73. 矩阵置零
java
class Solution {
public void setZeroes(int[][] matrix) {
int length=matrix.length;
int wingth=matrix[0].length;
// 使用集合记录需要置零的行和列
Set<Integer> n = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> m = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<wingth;j++){
if(matrix[i][j]==0){
n.add(i);
m.add(j);
}
}
}
for(int l:n){
for(int k=0;k<wingth;k++){
matrix[l][k]=0;
}
}
for(int g:m){
for(int h=0;h<length;h++){
matrix[h][g]=0;
}
}
}
}代码解读:矩阵置零(Set Matrix Zeroes)
这段代码实现了将矩阵中所有0元素所在的行和列全部置为0的功能。以下是详细解析:
1. 核心思路
问题要求:给定一个m×n的矩阵,如果某个元素为0,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为0。
解决方法:使用两个HashSet分别记录需要置零的行和列索引,然后统一处理。
2. 代码解析
(1) 初始化行列集合
java
Set<Integer> n = new HashSet<>(); // 存储需要置零的行索引 Set<Integer> m = new HashSet<>(); // 存储需要置零的列索引
n:记录包含0元素的行号
m:记录包含0元素的列号(2) 第一次遍历:标记0的位置
java
for(int i=0;i<length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<wingth;j++){ if(matrix[i][j]==0){ n.add(i); // 记录行号 m.add(j); // 记录列号 } } }
- 遍历整个矩阵,发现0时记录其行列索引。
(3) 行置零处理
java
for(int l:n){ for(int k=0;k<wingth;k++){ matrix[l][k]=0; // 将整行置零 } }
- 遍历所有标记行,将该行所有元素设为0。
(4) 列置零处理
java
for(int g:m){ for(int h=0;h<length;h++){ matrix[h][g]=0; // 将整列置零 } }
- 遍历所有标记列,将该列所有元素设为0。
3. 复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m×n),需要遍历矩阵两次(标记+置零)
空间复杂度:O(m+n),最坏情况下需要存储所有行和列索引
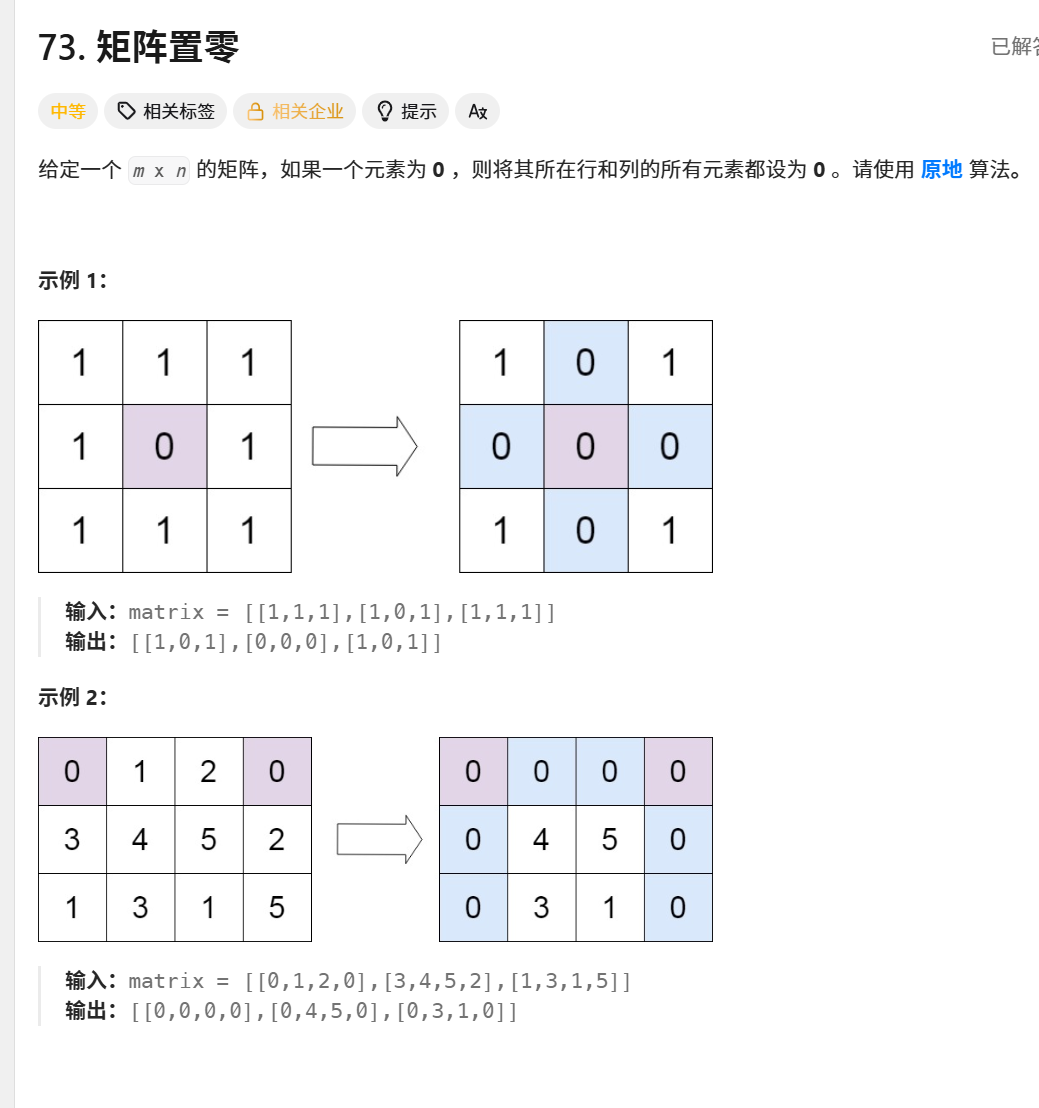
4. 示例演示
输入矩阵:
text
[ [1, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1] ]执行过程:
发现0在(1,1),记录行1和列1
将第1行全部置零:
[1,0,1]→[0,0,0]将第1列全部置零:
[1][0]→0
[2][0]→0(实际值不变)输出:
text
[ [1,0,1], [0,0,0], [1,0,1] ]
54. 螺旋矩阵

java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> order = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return order;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int left = 0, right = columns - 1;
int top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
// 1. 从左到右遍历上层
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order.add(matrix[top][column]);
}
// 2. 从上到下遍历右列
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order.add(matrix[row][right]);
}
// 3. 从右到左遍历下层(确保不是单行)
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order.add(matrix[bottom][column]);
}
// 4. 从下到上遍历左列(确保不是单列)
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order.add(matrix[row][left]);
}
}
// 边界收缩
left++; right--; top++; bottom--;
}
return order;
}
}代码解读:螺旋矩阵(Spiral Matrix)
这段代码实现了按顺时针螺旋顺序遍历二维矩阵的功能。以下是详细解析:
1. 核心思路
问题要求:将矩阵元素按从外到内顺时针顺序排列。
解决方法 :使用边界收缩法,通过四个边界指针(left, right, top, bottom)逐步向内层遍历。
2. 代码解析
(1) 初始化边界指针
java
int left = 0, right = columns - 1; // 左右边界(列) int top = 0, bottom = rows - 1; // 上下边界(行)
left/right控制列范围,top/bottom控制行范围。(2) 螺旋遍历
java
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) { // 1. 从左到右遍历上层 for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) { order.add(matrix[top][column]); } // 2. 从上到下遍历右列 for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) { order.add(matrix[row][right]); } // 3. 从右到左遍历下层(确保不是单行) if (left < right && top < bottom) { for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) { order.add(matrix[bottom][column]); } // 4. 从下到上遍历左列(确保不是单列) for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) { order.add(matrix[row][left]); } } // 边界收缩 left++; right--; top++; bottom--; }遍历顺序:
→ 左到右(上层)
↓ 上到下(右列)
← 右到左(下层,需判断非单行)
↑ 下到上(左列,需判断非单列)
(3) 边界收缩
每次完成一圈遍历后,四个边界同时向内收缩:
java
left++; // 左边界右移 right--; // 右边界左移 top++; // 上边界下移 bottom--; // 下边界上移
3. 示例演示
输入矩阵:
text
[ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ]执行过程:
第一圈:
→ 1→2→3
↓ 6→9
← 8→7
↑ 4
边界收缩:left=1, right=1, top=1, bottom=1
第二圈:
→ 5
边界收缩结束
输出 :
[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
4. 复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m×n),每个元素被访问一次
空间复杂度:O(1)(不考虑输出列表)
5. 关键点总结
边界条件:
检查
top < bottom和left < right避免重复遍历单行/列空矩阵直接返回
遍历顺序:
- 必须遵循→↓←↑的严格顺序
终止条件:
- 当
left > right或top > bottom时结束循环
48. 旋转图像
java
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < (n + 1) / 2; ++j) {
int temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - j - 1][i];
matrix[n - j - 1][i] = matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1];
matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] = matrix[j][n - i - 1];
matrix[j][n - i - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}代码解读:螺旋矩阵(Spiral Matrix)
1. 获取矩阵维度
java
int n = matrix.length;
作用:获取n×n矩阵的边长
示例 :3×3矩阵 →
n=32. 外层循环:控制旋转层数
java
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; ++i) {
含义:
n / 2:矩阵需要旋转的层数(如4×4矩阵有2层)
i:当前处理的层数索引(从外到内)示例:
4×4矩阵:
i取值0,1(两层)3×3矩阵:
i取值0(一层,中心点不动)3. 内层循环:处理当前层元素
java
for (int j = 0; j < (n + 1) / 2; ++j) {
含义:
(n + 1) / 2:处理奇偶矩阵差异
j:当前层元素的列索引设计原因:
奇数矩阵:中间列不需要处理(如3×3矩阵的
j取值0,1)偶数矩阵:全部列都需要处理
4. 四元素轮换核心逻辑
java
int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - j - 1][i]; matrix[n - j - 1][i] = matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1]; matrix[n - i - 1][n - j - 1] = matrix[j][n - i - 1]; matrix[j][n - i - 1] = temp;分步解析(以3×3矩阵的(0,0)点为例):
保存左上角:
java
int temp = matrix[0][0]; // temp = 1左下 → 左上:
java
matrix[0][0] = matrix[2][0]; // 1 ← 7右下 → 左下:
java
matrix[2][0] = matrix[2][2]; // 7 ← 9右上 → 右下:
java
matrix[2][2] = matrix[0][2]; // 9 ← 3temp → 右上:
java
matrix[0][2] = temp; // 3 ← 1坐标变换规律:
位置 坐标变换公式 示例(3×3) 左上 (i,j) (0,0) 左下 (n-j-1,i) (2,0) 右下 (n-i-1,n-j-1) (2,2) 右上 (j,n-i-1) (0,2) 5. 边界处理细节
奇数矩阵中心点:
当
n为奇数时,(n + 1) / 2确保中心点不被处理例如3×3矩阵的中心点(1,1)不会被遍历到
6. 时间复杂度分析
O(n²):每个元素被访问一次
空间复杂度O(1) :仅使用
temp临时变量7. 示例完整流程
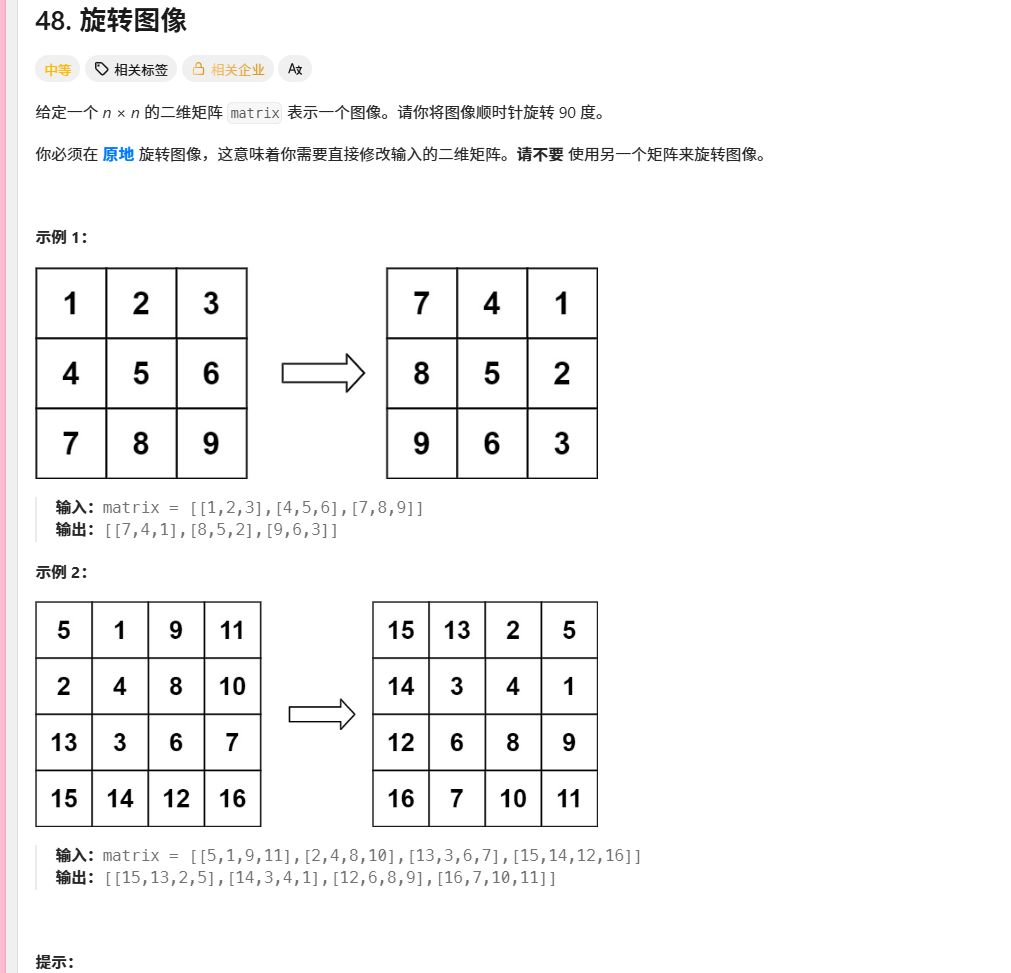
输入矩阵:
text
[ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ]旋转步骤:
外层(0,0)点开始:
四角交换:1←7←9←3←1
边中交换:2←4←8←6←2
结果:
text
[ [7, 4, 1], [8, 5, 2], [9, 6, 3] ]8. 关键设计思想
分层处理:将矩阵看作洋葱,逐层剥离
四元组交换:每组4个位置同时旋转
坐标映射:通过数学计算确定旋转后的位置
奇偶兼容 :
(n+1)/2的统一处理9. 常见误区提醒
边界错误:
错误:使用
j < n / 2会漏掉奇数列正确:必须用
(n + 1) / 2交换顺序:
- 必须逆时针或顺时针统一方向
中心点处理:
- 奇数矩阵中心点无需旋转
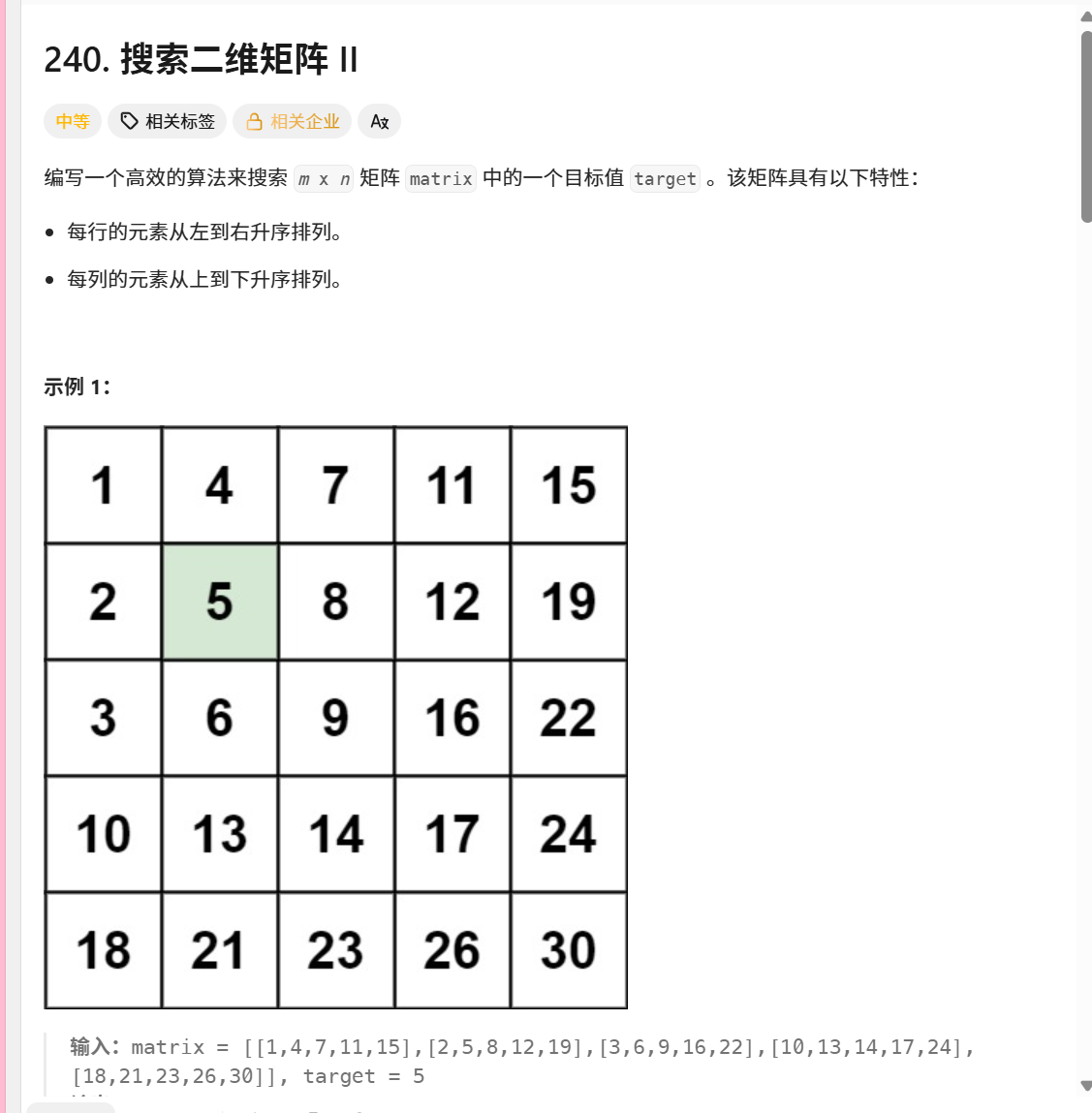
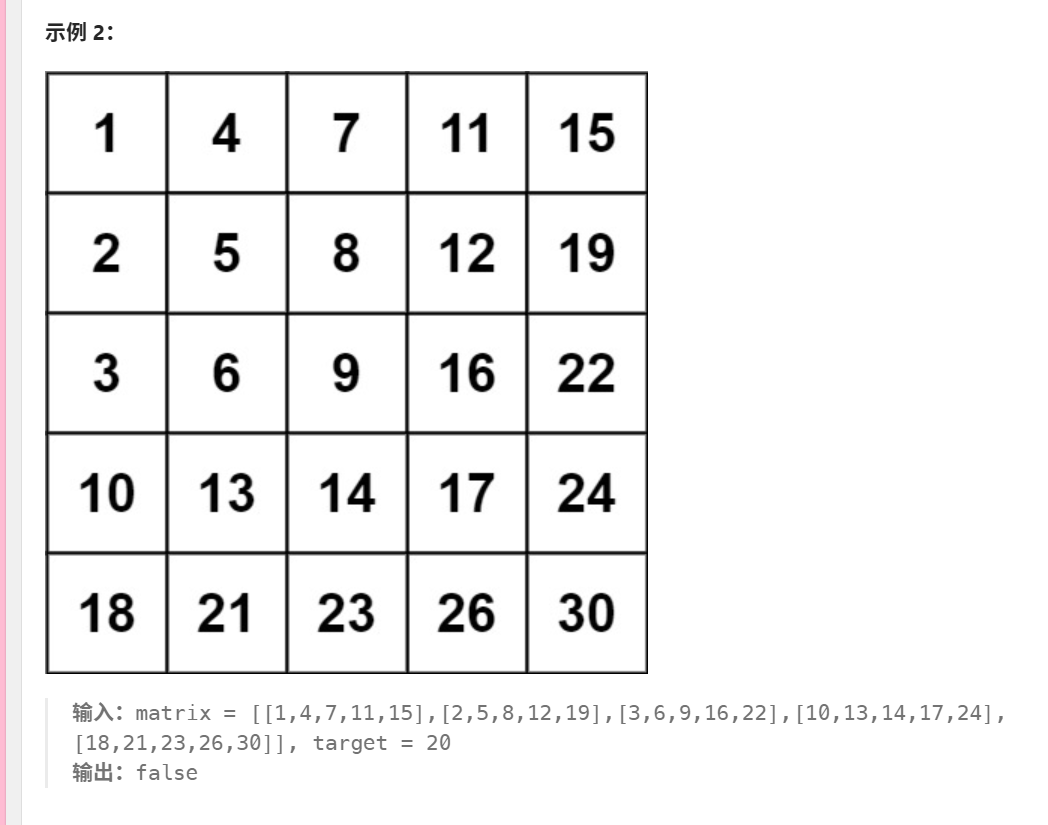
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
for (int[] row : matrix) {
for (int element : row) {
if (element == target) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
java
class Solution {
public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
int x = 0, y = n - 1;
while (x < m && y >= 0) {
if (matrix[x][y] == target) {
return true;
}
if (matrix[x][y] > target) {
--y;
} else {
++x;
}
}
return false;
}
}