
1.栈(Stack)
1.1 概念


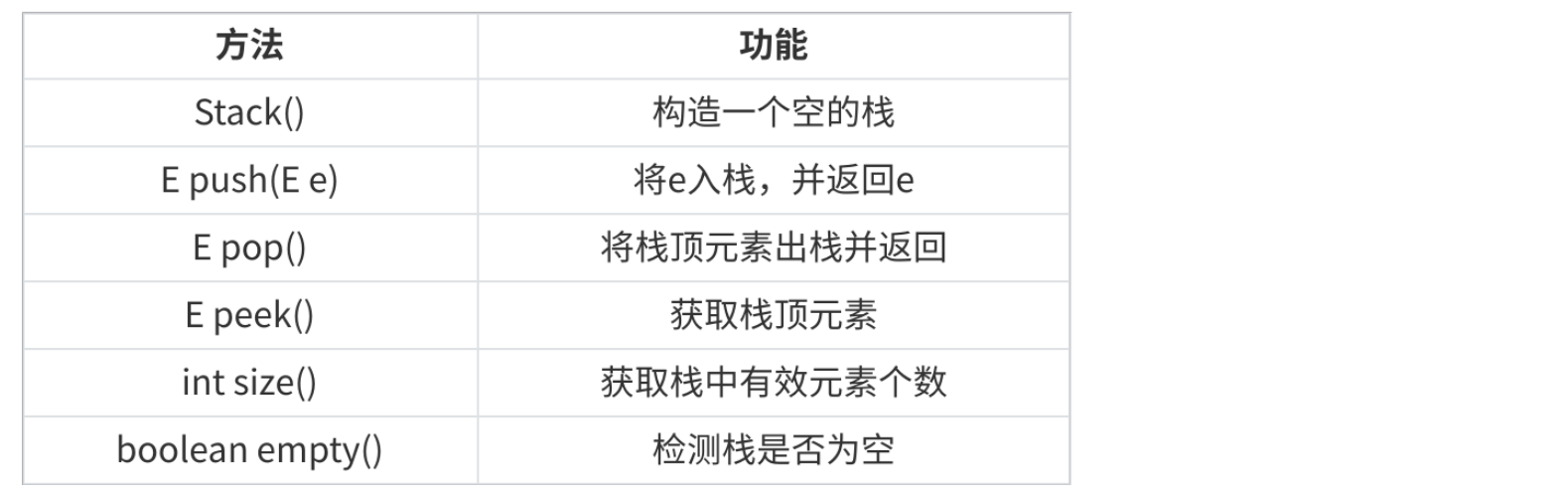
1.2 栈的模拟实现
java
// 模拟实现一个栈
// 可以基于顺序表(数组) 实现, 也可以基于链表来实现. 基于数组更简单
public class MyStack {
private String[] arr;
private int size;
public MyStack() {
arr = new String[1000];
size = 0;
}
public MyStack(int capacity) {
arr = new String[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 入栈 elem 就是 element 单词的缩写.
public void push(String elem) {
if (size == arr.length) {
// 扩容
resize();
}
// 实现一个尾插操作.
arr[size] = elem;
size++;
}
// 出栈
public String pop() {
if (size == 0) {
// 抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!");
}
// 取出栈顶元素, 最后一个元素
String elem = arr[size - 1];
// 把 size 进行 - 1
size--;
return elem;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
public String peek() {
if (size == 0) {
// 抛出异常
throw new RuntimeException("Stack is empty!");
}
String elem = arr[size - 1];
return elem;
}
private void resize() {
// 1. 创建一个更长的数组
String[] newArr = new String[arr.length * 2];
// 2. 把原数组中的元素复制到新数组中
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
newArr[i] = arr[i];
}
// 3. 把新数组赋值给原数组
arr = newArr;
}
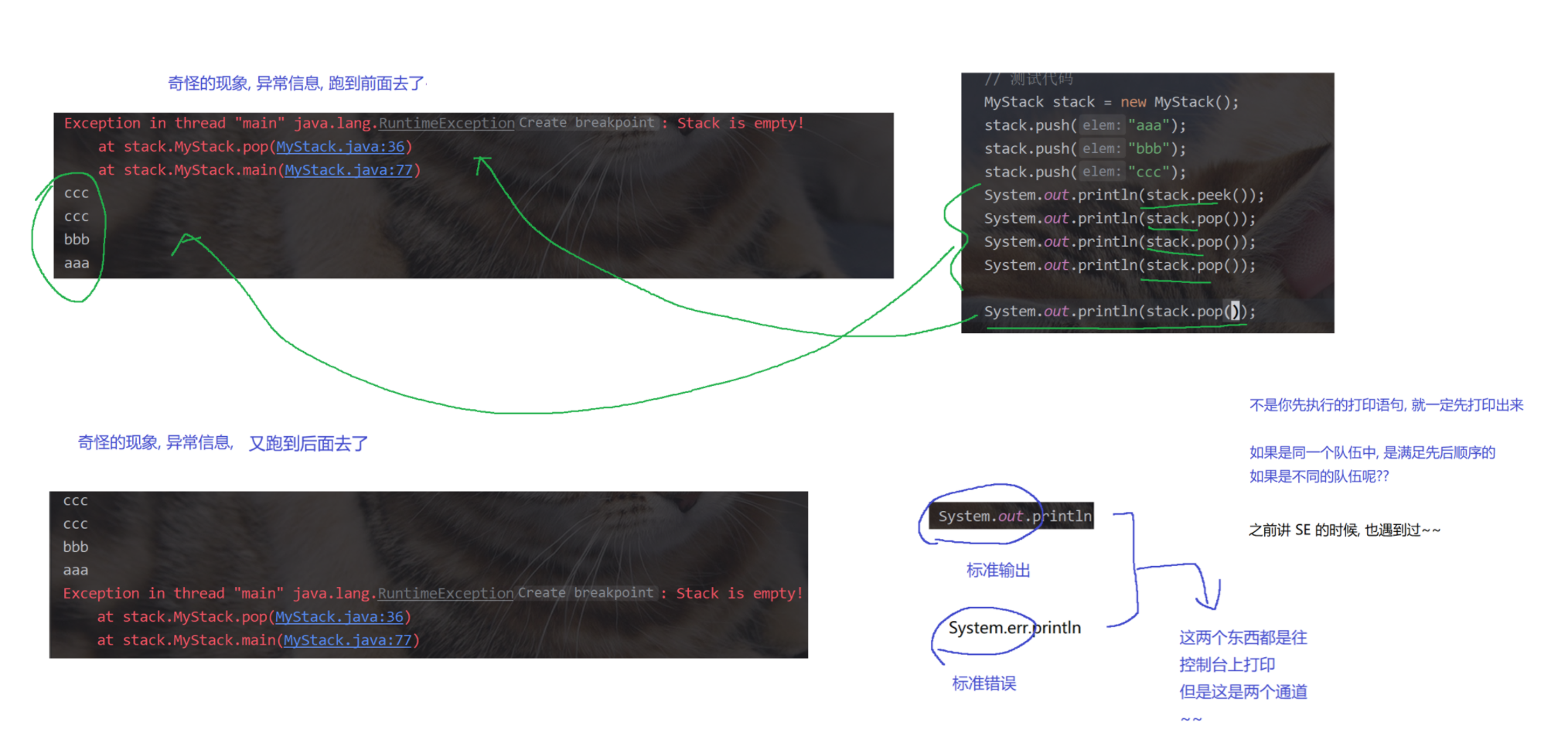
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试代码
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push("aaa");
stack.push("bbb");
stack.push("ccc");
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.pop());
//System.out.println(stack.pop());
}
}

1.3 栈的应用场景
(1) 改变元素的序列

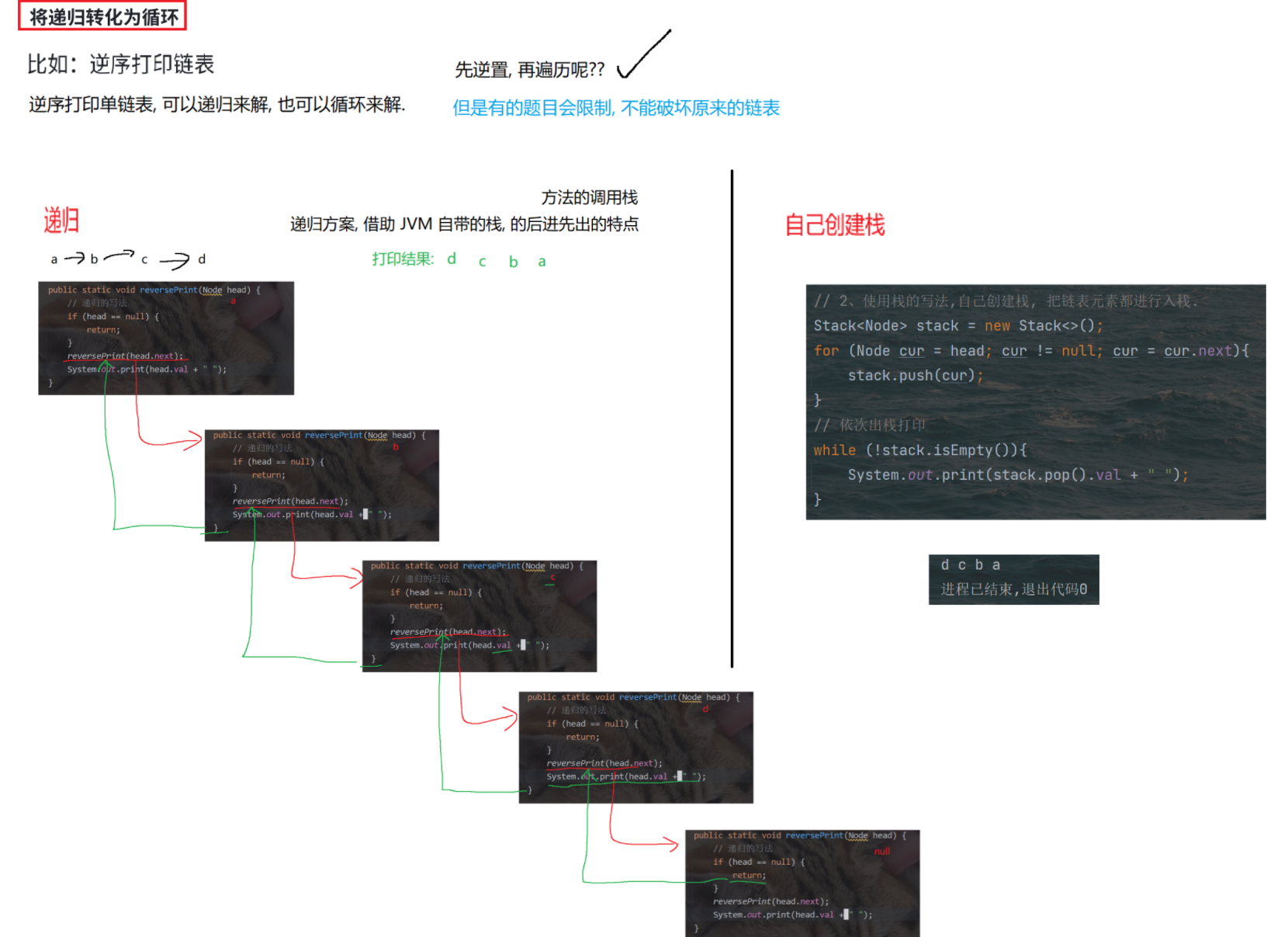
(2)将递归转化为循环
java
import java.util.Stack;
public class Test2 {
static class Node {
public String val;
public Node next;
public Node(String val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
//先创建一个单链表
public static Node build(){
Node a = new Node("a");
Node b = new Node("b");
Node c = new Node("c");
Node d = new Node("d");
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
c.next = d;
return a;
}
// 反向打印单链表.
public static void reversePrint(Node head) {
if(head == null) return;
// 1、递归的写法
// reversePrint(head.next);
// System.out.print(head.val + " ");
// 2、使用栈的写法,自己创建栈, 把链表元素都进行入栈.
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
for (Node cur = head; cur != null; cur = cur.next){
stack.push(cur);
}
// 依次出栈打印
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(stack.pop().val + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = build();
reversePrint(head);
}
}
(3)括号匹配
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/description/

java
public boolean isVaild(String s){
// 创建一个栈 泛型中要用char的包装类
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
// 针对字符串进行遍历, 取出每个字符
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
// 如果是左括号, 就入栈.
if(c == '[' || c == '(' || c == '{'){
stack.push(c);
continue;
}
// 如果是右括号, 就进行判定括号匹配.
if (c == ']' || c == ')' || c == '}') {
// 取出栈顶元素
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
// 如果栈为空, 无法取栈顶的.
// 由于当前读到了一个右括号, 要求必须得在栈里有一个匹配的左括号.
// 但是栈是空的, 说明没有匹配的左括号, 直接返回 false.
return false;
}
// 取出栈顶元素
char top = stack.pop();
// 判定是否匹配
if (top == '[' && c == ']') {
// 情况一, 匹配成功.
continue;
}
if (top == '(' && c == ')') {
// 情况二, 匹配成功.
continue;
}
if (top == '{' && c == '}') {
// 情况三, 匹配成功.
continue;
}
// 其他情况, 匹配失败.
return false;
}
}
// 整个循环结束, 再来检查栈是否为空.
// 如果栈为空, 说明所有括号都匹配成功.
// 如果栈不为空, 说明还有未匹配的左括号.
if (stack.isEmpty()) return true;
return false;
}(4)逆波兰表达式求值
https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/


java
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
// 1. 准备一个栈, 用来放操作数.
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 2. 遍历 tokens, 取出每个元素.
for (String token : tokens) {
// 3. 判定 token 是数字
if (isNumber(token)) {
// 直接入栈
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(token));
continue;
}
// 4. 判定 token 是运算符 出栈两个元素. 先出栈的是第二个操作数, 后出栈的是第一个操作数.
int num2 = stack.pop();
int num1 = stack.pop();
// 5. 判定当前的运算符是哪个, 进行运算, 把得到的结果, 重新入栈.
if (token.equals("+")) {
stack.push(num1 + num2);
} else if (token.equals("-")) {
stack.push(num1 - num2);
} else if (token.equals("*")) {
stack.push(num1 * num2);
} else if (token.equals("/")) {
stack.push(num1 / num2);
}
}
// 最终整个表达式的结果就是栈里的唯一的一个元素.
return stack.pop();
}
private static boolean isNumber(String token) {
// 如果 token 是运算符, 就返回 false, 否则返回 true.
if (token.equals("+") || token.equals("-") || token.equals("*") || token.equals("/")) return false;
return true;
}(5)出栈入栈次序匹配
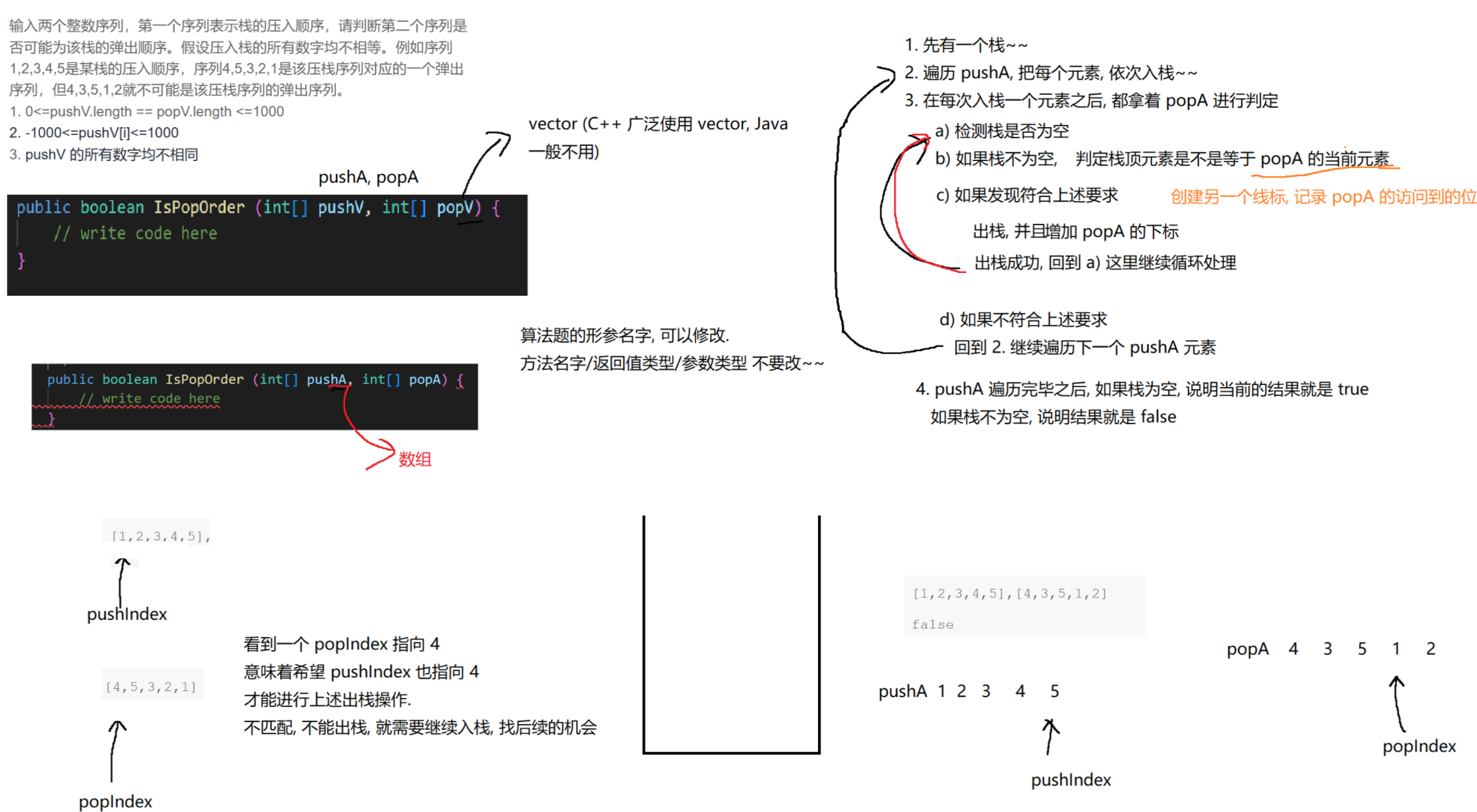
java
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushA, int[] popA) {
// 1. 准备一个栈
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 2. 针对 pushA 进行遍历
int pushIndex = 0;
int popIndex = 0;
for (; pushIndex < pushA.length; pushIndex++) {
// 3. 把当前的 pushIndex 指向的元素入栈.
stack.push(pushA[pushIndex]);
// 4. 拿着 popA 的当前元素和栈顶进行比较. 循环比较的过程. 只要比较成功, 出栈, 并且进行下次循环,
// 也就是比较 popA 的下一个元素和栈顶的关系.
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popA[popIndex]) {
stack.pop();
popIndex++;
}
// 上述条件不匹配, 说明当前 popIndex 指向的元素, 和栈顶元素不同的. 就需要再次入栈新的元素, 找新的机会.
// 此处就结束循环进入下次即可.
}
// 5. 当整个 pushA 遍历完毕, 说明 "所有的机会" 都用完了.
// 此时如果栈已经是空了, 说明前面 popA 的元素就都匹配成功; 如果栈非空, 还有 popA 的元素是无法匹配的.
if (stack.isEmpty()) return true;
return false;
}(6)最小栈
https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/


java
import java.util.Stack;
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
public MinStack() {
// 这个方法空着就行了, 不需要.
}
public void push(int val) {
// stack1 就是正常入栈.
stack1.push(val);
// 针对 stack2, 就需要比较 val 和 stack2 栈顶元素的大小, 把小的元素入栈.
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
// 如果 stack2 栈为空, 直接入栈.
stack2.push(val);
return;
}
int min = stack2.peek();
if (val < min) {
stack2.push(val);
} else {
stack2.push(min);
}
}
public void pop() {
if (stack1.isEmpty()) {
// 在做 OJ 题的时候, 不要抛出异常.
return;
}
// 把这两个栈的元素都出栈.
stack1.pop();
stack2.pop();
}
public int top() {
// 取正常的栈顶元素.
if (stack1.isEmpty()) {
// 由于不是 Integer, 无法返回 null. 而且右不能修改人家方法的返回值类型. 此处就返回 0 .
return 0;
}
return stack1.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
// 取 stack2 栈顶元素.
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
return stack2.peek();
}
}2.队列(Queue)
2.1 概念
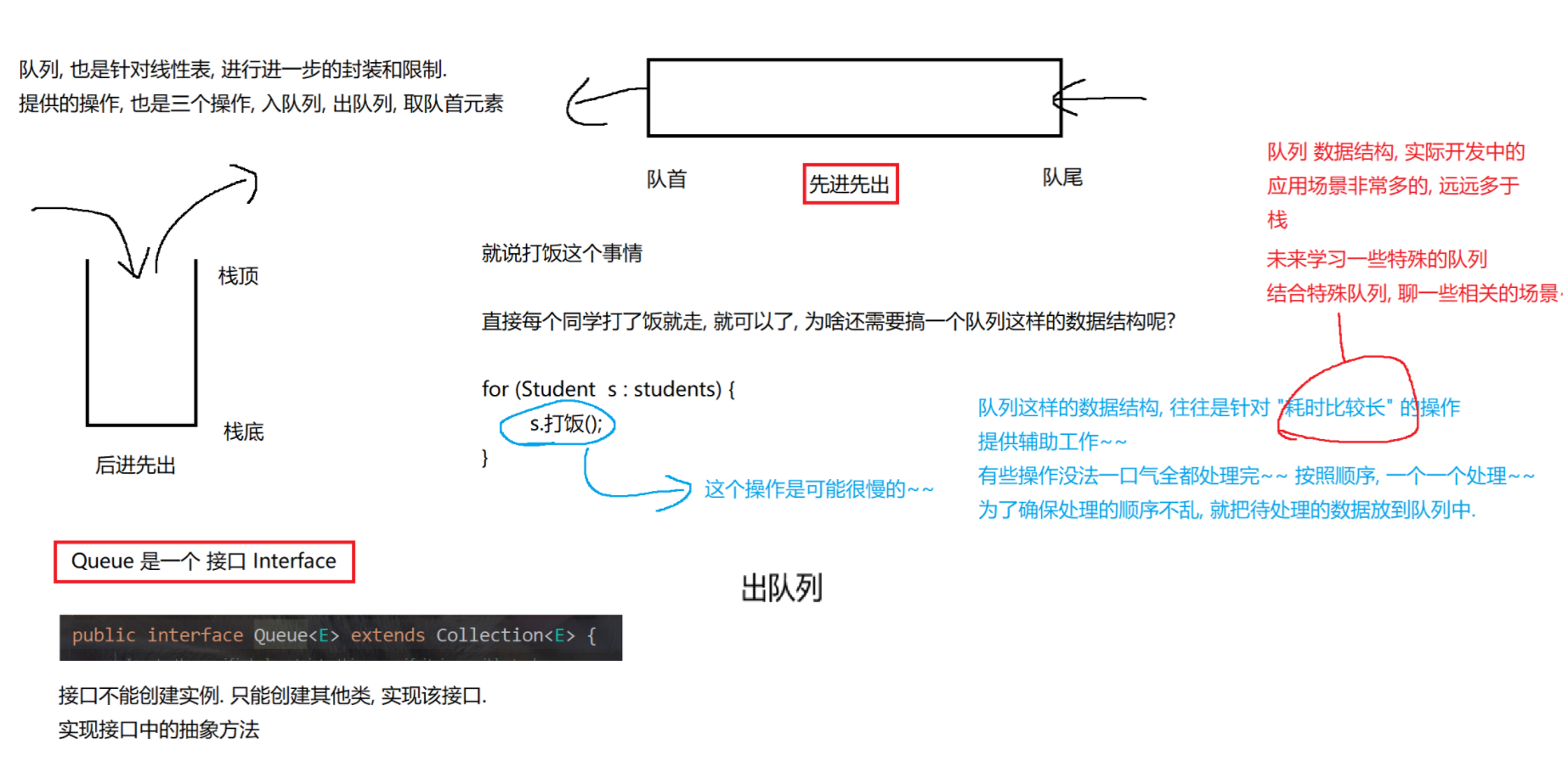

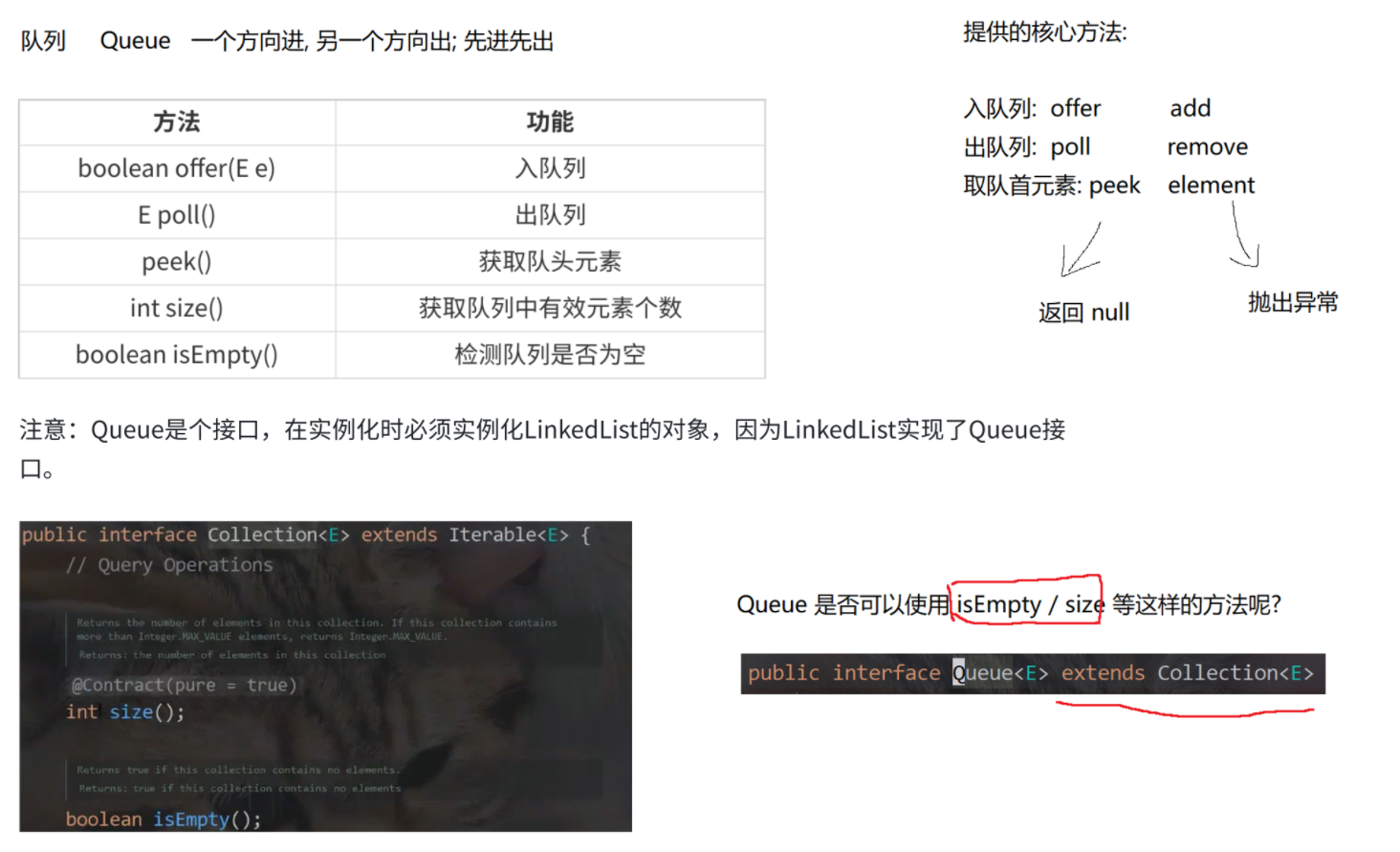
java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这个会编译失败. ArrayList 没有实现 Qeueue 接口.
// Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.remove());
// 判定队列为空, 下列两种写法均可. 其中 isEmpty 是 Collection 接口的方法. Queue 继承自 Collection
if (queue.peek() == null) { }
if (queue.isEmpty()) { }
// 创建一个基于数组的队列.
Queue<Integer> queue2 = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue2.offer(1);
queue2.offer(2);
queue2.offer(3);
queue2.offer(4);
System.out.println(queue2.peek());
System.out.println(queue2.poll());
System.out.println(queue2.poll());
System.out.println(queue2.poll());
System.out.println(queue2.poll());
}
}2.2 队列的模拟实现

(1)基于单链表
java
// 基于单链表实现队列.
public class MyQueue {
// 链表的一个节点.
static class Node{
public String val;
public Node next;
public Node(String val){
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
// 把队列的头部和尾部都记录下来.
// 基于链表实现队列(咱们采取这个做法, 这个做法, 链表的头/尾和队列的头/尾是一致的):
// 1. 入队 -> 尾插 2. 出队 -> 头删
// 也可以 (但是链表的头/尾和队列的头/尾是反着的)
// 1. 入队 -> 头插 2. 出队 -> 尾删
private Node head = null;
private Node tail = null;
// 入队 -> 尾插
public void offer(String val) {
Node newNode = new Node(val);
// 本身链表为空.
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
return;
}
// 链表非空.
tail.next = newNode;
// 尾插之后, 更新 tail 的指向.
tail = newNode;
}
// 出队 -> 头删
public String poll(){
if (head == null) return null;
// 保存头部节点的值.
// 接下来把这个节点删掉后, 需要返回这个值.
String val = head.val;
// 更新 head 的指向.
head = head.next;
// 如果链表的节点数目超出一个, 删掉一个元素, 不影响 tail 的指向.
// 但是, 如果链表的节点数目只有一个, 删掉这个元素, 此时 tail 就应该指向 null.
if (head == null) tail = null;
return val;
}
// 取队首元素
public String peek(){
if(head == null) return null;
return head.val;
}
// 是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return head == null;
}
// 求长度
public int size(){
int size = 0;
for(Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next) size++;
return size;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.offer("1");
queue.offer("2");
queue.offer("3");
queue.offer("4");
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 1
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 1
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 2
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 2
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 3
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 3
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 4
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 4
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // null
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // null
}
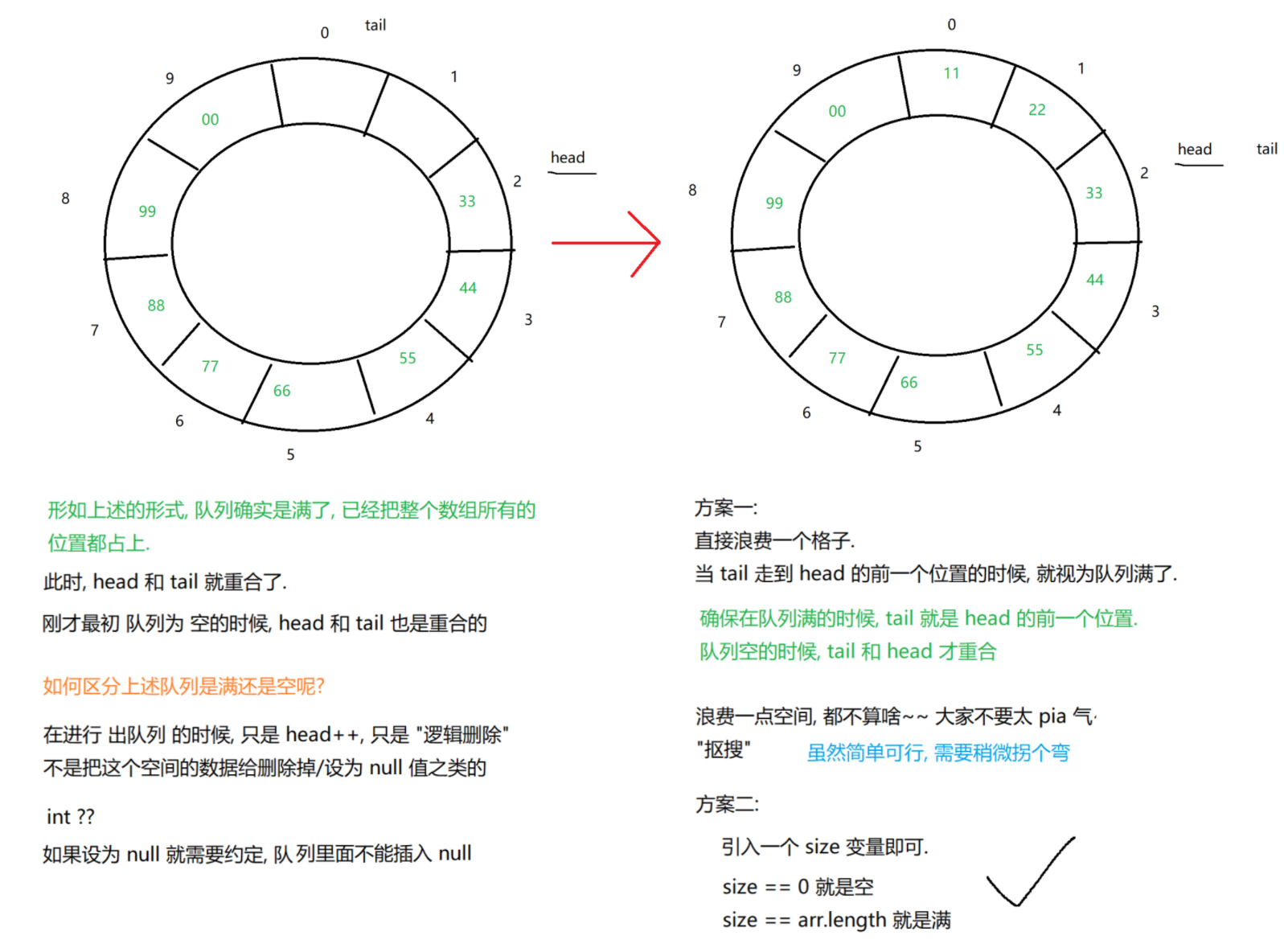
}(2)基于数组+循环队列

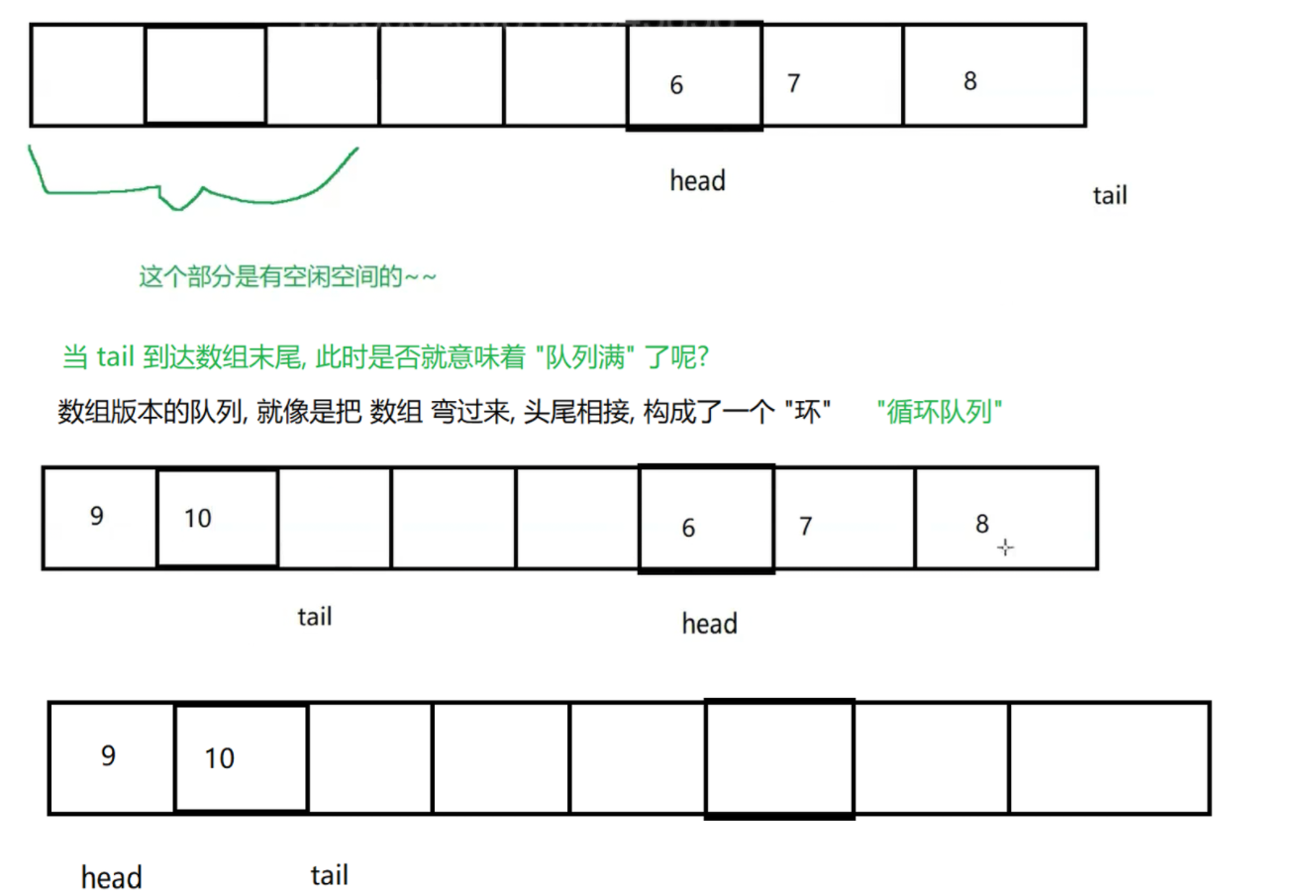

java
public class MyQueueByArray {
//基于数组实现队列
private String[] arr = null;
// 队首
private int head = 0;
// 队尾
private int tail = 0;
// 队列元素个数.
private int size = 0;
public MyQueueByArray() {
arr = new String[1000];
}
public MyQueueByArray(int capacity) {
arr = new String[capacity];
}
public void offer(String val) {
// 如果队列满了, 直接返回
if (size == arr.length) return; // 也可以抛出异常, 也可以进行扩容
// 把新的元素, 放到 tail 位置.
arr[tail] = val;
// 更新 tail 的指向.
tail++;
if (tail == arr.length) tail = 0;
// 更新 tail 指向, 还有另外一种写法
// 更推荐上面的写法, 而不是这里的 % 的写法.
// tail = (tail + 1) % arr.length;
// 更新队列的元素个数.
size++;
}
public String poll() {
// 如果队列为空, 直接返回 null
if (size == 0) return null;
// 取出队首元素, 保存起来, 以便接下来返回.
String val = arr[head];
// 更新 head 的指向.
head++;
if (head == arr.length) head = 0;
// 更新元素个数.
size--;
return val;
}
public String peek() {
if (size == 0) return null;
return arr[head];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueueByArray queue = new MyQueueByArray();
queue.offer("1");
queue.offer("2");
queue.offer("3");
queue.offer("4");
queue.offer("5");
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 1
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 1
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 2
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 3
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 4
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 5
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // null
}
}3.双端队列(Deque)
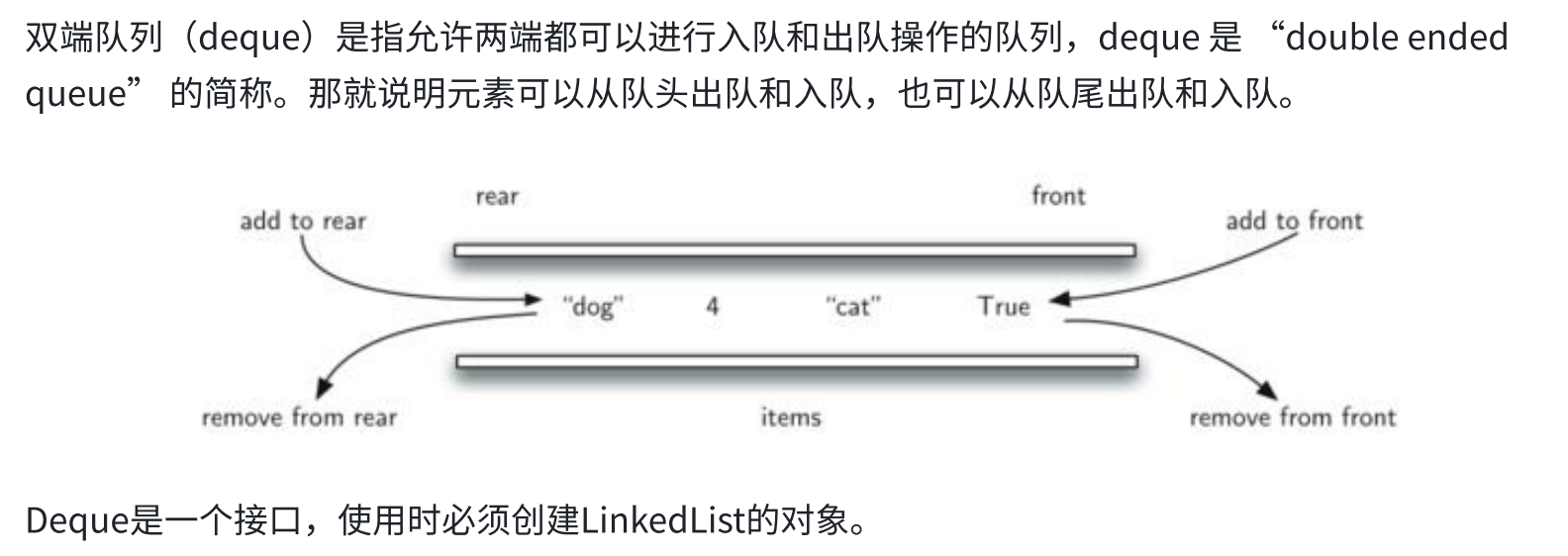
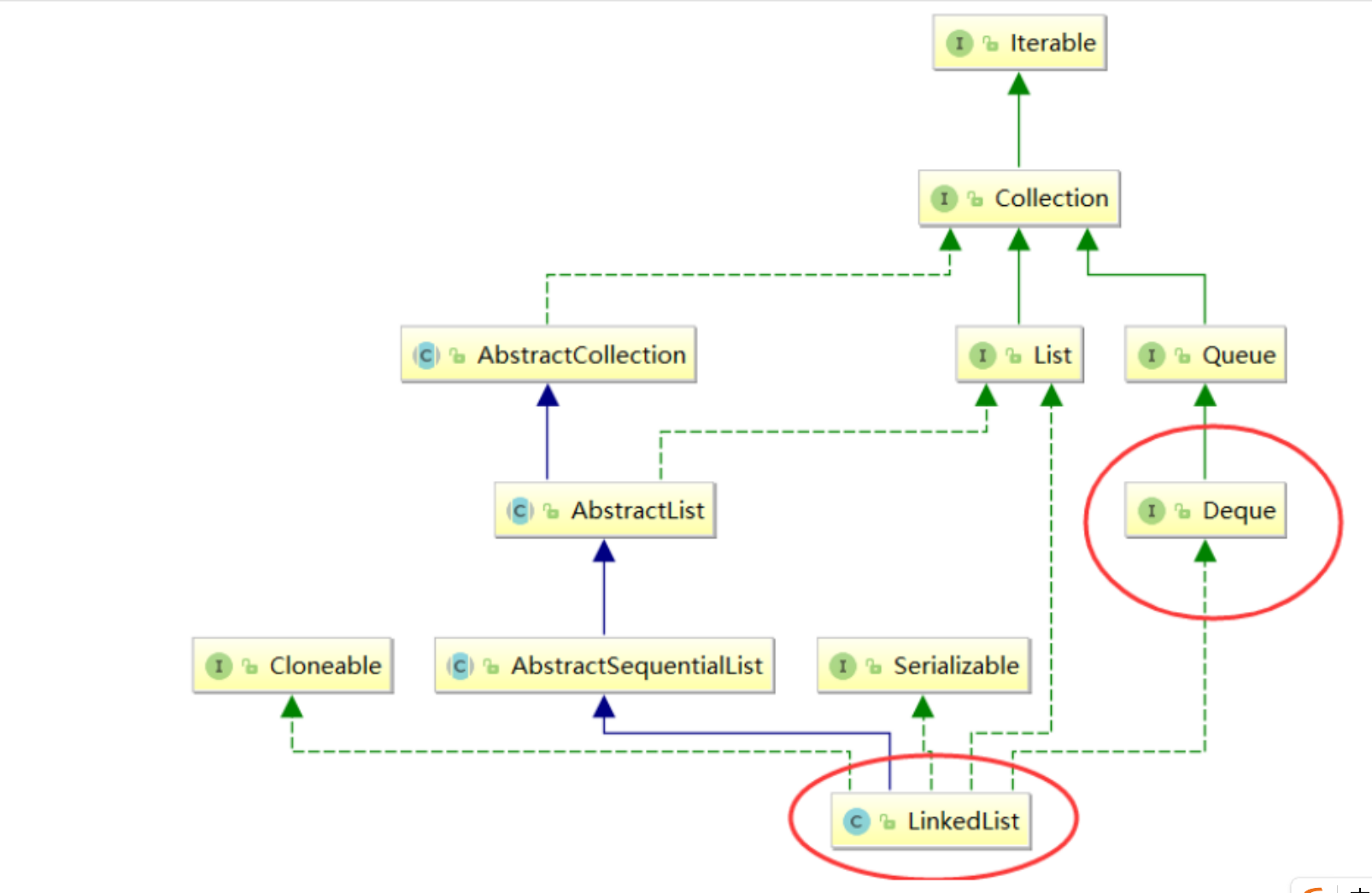
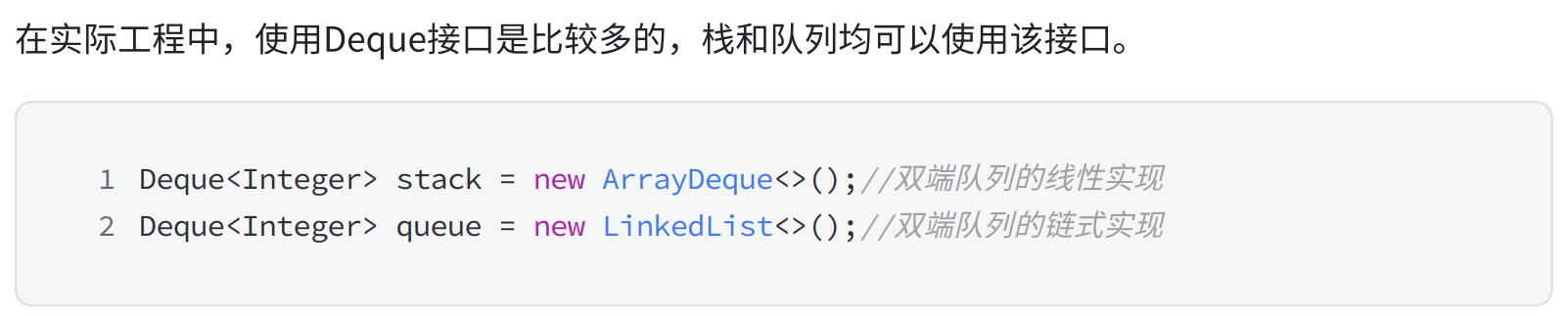
4.面试题
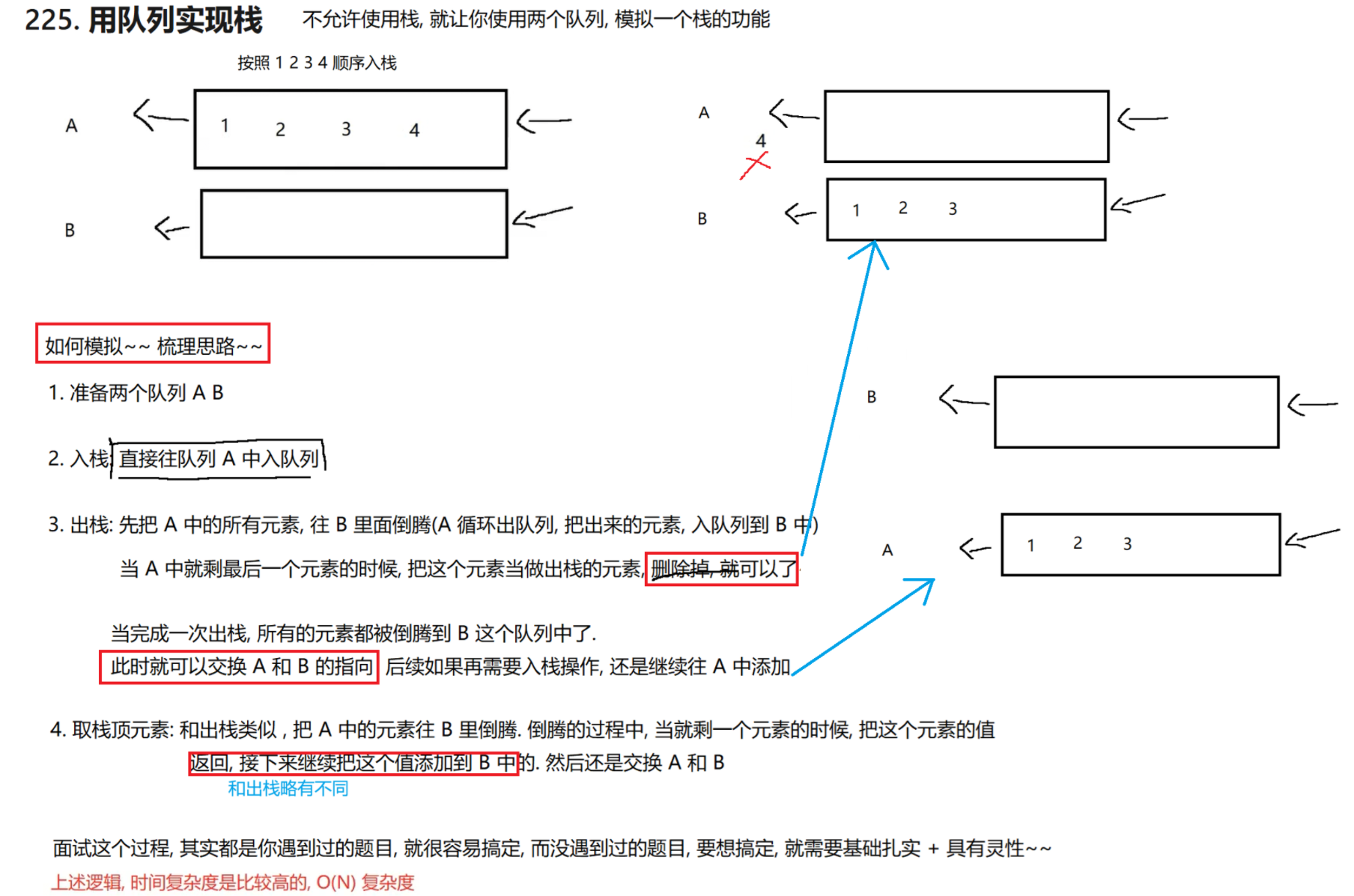
4.1 用队列实现栈
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/
java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
// 通过两个队列实现栈.
public class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> A = new LinkedList<>();
private Queue<Integer> B = new LinkedList<>();
public MyStack() {}
private void swap() {
Queue<Integer> tmp = A;
A = B;
B = tmp;
}
public void push(int x) {
// 入栈的时候
// 把 x 添加到队列 A 中.
A.offer(x);
}
public int pop() {
// 出栈的时候 判定一下是否为空 为空, 直接返回.
if (empty()) return 0;
// 把 A 中的元素往 B 里面倒腾. 直到 A 中就剩最后一个元素的时候, 这个元素就可以被删除了.
// 循环结束, 就剩一个元素.
while (A.size() > 1) {
int n = A.poll();
B.offer(n);
}
// 循环结束, 说明 A 中就剩一个元素了. 最后这个元素不能插入到 B 中.
int ret = A.poll();
// 交换 A 和 B.
swap();
return ret;
}
public int top() {
if (empty()) return 0;
// OJ 题不能抛出异常. 并且也不能修改 返回值类型为 Integer 此时也无法返回 null. 只能返回 0.
// 题目本身应该不会有栈为空再 top 的情况.
// 取栈顶元素, 也是把 A 的元素往 B 里倒腾.
while (A.size() > 1) {
int n = A.poll();
B.offer(n);
}
// 取出最后一个元素
int ret = A.poll();
// 把最后一个元素添加到 B 中. (和 pop 相比, 就只是这里多了一行, 别的地方都一样) .
B.offer(ret);
// 交换 A 和 B.
swap();
return ret;
}
public boolean empty() {
// 会交换 A 和 B. 所以 B 始终为 空的 . 抓住 A 的空就可以判定整体的 空.
return A.isEmpty();
}
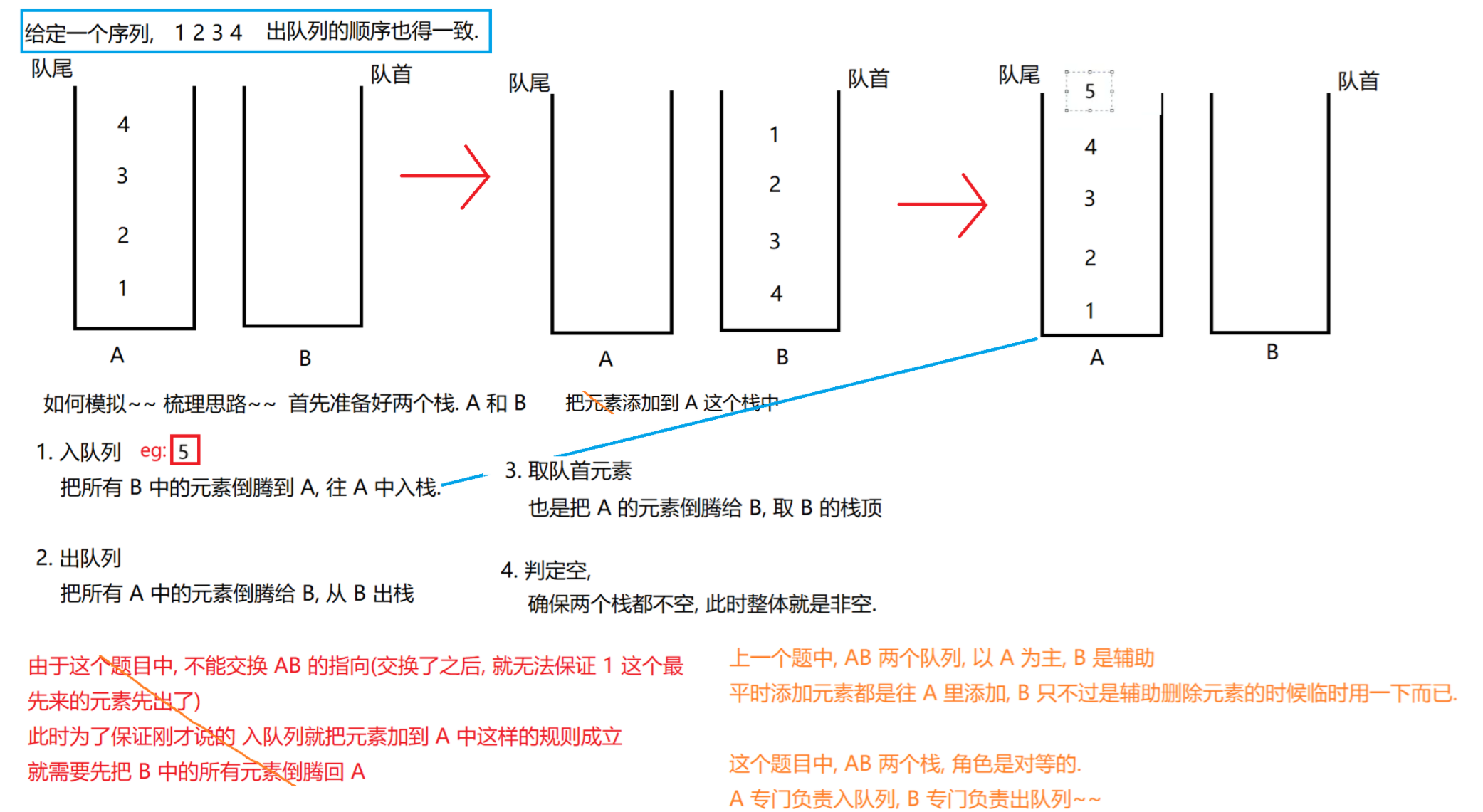
}4.2 用栈实现队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/description/

java
import java.util.Stack;
// 使用两个栈, 模拟实现队列.
public class MyQueueOJ {
// 创建两个栈 A 用于入队列, B 用于出队列.
Stack<Integer> A = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> B = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int x) {
// 先把 B 中的所有元素倒腾到 A 里, 然后把元素添加到 A 中.
while (!B.isEmpty()) { A.push(B.pop()); }
A.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
// 先把 A 中的所有元素倒腾到 B 里, 然后弹出 B 栈顶元素.
while (!A.isEmpty()) { B.push(A.pop()); }
return B.pop();
}
public int peek() {
// 先把 A 的所有元素倒腾到 B 里, 取 B 的栈顶元素.
while (!A.isEmpty())
return B.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return A.isEmpty() && B.isEmpty();
}
}