上接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44506615/article/details/151898818?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
完整代码:https://gitee.com/Duo1J/learn-open-gl | https://github.com/Duo1J/LearnOpenGL
视差贴图 (Parallax Map)
视差贴图类似法线贴图,它利用了视错觉,能够极大地提升表面细节,使之具有深度感
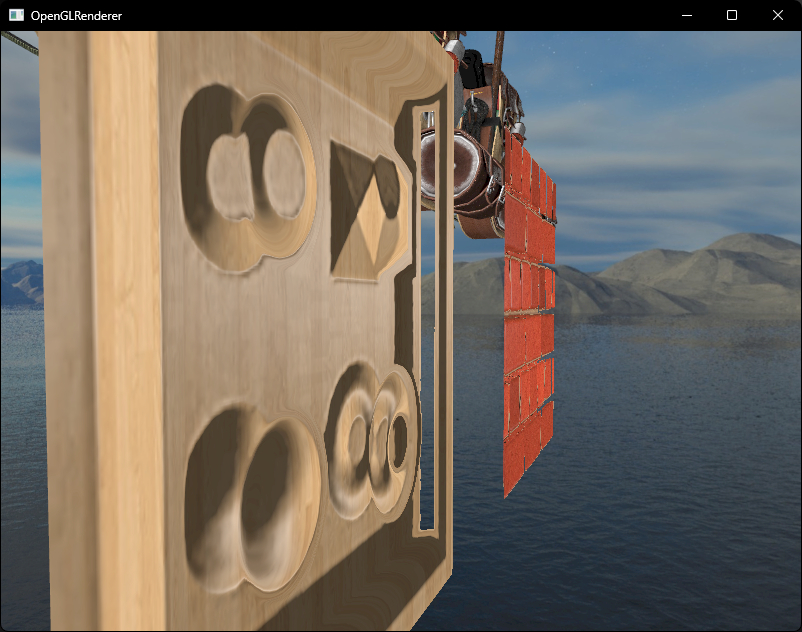
视差贴图背后的思想是通过修改 纹理坐标(UV) 来使一个片段的表面看起来比实际更高或是更低,如下图所示 (图片来自于LearnOpenGL)
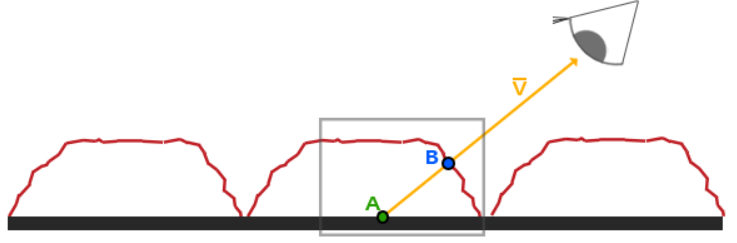
如果不进行干涉,观察者的视线就会落到点A上,我们的目的就是让A上的片段不再使用点A的纹理坐标,而是使用点B的纹理坐标进行采样,这样观察者的视线就仿佛落在了点B
首先准备一下要用到的纹理图片,我们绘制两种平面来看效果,砖墙和玩具盒,相关资源可在顶部Git仓库中找到
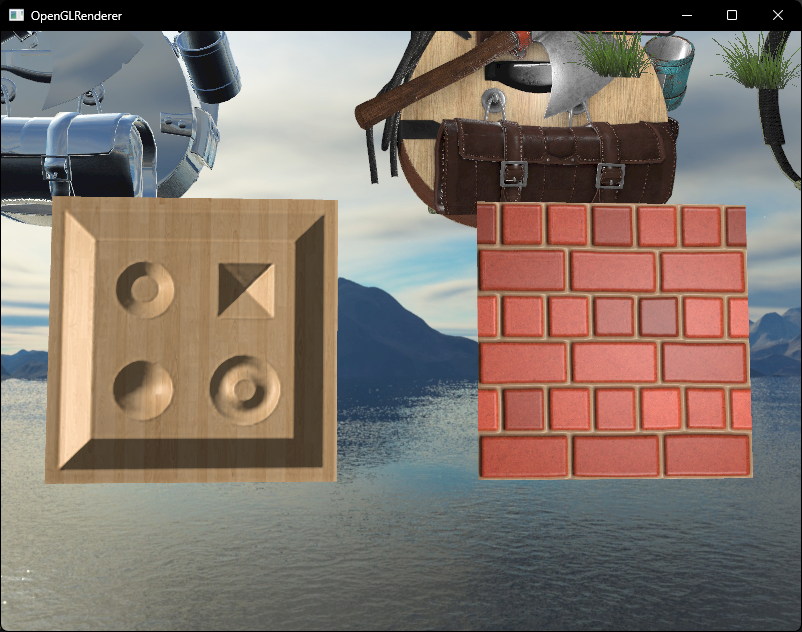
首先绘制两个平面,并应用法线贴图
Main.cpp
cpp
// ...
// 渲染视差Quad
void RenderParallax()
{
static unsigned int parallaxVAO = 0;
static unsigned int parallaxVBO;
if (parallaxVAO == 0)
{
// positions
glm::vec3 pos1(-1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
glm::vec3 pos2(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0);
glm::vec3 pos3(1.0, -1.0, 0.0);
glm::vec3 pos4(1.0, 1.0, 0.0);
// texture coordinates
glm::vec2 uv1(0.0, 1.0);
glm::vec2 uv2(0.0, 0.0);
glm::vec2 uv3(1.0, 0.0);
glm::vec2 uv4(1.0, 1.0);
// normal
glm::vec3 nm(0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
glm::vec3 tangent1, bitangent1;
glm::vec3 tangent2, bitangent2;
// - triangle 1
glm::vec3 edge1 = pos2 - pos1;
glm::vec3 edge2 = pos3 - pos1;
glm::vec2 deltaUV1 = uv2 - uv1;
glm::vec2 deltaUV2 = uv3 - uv1;
GLfloat f = 1.0f / (deltaUV1.x * deltaUV2.y - deltaUV2.x * deltaUV1.y);
tangent1.x = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.x - deltaUV1.y * edge2.x);
tangent1.y = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.y - deltaUV1.y * edge2.y);
tangent1.z = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.z - deltaUV1.y * edge2.z);
tangent1 = glm::normalize(tangent1);
bitangent1.x = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.x + deltaUV1.x * edge2.x);
bitangent1.y = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.y + deltaUV1.x * edge2.y);
bitangent1.z = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.z + deltaUV1.x * edge2.z);
bitangent1 = glm::normalize(bitangent1);
// - triangle 2
edge1 = pos3 - pos1;
edge2 = pos4 - pos1;
deltaUV1 = uv3 - uv1;
deltaUV2 = uv4 - uv1;
f = 1.0f / (deltaUV1.x * deltaUV2.y - deltaUV2.x * deltaUV1.y);
tangent2.x = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.x - deltaUV1.y * edge2.x);
tangent2.y = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.y - deltaUV1.y * edge2.y);
tangent2.z = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.z - deltaUV1.y * edge2.z);
tangent2 = glm::normalize(tangent2);
bitangent2.x = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.x + deltaUV1.x * edge2.x);
bitangent2.y = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.y + deltaUV1.x * edge2.y);
bitangent2.z = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.z + deltaUV1.x * edge2.z);
bitangent2 = glm::normalize(bitangent2);
GLfloat quadVertices[] = {
// Positions // normal // TexCoords // Tangent // Bitangent
pos1.x, pos1.y, pos1.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv1.x, uv1.y, tangent1.x, tangent1.y, tangent1.z, bitangent1.x, bitangent1.y, bitangent1.z,
pos2.x, pos2.y, pos2.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv2.x, uv2.y, tangent1.x, tangent1.y, tangent1.z, bitangent1.x, bitangent1.y, bitangent1.z,
pos3.x, pos3.y, pos3.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv3.x, uv3.y, tangent1.x, tangent1.y, tangent1.z, bitangent1.x, bitangent1.y, bitangent1.z,
pos1.x, pos1.y, pos1.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv1.x, uv1.y, tangent2.x, tangent2.y, tangent2.z, bitangent2.x, bitangent2.y, bitangent2.z,
pos3.x, pos3.y, pos3.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv3.x, uv3.y, tangent2.x, tangent2.y, tangent2.z, bitangent2.x, bitangent2.y, bitangent2.z,
pos4.x, pos4.y, pos4.z, nm.x, nm.y, nm.z, uv4.x, uv4.y, tangent2.x, tangent2.y, tangent2.z, bitangent2.x, bitangent2.y, bitangent2.z
};
glGenVertexArrays(1, ¶llaxVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, ¶llaxVBO);
glBindVertexArray(parallaxVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, parallaxVBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(quadVertices), &quadVertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 14 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 14 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(3 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 14 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(6 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(3);
glVertexAttribPointer(3, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 14 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(8 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(4);
glVertexAttribPointer(4, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 14 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(11 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
}
glBindVertexArray(parallaxVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}
int main()
{
// ...
Shader parallarShader("Shader/ParallaxVertex.glsl", "Shader/ParallaxFragment.glsl");
// ...
Texture bricksDiffuseTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Bricks_Diffuse.jpg", TextureType::DIFFUSE, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
Texture bricksNormalTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Bricks_Normal.jpg", TextureType::NORMAL, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
Texture bricksParallaxTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Bricks_Parallax.jpg", TextureType::DIFFUSE, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
Texture toyboxDiffuseTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Toybox_Diffuse.png", TextureType::DIFFUSE, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
Texture toyboxNormalTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Toybox_Normal.png", TextureType::NORMAL, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
Texture toyboxParallaxTex("F:/Scripts/Cpp/LearnOpenGL/learn-open-gl/Resource/parallax/T_Toybox_Parallax.png", TextureType::DIFFUSE, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
// [主循环]
// 绘制视差Quad
parallarShader.Use();
parallarShader.SetMat4("view", view);
parallarShader.SetMat4("projection", projection);
glm::mat4 parallaxModel(1);
parallaxModel = glm::translate(parallaxModel, glm::vec3(0, -3, 2));
parallarShader.SetMat4("model", parallaxModel);
parallarShader.SetVec3("lightPos", glm::vec3(1.7f, -2.8f, 5.0f));
parallarShader.SetVec3("viewPos", camera.transform.position);
parallarShader.SetInt("diffuseMap", 0);
parallarShader.SetInt("normalMap", 1);
parallarShader.SetInt("parallaxMap", 2);
glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE);
// 砖墙
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, bricksDiffuseTex.GetTextureID());
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, bricksNormalTex.GetTextureID());
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, bricksParallaxTex.GetTextureID());
RenderParallax();
//玩具盒
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, toyboxDiffuseTex.GetTextureID());
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, toyboxNormalTex.GetTextureID());
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, toyboxParallaxTex.GetTextureID());
glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE);
parallaxModel = glm::translate(parallaxModel, glm::vec3(-3, 0, 0));
parallarShader.SetMat4("model", parallaxModel);
RenderParallax();
glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE);
}ParallaxVertex.glsl 新建
cpp
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 normal;
layout (location = 2) in vec2 texCoords;
layout (location = 3) in vec3 tangent;
layout (location = 4) in vec3 bitangent;
out VS_OUT {
vec3 FragPos;
vec2 TexCoords;
vec3 TangentLightPos;
vec3 TangentViewPos;
vec3 TangentFragPos;
} vs_out;
uniform mat4 projection;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
void main()
{
gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(position, 1.0f);
vs_out.FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(position, 1.0));
vs_out.TexCoords = texCoords;
vec3 T = normalize(mat3(model) * tangent);
vec3 B = normalize(mat3(model) * bitangent);
vec3 N = normalize(mat3(model) * normal);
mat3 TBN = transpose(mat3(T, B, N));
vs_out.TangentLightPos = TBN * lightPos;
vs_out.TangentViewPos = TBN * viewPos;
vs_out.TangentFragPos = TBN * vs_out.FragPos;
}ParallaxFragment.glsl 新建
cpp
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in VS_OUT {
vec3 FragPos;
vec2 TexCoords;
vec3 TangentLightPos;
vec3 TangentViewPos;
vec3 TangentFragPos;
} fs_in;
uniform sampler2D diffuseMap;
uniform sampler2D normalMap;
uniform sampler2D depthMap;
void main()
{
vec3 viewDir = normalize(fs_in.TangentViewPos - fs_in.TangentFragPos);
vec2 texCoords = fs_in.TexCoords;
vec3 normal = texture(normalMap, texCoords).rgb;
normal = normalize(normal * 2.0 - 1.0);
vec3 color = texture(diffuseMap, texCoords).rgb;
// Ambient
vec3 ambient = 0.1 * color;
// Diffuse
vec3 lightDir = normalize(fs_in.TangentLightPos - fs_in.TangentFragPos);
float diff = max(dot(lightDir, normal), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * color;
// Specular
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, normal);
vec3 halfwayDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
float spec = pow(max(dot(normal, halfwayDir), 0.0), 32.0);
vec3 specular = vec3(0.2) * spec;
FragColor = vec4(ambient + diffuse + specular, 1.0f);
}编译运行
视差映射 (Parallax Mapping)
ParallaxFragment.glsl
cpp
uniform float heightScale;
// 视差映射
vec2 ParallaxMapping(vec2 texCoords, vec3 viewDir)
{
float depth = texture(parallaxMap, texCoords).r;
vec2 p = viewDir.xy / viewDir.z * (depth * depthScale);
return texCoords - p;
}
void main()
{
vec3 viewDir = normalize(fs_in.TangentViewPos - fs_in.TangentFragPos);
vec2 texCoords = ParallaxMapping(fs_in.TexCoords, viewDir);
// ...
}定义一个名为 ParallaxMapping 的函数,它接收UV坐标和视线方向
首先使用原始的UV坐标采样视差贴图获取深度值 depth
然后 viewDir.xy / viewDir.z 进行透视矫正
最后乘以采样来的深度值 depth 和外部传入的常量 depthScale 获取UV偏移量
Main.cpp
cpp
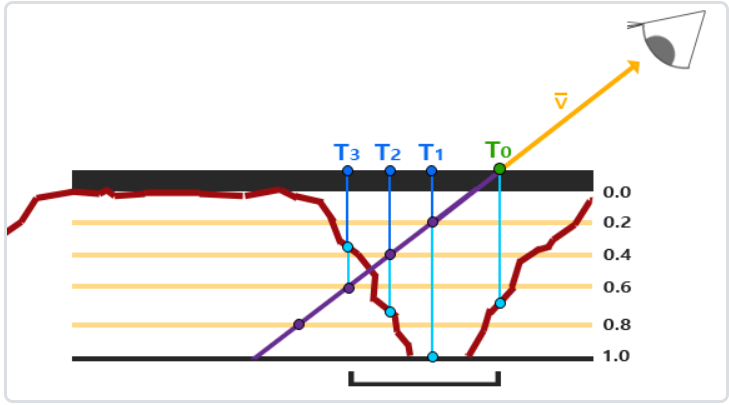
parallarShader.SetFloat("depthScale", 0.1f);编译运行,顺利的话可以看见以下图像
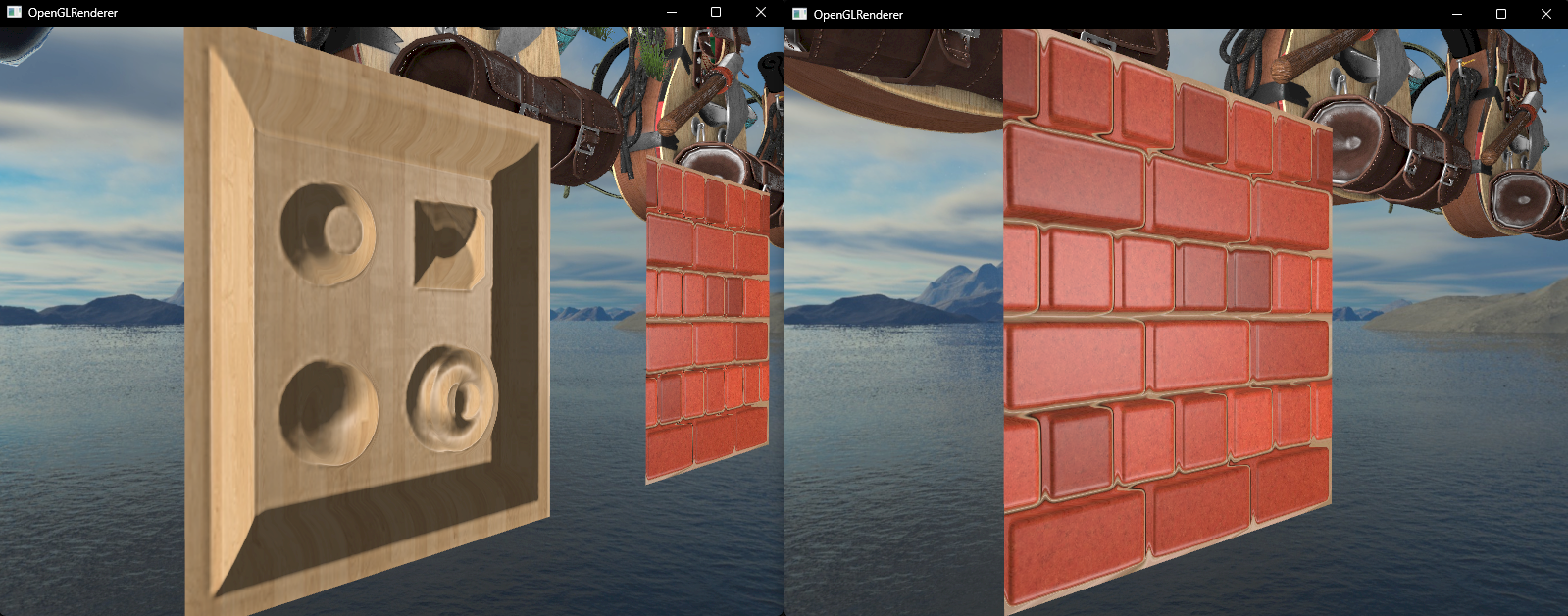
砖墙的边缘看起来还有点怪,这是因为纹理坐标经过偏移超出了 [0, 1] 的范围,我们需要进行剔除
ParallaxFragment.glsl
cpp
if(texCoords.x > 1.0 || texCoords.y > 1.0 || texCoords.x < 0.0 || texCoords.y < 0.0)
discard;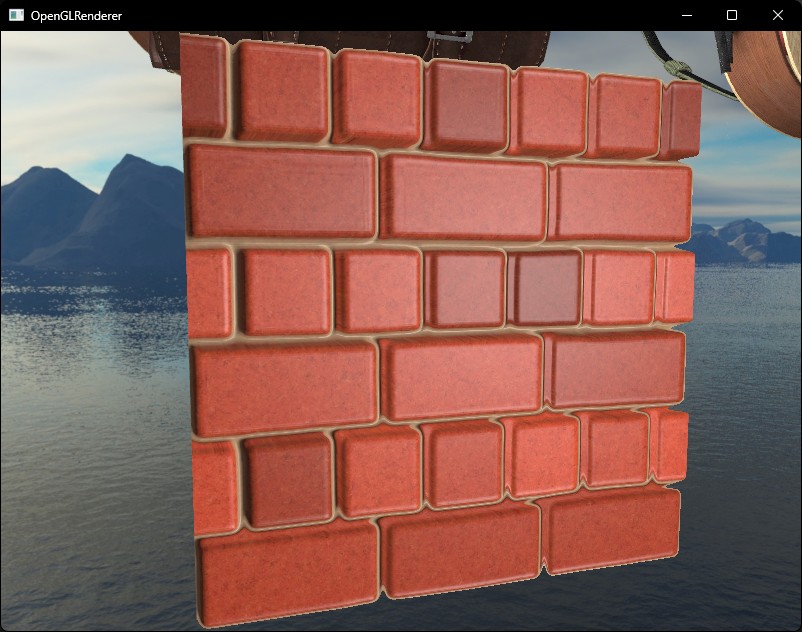
三、陡峭视差映射 (Steep Parallax Mapping)
如果以大角度的侧面进行观察会发现一些问题
这是因为我们目前只是进行了一个大致的视差映射,接下来使用陡峭视差映射 来获取更精确的结果
陡峭视差映射的基本思想是将总深度范围划分为同一个深度/高度的多个层,我们从上至下遍历深度层,如果该层的深度值高于了存储在深度贴图中的值则结束
cpp
// 陡峭视差映射
vec2 SteepParallaxMapping(vec2 texCoords, vec3 viewDir)
{
// 划分的层数
const float numLayers = 10;
// 每层大小
float layerDepth = 1.0 / numLayers;
// 当前层深度
float currentLayerDepth = 0.0;
// 纹理坐标变化量
vec2 P = viewDir.xy * depthScale;
vec2 deltaTexCoords = P / numLayers;
vec2 currentTexCoords = texCoords;
float currentDepthMapValue = texture(parallaxMap, currentTexCoords).r;
while (currentLayerDepth < currentDepthMapValue)
{
currentTexCoords -= deltaTexCoords;
currentDepthMapValue = texture(parallaxMap, currentTexCoords).r;
currentLayerDepth += layerDepth;
}
return currentTexCoords;
}编译运行,从侧面看效果好了很多
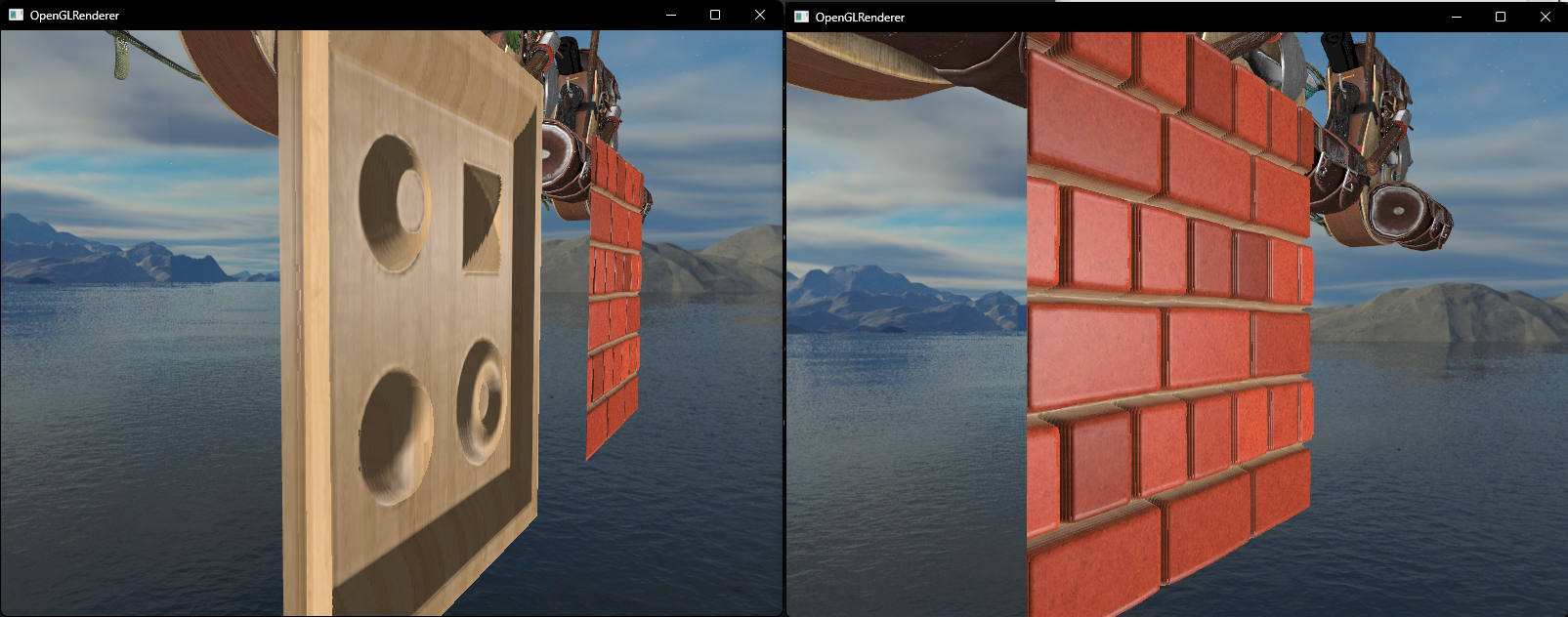
不过由于采样深度变化非连续,会出现断层问题

可以通过观察的角度来优化层数,倾斜角度越大层数越多,提供更好的性能的同时减轻断层的问题
cpp
const float minLayers = 8;
const float maxLayers = 32;
float numLayers = mix(maxLayers, minLayers, abs(dot(vec3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0), viewDir)));但断层的根本原因是因为采样深度变化非连续,接下来我们使用视差遮蔽映射来解决这个问题
四、视差遮蔽映射 (Parallax Occlusion Mapping)
视差遮蔽映射和陡峭视差映射类似,但不是直接使用目标层的纹理坐标,而是根据表面高度距离来在深度层之间进行线性插值
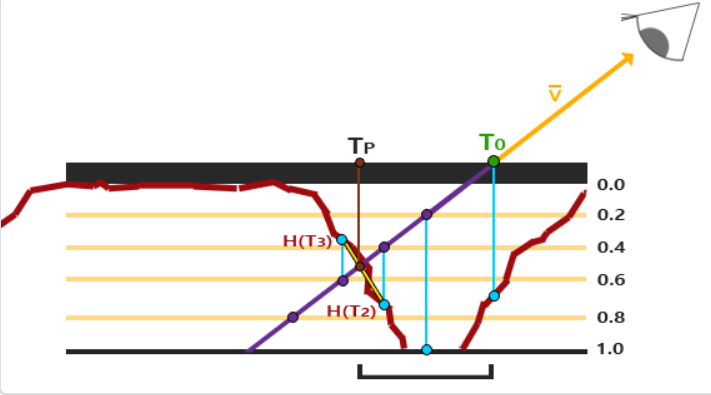
ParallaxFragment.glsl
cpp
// 视差遮蔽映射
vec2 ParallaxOcclusionMapping(vec2 texCoords, vec3 viewDir)
{
// 划分的层数
const float minLayers = 10;
const float maxLayers = 20;
float numLayers = mix(maxLayers, minLayers, abs(dot(vec3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0), viewDir)));
// 每层大小
float layerDepth = 1.0 / numLayers;
// 当前层深度
float currentLayerDepth = 0.0;
// 纹理坐标变化量
vec2 P = viewDir.xy / viewDir.z * depthScale;
vec2 deltaTexCoords = P / numLayers;
vec2 currentTexCoords = texCoords;
float currentDepthMapValue = texture(parallaxMap, currentTexCoords).r;
while(currentLayerDepth < currentDepthMapValue)
{
currentTexCoords -= deltaTexCoords;
currentDepthMapValue = texture(parallaxMap, currentTexCoords).r;
currentLayerDepth += layerDepth;
}
// 上一个深度的纹理坐标
vec2 prevTexCoords = currentTexCoords + deltaTexCoords;
// 获取两层的深度,用于后续插值
float afterDepth = currentDepthMapValue - currentLayerDepth;
float beforeDepth = texture(parallaxMap, prevTexCoords).r - currentLayerDepth + layerDepth;
// 插值权重
float weight = afterDepth / (afterDepth - beforeDepth);
vec2 finalTexCoords = prevTexCoords * weight + currentTexCoords * (1.0 - weight);
return finalTexCoords;
}编译运行,断层的问题好了很多
完整代码可在顶部Git仓库中找到
下接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44506615/article/details/151986616?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502