一、前情回顾
设置一个函数,对列表中的元素进行排序:
python
def sort_list(the_list):
"""
[3,1,2,4,4,5]
[1,3,2,4,4,5]
[1,2,3,4,4,5]
"""
for i in range(0,len(the_list)):
for j in range(i+1,len(the_list)):
if the_list[i]>the_list[j]:
the_list[i],the_list[j] = the_list[j],the_list[i]
return the_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
l=sort_list([3,1,2,4,4,5])
print(l)二、文件与异常
大多数程序遵循输入-处理-输出模型:首先输入数据,然后将处理的数据进行存储,最终显示,打印,传输。
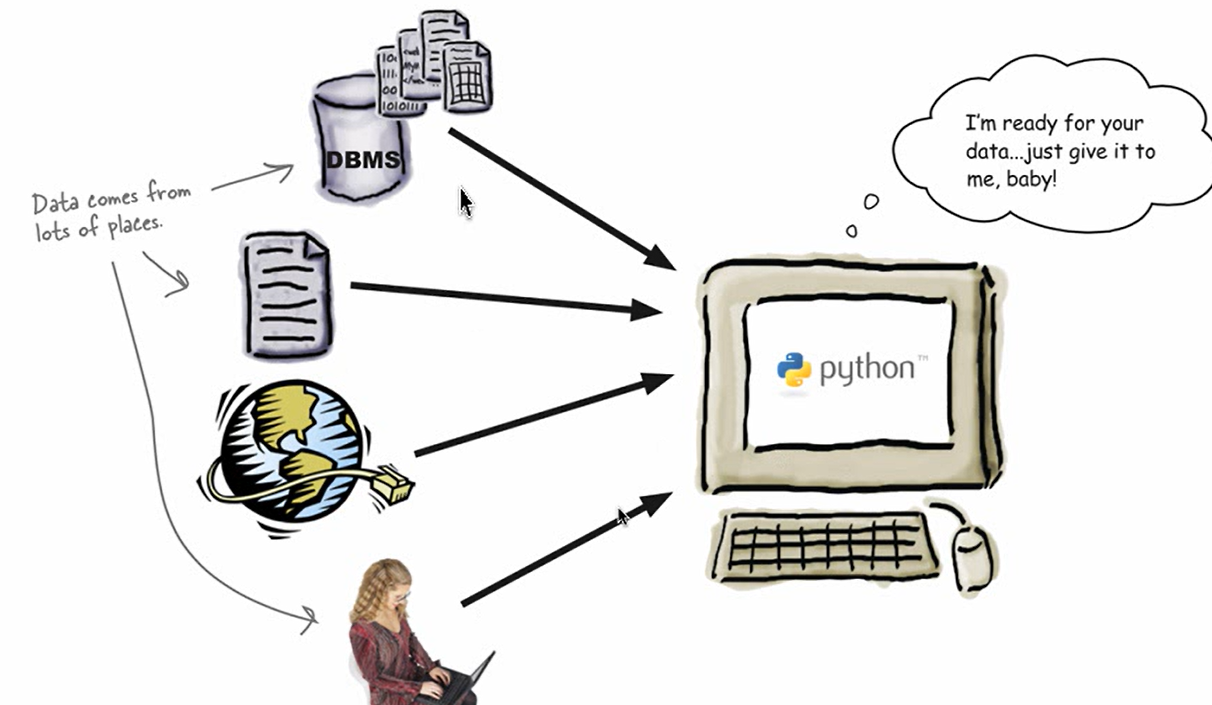
Python如何从文件中读取数据
Python基本输入机制是基于行的(open())
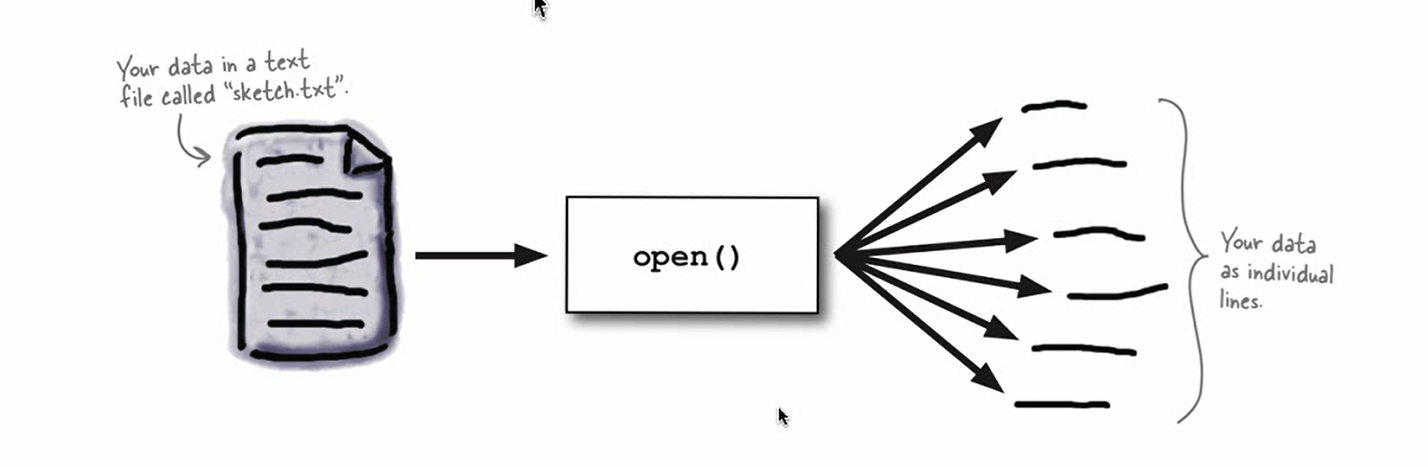
文件使用详解
python
### 使用语法
### data是open的文件对象
### filename是文件的字符串名
### mode文件类型操作的字符串
data=open(filename,mode)
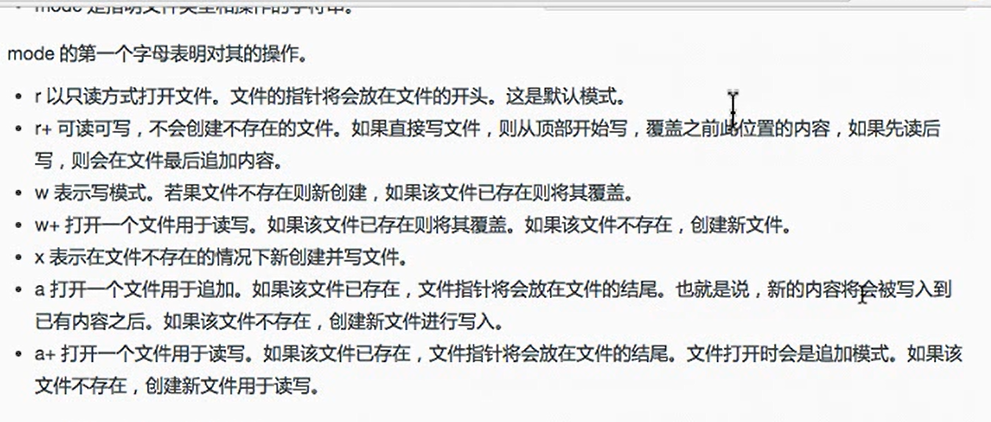
mode类型(r,r+(不会创建不存在的文件),w,w+,x,a,a+)
mode第二字母是文件类型(t表示文本,b表示二进制文件)
## method1
poem="望庐山瀑布,日照香炉生紫烟,遥看瀑布挂前川, 飞流直下三千尺, 疑是银河落九天"
print(len(poem))
font=open('libai.txt','wt')
font.write(poem)
font.close()
## method2
poem="望庐山瀑布,日照香炉生紫烟,遥看瀑布挂前川, 飞流直下三千尺, 疑是银河落九天"
print(len(poem))
font=open('libai.txt','w')
print(poem,file=font)
print(poem,file=font,sep='',end='') ## sep分隔符 end结尾符
font.close()
## demo3
fout=open('libai.txt','w')
offset=0
chunk=10
size=len(poem)
while True:
if offset>size:
break
fout.write(poem[offset:offset+chunk])
offset+=chunk
fout.close()
## demo4 如果使用x模式,文件已存在会报错,不存在时就会自行创建
fout=open('libai.txt','x')
offset=0
chunk=10
size=len(poem)
while True:
if offset>size:
break
fout.write(poem[offset:offset+chunk])
offset+=chunk
fout.close()mode参数的详解
python
data=open('sketch.txt')
print(data.readline()) ## data是整行读取
data.seek(0) ## 改变文件指针的方向
data=data.read() ## data整段读取
print(data)
## 循环遍历整个文段每一行
data=open('sketch.txt')
for i in data:
print(i)
## 由于所打开文件资源是有限的,所以应该及时关闭
data.close()
type(data)
>> <class '_io.TextIOWrapper'>文段内容的读取(read)
针对文本类的读写
python
### demo1 ## 读取数据
poem=''
fount=open('libai.txt','rt')
chunk=10
while True:
fragment=fount.read(chunk)
if not fragment:
break
poem+=fragment
print(poem)
### demo2 readline读取一行数据
poem=''
fount=open('libai.txt','rt')
while True:
frag=fount.readline()
if not frag:
break
poem+=frag
print(poem)
## demo3 写入数据
poem='望庐山瀑布\n日照香炉生紫烟\n遥看瀑布挂前川\n飞流直下三千尺\n疑是银河落九天'
fount=open('libai.txt','wt')
fount.write(poem)
print(len(poem))
fount.close()
## demo4 readlines读取整个列表
fount=open('libai.txt','rt')
lines=fount.readlines()
print(lines) ## ['望庐山瀑布\n', '日照香炉生紫烟\n', '遥看瀑布挂前川\n', '飞流直下三千尺\n', '疑是银河落九天']
fount.close()
## demo5 读取整个列表数据
fount=open('libai.txt','rt')
lines=fount.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line,end='')
fount.close()针对二进制文件文件的读写(bin)
python
## demo1 二进制文件(图片,视频)的写入
bdate=bytes(range(0,256))
print(bdate)
print(len(bdate))
fount=open('bfile','wb')
fount.write(bdate)
fount.close()
## demo2 二进制文件的读取和写入
bdate=bytes(range(0,256))
offset=0
size=100
fount=open('bfile','wb')
while True:
if offset>size:
break
fount.write(bdate[offset:offset+size])
offset+=size
else:
fount.close()
fount=open('bfile','rb')
bdate=fount.read()
print(bdate)
fount.close()
## demo3 文件写入
bdate=bytes(range(0,256))
offset=0
chunk=100
with open('bfile', 'wb') as f:
while True:
if offset >= chunk:
break
f.write(bdate[offset:offset+chunk])
offset+=chunk
## demo4 文件指针查看
with open('bfile','rb') as fin:
print(fin.tell()) ### 0
fin.seek(255)
print(fin.tell()) ### 255
bdata=fin.read()
print(bdata[0]) ### 255
print(bdata)with使用
with关键字自动关闭已经打开的文件
python
poem="望庐山瀑布,日照香炉生紫烟,遥看瀑布挂前川, 飞流直下三千尺, 疑是银河落九天"
with open('bfile','wt') as fout: ### 节省font.close()流程
fout.write(poem)针对文段内容进行处理
python
### 将被处理的文件变成列表
data=open('sketch.txt')
data2=data.readline()
print(data2.split(':'))
data.close()
### 将被处理的文件进行解包处理
data=open('sketch.txt')
data2=data.readline()
(role,line_spoken)=data2.split(':')
print(role,line_spoken)
data.close()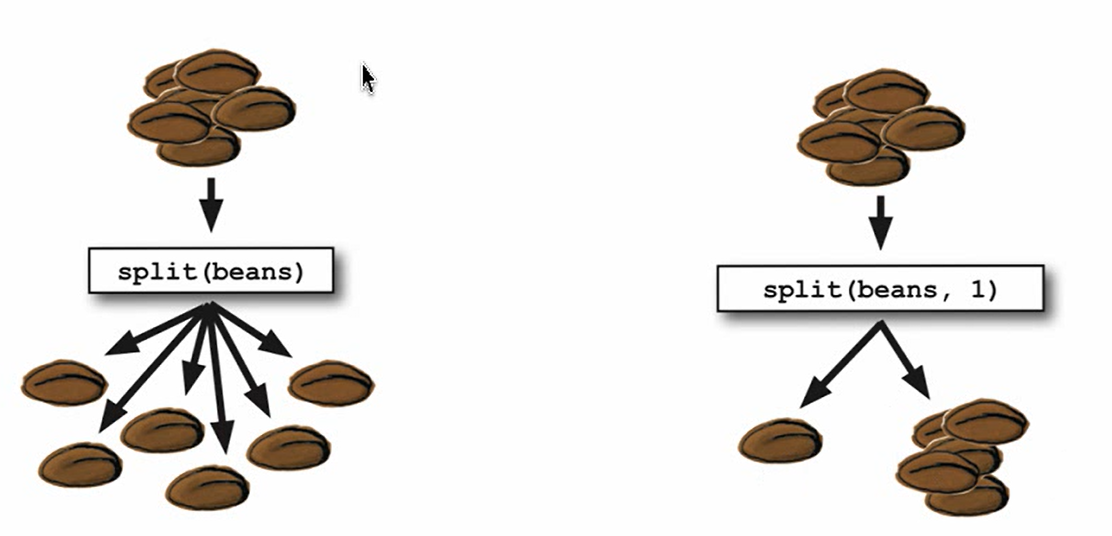
查找元素下标
python
### 查找索引所在的位置
each_line="Now let's get one thing quite clear: I most definitely told you!"
print(each_line.find(':'))
print(each_line[35])修正更改指定文本后(如果未查询到":"符号如何进行判断)
python
data=open('sketch.txt')
for line in data:
if line.find(":")!=-1:
role,spoken=line.split(':',1)
print(role,end='')
print('said',end='')
print(spoken,end='')异常控制流的处理

异常管理
try-except机制
python
try:
你的代码(导致运行错误环境)
except:
错误恢复代码
#### 使用示例
data=open('sketch.txt')
for line in data:
try:
(role,spoken)=line.split(':',1)
print(role,end=' ')
print('said',end='')
print(spoken,end='')
except:
pass捕获到异常并创建自定义异常信息
python
try:
print(5/0)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("you cant't divide by zero")
a=5
b=0
if b is 0:
print("you can't divide by zero")
########计算器练习##############
### 捕获除数为0的情况
print('Give me two numbers I will be devited them')
print('Enter q to quit')
while True:
num1 = int(input('First number: '))
num2 = int(input('Second number: '))
if num1 == 'q':
break
if num2 == 'q':
break
try:
answer = int(num1) / int(num2)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("you can't devide by 0")
else:
print(answer)try-except-else-finally处理流程
python
try:
A
except: my_exception
B1
except: my_exception
B2
else:
C3
finally:
D
执行顺序包括
A--->C3----->D
A---->B1----->D处理缺少文件
python
import os
if os.path.exists('sketch.txt'):
data=open('sketch.txt')
for line in data:
try:
(role,spoken)=line.split(':',1)
print(role,end='')
print('said',end='')
print(spoken)
except:
pass
data.close()
else:
print('The data is missing!')
### 对if判断逻辑修正后的版本
try:
data=open('sketch2.txt')
for line in data:
try:
(role,spoken)=line.split(':',1)
print(role,end='')
print('said',end='')
print(spoken)
except:
pass
data.close()
except:
print('the data file is missing')
## 处理指定异常
try:
data=open('sketch2.txt')
for line in data:
try:
(role,spoken)=line.split(':',1)
print(role,end='')
print('said',end='')
print(spoken)
except ValueError:
pass
data.close()
except IOError:
print('the data file is missing')常见使用的异常
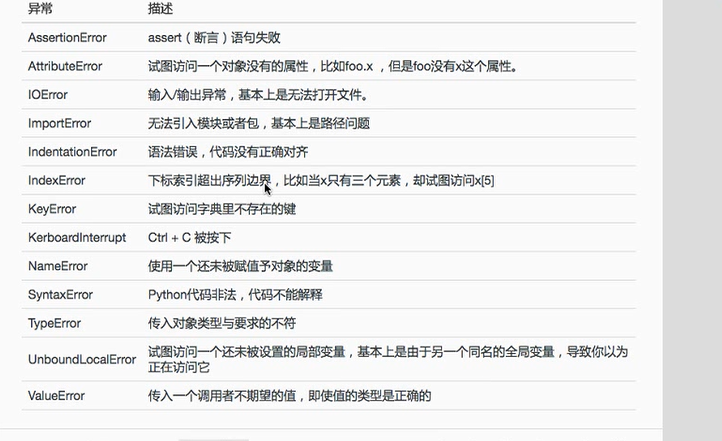
三、控制流的使用
选择控制
分为3种控制流格式(if-if-else,if-elif-else)
python
# method--1(if-else)
x=1
y=2
if x<y:
data=x
else:
data=y
print(data)
## method--2(三元运算符)
data=x if x<y else y
print(data)循环控制
1.while循环
python
## while示例
count=0
while count<9:
print(count)
count+=1
### 请求客户端的连接
while True:
pass
### while-else用法
count=0
while count<5:
print(count,"is less than 5")
count=count+1
else:
print(count,"is not less than 5")2.for循环
python
s=["a","b","c","d","e"]
found=False
for i in s:
if i.find("c")!=-1:
found=True
print('发现c')
break
if not found:
print('未发现c')3.break和continue
break是终止循环,而continue是结束本次循环跳转到下次循环
python
s=["a","b","c","d","e"]
found=False
for i in s:
if i.find('c')!=-1:
found=True
print('发现c')
break
else:
print('未发现c')循环打印列表项和索引
python
s=["a","b","c","d","e"]
for index,item in enumerate(s):
print(index,item)
### 有关于列表步长的使用
print(list(range(10))) ##[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(list(range(0,10,1))) ## [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(list(range(0,10,2))) ##[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
## 列表的压缩和解压
a=[1,2,3]
b=[4,5,6]
c=[4,5,6,7,8,9]
## 压缩
zipped=zip(a,b)
# print(list(zipped))
## 解压
print(list(zip(*zipped))) ##[(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6)]continue的运算
python
for i in ('hello'):
if i=='l':
continue
print(i)