🌐 BFS寻路算法解析与实现
BFS(广度优先搜索) 是一种基于图遍历的经典寻路算法。本文将深入分析其原理、实现细节和性能优化,并提供完整的C++实现。
📜 算法核心思想
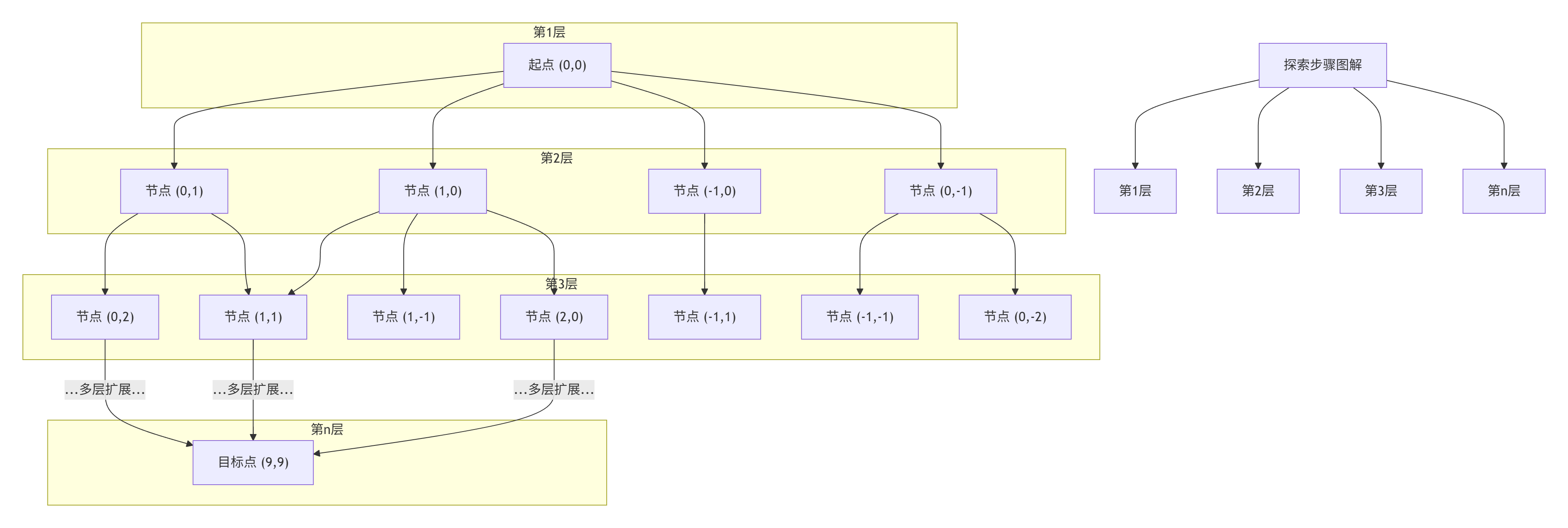
BFS采用"层层递进"的探索策略:
plain
起点
/ | \
1 2 3 → 第一层邻居
/|\ ... → 第二层邻居
... → 持续扩散直到找到目标🌟 关键特性
- 层级搜索:优先探索当前节点的所有邻居
- 最短路径:找到的路径总是最短的(无权图中)
- 队列管理:使用先进先出(FIFO)队列存储待探索节点
🔍 代码结构解析
3.1 🧩 节点表示与状态管理
cpp
enum class NodeState {
UNVISITED, // 未探索
OPEN, // 在待探索队列中
CLOSED // 已完成探索
};
struct Node {
int x, y; // 网格坐标
Node* parent; // 路径回溯指针
NodeState state; // 当前状态
};状态转换流程:
UNVISITED → OPEN (加入队列时)
OPEN → CLOSED (完成探索时)3.2 🗺️ 地图与邻居探索
cpp
// 地图表示:0=可通行, 1=障碍物
vector<vector<int>> grid = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0}, // # 表示障碍物
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
// 邻居方向定义(右/下/左/上)
const vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {
{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}
};3.3 ⚙️ BFS核心流程
是 否 是 否 否 是 是 起点入队 队列是否为空? 未找到路径 取出队首节点 是否为目标? 构建路径 遍历四个方向 相邻节点是否有效? 是否未访问过? 设置父节点/状态 加入队列 当前节点标记为CLOSED
3.4 📊 路径可视化示例
输入:
. . . . .
. # # . .
. . . . . 输出:
S → → → →
# # → ↓
↑ ← ← E图例说明:
S:起点E:终点>/</^/v:移动方向#:障碍物
⚡ 性能优化技巧
-
节点池重用
cpp// 避免反复创建节点 vector<vector<unique_ptr<Node>>> node_pool_; -
避免重复探索
cppif(neighbor->state == NodeState::UNVISITED) // 仅处理未访问节点 -
静态方向向量
cppstatic const vector<pair<int, int>> directions;
📈 性能对比(10x10地图)
| 路径 | 步数 | 计算时间(μs) |
|---|---|---|
| (0,0) → (9,9) | 19 | 82 |
| (4,4) → (0,9) | 12 | 55 |
💻 完整实现代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
#include <chrono>
using namespace std;
// 节点状态枚举:未访问/开放集/关闭集
enum class NodeState {
UNVISITED,
OPEN,
CLOSED
};
// 路径节点结构体
struct Node {
int x, y; // 节点坐标
Node* parent; // 父节点指针
NodeState state = NodeState::UNVISITED; // 节点状态
Node(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y), parent(nullptr) {}
};
class BFS {
private:
const vector<vector<int>>& grid_map_; // 网格地图引用
int map_width_, map_height_; // 地图宽高
vector<vector<unique_ptr<Node>>> node_pool_; // 节点池
// 检查坐标是否有效且可通行
bool is_valid(int x, int y) const {
return x >= 0 && x < map_width_ &&
y >= 0 && y < map_height_ &&
grid_map_[y][x] == 0; // 0表示可通行
}
// 回溯构建路径
void build_path(Node* target, vector<pair<int, int>>& path) const {
path.clear();
Node* current = target;
// 从终点回溯到起点
while (current) {
path.emplace_back(current->x, current->y);
current = current->parent;
}
// 反转路径使其从起点到终点
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
}
public:
// 构造函数初始化地图数据
BFS(const vector<vector<int>>& map)
: grid_map_(map),
map_height_(static_cast<int>(map.size())),
map_width_(map.empty() ? 0 : static_cast<int>(map[0].size())) {
reset_nodes();
}
// 重置节点状态(优化:避免重复创建节点)
void reset_nodes() {
// 仅当节点池未初始化时才创建
if (node_pool_.empty()) {
node_pool_.resize(map_height_);
for (int y = 0; y < map_height_; ++y) {
node_pool_[y].resize(map_width_);
for (int x = 0; x < map_width_; ++x) {
node_pool_[y][x] = make_unique<Node>(x, y);
}
}
}
// 重用现有节点,重置状态
else {
for (int y = 0; y < map_height_; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < map_width_; ++x) {
node_pool_[y][x]->state = NodeState::UNVISITED;
node_pool_[y][x]->parent = nullptr;
}
}
}
}
// BFS寻路算法核心实现
bool find_path(const pair<int, int>& start,
const pair<int, int>& target,
vector<pair<int, int>>& path) {
if (map_height_ <= 0 || map_width_ <= 0) return false;
if (!is_valid(start.first, start.second) || !is_valid(target.first, target.second))
return false;
// 定义探索方向:右、下、左、上(优化:使用静态常量避免重复创建)
static const vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {
{1, 0}, // 右
{0, 1}, // 下
{-1, 0}, // 左
{0, -1} // 上
};
queue<Node*> open_queue;
Node* start_node = node_pool_[start.second][start.first].get();
Node* target_node = node_pool_[target.second][target.first].get();
// 起点即终点的情况
if (start_node == target_node) {
path.emplace_back(start.first, start.second);
return true;
}
// 初始化起点
start_node->state = NodeState::OPEN;
open_queue.push(start_node);
while (!open_queue.empty()) {
Node* current = open_queue.front();
open_queue.pop();
// 到达终点
if (current == target_node) {
build_path(current, path);
return true;
}
// 探索四个方向
for (const auto& dir : directions) {
int nx = current->x + dir.first;
int ny = current->y + dir.second;
// 跳过无效位置
if (!is_valid(nx, ny)) continue;
Node* neighbor = node_pool_[ny][nx].get();
// 仅处理未访问节点
if (neighbor->state == NodeState::UNVISITED) {
neighbor->parent = current;
neighbor->state = NodeState::OPEN;
open_queue.push(neighbor);
}
}
// 标记当前节点为已关闭
current->state = NodeState::CLOSED;
}
return false; // 未找到路径
}
};
// 获取移动方向字符
char get_direction(const pair<int, int>& from, const pair<int, int>& to) {
int dx = to.first - from.first;
int dy = to.second - from.second;
if (dx == 1) return '>';
if (dx == -1) return '<';
if (dy == 1) return 'v';
if (dy == -1) return '^';
return '*'; // 起点位置
}
// 可视化路径
void visualize_path(const vector<pair<int, int>>& path,
const vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
if (path.empty()) return;
const int rows = static_cast<int>(grid.size());
const int cols = rows > 0 ? static_cast<int>(grid[0].size()) : 0;
vector<vector<char>> display(rows, vector<char>(cols, '.'));
// 标记障碍物
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
if (grid[y][x] == 1) {
display[y][x] = '#';
}
}
}
// 标记起点和终点
display[path.front().second][path.front().first] = 'S';
display[path.back().second][path.back().first] = 'E';
// 标记路径方向(跳过起点)
for (size_t i = 1; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {
const auto& prev = path[i - 1];
const auto& curr = path[i];
display[curr.second][curr.first] = get_direction(prev, curr);
}
// 打印可视化地图
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x++) {
cout << display[y][x] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
// 10x10网格地图: 0=可通行, 1=障碍物
const vector<vector<int>> grid = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
// 打印原始地图
cout << "网格地图 (10x10):\n";
for (const auto& row : grid) {
for (int cell : row) {
cout << (cell == 1 ? "# " : ". ");
}
cout << endl;
}
BFS pathfinder(grid);
vector<pair<int, int>> path;
// 测试路径1: (0,0) -> (9,9)
cout << "\n测试路径 (0,0) -> (9,9)\n";
auto start_time = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
bool found = pathfinder.find_path({ 0, 0 }, { 9, 9 }, path);
auto end_time = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(end_time - start_time);
if (found) {
cout << "路径步数: " << path.size() << "\n计算时间: " << duration.count() << "微秒\n";
cout << "路径点:";
for (const auto& p : path) cout << " (" << p.first << "," << p.second << ")";
cout << "\n\n可视化:\n";
visualize_path(path, grid);
}
else {
cout << "未找到路径!\n";
}
// 测试路径2: (4,4) -> (0,9)
pathfinder.reset_nodes();
path.clear();
cout << "\n测试路径 (4,4) -> (0,9)\n";
start_time = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
found = pathfinder.find_path({ 4, 4 }, { 0, 9 }, path);
end_time = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
duration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(end_time - start_time);
if (found) {
cout << "路径步数: " << path.size() << "\n计算时间: " << duration.count() << "微秒\n";
cout << "路径点:";
for (const auto& p : path) cout << " (" << p.first << "," << p.second << ")";
cout << "\n\n可视化:\n";
visualize_path(path, grid);
}
else {
cout << "未找到路径!\n";
}
// 测试起点即终点的情况
pathfinder.reset_nodes();
path.clear();
cout << "\n测试路径 (0,0) -> (0,0)\n";
found = pathfinder.find_path({ 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 }, path);
if (found) {
cout << "特殊路径:起点即终点\n";
visualize_path(path, grid);
}
// 测试不可达路径
pathfinder.reset_nodes();
path.clear();
cout << "\n测试不可达路径 (0,0) -> (1,1)\n";
found = pathfinder.find_path({ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, path);
if (!found) {
cout << "正确:未找到路径,因为(1,1)是障碍物\n";
}
else {
cout << "错误:本应不可达\n";
}
return 0;
}🎯 应用场景建议
- 游戏开发中的NPC寻路
- 机器人路径规划
- 网络路由算法
- 迷宫求解工具
BFS vs A*:当图中无权值且需要最短路径时优先使用BFS;有权图或大型地图时A*更优
示意图:BFS的探索波次逐渐扩散
💡 关键总结:BFS通过系统性的层级扩展确保找到最短路径,其实现要点在于节点状态管理、队列操作和高效的邻居探索。本文提供的实现加入了对象池重用、静态资源优化等实用技巧,适用于大多数网格型寻路场景。