前言🐻
类似 Cursor、Trae 此类的编程辅助 AI 已经流行一段时间了,它们能提高我们的编码效率。当你看到 AI 助手敏捷准确地回应指令,是不是好奇背后的原理?
我也有同样的疑问,正巧前段时间,字节旗下的 Trae 公开了核心模块的源码,我在阅读之后进行总结,理解到了此类辅助编程 AI 工具背后的实现原理,希望将其分享出来,所以写了这篇文章。
在这篇文章中,无论你是刚听说过 Agent 的新手,还是渴望深入了解 AI 的探索者,都能轻松跟上节奏。我们会先从基础的 Agent 入手,了解它如何接收和处理指令,接着为它添加调用工具、对话等 "超能力",最终见证一个编程辅助工具的诞生。
第一节:调用 LLM 接口实例🐥
要搭建一个 AI 工具,得先会用它的 "大脑"------ 大语言模型(LLM)。这一节用 OpenAI 接口举个简单例子,带你看看怎么调用 LLM,以及它能做些什么。
准备工作
- python 环境
- 去火山引擎随意找一个大语言模型,获取授权后,在下面的代码中填入 base_url、api_key、model。
- 找到对应模型调用的例子代码
调用示例:让 AI 提取天气查询中的地点和时间
下面代码让 AI 处理用户关于天气的询问,从中提取出地点和时间,并以 JSON 格式输出,直观展示 LLM 的信息提取能力:
python
from openai import OpenAI
env = parse_env_file()
base_url = ""
api_key = ""
model = ""
client = OpenAI(
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "分析用户关于天气的询问,用JSON格式输出,包含'地点'、'时间'两个键,每个键的值为对应的描述"},
{"role": "user", "content": "今天北京天气如何?"}
]
if __name__ == "__main__":
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
)
print(completion.choices[0].message.content)
# 运行后可能得到这样的结果: {"地点": "北京", "时间": "今天"}LLM 的核心能力在这里体现
从这个例子能看出 LLM 的能力:
- 信息提取:能从用户的自然语言询问中挑出地点和时间信息
- 按格式输出:严格按照要求以 JSON 格式呈现,方便后续程序处理(前提是选用的 LLM 足够智能,不然它很可能会返回一个不能解析为 JSON 的字符串。为了强制输出 JSON,调用的方法基本都内置了是否要输出为 JSON 的配置项)
- 多信息处理:即使一句话中包含多个地点和时间,也能对应和区分
这就是 Trae 的基础 ------ 调用 LLM 接口,让机器理解并处理用户需求中的关键信息。下一节会给它加 "自主决策" 功能,让它从 "被动提取信息" 变 "主动完成任务"。
第二节:调用工具的实例🐣
有了 LLM 处理信息的基础,接下来我们要给它配上 "工具包"------ 让 AI 能根据需求主动调用外部工具,完成更复杂的任务。这一节我们就来实现两个常用工具:查询天气预报和数字相加,并演示 AI 如何根据用户指令选择合适的工具。
工具定义。首先,我们需要定义两个工具函数,分别处理天气查询和数字相乘:
python
def get_current_weather(location, unit="摄氏度"):
# 实际调用天气查询 API 的逻辑
# 此处为示例,返回模拟的天气数据
return f"{location}今天天气晴朗,温度 25 {unit}。"
def multiplication(a, b):
return a * b让 AI 决定调用哪个工具。接下来,我们需要让 LLM 理解工具的功能,并根据用户的问题判断该调用哪个工具。这里我们通过设计 Prompt 来实现这一点:
python
import json
from openai import OpenAI
# LLM Client 参数
env = parse_env_file()
base_url = ""
api_key = ""
model = ""
client = OpenAI(
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
)
def get_current_weather(location, unit="摄氏度"):
# 实际调用天气查询 API 的逻辑
# 此处为示例,返回模拟的天气数据
return f"{location}今天天气晴朗,温度 25 {unit}。"
def multiplication(a, b):
return a * b
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_current_weather",
"description": "获取指定地点的天气信息,支持摄氏度和华氏度两种单位",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "地点的位置信息,例如北京、上海"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["摄氏度", "华氏度"],
"description": "温度单位,可选值为摄氏度或华氏度"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
},
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "multiplication",
"description": "计算两个数的乘积并返回结果",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"a": {
"type": "number",
"description": "参与乘法运算的第一个数"
},
"b": {
"type": "number",
"description": "参与乘法运算的第二个数"
}
},
"required": ["a", "b"]
}
}
}
]
messages = [
# {"role": "user", "content": "5乘以6结果是多少?"},
{"role": "user", "content": "北京今天多少度?"}
]
if __name__ == "__main__":
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
# 指定您创建的方舟推理接入点 ID,此处已帮您修改为您的推理接入点 ID
model=model,
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
tool_call = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
# 工具名称
tool_name = tool_call.function.name
# 如果判断需要调用查询天气工具,则运行查询天气工具
if tool_name == "get_current_weather":
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
tool_result = get_current_weather(**arguments)
print(tool_result)
# 假如是要算乘法
elif tool_name == "multiplication":
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
tool_result = multiplication(**arguments)
print(tool_result)运行上述代码,你会得到类似这样的输出:
python
调用get_weather的结果:深圳今天天气晴朗,温度 25 摄氏度。
调用 multiplication 的结果:30从这个例子中,我们可以看到工具调用的关键步骤:
-
定义工具 :明确每个工具的功能、输入参数和返回值
-
告诉 AI 工具信息 :通过 Prompt 让 LLM 知道有哪些工具可用,以及如何调用
-
AI 决策 :LLM 根据用户的问题,判断需要调用哪个工具,并生成对应的参数
-
执行工具调用 :根据 AI 的决策,调用相应的工具函数,并返回结果
有了工具调用能力,AI 就从单纯的信息处理者变成了能实际解决问题的助手。下一节,我们会将这些能力整合起来,构建一个简单的 Agent。
第三节:工具调用的原理🐷
上一节我们演示了 AI 如何调用天气预报和数字相加的工具,可能你会好奇:这背后的核心逻辑到底是什么?其实说穿了很简单 --------- 工具调用的本质,还是通过精心设计的 Prompt,引导 LLM 完成 "理解工具→选择工具→生成参数" 的全过程。
用 Prompt 让 AI "认识" 工具:就像给新人发工具说明书,我们在 Prompt 里写明工具信息:比如 get_weather 能查天气,需 location 和 date 参数;add_numbers 能做加法,需 a 和 b 参数。这些 "工具清单" 会让 LLM 提前 "记住" 工具特性。
用 Prompt 让 AI "选择" 工具:用户提问时,Prompt 会引导 LLM 对照工具清单做判断:问天气就选 get_weather,问加法就选 add_numbers ,并限制 "只能从清单里选"。
用 Prompt 让 AI "生成" 参数:选好工具后,Prompt 要求 LLM 从问题中提取参数并整理成 JSON。比如从 "北京明天的天气" 中拆出 location="北京" 和 date="明天",确保后续程序能直接使用。
简化的 Prompt 是这样的模板:
js
你现在需要处理用户的问题,可用工具如下:
{工具清单,包含名称、功能、参数要求}
请按以下步骤处理:
1. 分析用户问题,判断需要调用哪个工具
2. 从问题中提取工具所需的参数
3. 按这个格式返回结果:{"tool": "工具名", "parameters": {参数键值对}}是不是很简单?所谓的工具选择、总结参数,只不过是用 Prompt 包了一层。整个工具调用的流程,就是靠这样的 Prompt "指挥" LLM 完成的。没有高深的算法,没有复杂的黑科技,核心就是让大语言模型的理解能力和工具的执行能力结合起来。
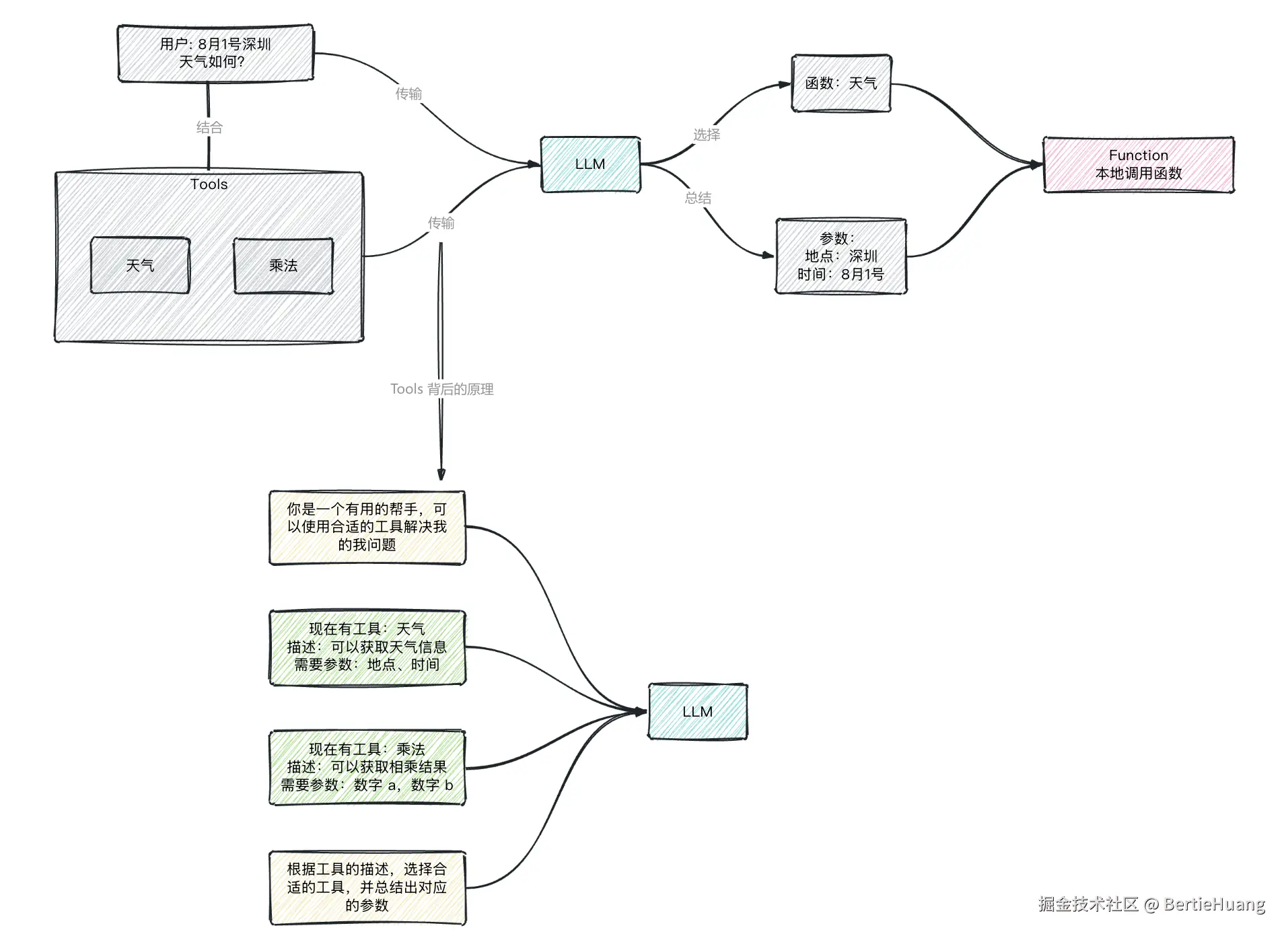
理解了这个原理,你就能明白:只要掌握了 Prompt 的设计技巧,理论上可以让 AI 调用任何工具 ------ 无论是查天气、算数字,还是调用数据库、发送邮件,甚至控制硬件设备。下一节,我们会基于这个原理,把 LLM 和工具调用整合起来,搭建一个更智能的 agent。
第四节:Bash Tool 🦄
前面我们了解了工具调用的通用原理,现在让我们聚焦 Trae 这款强大的工具,来看看它核心的 Bash Tool 是如何工作的。Trae 作为一款与 AI 深度集成的开发助手,能让开发者通过自然语言指令完成复杂的软件工程任务, Bash Tool 在其中扮演着关键角色。
首先,一个工具无非 3 个因素:1、函数描述;2:参数描述;3:执行函数。在源码中, Bash Tool 的函数描述是:
python
description = """Run commands in a bash shell
* When invoking this tool, the contents of the "command" parameter does NOT need to be XML-escaped.
* You have access to a mirror of common linux and python packages via apt and pip.
* State is persistent across command calls and discussions with the user.
* To inspect a particular line range of a file, e.g. lines 10-25, try 'sed -n 10,25p /path/to/the/file'.
* Please avoid commands that may produce a very large amount of output.
* Please run long lived commands in the background, e.g. 'sleep 10 &' or start a server in the background.
"""翻译为中文是:
ini
description = """在 bash shell 中运行命令
调用此工具时,"command" 参数的内容无需进行 XML 转义。
你可以通过 apt 和 pip 访问常见的 Linux 和 Python 软件包镜像。
状态在命令调用和与用户的对话过程中是持久的。
若要查看文件的特定行范围(例如第 10-25 行),可以尝试使用命令 "sed -n 10,25p /path/to/the/file"。
请避免使用可能产生大量输出的命令。
请在后台运行长时间运行的命令,例如 "sleep 10 &" 或在后台启动服务器。"""总结就是根据用户的意思,拟 Bash Command 并执行。下一步我们来看参数描述:
python
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "bash",
"description": description,
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"command": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The bash command to run."
},
"restart": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Set to true to restart the bash session."
}
},
"required": ["command", "restart"]
}
}
}
]Command 很好理解,就是运行的 Bash 命令。 Restart 描述的是新开一个 Bash Session,可以理解为新开一个终端窗口,每一个 Session 内维护着 Bash 的上下文关系,比如环境变量和当前目录。
有了工具描述和参数,那么下面就是执行函数。这里包含一个数据类,用于描述工具函数执行的结果。主体是 execute 函数,在这个函数里,获取到 LLM 总结出来的参数,然后传给 run_bash 函数执行:
python
@dataclass
class ToolExecResult:
"""Intermediate result of a tool execution."""
output: str | None = None
error: str | None = None
error_code: int = 0
async def execute(arguments):
# 源码中的 session 维护逻辑比较复杂,并非必须实现,放在文中反倒会影响理解,在此略过
# if arguments.get("restart"):
# if self._session:
# self._session.stop()
# self._session = _BashSession()
# await self._session.start()
#
# return ToolExecResult(output="tool has been restarted.")
command = str(arguments["command"]) if "command" in arguments else None
if command is None:
return ToolExecResult(
error=f"No command provided for the bash tool",
error_code=-1,
)
try:
return await run_bash(command)
except Exception as e:
return ToolExecResult(error=f"Error running bash command: {e}", error_code=-1)接着是执行 Bash 函数。这个函数中,主要做 2 个事情,第一是命令的执行,然后返回执行输出,这是主要的核心功能。第二是 Sentinel,用于辅助标识命令的执行完成信息,非必须。
python
async def run_bash(command: str):
"""
异步执行Bash命令并获取输出结果和错误信息
该函数通过创建子进程运行Bash命令,使用特殊标记(sentinel)跟踪命令执行完成状态,
并捕获命令的返回码、标准输出和标准错误。适用于需要异步执行Shell命令的场景。
如果没有这个标记,程序无法区分 "命令还在运行,后续还有输出" 和 "命令已经结束"。
比如执行echo "hello",输出是hello,程序看到这个输出后,无法确定是不是还有后续内容;
但加上sentinel后,输出会是hello,,,,bash-command-exit-0-banner,,,,,程序看到标记就知道命令已结束,hello是有效输出,返回码是0。
"""
# 输出检查延迟时间(秒),避免过于频繁地检查输出缓冲区
_output_delay: float = 0.2
# 命令执行超时时间(秒),超过此时长将终止等待
_timeout: float = 120.0
# 命令执行结束的标记字符串,用于识别命令何时完成
# 其中__ERROR_CODE__会被替换为实际的错误码变量($?或!errorlevel!)
_sentinel: str = ",,,,bash-command-exit-__ERROR_CODE__-banner,,,,"
# 创建Bash子进程,配置输入输出管道
# shell=True表示通过shell执行命令
# stdin=PIPE: 允许向子进程输入数据
# stdout=PIPE: 捕获子进程的标准输出
# stderr=PIPE: 捕获子进程的标准错误
# preexec_fn=os.setsid: 在Unix系统中创建新的进程组,避免信号干扰
_process = await asyncio.create_subprocess_shell(
"/bin/bash",
shell=True,
bufsize=0, # 无缓冲,实时读写
stdin=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
preexec_fn=os.setsid,
)
# 类型断言:确保输入输出管道已正确创建(非None)
assert _process.stdin
assert _process.stdout
assert _process.stderr
# 初始化命令返回码
error_code = 0
# 解析标记字符串,分离出错误码前后的部分
# 例如将",,,,bash-command-exit-__ERROR_CODE__-banner,,,"拆分为:
# sentinel_before = ",,,,bash-command-exit-"
# pivot = "__ERROR_CODE__"
# sentinel_after = "-banner,,,,"
sentinel_before, pivot, sentinel_after = _sentinel.partition("__ERROR_CODE__")
# 确保成功拆分出了__ERROR_CODE__部分
assert pivot == "__ERROR_CODE__"
# 根据操作系统类型选择错误码获取方式
# Windows使用!errorlevel!,Unix-like系统使用$?
errcode_retriever = "!errorlevel!" if os.name == "nt" else "$?"
# 选择命令分隔符,Windows使用&,Unix-like系统使用;
command_sep = "&" if os.name == "nt" else ";"
# 向子进程的标准输入写入命令
# 命令格式:[用户命令] [分隔符] echo [替换了错误码变量的标记]
# 例如:ls -l ; echo ,,,,bash-command-exit-$?-banner,,,,
_process.stdin.write(
command.encode() # 将命令字符串编码为字节流
+ f"{command_sep} echo {_sentinel.replace('__ERROR_CODE__', errcode_retriever)}\n".encode()
)
# 确保数据被真正发送到子进程
await _process.stdin.drain()
# 读取子进程输出,直到发现结束标记
try:
# 设置超时上下文管理器,超过指定时间未完成则抛出TimeoutError
async with asyncio.timeout(_timeout):
while True:
# 等待一小段时间再检查输出,减少CPU占用
await asyncio.sleep(_output_delay)
# 直接读取标准输出缓冲区的内容
output: str = _process.stdout._buffer.decode()
# 检查是否已出现标记的前半部分,判断命令是否已执行完成
if sentinel_before in output:
# 从输出中分离出实际命令输出和标记部分
# rpartition从右侧查找分隔符,确保只拆分一次
output, pivot, exit_banner = output.rpartition(sentinel_before)
assert pivot # 确保成功拆分
# 从标记部分提取错误码
error_code_str, pivot, _ = exit_banner.partition(sentinel_after)
# 验证错误码格式是否正确(必须是数字)
if not pivot or not error_code_str.isdecimal():
continue # 格式不正确则继续等待
# 将错误码转换为整数
error_code = int(error_code_str)
break # 成功获取结果,退出循环
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
# 标记超时状态
_timed_out = True
# 抛出超时错误,说明命令执行时间过长
raise f"timed out: bash has not returned in {_timeout} seconds and must be restarted" from None
# 处理输出:移除末尾的换行符(如果存在)
if output.endswith("\n"):
output = output[:-1]
# 读取标准错误缓冲区的内容
error: str = _process.stderr._buffer.decode()
# 处理错误输出:移除末尾的换行符(如果存在)
if error.endswith("\n"):
error = error[:-1]
# 清空输出和错误缓冲区,确保下次执行命令时不会受到残留数据影响
_process.stdout._buffer.clear()
_process.stderr._buffer.clear()
return ToolExecResult(output=output, error=error,
error_code=error_code)Bash Tool 的主要素我已经向你介绍完了,下面是该工具完整的代码例子,你需要修改 messages 中 的 content 适配你的实际情况,来让工具来替你执行 Bash 命令:
python
import asyncio
import json
import os
from dataclasses import dataclass
from openai import OpenAI
base_url = ""
api_key = ""
model = ""
client = OpenAI(
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
)
@dataclass
class ToolExecResult:
"""Intermediate result of a tool execution."""
output: str | None = None
error: str | None = None
error_code: int = 0
description = """Run commands in a bash shell
* When invoking this tool, the contents of the "command" parameter does NOT need to be XML-escaped.
* You have access to a mirror of common linux and python packages via apt and pip.
* State is persistent across command calls and discussions with the user.
* To inspect a particular line range of a file, e.g. lines 10-25, try 'sed -n 10,25p /path/to/the/file'.
* Please avoid commands that may produce a very large amount of output.
* Please run long lived commands in the background, e.g. 'sleep 10 &' or start a server in the background.
"""
tools = [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "bash",
"description": description,
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"command": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The bash command to run."
},
"restart": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "Set to true to restart the bash session."
}
},
"required": ["command", "restart"]
}
}
}
]
async def run_bash(command: str):
"""
异步执行Bash命令并获取输出结果和错误信息
该函数通过创建子进程运行Bash命令,使用特殊标记(sentinel)跟踪命令执行完成状态,
并捕获命令的返回码、标准输出和标准错误。适用于需要异步执行Shell命令的场景。
如果没有这个标记,程序无法区分 "命令还在运行,后续还有输出" 和 "命令已经结束"。
比如执行echo "hello",输出是hello,程序看到这个输出后,无法确定是不是还有后续内容;
但加上sentinel后,输出会是hello,,,,bash-command-exit-0-banner,,,,,程序看到标记就知道命令已结束,hello是有效输出,返回码是0。
"""
# 输出检查延迟时间(秒),避免过于频繁地检查输出缓冲区
_output_delay: float = 0.2
# 命令执行超时时间(秒),超过此时长将终止等待
_timeout: float = 120.0
# 命令执行结束的标记字符串,用于识别命令何时完成
# 其中__ERROR_CODE__会被替换为实际的错误码变量($?或!errorlevel!)
_sentinel: str = ",,,,bash-command-exit-__ERROR_CODE__-banner,,,,"
# 创建Bash子进程,配置输入输出管道
# shell=True表示通过shell执行命令
# stdin=PIPE: 允许向子进程输入数据
# stdout=PIPE: 捕获子进程的标准输出
# stderr=PIPE: 捕获子进程的标准错误
# preexec_fn=os.setsid: 在Unix系统中创建新的进程组,避免信号干扰
_process = await asyncio.create_subprocess_shell(
"/bin/bash",
shell=True,
bufsize=0, # 无缓冲,实时读写
stdin=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
stdout=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=asyncio.subprocess.PIPE,
preexec_fn=os.setsid,
)
# 类型断言:确保输入输出管道已正确创建(非None)
assert _process.stdin
assert _process.stdout
assert _process.stderr
# 初始化命令返回码
error_code = 0
# 解析标记字符串,分离出错误码前后的部分
# 例如将",,,,bash-command-exit-__ERROR_CODE__-banner,,,"拆分为:
# sentinel_before = ",,,,bash-command-exit-"
# pivot = "__ERROR_CODE__"
# sentinel_after = "-banner,,,,"
sentinel_before, pivot, sentinel_after = _sentinel.partition("__ERROR_CODE__")
# 确保成功拆分出了__ERROR_CODE__部分
assert pivot == "__ERROR_CODE__"
# 根据操作系统类型选择错误码获取方式
# Windows使用!errorlevel!,Unix-like系统使用$?
errcode_retriever = "!errorlevel!" if os.name == "nt" else "$?"
# 选择命令分隔符,Windows使用&,Unix-like系统使用;
command_sep = "&" if os.name == "nt" else ";"
# 向子进程的标准输入写入命令
# 命令格式:[用户命令] [分隔符] echo [替换了错误码变量的标记]
# 例如:ls -l ; echo ,,,,bash-command-exit-$?-banner,,,,
_process.stdin.write(
command.encode() # 将命令字符串编码为字节流
+ f"{command_sep} echo {_sentinel.replace('__ERROR_CODE__', errcode_retriever)}\n".encode()
)
# 确保数据被真正发送到子进程
await _process.stdin.drain()
# 读取子进程输出,直到发现结束标记
try:
# 设置超时上下文管理器,超过指定时间未完成则抛出TimeoutError
async with asyncio.timeout(_timeout):
while True:
# 等待一小段时间再检查输出,减少CPU占用
await asyncio.sleep(_output_delay)
# 直接读取标准输出缓冲区的内容
output: str = _process.stdout._buffer.decode()
# 检查是否已出现标记的前半部分,判断命令是否已执行完成
if sentinel_before in output:
# 从输出中分离出实际命令输出和标记部分
# rpartition从右侧查找分隔符,确保只拆分一次
output, pivot, exit_banner = output.rpartition(sentinel_before)
assert pivot # 确保成功拆分
# 从标记部分提取错误码
error_code_str, pivot, _ = exit_banner.partition(sentinel_after)
# 验证错误码格式是否正确(必须是数字)
if not pivot or not error_code_str.isdecimal():
continue # 格式不正确则继续等待
# 将错误码转换为整数
error_code = int(error_code_str)
break # 成功获取结果,退出循环
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
# 标记超时状态
_timed_out = True
# 抛出超时错误,说明命令执行时间过长
raise f"timed out: bash has not returned in {_timeout} seconds and must be restarted" from None
# 处理输出:移除末尾的换行符(如果存在)
if output.endswith("\n"):
output = output[:-1]
# 读取标准错误缓冲区的内容
error: str = _process.stderr._buffer.decode()
# 处理错误输出:移除末尾的换行符(如果存在)
if error.endswith("\n"):
error = error[:-1]
# 清空输出和错误缓冲区,确保下次执行命令时不会受到残留数据影响
_process.stdout._buffer.clear()
_process.stderr._buffer.clear()
return ToolExecResult(output=output, error=error,
error_code=error_code)
async def execute(arguments):
# 源码中的 session 维护逻辑比较复杂,并非必须实现,放在文中反倒会影响理解,在此略过
# if arguments.get("restart"):
# if self._session:
# self._session.stop()
# self._session = _BashSession()
# await self._session.start()
#
# return ToolExecResult(output="tool has been restarted.")
command = str(arguments["command"]) if "command" in arguments else None
if command is None:
return ToolExecResult(
error=f"No command provided for the bash tool",
error_code=-1,
)
try:
return await run_bash(command)
except Exception as e:
return ToolExecResult(error=f"Error running bash command: {e}", error_code=-1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "在 /root 目录下新建 hello.txt 文件"}
]
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
tools=tools
)
tool_call = completion.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
# 工具名称
tool_name = tool_call.function.name
if tool_name == "bash":
arguments = json.loads(tool_call.function.arguments)
# {'command': 'touch /root/hello.txt', 'restart': False}
result = asyncio.run(execute(arguments))至此该系列的第一章结束,这一章中我向你描述了 Agent 和其工具的使用方法和原理,还有 Trae 核心的工具之一:Bash Tool。在下一篇中,我将继续向你介绍 Trae 其他的核心工具。假如在阅读过程中碰到任何问题,都欢迎在评论区留言,我会尽快回复。
Trae Agent 源码地址:github.com/bytedance/t...
源码量在 3000 行左右,压力较小,推荐阅读。