1. 写在前面
最近在搞一个"大曲率弯道"场景的数据挖掘,里面有个逻辑是给定自车的定位坐标和车道线的坐标点,根据点到线段的距离,去找到自车所在的车道中心线。
然后发现这个计算其实在很多场景中都是可以用到的,所以就想通过一篇文章来整理下这块的原理和代码实战,算是把学校学习的向量知识真正的应用到实战中。
2. 原理
首先得知道一个点:点到线段最短距离的运算与点到直线的最短距离的运算二者之间存在一定的差别 ,即求点到线段最短距离时需要考虑参考点在沿线段方向的投影点是否在线段 上,若在线段上才可采用点到直线距离公式。
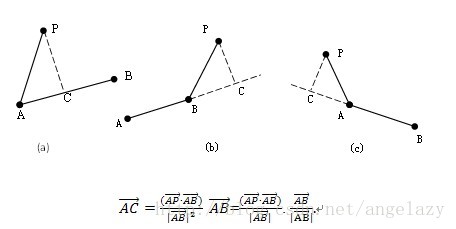
三种情况:
- 点在投射在线段上, 点到线段的距离 等效 点到直线的距离, 图(a)
- 点在线段外, 点到线段的距离为该点到最近短点的距离, 图(b)(c )
- 点在线段上, 点到线段的距离为0
参考这篇文章, 介绍3种方法:

3. 实战
有了理论, 下面给出代码实战, 用python实现了两版。
python
import numpy as np
import math
# 向量之间直接运算
def distance_point_to_segment(point, segment_start, segment_end):
"""
计算点到线段的最短距离
:param point: 点的坐标,形如(x, y)
:param segment_start: 线段起点坐标,形如(x, y)
:param segment_end: 线段终点坐标,形如(x, y)
:return: 最短距离
"""
segment_vec = segment_end - segment_start
point_vec = point - segment_start
projection_length = np.dot(point_vec, segment_vec) / np.dot(segment_vec, segment_vec)
if projection_length < 0:
return np.linalg.norm(point_vec)
elif projection_length > 1:
return np.linalg.norm(point - segment_end)
else:
projection = segment_start + projection_length * segment_vec
return np.linalg.norm(point - projection)
# 如果用坐标的计算方式
def distance_point_to_line_segment(point, start, end):
"""
计算点到线段的距离
:param point: 点 (x, y)
:param start: 线段起点 (x, y)
:param end: 线段终点 (x, y)
:return: 点到线段的距离
"""
px, py = point
sx, sy = start
ex, ey = end
# 计算线段的长度
line_length = math.sqrt((ex - sx) ** 2 + (ey - sy) ** 2)
if line_length == 0:
return math.sqrt((px - sx) ** 2 + (py - sy) ** 2)
# 计算点到线段所在直线的投影比例
dot_product = ((px - sx) * (ex - sx) + (py - sy) * (ey - sy)) / (line_length ** 2)
if dot_product < 0:
return math.sqrt((px - sx) ** 2 + (py - sy) ** 2)
elif dot_product > 1:
return math.sqrt((px - ex) ** 2 + (py - ey) ** 2)
else:
# 计算投影点的坐标
proj_x = sx + dot_product * (ex - sx)
proj_y = sy + dot_product * (ey - sy)
return math.sqrt((px - proj_x) ** 2 + (py - proj_y) ** 2)
# 三个点计算曲率
def get_lane_curve(lane, closest_end_point_idx):
point_len = len(lane.geometry.points)
point_1 = lane.geometry.points[closest_end_point_idx]
point_0 = lane.geometry.points[min(closest_end_point_idx + 12, point_len - 2)]
point_2 = lane.geometry.points[max(closest_end_point_idx - 8, 0)]
cur_point = np.array((point_1.xyz.x, point_1.xyz.y))
points = lane.geometry.points
# 向后搜索30米的点(point_0)
for i in range(closest_end_point_idx, point_len):
next_point = np.array((points[i].xyz.x, points[i].xyz.y))
if np.linalg.norm(next_point - cur_point) >= 15:
point_0 = points[i]
break
# 向前搜索30米的点(point_2)
for i in range(closest_end_point_idx, -1, -1):
next_point = np.array((points[i].xyz.x, points[i].xyz.y))
if np.linalg.norm(next_point - cur_point) >= 15:
point_2 = points[i]
break
point_0 = np.array((point_0.xyz.x, point_0.xyz.y))
point_1 = np.array((point_1.xyz.x, point_1.xyz.y))
point_2 = np.array((point_2.xyz.x, point_2.xyz.y))
x0, y0 = point_0
x1, y1 = point_1
x2, y2 = point_2
cross_product = (x1 - x0) * (y2 - y0) - (x2 - x0) * (y1 - y0)
if cross_product == 0:
curve_radius = float('inf')
else:
# 计算三边长度
ab = np.linalg.norm(point_1 - point_0)
bc = np.linalg.norm(point_1 - point_2)
ca = np.linalg.norm(point_0 - point_2)
# 计算曲率半径
curve_radius = (ab * bc * ca) / (2 * abs(cross_product))
return curve_radiuslua实现了一版
lua
-- 计算点到线段的最短距离
function distance_point_to_segment(point, segment_start, segment_end)
local segment_vec = vec_sub(segment_end, segment_start)
local point_vec = vec_sub(point, segment_start)
local segment_length_sq = vec_dot(segment_vec, segment_vec)
if segment_length_sq == 0 then
return vec_norm(point_vec)
end
-- 限制在[0,1]区间
local t = vec_dot(point_vec, segment_vec) / segment_length_sq
t = math.max(0, math.min(1, t))
local projection = vec_add(segment_start, vec_mul_scalar(segment_vec, t))
return vec_norm(vec_sub(point, projection))
end参考资料: