写在前面
这道题目好像是 2025年9月12日参加华为ai岗位的机试考试的一道题目。题目网上有原题,也有类似的解答,我这里主要是讲一讲我对这道题目的想法,以及通过 C + + C++ C++ 编写的代码。(网上的都是 P y t h o n Python Python 写的代码),本人还是习惯使用 C + + C++ C++ 编写。
题目
b站上有个视频,专门讲解了这道题目的思路:华为9月12日AI岗考试题讲解-二叉树中序遍历的第k个祖先节点|BFS建树,中序遍历,模拟
题目的大致意思是(具体详见:二叉树中序遍历的第k个祖先节点):

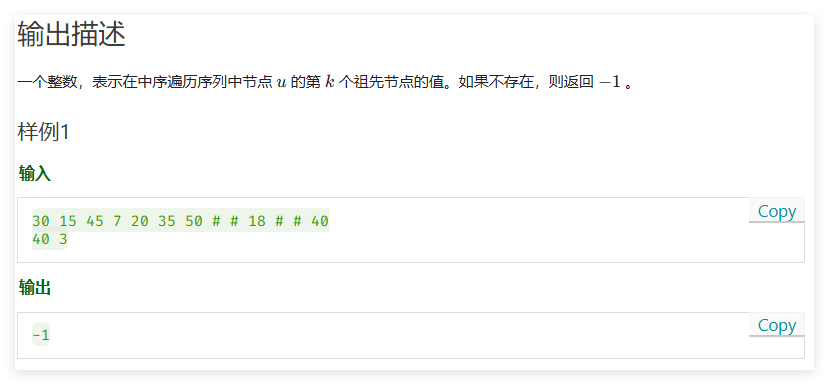
我的思路
我的思路就是:
- 首先对输入的数据节点进行建树,这里就需要构建一个结构体 construct TreeNode ,然后建立二叉树,同时子节点有个 fa 指针,指向父节点,便于后续操作。
- 接着对二叉树进行中序遍历,并将结果存入到一个 inorderResult 数组中。
- 接着在 inorderResult 数组中找到需要找寻的节点 node 的位置,然后标记其所有的父节点的 isAncestor = 1,表示是该节点的祖先节点
- 最后从该位置向前遍历,每找到一个 isAncestor = 1 的节点,则 k--,直到 k==0,返回该位置的节点值。要是遍历到第一个元素 k 依旧不为 0 的话,返回 -1 即可。
于是我根据上述思路,编写的代码如下:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
int isAncestor = 0;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode *fa; // 用来找寻父节点
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr), fa(nullptr) {}
};
// 从输入字符串构建二叉树(层次遍历输入,# 表示 null)
TreeNode *buildTree(const vector<string> &parts)
{
if (parts.empty() || parts[0] == "#")
return nullptr;
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(stoi(parts[0]));
root->fa = nullptr;
queue<TreeNode *> q; // 引入一个队列,方便建树
q.push(root);
size_t i = 1;
while (!q.empty() && i < parts.size())
{
TreeNode *node = q.front();
q.pop();
// 左子节点
if (i < parts.size() && parts[i] != "#")
{
node->left = new TreeNode(stoi(parts[i]));
node->left->fa = node; // 标记其父节点
q.push(node->left);
}
else
node->left = nullptr; // 表示 parts[i] == "#" ,此时其左子节点为空
i++;
// 右子节点
if (i < parts.size() && parts[i] != "#")
{
node->right = new TreeNode(stoi(parts[i]));
node->right->fa = node;
q.push(node->right);
}
else
node->right = nullptr;
i++;
}
return root;
}
// 中序遍历,将节点值存入 result
void inorder(TreeNode *root, vector<TreeNode *> &result)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
inorder(root->left, result);
result.push_back(root);
inorder(root->right, result);
}
int main()
{
string line;
getline(cin, line); // 读取整行输入
int node, k;
cin >> node >> k; // 读取 node , k
// 去除首尾空格
// size_t start = line.find_first_not_of(" \t");
// size_t end = line.find_last_not_of(" \t");
// if (start == string::npos)
// {
// cout << -1 << endl;
// return 0;
// }
// line = line.substr(start, end - start + 1);
// 按空格分割字符串
vector<string> parts;
stringstream ss(line);
string token;
while (ss >> token)
parts.push_back(token);
// 构建树
TreeNode *root = buildTree(parts);
// 中序遍历
vector<TreeNode *> inorderResult;
inorder(root, inorderResult);
// 找到目标节点在中序遍历中的位置
int len = inorderResult.size();
int temp = 0;
for (; temp < len; temp++)
if (inorderResult[temp]->val == node)
break;
// 目标节点的祖先节点的 isAncestor 为 1
TreeNode *current = inorderResult[temp];
while (current->fa != nullptr)
{
current->fa->isAncestor = 1;
current = current->fa;
}
// 查询第 k 个祖先节点
for (int i = temp - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (inorderResult[i]->isAncestor == 1)
k--;
if (k == 0)
{
cout << inorderResult[i]->val << endl;
// 重置 isAncestor 标记
for (TreeNode *node : inorderResult)
node->isAncestor = 0;
return 0;
}
}
// 重置 isAncestor 标记
for (TreeNode *node : inorderResult)
node->isAncestor = 0;
// 遍历完 k 都不为 0 ,输出 -1 即可。
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}我参加的一次
非常荣幸,我参加了2025年9月17号华为 ai 的机考,题目感觉出的不是很难,都是我复习到的,于是考试结果也还不错。
详细题目参见:CodeFun 2000
选择题就不做说明了,主要讲解一下编程题吧:
题目一(300分):大模型分词
题目详见:大模型分词
刚好我力扣刷到了 hot100 的动态规划专题,因此一看这道题目就是使用动态规划进行求解,只是需要对输入进行预处理即可,于是可以选择使用 C++ 中的 unordered_map 进行映射存储。
cpp
// we have defined the necessary header files here for this problem.
// If additional header files are needed in your program, please import here.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <climits>
// #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int maxScore(const string &text, const unordered_map<string, int> &confidence, const unordered_map<string, int> &transfer)
{
int n = text.length();
vector<int> dp(n + 1, INT_MIN);
dp[0] = 0;
// 每个位置记录一下最优的前驱
vector<int> prev(n + 1, -1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
string word = text.substr(j, i - j);
if (confidence.find(word) != confidence.end())
{
int word_score = confidence.at(word);
int transition_score = 0;
// 不是第一个词的话,检查转移分数?
if (j > 0 && prev[j] != -1)
{
string prev_word = text.substr(prev[j], j - prev[j]);
string transition_key = prev_word + " " + word;
if (transfer.find(transition_key) != transfer.end())
{
transition_score = transfer.at(transition_key);
}
}
int total_score = dp[j] + word_score + transition_score;
if (total_score > dp[i])
{
dp[i] = total_score;
prev[i] = j; // 更新前驱位置
}
}
}
}
return dp[n] == INT_MIN ? 0 : dp[n];
}
int main()
{
// please define the C++ input here. For example: int a,b; cin>>a>>b;;
// please finish the function body here.
// please define the C++ output here. For example:cout<<____<<endl;
// 读入英文单词
string text;
// 读入 n 和 m
int n, m;
cin >> text;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<string, int> confidence;
// 已标注词元和置信度分数P,使用哈希进行存储
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string word;
int score;
cin >> word >> score;
confidence[word] = score;
}
cin >> m;
// 转移分数数据:起始词、下一个词、转移分数加分X、空格分隔
unordered_map<string, int> transfer;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
string prevWord, nextWord;
int score;
cin >> prevWord >> nextWord >> score;
transfer[prevWord + " " + nextWord] = score;
}
int result = maxScore(text, confidence, transfer);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}但是这段代码在华为的评判系统的只过了 90% 的测试用例,还有 10% 没有通过,因此不知道主要问题在哪里,读者若有发现,麻烦详细解答一下,笔者在此不胜感激。
题目二(150分):大模型Attention模块开发
题目详见:大模型Attention模块开发
感觉要是知道点 T r a n s f o r m e r Transformer Transformer 的都应该知道这个 A t t e n t i o n Attention Attention 模块,因此这道题目还是比较好写的:
python
# If you need to import additional packages or classes, please import here.
import numpy as np
def attention_module(n, m, h):
# 构建全 1 的矩阵
X = np.ones((n, m))
# 构建上三角矩阵
W1 = np.triu(np.ones((m, h)))
W2 = np.triu(np.ones((m, h)))
W3 = np.triu(np.ones((m, h)))
# 计算 Q K V
Q = np.dot(X, W1)
K = np.dot(X, W2)
V = np.dot(X, W3)
# 计算
QK_T = np.dot(Q, K.T)/np.sqrt(h)
# 计算 softmax(QK_T)
M = np.exp(QK_T)
softmax_QK_T = M / np.sum(M, axis=1, keepdims=True)
Y = np.dot(softmax_QK_T, V)
return int(np.round(np.sum(Y)))
def func():
# please define the python3 input here. For example: a,b = map(int, input().strip().split())
# please finish the function body here.
# please define the python3 output here. For example: print().
# 读入输入
n, m, h = map(int, input().strip().split())
print(attention_module(n, m, h))
if __name__ == "__main__":
func()