1.list的说明与使用
1.1list的说明
附个链接:cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/#google_vignette,list其实与我们之前学过的string,vector非常类似,接下来详细介绍list常用的一些接口
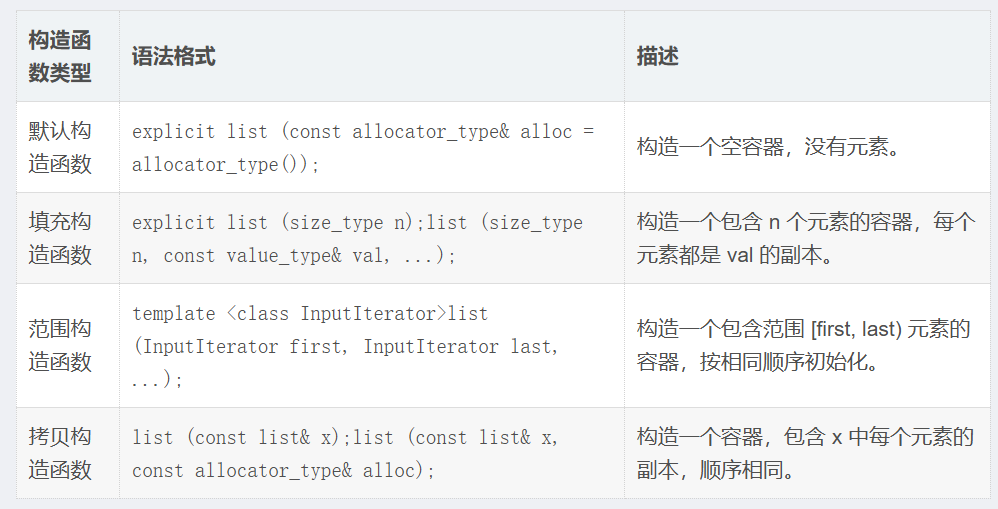
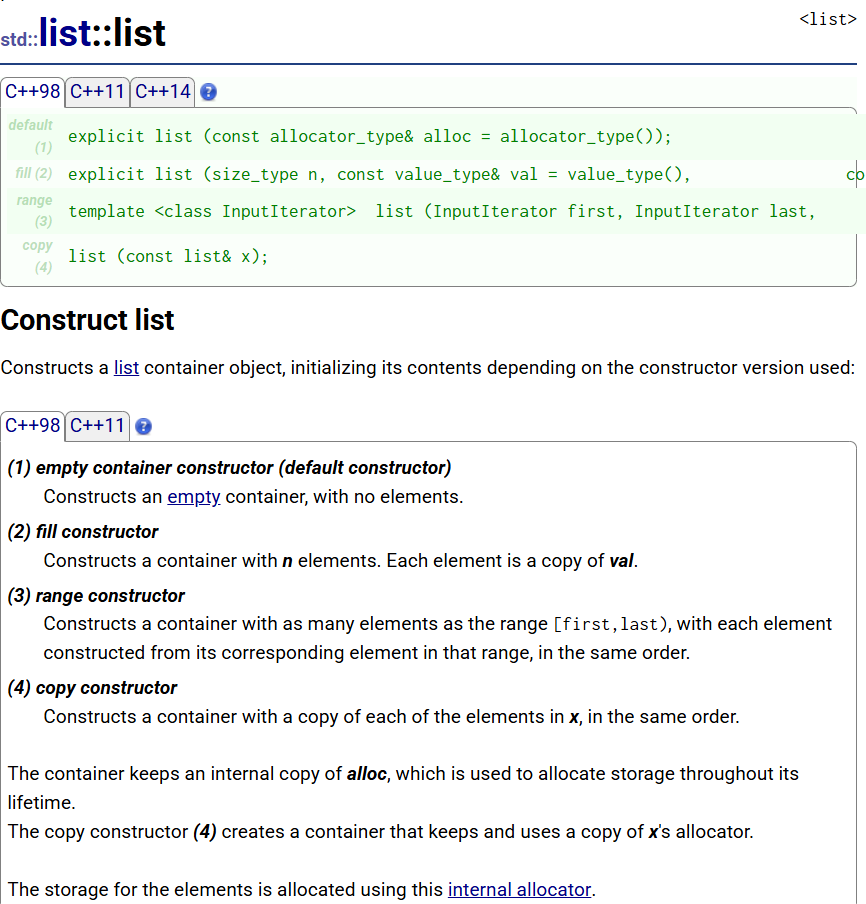
1.2list构造函数
以下列举listC++98的构造函数:
1.3list的iterator
函数名 描述 begin返回指向容器第一个元素的迭代器 end返回指向容器末尾(最后一个元素之后)的迭代器 rbegin返回指向反向容器第一个元素的反向迭代器 rend返回指向反向容器末尾的反向迭代器 cbegin返回指向容器第一个元素的常量迭代器 cend返回指向容器末尾的常量迭代器 crbegin返回指向反向容器第一个元素的常量反向迭代器 crend返回指向反向容器末尾的常量反向迭代器 list不支持operator[]这是因为如果list要实现,那么效率很低(要一个一个遍历)
cppvoid test_list01() { list<int> lt; lt.push_back(1); lt.push_back(2); lt.push_back(3); lt.push_back(4); list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin(); while (it != lt.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } //可以用迭代器就可以用范围for for (const auto& e : lt) { cout << e << " "; } //迭代器不支持+ /*it = lt.begin(); lt.erase(it+3);*/ }
拓展:STL迭代器类别详解(性质由底层结构决定,并且决定了可以用哪些算法)
输入迭代器 (Input Iterator)
支持单向只读访问,适用于单遍扫描算法。操作包括前向递增(
++)、解引用(*,仅右值)、成员访问(->)以及相等性比较(==/!=)。典型应用如从输入流读取数据,示例容器为istream_iterator。输出迭代器 (Output Iterator)
支持单向只写访问,适用于单遍扫描算法。操作仅包含前向递增(
++)和解引用(*,仅左值),常用于写入数据到输出流,示例容器为ostream_iterator。前向(单向)迭代器 (Forward Iterator)
扩展输入迭代器功能,支持读写操作和多遍扫描。允许重复解引用和移动,适用于需多次遍历的场景。示例容器包括
std::forward_list、std::unordered_map和std::unordered_set。双向迭代器 (Bidirectional Iterator)
在前向迭代器基础上增加双向移动能力,支持前置和后置递减(
--)。适用于需要逆向遍历的容器,如std::list、std::map和std::set。随机访问迭代器 (Random Access Iterator)
功能最强大,支持随机访问和算术运算。额外操作包括:
- 偏移运算(
it + n、it - n、it += n、it -= n)- 距离计算(
it1 - it2)- 下标访问(
it[n],等价于*(it + n))- 关系比较(
<、>、<=、>=)
典型容器为std::vector、std::deque、std::array及普通指针(如int*)。关键区别
- 访问方向:输入/输出迭代器仅单向,双向迭代器可逆向移动。
- 读写能力:输入迭代器只读,输出迭代器只写,其余均支持读写。
- 随机访问:仅随机访问迭代器支持直接跳转和算术运算。
能力强度 :输入/输出迭代器 < 前向迭代器 < 双向迭代器 < 随机访问迭代器。
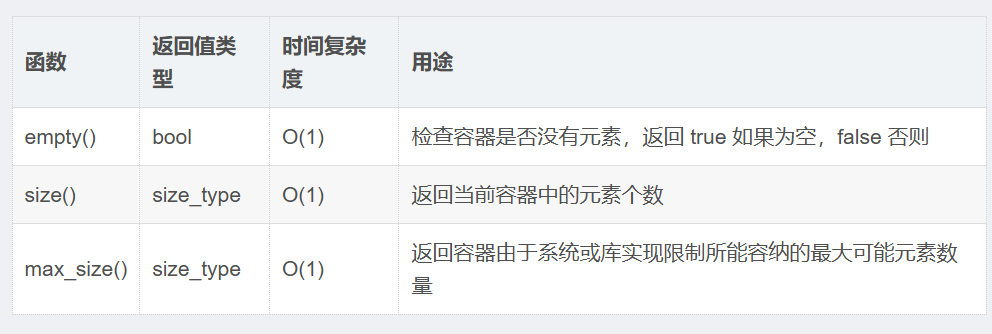
1.4list的容量相关成员函数
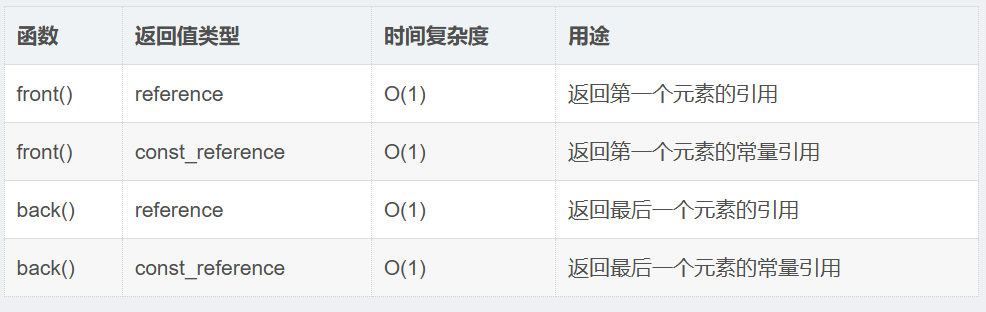
1.5list的元素访问成员函数
注意:
在调用
front()或back()之前,必须确保容器不为空空容器调用这些函数会导致未定义行为
建议先使用
empty()检查容器状态reference就是引用
1.6修改器成员函数
assign
参数 :
size_type n, const T& val或InputIterator first, InputIterator last
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(n)
用途:用指定数量的相同值或另一个序列中的元素替换链表当前内容。
push_front
参数 :
const T& value
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:在链表头部插入一个新元素,无需移动其他元素。
pop_front
参数 :无
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:删除链表头部的元素,链表不为空时调用。
push_back
参数 :
const T& value
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:在链表尾部追加一个新元素,无需移动其他元素。
pop_back
参数 :无
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:删除链表末尾的元素,链表不为空时调用。
insert
参数 :
iterator position, const T& value(多种重载)
返回值 :iterator
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:在指定位置插入一个或多个元素,返回指向新插入元素的迭代器。
erase
参数 :
iterator position或iterator first, iterator last
返回值 :iterator
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:删除指定位置或范围内的元素,返回指向被删除元素之后位置的迭代器。
swap
参数 :
list& other
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(1)
用途:高效交换两个链表的内容,仅交换内部指针。
resize
参数 :
size_type n, const T& val = T()
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(n)
用途:调整链表大小,若新大小超过当前大小,则用默认值或指定值填充;否则删除多余元素。
clear
参数 :无
返回值 :void
时间复杂度 :O(n)
用途:清空链表,删除所有元素并释放内存。注意emplace系列现在这个阶段不会介绍,可以理解emplace类似push系列
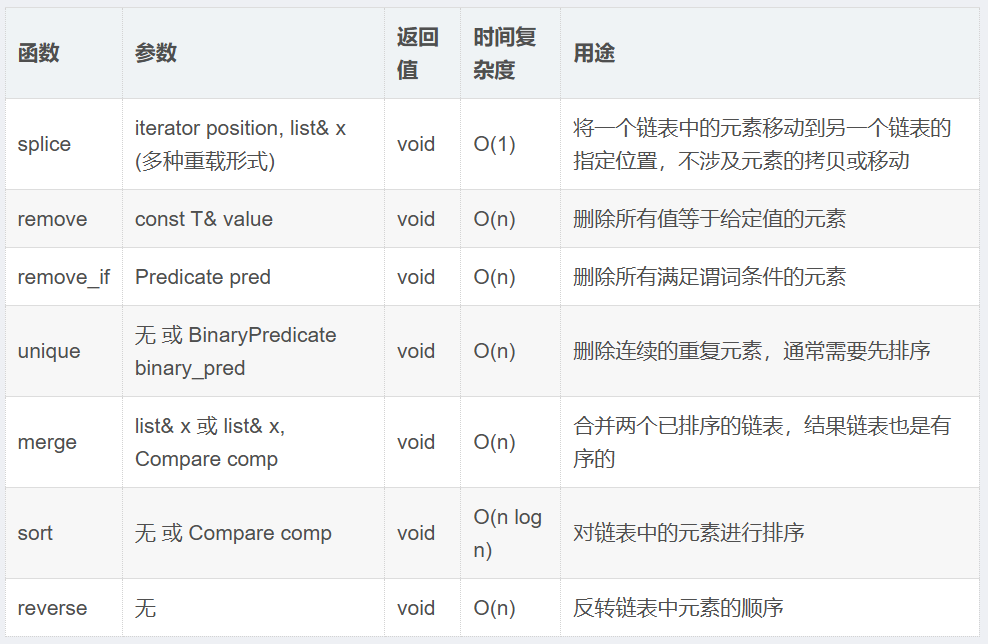
1.7list 操作成员函数
2.list模拟实现
2.1list的push_back
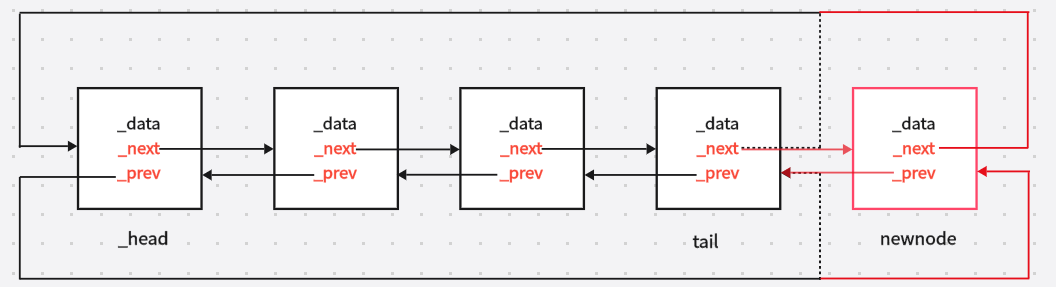
cppvoid push_back(const T& x) { Node* newnode = new Node(x); Node* tail=_head->_prev; tail->_next = newnode; newnode->prev = tail; newnode->_next = _head; _head->_prev = newnode; }
2.2list的iterator(重点)
我们之前学过的string,vector底层都是顺序表,所以之前模拟实现的iterator,++进行迭代或者*解引用访问数据就可以是原生指针,但是如果这里还使用原生指针,就会出现问题:
- 解引用访问的是当前节点,而不是当前节点的数据
- 无法进行++迭代,因为节点地址不连续
这里就给出一个解决方案,封装一个迭代器类接着重载运算符实现++和解引用
ps:迭代器本身就是节点的指针,只是节点的指针不满足那些需求(++,*,...),所以用类去包装一层重载运算符,因此迭代器里面真正的数据还是节点的指针
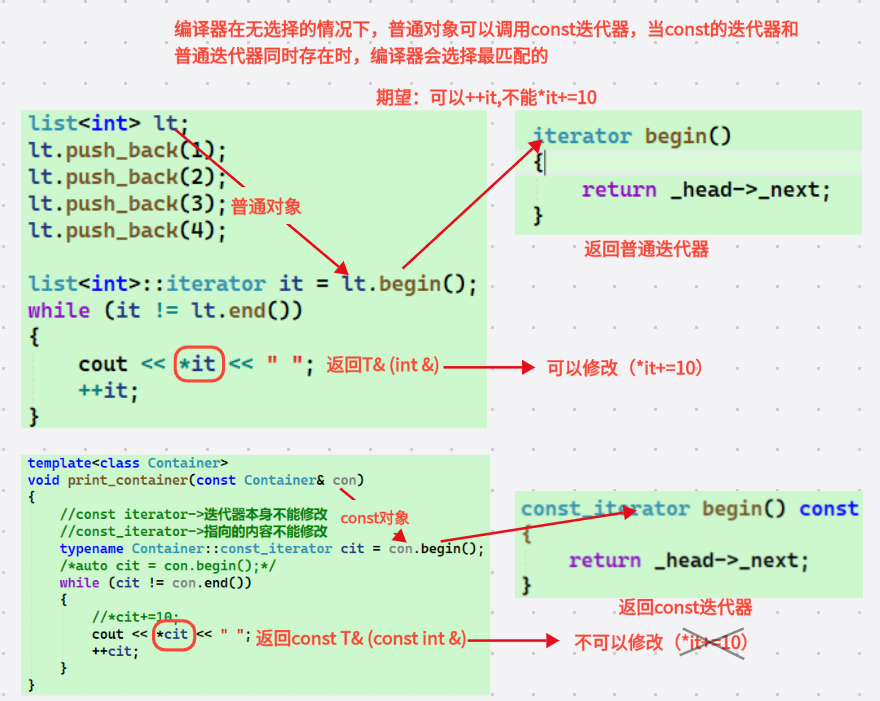
cppiterator begin() { /*iterator it(_head->_next); return it;*///有名对象 /*return iterator(_head->_next);*///匿名对象 return _head->_next;//隐式类型转换 } iterator end()//end是数据的下一个位置,也就是_head { return _head; }这里给了三种返回iterator的方法:
- 构造有名对象
- 构造匿名对象
- 隐式类型转换,将节点的指针转换为iterator
opreator->的实现
我们在用到结构的指针时会使用到->
cppstruct AA { int _a1 = 1; int _a2 = 2; }; void test_list02() { list<AA> lta; lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); list<AA>::iterator ita = lta.begin(); while (ita != lta.end()) { //cout << *ita << " ";err解决方法:1.给AA实现一个流插入2.重载->3.:如下面语句 cout << (*ita)._a1 << (*ita)._a2 << endl; //特殊处理,本来是两个->,为了可读性,省略了一个 cout << ita.operator->()->_a1 << ita->_a2 << endl; ++ita; } cout << endl; }法一:重载流插入
cppstruct AA { int _a1 = 1; int _a2 = 2; // 重载流插入运算符 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const AA& aa) { out << "a1:" << aa._a1 << " a2:" << aa._a2; return out; } };法二:重载->
cppT* operator->() { return &_node->_data; }但这里可能有些读者会感到困惑,ita调用->,operator->返回T*(aa*)也就是_data的地址,那么aa*是怎么访问_a1和_a2的呢,实际上这里时两个->
- 第一个->是运算符重载,调用operator->返回aa*指针
- 第二个->是结构体指针的原生指针解引用
但编译器这里做了特殊处理(为了可读性两个->不方便)于是就省略了第二个箭头
方法三:直接访问成员,上面代码有演示。
const迭代器的实现
我们在实现普通迭代器之后,将之前写过的打印任意容器的函数粘贴过来
cpptemplate<class Container> void print_container(const Container& con) { for (auto e : con) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl; }在调用print_container(lta);发现程序报错,但是在这个函数外面使用范围for就正常,其实这里就涉及const迭代器问题
con是const Container&但
begin()和end()返回的是普通迭代器const 对象只能调用 const 成员函数
那么就要实现const的迭代器类。这里就要注意,之所以不直接使用const来修饰iterator,而是单独封装一个const_iterator类是因为
1.
const iterator的含义(修饰的是iterator本身)
it本身是 const(不能++it)但
*it仍然可以修改内容2.
const_iterator的含义
it本身可以移动(可以++it)但
*it是 const 的(不能修改指向的内容)这里再提一下按需实例化的概念:
模板采用两阶段编译检查:
- 定义阶段:只检查不依赖模板参数的语法(如缺少分号、括号不匹配等)
- 实例化阶段:检查依赖模板参数的语义(如成员访问、运算符重载等)
如果Container的const_iterator解引用返回const引用:
- 在模板定义阶段不会报错(语法正确)
- 但在实例化阶段会报错:给常量赋值
这就是模板的"按需实例化"特性------错误检查延迟到实际使用时进行。
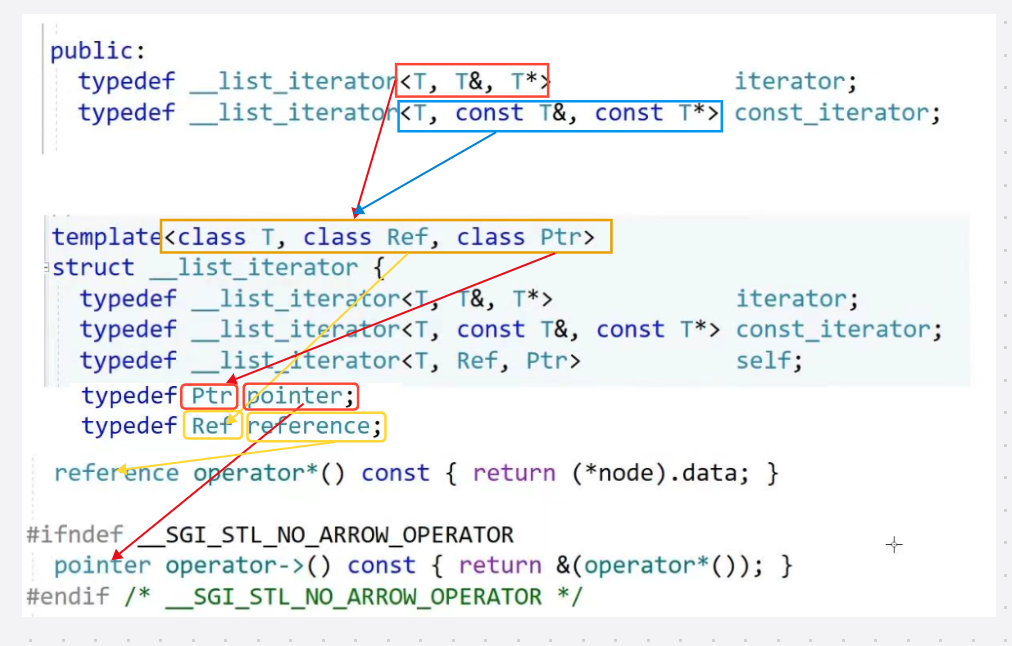
我们发现单独封装一个list_const_iterator类只有*,->不一样,太冗余了,这里还有其他的方式这里介绍一个模板共享的方式
通过共享同一个模板来减少代码重复,普通对象,和const对象,分别增加两个模板参数Ref和Ptr,Ref作为operaor*的返回值,Ptr作为operator->的返回值 ,但是这个其实与我们之前的方式没有本质区别 ,这里也是有两个类,之前的两个类是我们自己实现的两个类,而这里是实现了类模板给编译器,编译器实例化出来了两个类
list的迭代器失效问题
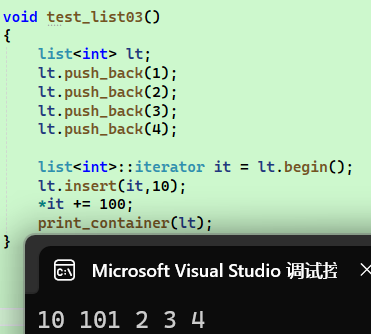
由于链表的空间不是连续的,在使用insert()进行插入操作不会引起迭代器失效的问题
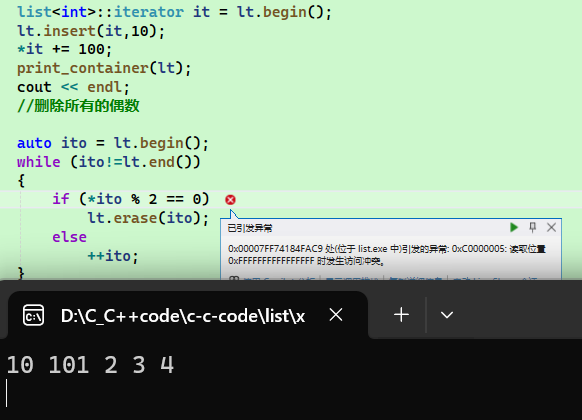
我们发现在it前面执行插入10操作后对当前的迭代器执行+=100操作正常,所以insert就没有迭代器失效的问题。但是我们接着来看erase
在
erase(ito)后,ito指向的节点已经被删除,但ito本身仍然指向那个已经被释放的内存地址。ito是野指针,于是+或者解引用程序崩溃,所以与之前一样,erase要实现返回下一个有效迭代器来更新迭代器
cpp//iterator erase(iterator pos) //{ // assert(pos != end()); // Node* prev = pos._node->_prev; // Node* next = pos._node->_next; // prev->_next = next; // next->_prev = prev; // // delete pos._node; // --_size; // return next; //} auto ito = lt.begin(); while (ito!=lt.end()) { if (*ito % 2 == 0) ito = lt.erase(ito); else ++ito; } print_container(lt);
2.3list的insert,push_front,push_back
其实我们在实现完insert后就可以直接调用insert的逻辑来进行头插和尾插了
cppvoid insert(iterator pos, const T& x) { Node* cur = pos._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(x); //prev newnode cur newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; newnode->_prev = prev; prev->_next = newnode; ++_size; } void push_back(const T& x) { insert(end(),x); } void push_front(const T& x) { insert(begin(), x); }
2.4list的erase,pop_back,pop_front
注意在实现erase的时候,不能将哨兵位删除
cppvoid erase(iterator pos) { assert(pos != end()); Node* prev = pos._node->_prev; Node* next = pos._node->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete pos._node; --_size; } void pop_back() { erase(--end());//end()返回的是_head所以要-- } void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
2.5list的析构函数,clear
要实现链表的clear函数。我们要遍历链表,一个一个节点释放,析构函数则是在clear函数基础上将头节点释放
cpp~list() { clear(); delete _head; _head = nullptr; } void clear() { auto it = begin(); while (it!=end()) { it = erase(it); } }
2.6list的拷贝构造,空初始化函数,operator=
还是与之前一样当我们没有显示写拷贝构造或者赋值重载时,编译器自动生成的是浅拷贝,两个list指向同一块资源,就会出现问题。这里实现深拷贝
cpplist(const list<T>& lt) { for (auto& e : lt) { push_back(e); } }这里还是有问题,因为调用push_back的前提是要有哨兵位,而且哨兵位的_next和_prev要指向自己形成最初的闭环结构,所以这里在实现一个空初始化函数
cppvoid empty_init() { _head = new Node(T());//这里是哨兵头节点,不能直接给0初始化这是因为T有可能是自定义类型 _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; _size = 0; } //lt2(lt1) list(const list<T>& lt) { empty_init(); for (auto& e : lt) { push_back(e); } }赋值重载实现:
cppvoid swap(list<int>& lt) { std::swap(_head, lt._head); std::swap(_size, lt._size); } //lt3 = lt1 list<T>& operator=(list<T>lt) { swap(lt); return *this; }传值传参,形参lt是lt1的拷贝,然后将lt3的旧值与形参交换,则lt3就得到了新值,旧值给了形参出了作用域就销毁
3.模拟实现list完整代码
List.h
cpp#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<assert.h> namespace name { template<class T> class list_node { public: T _data; list_node<T>* _next; list_node<T>* _prev; list_node(const T& data=T())//自定义类型调用默认构造 :_data(data) ,_next(nullptr) ,_prev(nullptr) {} }; template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr> class list_iterator//也可以使用struct(默认为public) { public: typedef list_node<T> Node; typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self; Node* _node; list_iterator(Node* node) :_node(node) { } Ref operator*()//返回引用支持修改 { return _node->_data; } Ptr operator->() { return &_node->_data; } Self& operator++()//返回自己类型的迭代器 { _node = _node->_next; return *this; } Self& operator++(int)//后置++ { Self tmp(*this); _node = _node->_next; return tmp; } Self& operator--()//返回自己类型的迭代器 { _node = _node->_prev; return *this; } Self& operator--(int)//后置-- { Self tmp(*this); _node = _node->_prev; return tmp; } bool operator!=(const Self& s)const { return _node != s._node; } bool operator==(const Self& s)const { return _node == s._node; } }; //template<class T> //class list_iterator//也可以使用struct(默认为public) //{ //public: // typedef list_node<T> Node; // typedef list_iterator<T> Self; // Node* _node; // list_iterator(Node* node) // :_node(node) // {} // T& operator*()//返回引用支持修改 // { // return _node->_data; // } // T* operator->() // { // return &_node->_data; // } // Self& operator++()//返回自己类型的迭代器 // { // _node = _node->_next; // return *this; // } // Self& operator++(int)//后置++ // { // Self tmp(*this); // _node = _node->_next; // return tmp; // } // Self& operator--()//返回自己类型的迭代器 // { // _node = _node->_prev; // return *this; // } // Self& operator--(int)//后置-- // { // Self tmp(*this); // _node = _node->_prev; // return tmp; // } // bool operator!=(const Self&s)const // { // return _node != s._node; // } // bool operator==(const Self& s)const // { // return _node == s._node; // } //}; //template<class T> //class list_const_iterator//也可以使用struct(默认为public) //{ //public: // typedef list_node<T> Node; // typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self; // Node* _node; // list_const_iterator(Node* node) // :_node(node) // { // } // const T& operator*()//返回const引用不支持修改 // { // return _node->_data; // } // const T* operator->() // { // return &_node->_data; // } // Self& operator++()//返回自己类型的迭代器 // { // _node = _node->_next; // return *this; // } // Self& operator++(int)//后置++ // { // Self tmp(*this); // _node = _node->_next; // return tmp; // } // Self& operator--()//返回自己类型的迭代器 // { // _node = _node->_prev; // return *this; // } // Self& operator--(int)//后置-- // { // Self tmp(*this); // _node = _node->_prev; // return tmp; // } // bool operator!=(const Self& s)const // { // return _node != s._node; // } // bool operator==(const Self& s)const // { // return _node == s._node; // } //}; template<class T> class list { typedef list_node<T> Node; public: //typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator; //typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;//注意typedef也是受到访问限定符的限制的,也就是说 //iterator可以在外面使用而Node不行 typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator; typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; iterator begin() { /*iterator it(_head->_next); return it;*///有名对象 /*return iterator(_head->_next);*///匿名对象 return _head->_next; } iterator end()//end是数据的下一个位置,也就是_head { return _head; } const_iterator begin() const { return const_iterator(_head->_next); } const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(_head); } list() { _head = new Node(T());//这里是哨兵头节点,不能直接给0初始化这是因为T有可能是自定义类型 _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; _size = 0; } list(initializer_list<T> il) { empty_init();//给一个哨兵位节点 for (auto& e : il) { push_back(e); } } ~list() { clear(); delete _head; _head = nullptr; } void clear() { auto it = begin(); while (it!=end()) { it = erase(it); } } void empty_init() { _head = new Node(T());//这里是哨兵头节点,不能直接给0初始化这是因为T有可能是自定义类型 _head->_next = _head; _head->_prev = _head; _size = 0; } //lt2(lt1) list(const list<T>& lt) { empty_init(); for (auto& e : lt) { push_back(e); } } void swap(list<int>& lt) { std::swap(_head, lt._head); std::swap(_size, lt._size); } //lt3 = lt1 list<T>& operator=(list<T>lt) { swap(lt); return *this; } //void push_back(const T& x) //{ // Node* newnode = new Node(x); // Node* tail=_head->_prev; // tail->_next = newnode; // newnode->_prev = tail; // newnode->_next = _head; // _head->_prev = newnode; // _size++; //} iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) { Node* cur = pos._node; Node* prev = cur->_prev; Node* newnode = new Node(x); //prev newnode cur newnode->_next = cur; cur->_prev = newnode; newnode->_prev = prev; prev->_next = newnode; ++_size; return newnode; } void push_back(const T& x) { insert(end(),x); } void push_front(const T& x) { insert(begin(), x); } iterator erase(iterator pos) { assert(pos != end()); Node* prev = pos._node->_prev; Node* next = pos._node->_next; prev->_next = next; next->_prev = prev; delete pos._node; --_size; return next; } void pop_back() { erase(--end());//end()返回的是_head所以要-- } void pop_front() { erase(begin()); } size_t size()const { return _size; } bool empty()const { //也可以 /*return _head->next == _head;*/ return _size == 0; } private: Node* _head; size_t _size;//为了防止遍历,这里加一个成员size记录list的大小 }; /*template<class Container>//声明 void print_container(const Container& con);*/ template<class Container> void print_container(const Container& con) { //const iterator->迭代器本身不能修改 //const_iterator->指向的内容不能修改 typename Container::const_iterator cit = con.begin();//要加typename来取模板里面的内容 //list<int>::const_iterator cit = con.begin(); /*auto cit = con.begin();*/ while (cit != con.end()) { //*cit+=10; cout << *cit << " "; ++cit; } } struct AA { int _a1 = 1; int _a2 = 2; }; }
Test.cpp
cpp#pragma once #include"List.h" namespace name { void test_list01() { list<int> lt; lt.push_back(1); lt.push_back(2); lt.push_back(3); lt.push_back(4); list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin(); while (it != lt.end()) { cout << *it << " "; ++it; } cout << endl; //可以用迭代器就可以用范围for for (const auto& e : lt) { cout << e << " "; } cout << endl; print_container(lt); } void test_list02() { list<AA> lta; lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); lta.push_back(AA()); list<AA>::iterator ita = lta.begin(); while (ita != lta.end()) { //cout << *ita << " ";err解决方法:1.给AA实现一个流插入2.重载->3.:如下面语句 cout << (*ita)._a1 << (*ita)._a2 << endl; //特殊处理,本来是两个->,为了可读性,省略了一个 cout << ita.operator->()->_a1 << ita->_a2 << endl; ++ita; } cout << endl; } void test_list03() { list<int> lt; lt.push_back(1); lt.push_back(2); lt.push_back(2); lt.push_back(3); lt.push_back(4); list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin(); lt.insert(it,10); *it += 100; print_container(lt); cout << endl; //删除所有的偶数 auto ito = lt.begin(); while (ito!=lt.end()) { if (*ito % 2 == 0) ito = lt.erase(ito); else ++ito; } print_container(lt); } void test_list04() { list<int> lt1; lt1.push_back(1); lt1.push_back(2); lt1.push_back(3); lt1.push_back(4); list<int> lt2(lt1); print_container(lt1); print_container(lt2); list<int> lt3; lt3 = lt1; print_container(lt2); } void function(const list<int>& lt) { cout<<"fuhction:"<< endl; print_container(lt); cout << endl; } void test_list05() { auto il = {10,20,30}; //class std::initializer_list<int> cout<<typeid(il).name()<<endl; //initializer_list类里面有两个指针,一个指向列表开始位置,一个指向结束位置 cout << sizeof(il) << endl; list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };//隐式类型转换 list<int> lt2({ 1,2,3,4,5,6 });//直接构造 print_container(lt1); print_container(lt2); cout << endl; const list<int>& lt = {1,2,3,4,5,6};//引用临时对象 function(lt1); function({ 1,2,3,4,5,6 });//单参数构造函数支持隐式类型转换 } } int main() { //name::test_list01(); //name::test_list02(); //name::test_list03(); //name::test_list04(); name::test_list05(); }