多任务爬虫
进程 (multiprocessing)
作用
-
并行执行任务
- 每个进程有独立的 Python 解释器和内存空间
- 可以同时利用多核 CPU,真正做到并行
- 特别适合 CPU 密集型任务(大计算量、数据处理、图像处理等)
-
绕过 GIL 限制
- Python 的多线程受 GIL(全局解释器锁) 限制,CPU 密集型任务不能同时执行
- 多进程每个进程独立运行,不受 GIL 限制
-
进程间通信(IPC)
- 提供
Queue、Pipe、共享内存Value、Array等方式,方便进程之间传递数据
- 提供
-
创建进程
def index1(num):
print(f'index1:{num}')创建子进程
方法一
t2=Process(target=index1,args=(1,))
方法二
t3=Process(target=index1,kwargs={'num':2})
-
启动进程
t2.start()
-
等待进程(执行完t2才执行后面代码)
t2.join()
守护进程 就是一种 在后台运行、随主进程存在的子进程 ,
它有两个特点:
- 独立后台运行:通常用来执行辅助任务,不需要用户交互。
- 随主进程退出而结束:当主进程结束时,所有守护进程会被自动终止。
-
设置为守护进程
t2.daemon=True
进程队列工作机制
-
当你往
JoinableQueue里put(item)一个任务时,内部会将 "未完成的任务计数(unfinished tasks count)" 加一。 -
消费者(worker)进程/线程从队列
get()任务,做处理。处理完成后,调用queue.task_done(),这样未完成任务计数减一。 -
如果有代码调用
queue.join(),那么这个调用会阻塞,直到 未完成的任务计数降到 0 为止,也就是所有放入队列的任务都被取出并且调用过task_done()。然后join()会解除阻塞。 -
如果调用
task_done()的次数比put()的次数多,就会抛出ValueError,因为这表示多次标记完成,和任务实际不符。
-
创建进程队列
from multiprocessing import JoinableQueue
q = JoinableQueue() -
进程队列等待
q.join()
-
进程队列继续执行
q.task_done()
线程(threading)
作用:能让你的程序同时执行多个任务
-
创建线程
from threading import Thread
def index(num):
print(f'index:{num}')
t1=Thread(target=index,args=(1,)) -
启动线程
t1.start()
守护线程就是一种后台运行的线程 ,当主线程结束时,它会自动退出,不会阻止程序结束。
-
设置为守护线程
t1.daemon=True
-
多线程队列
import queue
q=queue.Queue()
线程和进程使用方法是差不多一样的
协程 (asyncio)
协程(Coroutine )是一种 用户态的轻量级"线程" ,它可以在一个线程内执行多个任务,通过主动让出控制权 来实现并发,而不是依赖操作系统调度线程。
协程作用
-
减少线程开销:不需要频繁创建/切换线程。
-
提高 I/O 并发:在网络爬虫、爬取网页、下载文件等场景特别有效。
-
简化异步编程:比传统回调方式更直观。
import asyncio
async def task(n):
print(f"开始任务 {n}")
await asyncio.sleep(1) # 模拟 I/O 操作
print(f"结束任务 {n}")
return n*2async def main():
# 并发执行多个协程
results = await asyncio.gather(task(1), task(2), task(3))
print(results)asyncio.run(main())
async def定义协程函数。await用于等待耗时操作,不阻塞其他协程。asyncio.gather可以并发执行多个协程。
进程、线程与协程的区别
| 进程(Process) | 线程(Thread) | 协程(Coroutine) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 资源拥有 | 拥有独立地址空间和系统资源 | 共享进程的内存空间和资源 | 运行在单个线程内,共享线程资源 |
| 从属关系 | 独立存在 | 必须属于某个进程 | 必须运行在某个线程之上 |
| 调度单位 | 操作系统资源分配的基本单位 | 操作系统调度的基本单位 | 程序员在用户态控制的调度单位 |
| 切换方式 | 由操作系统内核完成,上下文切换成本高 | 由操作系统调度,上下文切换成本中等 | 由用户代码控制(如 await / yield),切换成本最低 |
| 切换开销 | 大(需要切换内存地址空间、页表、寄存器等) | 中(只切换寄存器、栈等线程上下文) | 小(不涉及系统调用,只在用户态切换栈) |
| 通信方式 | 使用 IPC(如管道、信号、共享内存、消息队列) | 通过共享内存通信(需加锁同步) | 共享内存、协作式执行,一般不需要锁 |
| 并发与并行 | 可实现并行(多个进程可在多核上同时运行) | 可实现并行(多个线程可在多核上运行) | 通常为并发(单线程异步切换),非真正并行 |
| 创建与销毁 | 创建/销毁开销最大 | 创建/销毁比进程小 | 创建极快(纯用户态),几乎无开销 |
| 异常影响 | 一个进程崩溃不会影响其他进程 | 一个线程崩溃可能导致整个进程崩溃 | 单个协程出错不会影响其他协程(除非未捕获异常) |
| 可靠性 | 高,进程隔离好 | 中,共享资源导致风险 | 高,共享少且协作式执行 |
| 实现层级 | 内核态 | 内核态 | 用户态 |
| 适用场景 | 多进程架构、服务隔离、安全要求高 | 多任务并行、I/O 密集型任务 | 异步 I/O、高并发(如网络爬虫、异步服务器等) |
| 代表技术 | multiprocessing、系统守护进程 |
threading、Java Thread |
asyncio、gevent、go routine |
进程池和线程池和协程池的区别(了解)
| 项目 | 进程池 | 线程池 | 协程池 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 运行层级 | 操作系统(多进程) | 操作系统(单进程多线程) | 用户态(单线程多协程) |
| 调度者 | 操作系统内核 | 操作系统内核 | 程序员/事件循环 |
| 并发模式 | 并行(多核可同时执行) | 并发(多线程共享内存) | 并发(单线程异步切换) |
| 适用任务 | CPU 密集型 | I/O 密集型 | 高并发 I/O、异步任务 |
| 代表模块(Python) | multiprocessing.Pool |
ThreadPoolExecutor |
asyncio.Semaphore / aiomultiprocess |
| 资源消耗 | 高 | 中 | 极低 |
| 管理复杂度 | 中 | 低 | 稍高(需事件循环) |
案例:获取LoL所有皮肤图片(https://101.qq.com/#/hero)
通过分析发现英雄数据都在这个请求里
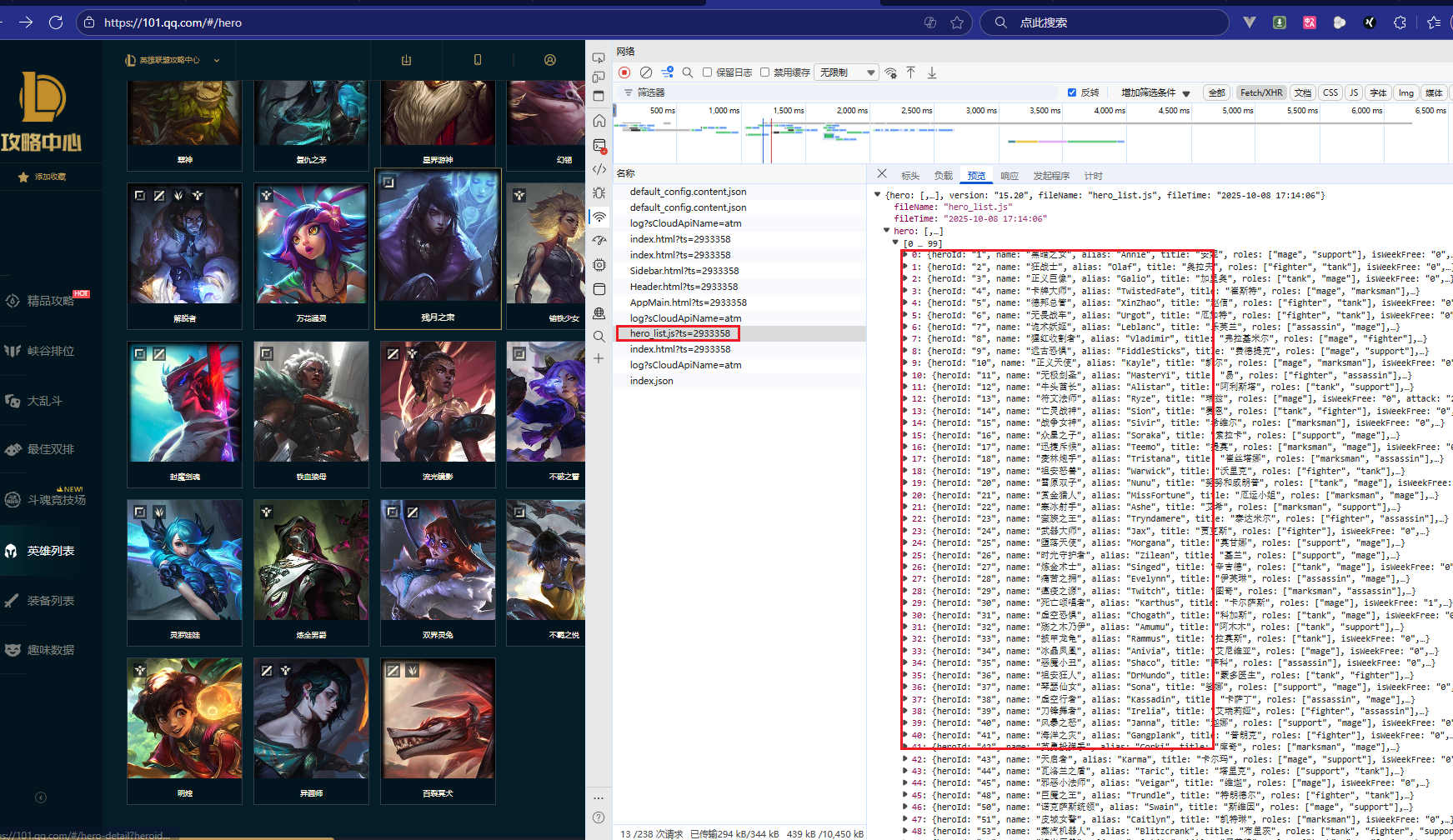
点击英雄,然后点"皮肤详情"
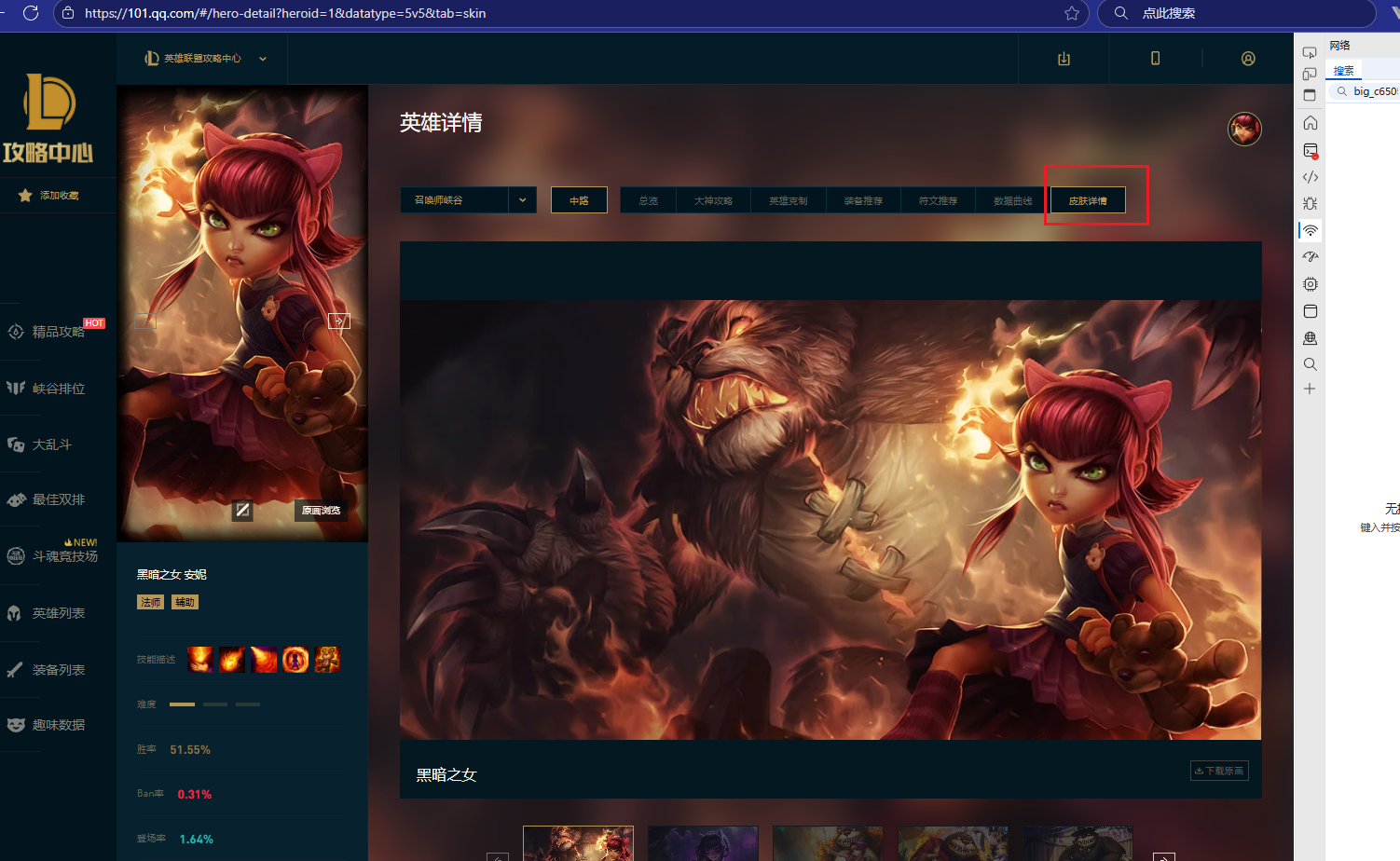
通过抓包发现皮肤图片请求
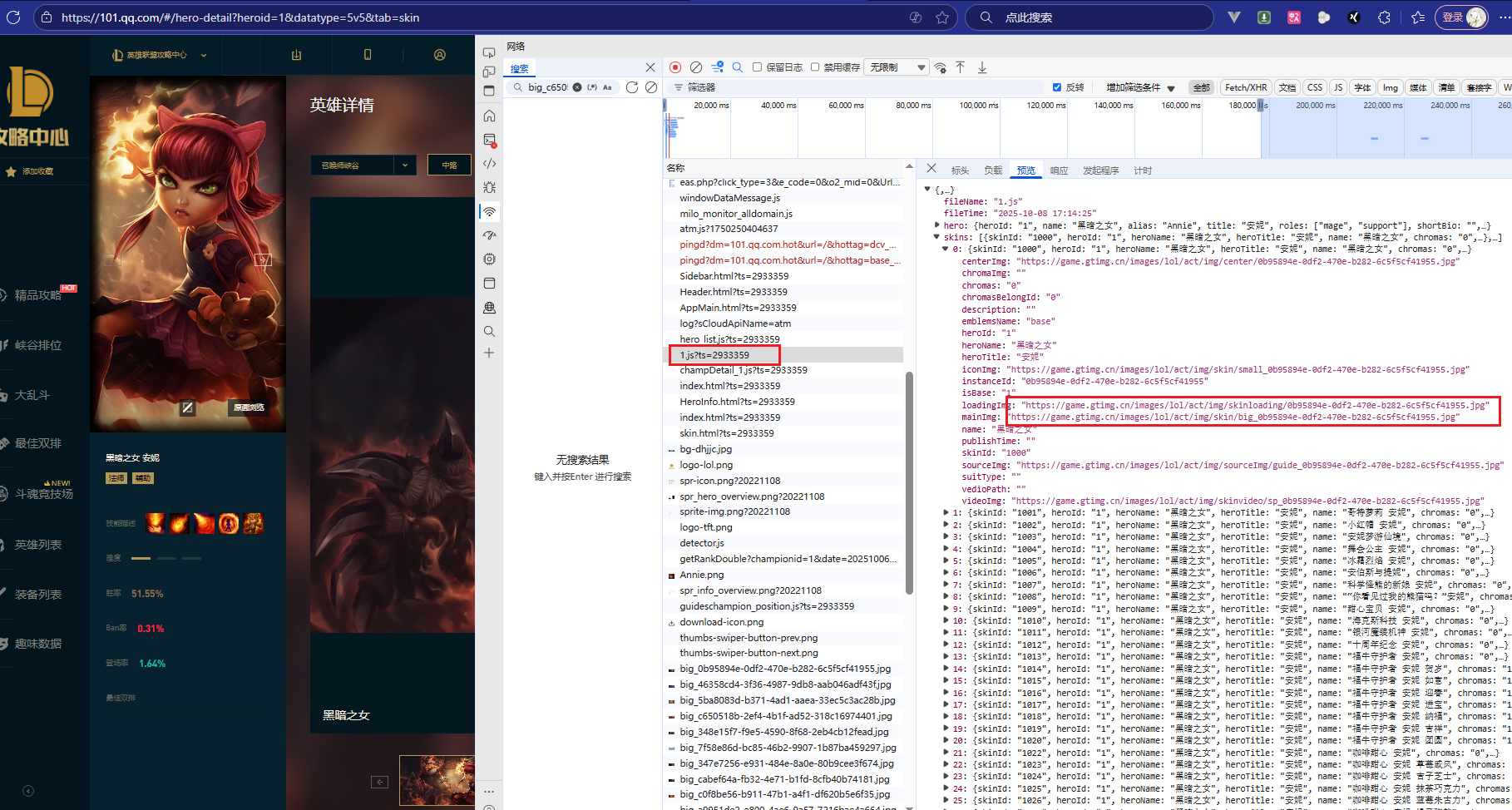
模拟上述请求,获取所有英雄皮肤代码
import json
import os
from textwrap import indent
import chardet
from requests_html import HTMLSession
session=HTMLSession()
hero_list_url='https://game.gtimg.cn/images/lol/act/img/js/heroList/hero_list.js'
headers={
'user-agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/141.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/141.0.0.0',
}
hero_list_response=session.get(url=hero_list_url,headers=headers)
if hero_list_response.status_code==200:
print("获取英雄列表成功\n")
# # 自动检测编码
# detected=chardet.detect(hero_list_response.content)
# encoding=detected['encoding'] # print(encoding)
# 解码
hero_list_content = hero_list_response.content.decode()
hero_list_content = json.loads(hero_list_content)
# print(json.dumps(hero_list_content,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4))
if not os.path.exists('LOL皮肤'):
os.mkdir('LOL皮肤')
for hero in hero_list_content['hero']:
print(f'英雄名字:{hero["name"]}_{hero["title"]}_{hero["heroId"]}')
# 获取英雄皮肤图片
hero_skin_url = f'https://game.gtimg.cn/images/lol/act/img/js/hero/{hero["heroId"]}.js'
hero_skin_response = session.get(url=hero_skin_url)
if hero_skin_response.status_code==200:
hero_skin_content = hero_skin_response.content.decode()
hero_skin_content = json.loads(hero_skin_content)
# print(f"英雄皮肤数据:{json.dumps(hero_skin_content,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)}")
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}')
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone')
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc')
for hero_skin in hero_skin_content['skins']:
# 皮肤名字
name = hero_skin['name'].replace('/',' ')
# 手机端皮肤url
phone_url = hero_skin['loadingImg']
# 电脑端皮肤url
pc_url = hero_skin['centerImg']
# 过滤数据中缺少数据的,防止干扰数据
if phone_url!='' and pc_url!='' :
# 下载图片
phone_response = session.get(url=phone_url)
with open(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone/{name}.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(phone_response.content)
pc_response = session.get(url=pc_url)
with open(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc/{name}.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(pc_response.content)
if phone_response.status_code==200 and pc_response.status_code==200:
print(f'下载{hero["name"]} 的 {name} 皮肤成功')
else:
print(f'下载{hero["name"]} 的 {name} 皮肤失败 phone: {phone_response.status_code} pc:{pc_response.status_code}')
print(f'下载{hero["name"]} 皮肤完毕\n')
else:
print(f'获取 {hero["name"]} 英雄皮肤失败')
print("\n下载完毕")
else:
print("获取英雄列表失败",hero_list_response.status_code)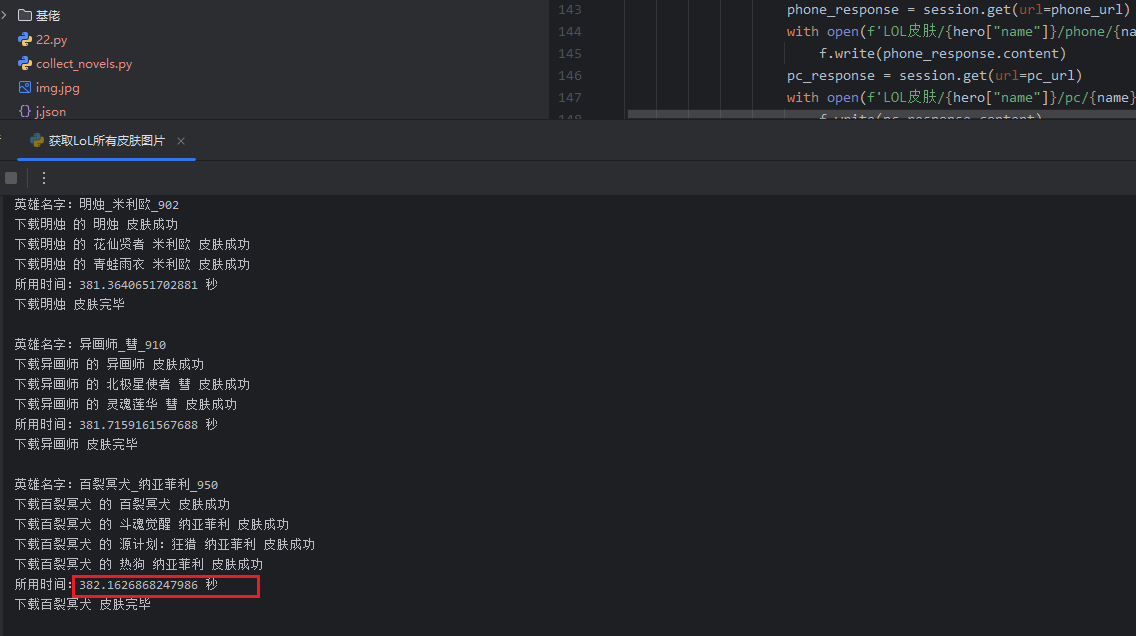
使用进程更改代码(加快执行时间)
import json
import os
import time
from multiprocessing import Process
from textwrap import indent
import chardet
from requests_html import HTMLSession
def task(session,hero):
# 获取英雄皮肤图片
hero_skin_url = f'https://game.gtimg.cn/images/lol/act/img/js/hero/{hero["heroId"]}.js'
hero_skin_response = session.get(url=hero_skin_url)
if hero_skin_response.status_code == 200:
hero_skin_content = hero_skin_response.content.decode()
hero_skin_content = json.loads(hero_skin_content)
# print(f"英雄皮肤数据:{json.dumps(hero_skin_content,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)}")
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}')
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone')
if not os.path.exists(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc'):
os.mkdir(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc')
for hero_skin in hero_skin_content['skins']:
# 皮肤名字
name = hero_skin['name'].replace('/', ' ')
# 手机端皮肤url
phone_url = hero_skin['loadingImg']
# 电脑端皮肤url
pc_url = hero_skin['centerImg']
# 过滤数据中缺少数据的,防止干扰数据
if phone_url != '' and pc_url != '':
# 下载图片
phone_response = session.get(url=phone_url)
with open(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/phone/{name}.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(phone_response.content)
pc_response = session.get(url=pc_url)
with open(f'LOL皮肤/{hero["name"]}/pc/{name}.png', 'wb') as f:
f.write(pc_response.content)
if phone_response.status_code == 200 and pc_response.status_code == 200:
print(f'下载{hero["name"]} 的 {name} 皮肤成功')
else:
print(
f'下载{hero["name"]} 的 {name} 皮肤失败 phone: {phone_response.status_code} pc:{pc_response.status_code}')
print(f'下载{hero["name"]} 皮肤完毕\n')
else:
print(f'获取 {hero["name"]} 英雄皮肤失败')
if __name__=='__main__':
session = HTMLSession()
hero_list_url = 'https://game.gtimg.cn/images/lol/act/img/js/heroList/hero_list.js'
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/141.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/141.0.0.0',
}
hero_list_response = session.get(url=hero_list_url, headers=headers)
if hero_list_response.status_code == 200:
print("获取英雄列表成功\n")
# # 自动检测编码
# detected=chardet.detect(hero_list_response.content)
# encoding=detected['encoding'] # print(encoding)
# 解码
hero_list_content = hero_list_response.content.decode()
hero_list_content = json.loads(hero_list_content)
# print(json.dumps(hero_list_content,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4))
if not os.path.exists('LOL皮肤'):
os.mkdir('LOL皮肤')
for hero in hero_list_content['hero']:
print(f'英雄名字:{hero["name"]}_{hero["title"]}_{hero["heroId"]}')
t1=Process(target=task,args=(session,hero))
t1.start()
end_time=time.time()
print("\n下载完毕")
else:
print("获取英雄列表失败", hero_list_response.status_code)直接速度提升一大截

如果你在阅读过程中也有新的见解,或者遇到类似问题,🥰不妨留言分享你的经验,让大家一起学习。
喜欢本篇内容的朋友,记得点个 👍点赞,收藏 并 关注我,这样你就不会错过后续的更多实用技巧和深度干货了!
期待在评论区看到你的声音,我们一起成长、共同进步!😊