文章目录
在使用string类时,必须包含头文件。
cpp
#include<string>
using namespace std;auto
1.auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得。
2.用auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型时则必须加&。
3.auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用。
4.auto不能直接用来声明数组。
cpp
void Test() {
int a = 10;
auto b = a;
auto c = 'a';
cout << typeid(b).name() << endl; //int
cout << typeid(c).name() << endl; //char
}范围for
1.对于一个有范围的集合而言,for循环后的括号由冒号 : 分为两部分,第一部分时范围内用于迭代的遍历。第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代,自动获取数据,自动判断结束。
2.范围for可以作用到数组和容器对象上进行遍历。
3.范围for的容器遍历实际上就是替换为迭代器。
cpp
void Test() {
int array98[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array98) / sizeof(array98[0]); ++i) {
array98[i] *= 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(array98) / sizeof(array98[0]); ++i) {
cout << array98[i] << " ";
}
//运行结果 2 4 6 8 10 12
cout << endl;
int array11[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
for (int ch : array11) {
ch *= 2;
}
for (int ch : array11) {
cout << ch << " ";
}
//运行结果 1 2 3 4 5 6
cout << endl;
}在以上代码中,普通的遍历会改变数组原有的值,在范围for中,遍历不会改变原有的值。本质是,范围for的遍历是对原有值得复制 ,对复制得值进行操作,不会改变原有得值。
string类常用接口
string类对象常见得构造
1.构造空得string类对象。
cpp
void Test() {
//string();
//构造空得string类对象
string s1;
cin >> s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
}2.将c格式字符串构造string类对象。
cpp
void Test() {
//string(const char* s)
//将c格式字符串构造string类对象
string s2("123");
cout << s2 << endl;
}3.拷贝构造。
cpp
void Test() {
string s2("123");
//string(const string& str);
//拷贝构造
string s3(s2);
cout << s3 << endl;
}string类对象得修改操作
1.从str中pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
//长度超过最大下标,默认在最后一个字符结束
//string(const string& str, size_t pos, size_t n);
string s2(s1, 6, 3); //下标,长度
cout << s2 << endl;
//运行结果 wor
string s3;
s3 = s1.substr(6, 3); //下标,长度
cout << s3 << endl;
//运行结果 wor
string s4(s1, 6);
cout << s4 << endl;
//运行结果 world
}2.初始化前n个字符。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1("hello world",5);
cout << s1 << endl;
//运行结果 hello
}3.连续的n个字符初始化
cpp
void Test1() {
//连续的n个字符初始化
//string(size_t n, char c);
string s1(10, 'x');
cout << s1 << endl;
//运行结果 xxxxxxxxxx
}string类对象得容量操作
1.返回字符串有效长度。size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()得原因是为了与其他容器得接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
size()
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() << endl;
//运行结果 11
}length()
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.length() << endl;
//运行结果 11
}2.返回空间总大小。
空间总大小不包含 \0
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//运行结果 15
}3.检测字符串是否为空串, 是返回true,否则返回false。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.empty() << endl;
//运行结果 0(false)
string s2;
cout << s2.empty() << endl;
//运行结果 1(true)
}4.清空有效字符。clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
只清数据不清空间。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() << endl; //11
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //15
s1.clear();
cout << s1.size() << endl; //0
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //15
}5.为字符出啊预留空间。reserve为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserve不会改变容量大小。
本质是扩充容量。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //15
s1.reserve(100);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //111
}6.将字符串容量缩小到是能容纳size()的最小容量。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
//大于容量会扩容,小了容量不会变
s1.reserve(100); //保留、预留
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
//将容量缩到能容纳size()的最小容量
s1.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}7.将有效字符得个数改成n个,多出得空间用字符填充。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.size() << endl; //11
s1.resize(2);
cout << s1.size() << endl; //2
cout << s1 << endl; //he
}string类对象的访问及遍历操作
1.从遍历认识迭代器。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1("hello world");
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); ++i) {
cout << s1[i];
}
cout << endl;
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
for (it; it != s1.end(); it++) {
cout << *it;
}
cout << endl;
}begin()指向字符串首位,如图所示。end()指向 \0 的位置。
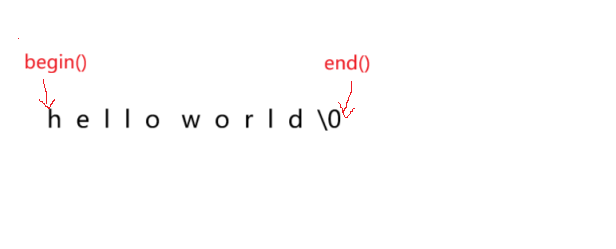
2.反向迭代器。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1("hello world");
for (int i = s1.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
cout << s1[i];
}
cout << endl;
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
for (rit; rit != s1.rend(); rit++) {
cout << *rit;
}
cout << endl;
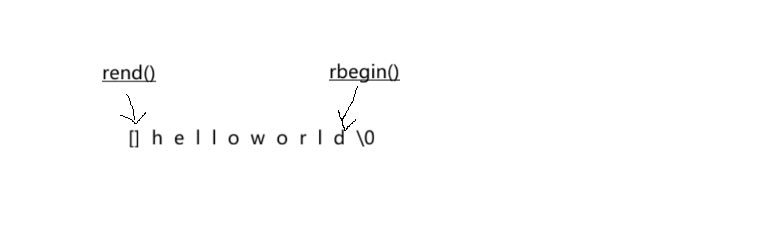
}rbegin()指向字符串最后一位,rend()指向字符串第一位的前一位。
string类对象的修改操作
push_back()
1.在字符串后尾插字符c。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
s1.push_back('c');
//运行结果 hello worldc
cout << s1 << endl;
}append()
2.在字符串后追加一个字符串。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
s1.append("123456");
//运行结果 hello world123456
cout << s1 << endl;
}operator+()
3.在字符串后追加字符串str。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
string str("123456");
s1 += str;
//运行结果 hello world123456
cout << s1 << endl;
}c_str()
4.返回c格式字符串。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1("hello world");
//运行结果 hello world
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}find()
5.从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置。
pos的类型不能为size_t类型,当查找不到字符的时候,会返回-1,而size_t类型中全是正数。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
//从下标0处开始查找字符空格
int pos = s1.find(' ', 0);
//运行结果 5
cout << pos << endl;
}rfind()
6.从字符串pos位置开始往前查找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1("hello world");
//从下标10处开始查找字符空格
int pos = s1.rfind(' ', 10);
//运行结果 5
cout << pos << endl;
}substr()
7.在字符串中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1 = "hello world";
string str = s1.substr(3,5); //pos len
//运行结果 lo wo
cout << str << endl;
}string类输入
getline()
当输入得字符串中含有空格时,我们得输入只会截取空格前的字符串,不会截取空格后的字符串,这与我们的预期不符。
使用getline()输入,遇到 \0 才会停止输入。
cpp
void Test() {
string s1,s2;
//输入 eqw rw rwert
getline(cin,s2);
//输入 eqw rw rwert
cin >> s1;
//运行结果 eqw
cout << s1 << endl;
//运行结果 eqw rw rwert
cout << s2 << endl;
}getline() 遇到自定义字符停止。
遇到字符*停止输入。
cpp
void Test13() {
string s1;
//输入 eqw rw ew*l rwert
getline(cin,s1,'*');
//输出结果 eqw rw ew
cout << s1 << endl;
}
觉得我回答有用的话,记得点个关注哟!谢谢支持!