kafka的服务端是如何进行nio操作的
基于Kafka2.1解读Producer原理
基于Kafka2.1解读Consumer原理
文章目录
- kafka的服务端是如何进行nio操作的
- 前言
- 1、nio是什么?
- 2、原生的nio,服务端代码如何实现
-
- [2.1 一个Selector的demo](#2.1 一个Selector的demo)
- [2.2 两个Selector的demo](#2.2 两个Selector的demo)
- [2.3 多个Selector的demo](#2.3 多个Selector的demo)
- [3、 Kafka服务端怎么做的](#3、 Kafka服务端怎么做的)
-
- [3.1 Acceptor的accept事件处理](#3.1 Acceptor的accept事件处理)
- [3.2 Processor的IO事件处理](#3.2 Processor的IO事件处理)
-
- [3.2.1 org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector](#3.2.1 org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector)
- [3.2.2 KafkaChannel](#3.2.2 KafkaChannel)
- [3.3 小结](#3.3 小结)
- 总结
前言
相信对于nio,写java的同志背起八股文一定是一套又一套的;
但是实际自己业务代码进行使用应该很少,当然常见的是netty、Redis、Kafka。
今天咱们就Kafka3.7的源码,解读下Kafka的server端是怎么进行nio来进行non-blocking IO 操作的
1、nio是什么?
下面是我问豆包,它给我的回答:
NIO(Non-blocking I/O,非阻塞 I/O)是 Java 中用于高效处理 I/O 操作的 API,从 JDK 1.4 开始引入,主要用于解决传统 IO(BIO,Blocking I/O)在高并发场景下的性能瓶颈。
NIO 的核心特点包括:
非阻塞模式 :传统 BIO 中,I/O 操作(如读取数据)会阻塞线程直到操作完成,而 NIO 允许线程在等待 I/O 操作时执行其他任务,大幅提高了线程利用率。
缓冲区(Buffer) :NIO 以缓冲区为数据处理的中心,所有数据读写都必须通过缓冲区进行。缓冲区是一个固定大小的内存块,可更高效地管理数据。
通道(Channel) :通道是数据传输的双向通道,不同于传统 IO 的单向流(InputStream/OutputStream),可以同时进行读写操作,支持文件、网络套接字等多种数据源。
选择器(Selector) :这是 NIO 的关键组件,一个选择器可以监听多个通道的事件(如连接就绪、数据可读等),使单一线程能高效管理多个通道,非常适合高并发场景。
NIO 的典型应用场景包括:
- 高并发网络服务器(如 Web 服务器、即时通讯系统)
- 需要高效处理大量 I/O 操作的应用
- 对性能要求较高的分布式系统
与传统 BIO 相比,NIO 的编程模型更为复杂,但在处理大量并发连接时能显著提升系统吞吐量和响应性能,是 Java 高性能 I/O 编程的重要基础。Java NIO 后来发展为 NIO.2(在 JDK 7 中引入),增加了更多特性如异步 I/O 支持。
2、原生的nio,服务端代码如何实现
以下代码demo都是通过豆包实现的
2.1 一个Selector的demo
java
public class NioServer {
// 缓冲区大小
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
// 端口号
private static final int PORT = 8888;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 创建ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册到Selector,关注连接事件
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("NIO服务器已启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待就绪的事件,返回就绪的通道数量
int readyChannels = selector.select();
// 如果没有就绪的通道,继续等待
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
// 获取所有就绪的事件
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
// 处理连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key, selector);
}
// 处理读事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
// 移除已处理的事件,避免重复处理
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 处理连接事件
private static void handleAccept(SelectionKey key, Selector selector) throws IOException {
// 获取ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
// 接受客户端连接
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) {
System.out.println("新客户端连接: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册到Selector,关注读事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 向客户端发送欢迎消息
String welcomeMsg = "欢迎连接NIO服务器!\n";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(welcomeMsg.getBytes());
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
// 处理读事件
private static void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// 获取SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
// 读取数据
int bytesRead = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
System.out.println("客户端断开连接: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
socketChannel.close();
key.cancel();
return;
}
// 切换到读模式
buffer.flip();
// 转换为字符串
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes).trim();
System.out.println("收到来自 " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 的消息: " + message);
// 回复客户端
String response = "服务器已收到: " + message + "\n";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(response.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(buffer);
}
}2.2 两个Selector的demo
java
public class TwoSelectorNioServer {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
private static final int PORT = 8888;
// 用于处理连接事件的Selector
private Selector acceptSelector;
// 用于处理读写事件的Selector
private Selector ioSelector;
public TwoSelectorNioServer() throws IOException {
// 初始化两个Selector
acceptSelector = Selector.open();
ioSelector = Selector.open();
}
public void start() throws IOException {
// 创建ServerSocketChannel并配置
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将ServerSocketChannel注册到acceptSelector,只关注ACCEPT事件
serverSocketChannel.register(acceptSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("NIO服务器已启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
System.out.println("使用两个Selector分离处理连接和IO事件");
// 启动处理连接事件的线程
Thread acceptThread = new Thread(new AcceptHandler());
acceptThread.setName("Accept-Thread");
acceptThread.start();
// 启动处理IO事件的线程
Thread ioThread = new Thread(new IOHandler());
ioThread.setName("IO-Thread");
ioThread.start();
}
// 处理连接事件的线程
private class AcceptHandler implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 等待连接事件
int readyChannels = acceptSelector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = acceptSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
// 处理新连接
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
if (clientChannel != null) {
System.out.println("新客户端连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 配置为非阻塞模式
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将新连接注册到IO Selector,关注读事件
clientChannel.register(ioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 发送欢迎消息
String welcomeMsg = "欢迎连接NIO服务器!\n";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(welcomeMsg.getBytes());
clientChannel.write(buffer);
// 唤醒IO Selector,使其立即处理新注册的通道
ioSelector.wakeup();
}
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 处理IO事件的线程
private class IOHandler implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 等待IO事件
int readyChannels = ioSelector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = ioSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
if (key.isReadable()) {
// 处理读事件
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 处理读取数据
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
int bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
System.out.println("客户端断开连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
clientChannel.close();
key.cancel();
return;
}
// 处理读取到的数据
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes).trim();
System.out.println("收到来自 " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 的消息: " + message);
// 回复客户端
String response = "服务器已收到: " + message + "\n";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(response.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
clientChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new TwoSelectorNioServer().start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}2.3 多个Selector的demo
多个Selector实现nio,其中只有一个Selector处理accept事件,其他Selector实现IO事件
java
public class MultiSelectorNioServer {
private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
private static final int PORT = 8888;
private static final int IO_SELECTOR_COUNT = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); // IO Selector数量,通常设为CPU核心数
// 处理Accept事件的Selector
private final Selector acceptSelector;
// 处理IO事件的Selector数组
private final Selector[] ioSelectors;
// 用于轮询选择IO Selector的计数器
private final AtomicInteger selectorIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
public MultiSelectorNioServer() throws IOException {
this.acceptSelector = Selector.open();
this.ioSelectors = new Selector[IO_SELECTOR_COUNT];
// 初始化所有IO Selector并启动对应的处理线程
for (int i = 0; i < IO_SELECTOR_COUNT; i++) {
ioSelectors[i] = Selector.open();
Thread ioThread = new Thread(new IOHandler(ioSelectors[i]), "IO-Thread-" + i);
ioThread.start();
}
}
public void start() throws IOException {
// 创建并配置ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 注册ACCEPT事件到acceptSelector
serverSocketChannel.register(acceptSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("多Selector NIO服务器已启动,监听端口: " + PORT);
System.out.println("Accept线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("IO Selector数量: " + IO_SELECTOR_COUNT);
// 启动Accept事件处理线程
Thread acceptThread = new Thread(new AcceptHandler(), "Accept-Thread");
acceptThread.start();
}
// 处理Accept事件的线程
private class AcceptHandler implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 等待连接事件
int readyChannels = acceptSelector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = acceptSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel clientChannel = serverChannel.accept();
if (clientChannel != null) {
System.out.println("新客户端连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress());
// 配置为非阻塞模式
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 轮询选择一个IO Selector来处理这个连接
Selector ioSelector = chooseIOSelector();
// 向客户端发送欢迎消息
String welcomeMsg = "欢迎连接多Selector NIO服务器!\n";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(welcomeMsg.getBytes());
clientChannel.write(buffer);
// 注册到选中的IO Selector,关注读事件
// 使用synchronized确保注册操作的线程安全
synchronized (ioSelector) {
clientChannel.register(ioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 唤醒IO Selector,使其立即处理新注册的通道
ioSelector.wakeup();
}
}
// 轮询选择IO Selector,保证负载均衡
private Selector chooseIOSelector() {
int index = selectorIndex.getAndIncrement() % IO_SELECTOR_COUNT;
return ioSelectors[Math.abs(index)];
}
}
// 处理IO事件的线程
private class IOHandler implements Runnable {
private final Selector ioSelector;
public IOHandler(Selector ioSelector) {
this.ioSelector = ioSelector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
// 等待IO事件
int readyChannels = ioSelector.select();
if (readyChannels == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = ioSelector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = keyIterator.next();
keyIterator.remove();
// 确保通道有效
if (!key.isValid()) {
continue;
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER_SIZE);
int bytesRead = clientChannel.read(buffer);
if (bytesRead == -1) {
// 客户端关闭连接
System.out.println("客户端断开连接: " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress() +
" (处理线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ")");
clientChannel.close();
key.cancel();
return;
}
// 处理读取到的数据
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
String message = new String(bytes).trim();
System.out.println("收到来自 " + clientChannel.getRemoteAddress() +
" 的消息: " + message +
" (处理线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ")");
// 回复客户端
String response = "服务器已收到: " + message + "\n";
buffer.clear();
buffer.put(response.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
clientChannel.write(buffer);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new MultiSelectorNioServer().start();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
我印象中,Redis的nio就是通过一个Selector实现的,而netty和Kafka就是多个Selector实现的,此处就抽象为两个Selector,分别处理accept、IO事件,也就是传说中的reactor模式了
3、 Kafka服务端怎么做的
如上文,Kafka是基于多个Selector做的,所以参考2.3多个Selector的demo 相对比较好理解一些
Kafka有两个比较重要的类,分别是 Acceptor 和 Processor。看名字其实就能大概看出来了,Acceptor 是用来处理 accept 事件的,而Processor是处理IO事件的。
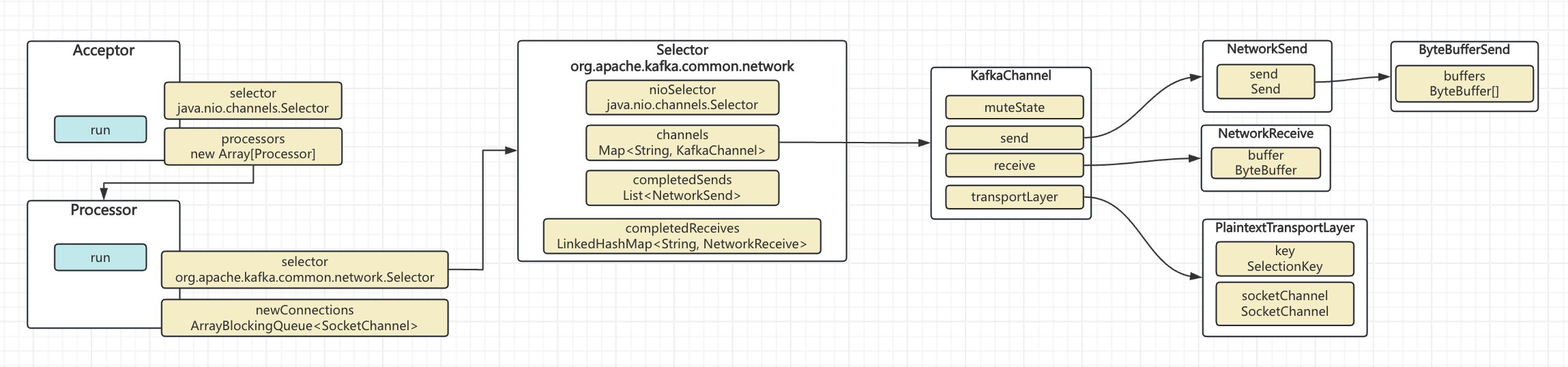
可以看到 Acceptor 和 Processor 上都有Selector,同时Acceptor有个processors属性,也就是支持多个processor来处理IO事件,不过需要注意的是Acceptor和Processor上的selector属性是不同的类型
3.1 Acceptor的accept事件处理
和2.3的多个Selector的demo类型,Acceptor线程run起来之后,接受client请求,通过selector进行accept之后,就会生成socketChannel,同时通过synchronized从processors里选择一个processor,
1. 通过 selectionKey 获取到socketChannel
2. 通过synchronized从processors里获得一个processor
3. processor将该socketChannel放进自己的newConnections里3.2 Processor的IO事件处理
Processor线程run起来之后,从newConnections中poll一个socketChannel,然后把该socketChannel在selector上注册读事件
newConnections:保存的是accept之后待处理的socketChannel
selector:见3.2.1介绍
3.2.1 org.apache.kafka.common.network.Selector
selector:java.nio.channels.Selector
channels:保存的是该processor处理的kafkaChannel(这个后面介绍)
completedReceives:保存的是一次select操作,从不同kafkaChannel获取到的值
completedSends:保存的是一次select操作,从不同kafkaChannel写入的值
3.2.2 KafkaChannel
KafkaChannel其实就是对原生的socketChannel的增强版,只不过同时保存了IO数据
muteState:记录的是该Channel的静音状态,该字段控制当前kafkaChannel上socketChannel的一次produceRequest的处理(producer发送的一次请求),后续文章详细讲解
send:想要往该kafkaChannel上写的数据
receive:从该kafkaChannel上读取到的数据
transportLayer:这个其实就是java原生的socketChannel,同时保存了下selectionKey
3.3 小结
可以看到Kafka的不管是Selector还是KafkaChannel都是对java nio的Selector、socketChannel的二次封装而已,然后再把该Channel和Selector的IO数据保存下来,做个临时备份
你一定想问,保存下来干嘛呢?
当然是具体的Kafka计算操作了,其实整个架构理念和Kafka的producer有点类似:计算和IO进行解耦
producer:计算 + IO
server:IO + 计算
总结
本文基于java原生nio,进行延展推理讲解了Kafka 服务端的IO流程,为后续解读Kafka的计算流程奠定一个基础。
欢迎沟通~