引入
在邻接矩阵之后,为了提升空间利用率而引出了邻接表。邻接表适用于计算有向图中顶点的出度数、逆邻接表适用于计算有向图中顶点的入度数。十字链表可以同时满足这两个要求。
十字链表是一种用于表示有向图的数据结构,它的核心特点是将"以弧尾为线索的链表"和"以弧头为线索的链表"交叉结合:
- 每条弧(有向边)同时属于两个链表:一个是以其弧尾顶点为起点 的"出边链表",另一个是以其弧头顶点为终点 的"入边链表"。
- 这种"交叉链表"的结构,让它能高效地处理有向图的入度、出度查询,以及弧的增删操作,因此命名为 CrossLinkGraph (十字链接图)。
十字链表的优缺点
- 优点:
适合稀疏矩阵的高效存储,节省空间。
支持快速按行或按列遍历非零元素。 - 缺点:
实现复杂度较高,需维护双向链表。
随机访问元素性能较差,需遍历链表
结构示图
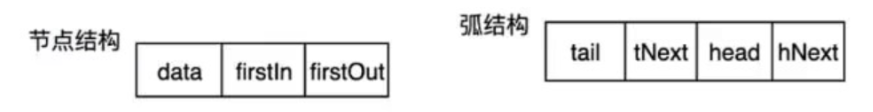
tNext表示的是除head之外以tail为弧尾的弧头节点。
同样,hNext表示的是除tail之外以head为弧头的弧尾节点。
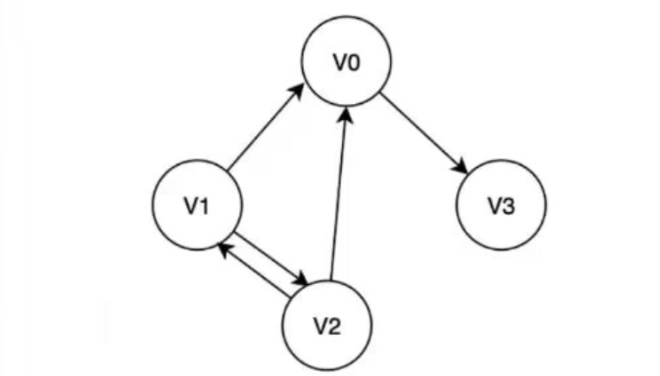
例图:
对应结构模型:
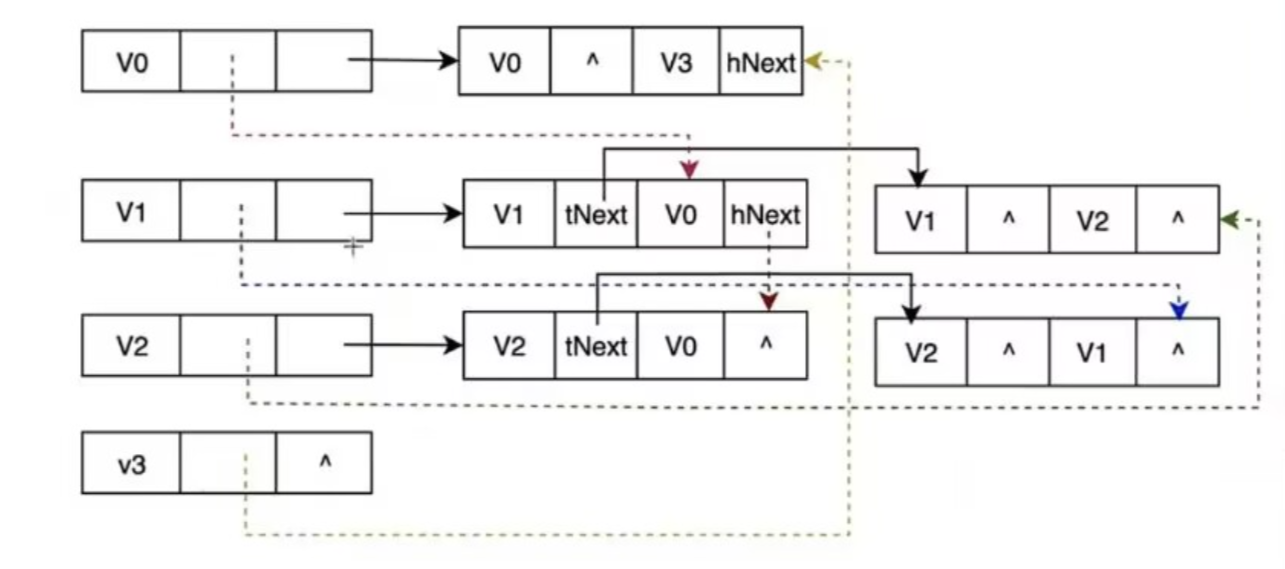
每个弧(有向边)用一个 ArcBox 节点表示,每个顶点用包含 firstIn (入度链头)和 firstOut (出度链头)的节点表示。
上图结构模型中的实线代表出边(从当前顶点指出去,即当前节点做为弧尾),虚线代表入边(从其他节点指向当前顶点,即当前节点做为弧头)。
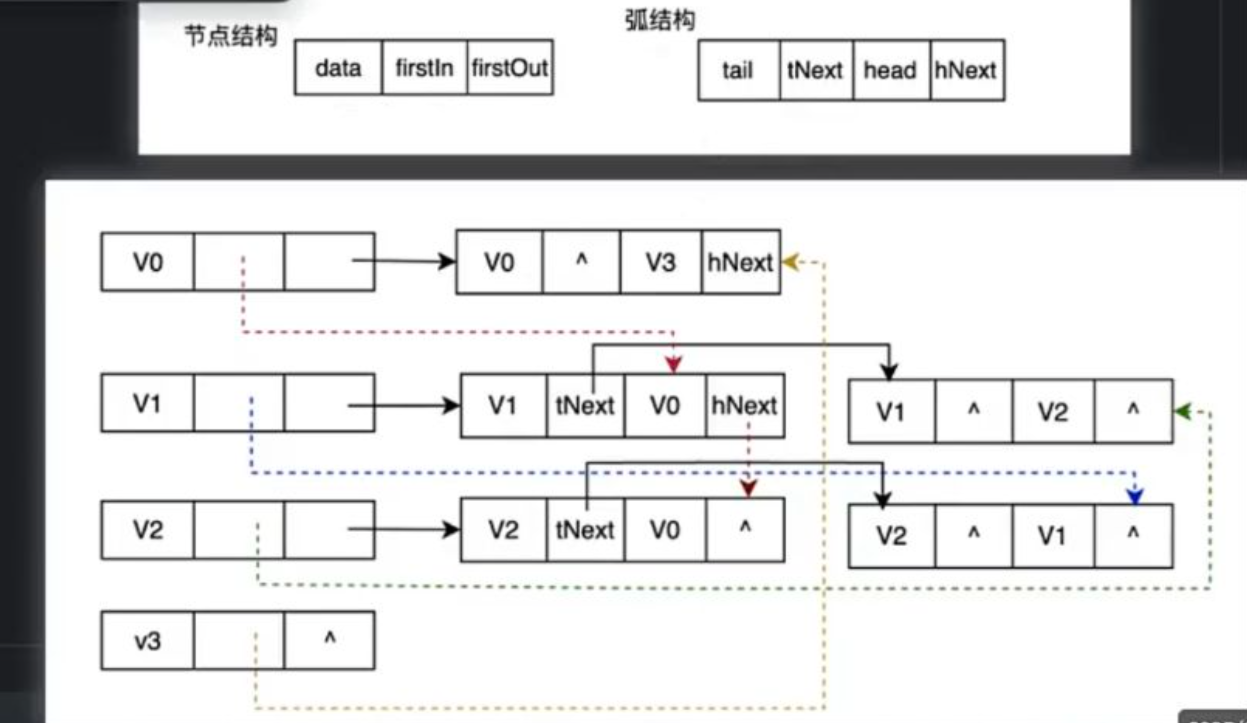
例如(为方便观察下面贴的图片是重复的):
-
实线部分
v0的节点结构中firstOut指向的边结构是以v0为弧尾的,以v0为弧尾的节点是v3,所以边结构中head为v3,tNext表示除v3之外仍然以v0为弧尾的节点,显然没有了,所以只能为空。
-
虚线部分
v0的firstIn就是当v0作为弧头被其他节点指向时的数据,它表示的是指向v0的节点,也就是以v0为弧头的弧尾节点。v1,v2就是这样的节点,按次序进行指向,所以v0的firstIn就指向以v1为弧尾的弧头位置(还是v0)。而hNext就是指向除v1之外且以v0作为弧头的弧尾节点的边结构,这里是v0与v2节点之间的,则hNext就指向以v0作为弧头,v2为弧尾的边结构的hNext(方便再次寻找以v0作为弧头的弧尾节点的其他节点)。找到这里对于v0就没有满足条件的节点了,所以hNext指向空。
注意:在十字链表中,同一条弧(有向边)会同时出现在"出边链表"和"入边链表"中:
- 从弧尾顶点的角度,这条弧是"出边",存储在 firstOut 链表中;
- 从弧头顶点的角度,这条弧是"入边",存储在 firstIn 链表中。
但本质上,这是同一块内存( ArcBox 结构体)被两个链表指针同时引用。因此 releaseCrossGraph只通过"出边/或入边链表"遍历(下面采用的是出边遍历)并释放所有弧的内存,同时保证了内存的不重复释放。
头文件
c
#pragma once
//十字链表的边结构
typedef struct arcBox{
int tailVertex;
struct arcBox* tailNext;
int headVertex;
struct arcBox* headNext;
int weight;
}ArcBox;
//十字链表的顶点结构
typedef struct {
int no;
const char* show;
ArcBox* firstIn; //该节点的入度
ArcBox* firstOut; //该节点的出度
}CrossVertex;
//利用十字链表的结构实现图结构
typedef struct {
CrossVertex* nodes;
int numVertex;
int numEdge;
}CrossGraph;
CrossGraph* createCrossGraph(int n);
void releaseCrossGraph(CrossGraph* graph);
void initCrossGraph(CrossGraph* graph, const char* names[], int num);
void addCrossArc(CrossGraph* graph, int tail, int head, int w);
//计算编号为no的节点的入度
int inDegreeCrossGraph(const CrossGraph* graph, int no);
//计算编号为no的节点的出度
int outDegreeCrossGraph(const CrossGraph* graph, int no);功能实现
创建
c
CrossGraph* createCrossGraph(int n) {
CrossGraph* graph = (CrossGraph*)malloc(sizeof(CrossGraph));
if (graph == NULL)return NULL;
graph->nodes = (CrossVertex*)malloc(sizeof(CrossVertex)*n);
if (graph->nodes == NULL)
{
free(graph);
return NULL;
}
graph->numEdge = 0;
graph->numVertex = n;
return graph;
}释放
c
void releaseCrossGraph(CrossGraph* graph) {
int numEdges = 0; //依次释放:边,节点,图
if (graph) {
if (graph->nodes) {
for (int i = 0; i < graph->numVertex; i++) {
ArcBox* box = graph->nodes[i].firstOut;
ArcBox* tmp;
while (box) {
tmp = box;
box = box->tailNext;
free(tmp);
numEdges++;
}
}
printf("released %d edges\n", numEdges);
free(graph->nodes);
}
free(graph);
}
}初始化
c
void initCrossGraph(CrossGraph* graph, const char* names[], int num) {
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
graph->nodes[i].no = i;
graph->nodes[i].show = names[i];
graph->nodes[i].firstIn = graph->nodes[i].firstOut = NULL;
}
}添加边
c
//添加一条以tail为弧尾,以head为弧头的边
void addCrossArc(CrossGraph* graph, int tail, int head, int w) {
ArcBox* box = (ArcBox*)malloc(sizeof(ArcBox));
if (box==NULL)return ;
box->weight = w;
//从出度关系上进行插入(头插法)
box->tailVertex = tail;
box->tailNext = graph->nodes[tail].firstOut;
graph->nodes[tail].firstOut = box;
//从入度关系上进行插入(头插法)
box->headVertex = head;
box->headNext = graph->nodes[head].firstIn;
graph->nodes[head].firstIn = box;
}计算入度
c
int inDegreeCrossGraph(const CrossGraph* graph, int no)
{
int count = 0;
ArcBox* box = graph->nodes[no].firstIn;
while (box!=NULL) {
count++;
box = box->headNext;
}
return count;计算出度
c
int outDegreeCrossGraph(const CrossGraph* graph, int no) {
int count = 0;
ArcBox* box = graph->nodes[no].firstOut;
while (box) {
count++;
box = box->tailNext;
}
return count;
}功能调用
c
void setupCrossGraph(CrossGraph* graph) {
const char* nodeName[] = {"v0","v1","v2","v3"};
initCrossGraph(graph, nodeName, 4);
addCrossArc(graph, 0, 3, 1);
addCrossArc(graph, 1, 0, 1);
addCrossArc(graph, 1, 2, 1);
addCrossArc(graph, 2, 0, 1);
addCrossArc(graph, 2, 1, 1);
}
int main() {
int n = 4;
CrossGraph* graph = createCrossGraph(n);
if (graph == NULL) {
return -1;
}
setupCrossGraph(graph);
printf("V0的入度:%d\n", inDegreeCrossGraph(graph, 2));
printf("V0的出度:%d\n", outDegreeCrossGraph(graph, 2));
releaseCrossGraph(graph);
return 0;
}