二叉搜索树
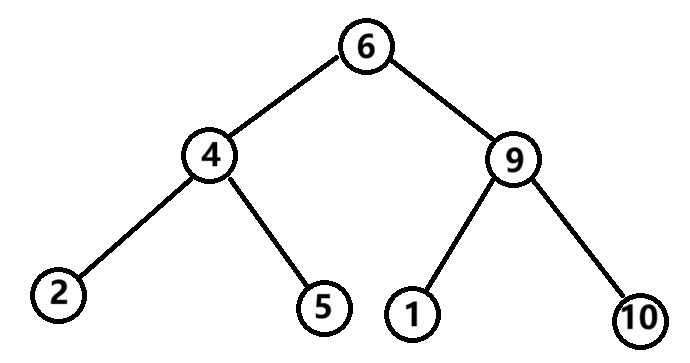
像上图这样满足,任意一棵子树的左子树小于该子树的根结点,右子树大于该子树的根结点,满足这样的条件,则这种树就被称为二叉搜索树。
java
public class BinarySearchTree {
static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public TreeNode root = null;
public boolean search(int val) {
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.val > val){
cur = cur.left;
}else if(cur.val < val) {
cur = cur.right;
}else{
return true ;
}
}
return false;
}
public void insert(int val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
if(root==null){
root=node;
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode parent = null;
while(cur!=null){
parent = cur;
if(cur.val>val){
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur.val<val){
cur=cur.right;
}else{
return;
}
}
if(parent.val>val){
parent.left = node;
}else if(parent.val<val) {
parent.right = node;
}
}
public void remove(int val){
if(root==null){
return;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode parent = null;
while(cur!=null) {
if(cur.val>val){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.left;
}else if(cur.val<val){
parent=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}else{
removeNode(parent,cur);
}
}
}
private void removeNode(TreeNode parent,TreeNode cur) {
if(cur.left == null) {//以cur为根左树为空的情况
if(cur==root){//parent和cur在一起(顶根为要删除的节点时)
root=cur.right;
}else if(cur==parent.left){//cur为要删除元素并且走到了parent左边,cur左边为空,把parent的左边接上cur的右边
parent.left=cur.right;
}else{//cur为要删除元素并且走到了parent右边,cur左边为空,把parent的右边接上cur的右边
parent.right=cur.right;
}
} else if (cur.right == null) {//以cur为根右树为空的情况
if(cur==root){
root=cur.left;
}else if(cur==parent.left){
parent.left=cur.left;
}else{
parent.right=cur.left;
}
}else{//cur左右都不为空的情况************
TreeNode targetParent = cur;
TreeNode target = cur.left;
while(target.right!=null){
targetParent = target;
target = target.right;
}
cur.val=target.val;
if(target==targetParent.right){
targetParent.right=target.left;
}else{
targetParent.left=target.left;
}
}
}
}二叉搜索树的模拟只要遵循二叉搜索树的特性即可。
单支的二叉搜索树
如果插入的顺序不恰当,二叉搜索树就会出现只有单支的情况
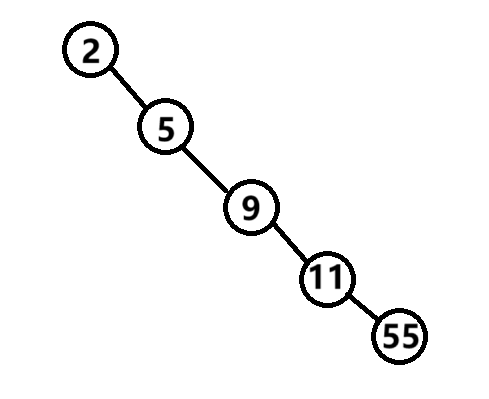
这样也属于二叉搜索树,但是由于另一半枝没有放入元素,我们对该种搜索树进行操作时,效率必然会有所下降。
Map和Set
先了解一下Map和Set的概念,以及两者的区别。
首先这两种集合是高效的搜索容器,很适合动态查找,不同于我们以前学过的其他数据结构,那些数据结构进行动态查找都需要不小的时间复杂度。
Map是一种Key-Value模型,kv模型的意思就是,如果你往里面存放数据,那就需要提供key 和 value的值,我们也称这种模型为键值对模型。例如我们要统计某单词在英语试卷中出现的次数,
<单词,单词出现的次数>对应的就是 Key 和 Value
Set是一种Key模型,如果你往里面存放数据,只需要提供一个数据Key,但是Set不允许有重复的数据,所以Set更偏向于去重,查找是否存在目标数据
TreeMap
TreeMap就是结合了刚刚提到的KeyValue模型和搜索树,实际上TreeMap底层是红黑树,现阶段还没学到红黑树,这里不细说它的结构
java
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
TreeMap<String,Integer> map2 = new TreeMap<>();创建一个TreeMap有以上两种格式,推荐使用第一种
Map有几个核心的方法
java
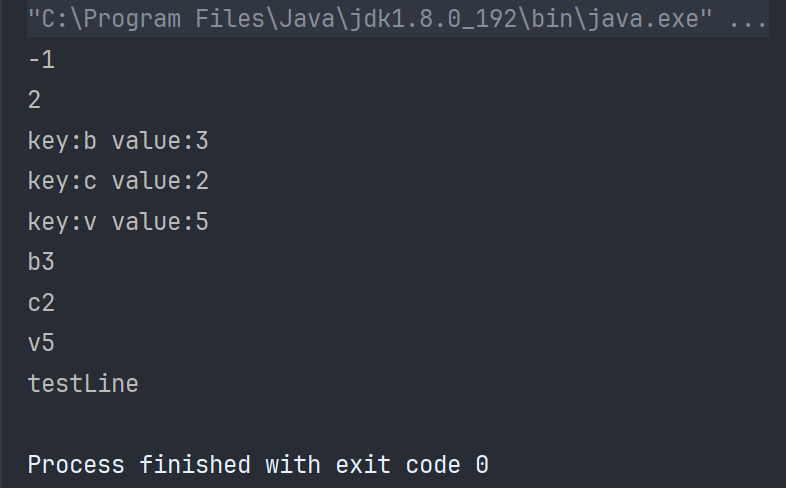
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();//key value type
TreeMap<String,Integer> map2 = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("b",3);
map.put("c",2);
map.put("v",5);
int val = map.getOrDefault("d",-1);//如果存在key就返回key的value,不存在就返回Default(-1)
System.out.println(val);
val = map.get("c");
System.out.println(val);
Set<String> set = map.keySet();//收集key
Collection<Integer> collection=map.values();//收集value
Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();//搜索树上每一个节点放的都是Map.Entry
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry :entries) {
System.out.println("key:"+entry.getKey()+" value:"+entry.getValue());
}
for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry :map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+entry.getValue());
}
}
TreeSet
Set是纯Key模型,适合查找存在
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("g");
set.add("tq");
set.remove("a");
boolean flag =set.contains("g");
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println(set);
}
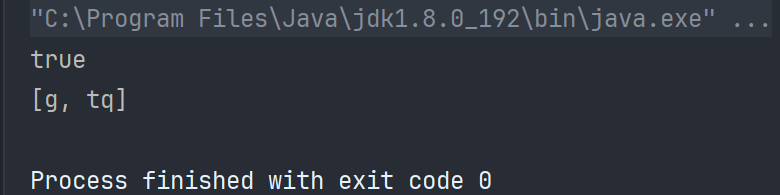
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
set.add("a");
set.add("g");
set.add("tq");
set.add("a");
// set.remove("a");
boolean flag =set.contains("g");
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println(set);
}
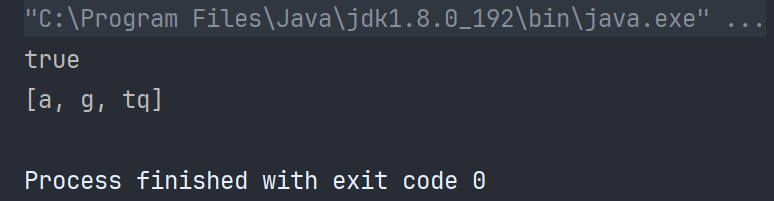
TreeSet的底层也是红黑树
哈希表
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素时,必须要经过关键 码的多次比较。
顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即O(log2(N) ),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中 元素的比较次数。
但是哈希表不一样,哈希表可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。
冲突
要明白什么是哈希表的冲突之前,不防这样设想一下,假若有5个数据,他的范围在1到10之间
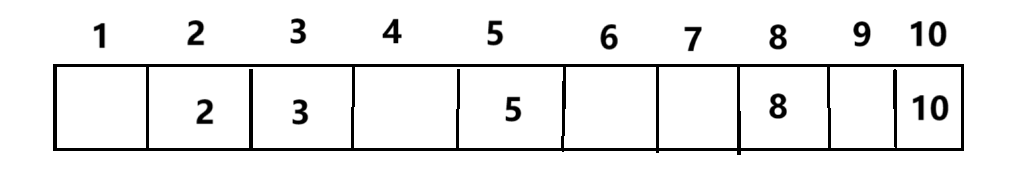
这个时候我们不难发现,如果创建一个带有1到10下标的表格把对应数据存放起来,这样一来我们将来要找目标数据的时候就会很方便,只需要对应下标就可以找到。
但是如果保持5个数据数量不变的情况下,但是把范围改变至1到20,并且这个时候我们不能把表进行扩容
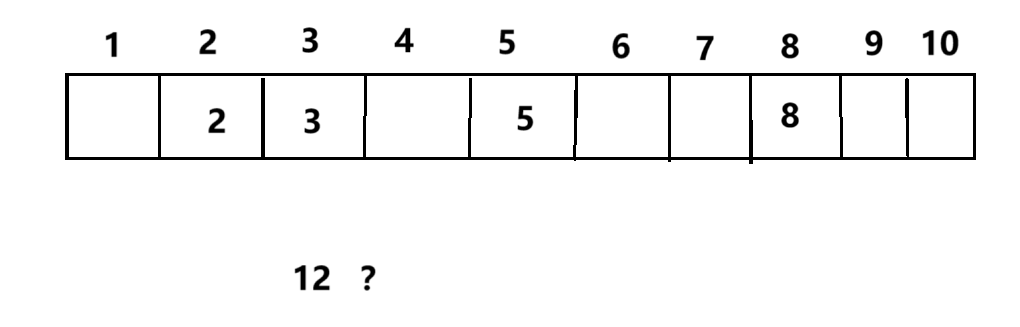
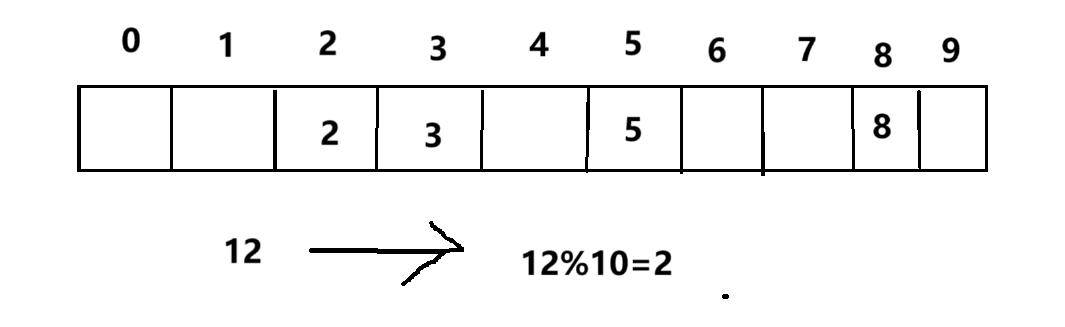
假若这个时候指定规则,不管目标数据为个位数还是十位数,数据的个位数是什么我们就放到什么位置,这个时候我们把12放到2下标的位置,表的内容就产生了冲突。
哈希函数
针对冲突的发生,又引出了一个概念,哈希函数可以有很多种,举个常见的,线性函数,比如: Hash(Key)= A*Key + B ,但是大多数情况下,我们使用除留余数法,函数为: Hash(Key)= Key % 表长
负载因子
散列表的负载因子=元素个数/表长,通常来说负载因子越小,冲突的概率越低,就像马路一样,如果马路越宽,那么堵车的可能性也会变低。我们通常扩展列表的长度来使得负载因子扩展,通常情况下,如果负载因子达到了0.75,我们就要对散列表进行扩容
解决冲突
既然有了哈希函数,并且产生了冲突,那我们就要解决冲突,解决冲突可以分为两种方式,开散列和闭散列。
首先来说说闭散列,闭散列我们通常采用线性探测的方式来解决冲突,按上面的例子来简单说就是,12得到的结果是2要放在2的位置,但是2已经有了数据,这个时候我们就把12放到下一个为空的位置
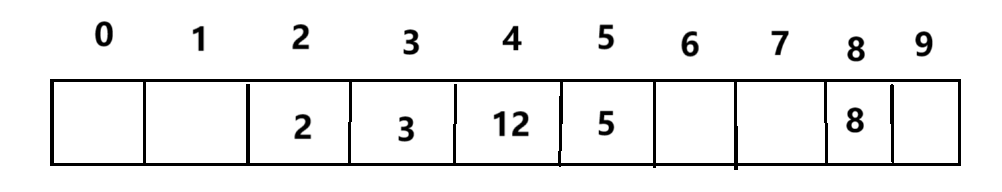
这种解决方式虽然简单粗暴,但是必然会影响查找的时间复杂度,以为增加后续可能发生的冲突
所以我们就要用开散列的方法
哈希桶
哈希表的底层就是哈希桶,哈希桶是什么呢?哈希桶就是在前面我们画的表格的基础上,每一个表格都宽展出一个链表,使得一个下标能存放更多的数据
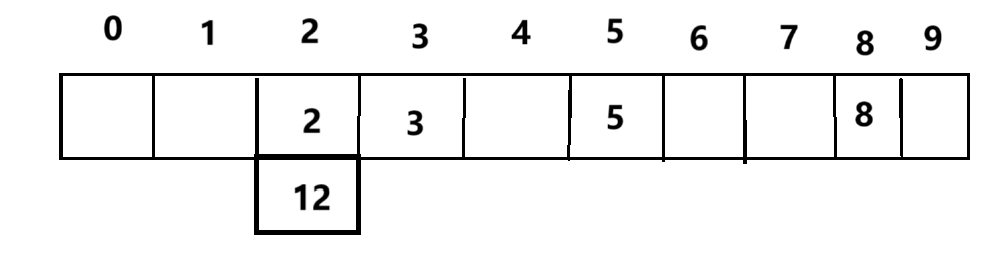
java
public class HashBucket {//哈系桶是哈希查找的关键
static class Node{
public int key;
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int key,int value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public Node[] array;
public int usedSize;
public HashBucket() {
array = new Node[10];
}
public void putLast (int key,int value){//尾插法,这里的尾差指的是,在表对应的位置上,对链表结构进行尾插
int index = key % array.length;
Node node = new Node(key,value);
if(array[index] == null){//第一次插入
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >=0.75){
resize();
}
return;
}
Node cur = array[index];//若不是第一次插入,则进行尾插
while(cur.next!=null){//尾插
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75){
resize();
}
}
public void putFirst (int key , int value) {
int index = key % array.length;
Node node = new Node(key,value);
Node cur = array[index];
//先遍历一遍链表结构,检查是否存在当前的key
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key==key){
cur.value = value;//若存在当前key,则把当前的value更新掉
return;
}
}
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
if(loadFactor() >= 0.75){
resize();
}
}
private double loadFactor() {//算负载因子
return usedSize*1.0/array.length;
}
private void resize(){//如果负载因子大于0.75就对表进行扩容
Node[] tempArray = new Node[array.length*2];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {//遍历原来的表
Node cur = array[i];
while(cur != null) {//找到非空的表位
Node curNext = cur.next;//先记录下表位的next,后续会对next进行修改,所以要进行next的备份
int newIndex = cur.key % tempArray.length;//算出表位链表上的key对应新表的位置,如13%20=13,就找到13位置
cur.next = tempArray[newIndex];//头插到新表里,这样就把key:13从链表中分离出来了
tempArray[newIndex] = cur;
cur = curNext;//遍历表位的链表
}
}
array=tempArray;//覆盖旧表
}
public int get(int key) {
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while(cur!=null){
if(cur.key == key){
return cur.value;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}HashMap
java
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("你好",1);
map.put("再见",2);
map.put("嗨",3);
System.out.println(map.containsKey("你好"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(3));
System.out.println(map.get("你好"));
System.out.println(map);
}
}
和TreeMap的方法种类没有区别,但是底层结构上有所区别,HashMap的底层是哈希桶(HashBucket),TreeMap的底层是红黑树。从先阶段的简单层面来说,可以把HashMap理解成一个两行的列表
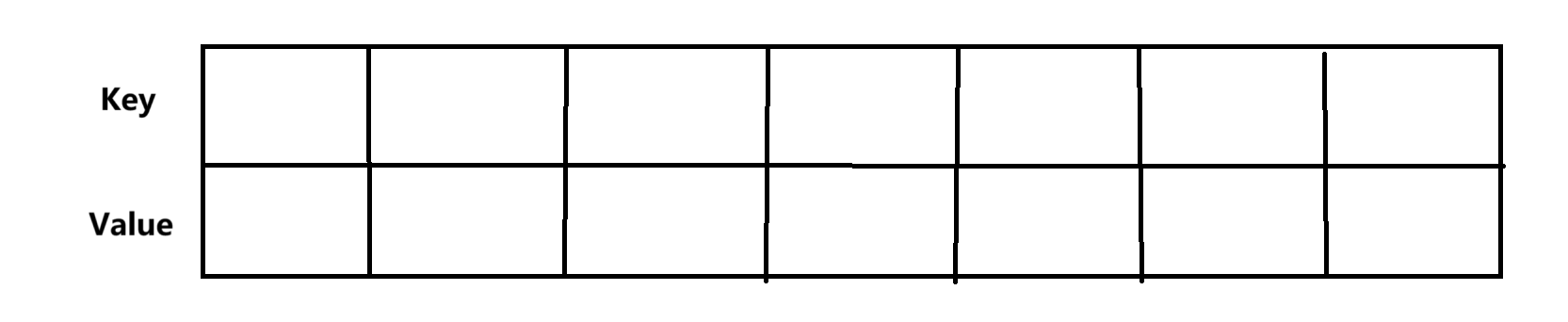
Key和Value的类型可以自己定义,可以是<String,Integer>,也可以是<String,String>,这一点在某些算法中有所体现。
HashSet
java
public class TestHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
set.add(4);
System.out.println(set.contains(2));
set.remove(2);
System.out.println(set);
}
}
相比于TreeSet,HashSet的效率更高,因为HashSet不需要进行额外的数据对比操作,在其他方面基本于TreeSet无异。具体要TreeSet还是HashSet需要结合实际来考虑。