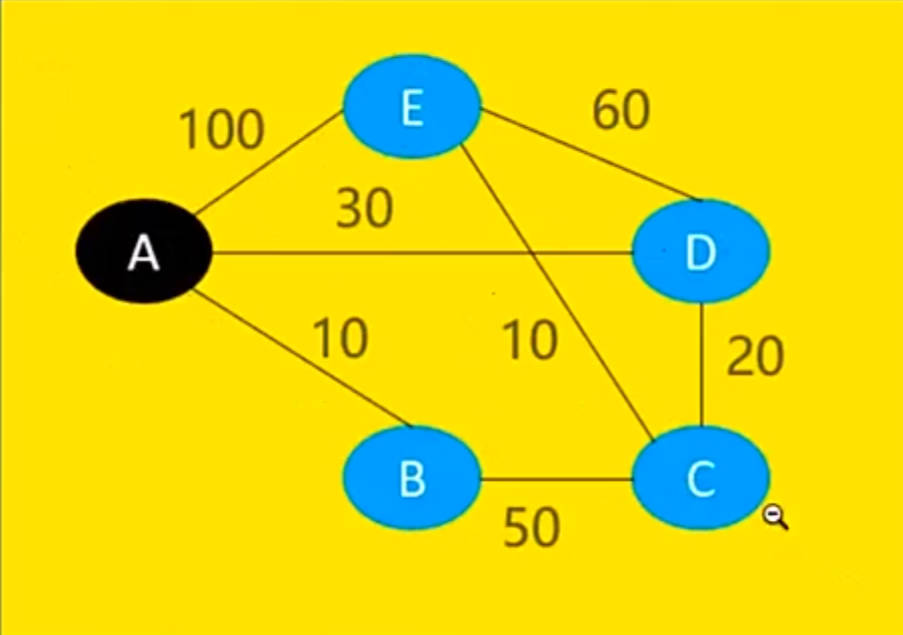
a.如下图当我们把每个点之间的路径当做绳子,最开始所有点平放在桌面上,把a提起来时顶点离开桌面的顺序取决于其到A的距离
b.下图离开桌面的顺序为A,B,D,C,E
c.当所有顶点离开桌面时,绷直的绳子就是他到其他顶点的最短路径
2.代码逻辑
首先我们需要三个数组
a.dist是源点到其他顶点的距离
b.path是记录到该顶点前经过的顶点
c.check描述该点是否被访问过
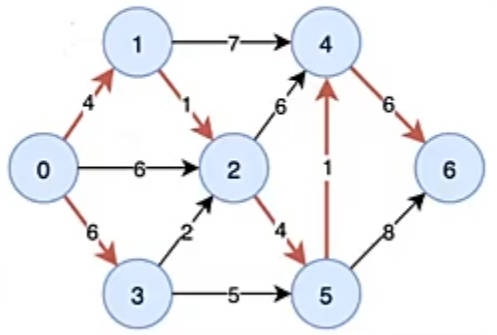
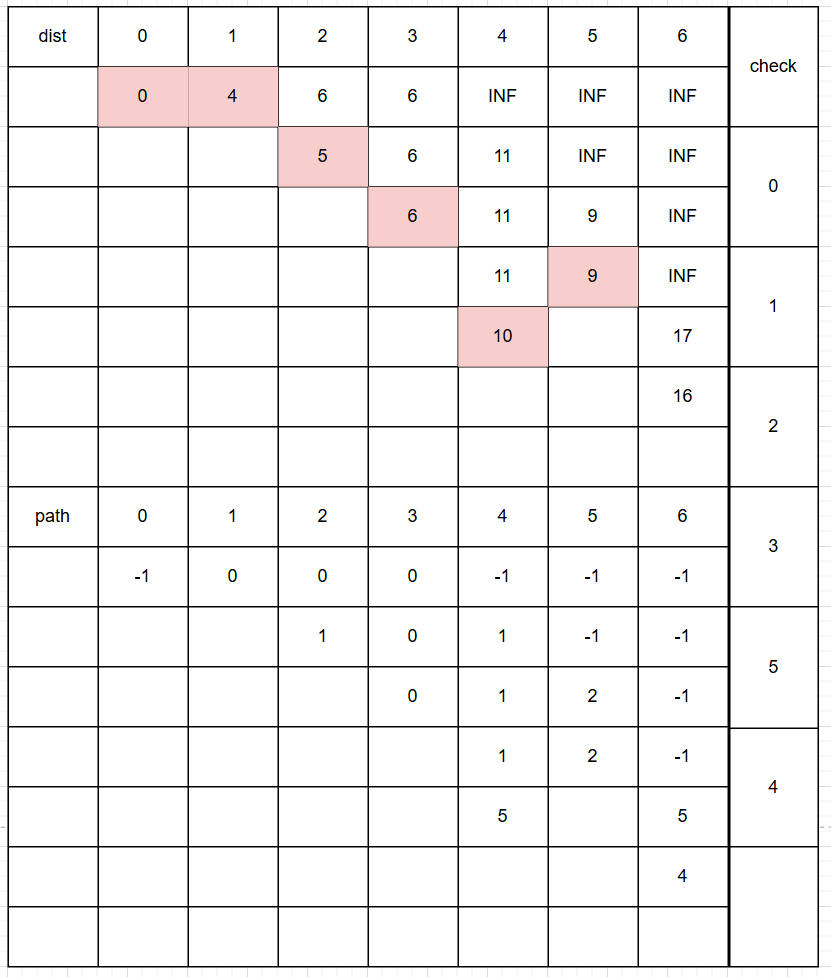
我们图结构如下,假如单源点为0,标记mark[0]为1,更新0的邻接点的dist和path
更新dist和path:假如该点未被激活过且新的路径长度比当前更短就覆盖当前路径长度并更新path,否则不更新
找与当前节点边最短的邻接点为待激活点,重复上述单源点的操作
二,Dijkstra代码实现
1.头文件中的接口
cpp
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/4.
//
#ifndef DIJKSTRA_H
#define DIJKSTRA_H
#include "../MatrixGraph/MatrixGraph.h"
void DijkstraMGraph(MGraph *graph, int start, int *dist, int *path);
void showShortPath(const int*path,int sum,int pos);
#endif //DIJKSTRA_H2.将头文件中的接口一一实现
cpp
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/4.
//
#include "Dijkstra.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void DijkstraMGraph(MGraph *graph, int start, int *dist, int *path) {
//1.初始化激活第一个顶点
int*mark=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph->nodeNum);
for (int i=0;i<graph->nodeNum;++i) {
dist[i]=graph->edges[start][i];
mark[i]=0;
if (graph->edges[start][i]<INF) {
path[i]=start;
}else {
path[i]=-1;
}
}
dist[start]=0;
path[start]=-1;
mark[start]=1;
//2.核心循环
for (int i=0;i<graph->nodeNum-1;++i) {
int mini=INF,k=0;
for (int j=0;j<graph->nodeNum;++j) {
//3.找到最小值为待激活点
if (mark[j]==0&&dist[j]<mini) {
mini=dist[j];
k=j;
}
}
mark[k]=1;
//4.激活,更新dist和path
for (int j=0;j<graph->nodeNum;++j) {
if (mark[j]==0&&dist[k]+graph->edges[k][j]<dist[j]) {
dist[j]=dist[k]+graph->edges[k][j];
path[j]=k;
}
}
}
free(mark);
}
void showShortPath(const int *path, int sum, int pos) {
int*stack=malloc(sizeof(int)*sum);
int top=-1;
//1.倒序入栈
while (path[pos]!=-1) {
stack[++top]=pos;
pos=path[pos];
}
stack[++top]=pos;
//2.顺序出栈,遍历
while (top!=-1) {
printf("%d\t",stack[top--]);
}
printf("\n");
free(stack);
}3.测试代码是否有bug
cpp
//
// Created by 27893 on 2025/8/4.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "Dijkstra.h"
void setup(MGraph*graph) {
const char *names[] = {"0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6",};
initMGraph(graph, names, sizeof(names) / sizeof(names[0]), 1, INF);
addMGraph(graph, 0, 1,4);
addMGraph(graph, 0, 2, 6);
addMGraph(graph, 0, 3, 6);
addMGraph(graph, 1, 2, 1);
addMGraph(graph, 1, 4, 7);
addMGraph(graph, 2, 4, 6);
addMGraph(graph, 2, 5, 4);
addMGraph(graph, 3, 5, 5);
addMGraph(graph, 3, 2, 2);
addMGraph(graph, 4, 6, 6);
addMGraph(graph, 5, 4, 1);
addMGraph(graph, 5, 6, 8);
}
int main() {
MGraph graph;
setup(&graph);
int*dist=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph.nodeNum);
int*path=malloc(sizeof(int)*graph.nodeNum);
if (dist==NULL||path==NULL) {
return -1;
}
DijkstraMGraph(&graph,0,dist,path);
printf("from #0 to #5:dist:%d\n",dist[5]);
showShortPath(path,graph.nodeNum,5);
printf("from #0 to #6:dist:%d\n",dist[6]);
showShortPath(path,graph.nodeNum,6);
free(dist);
return 0;
}