目录
- 前言
- 一、实现步骤
-
- [1. 准备DOM引用](#1. 准备DOM引用)
- [2. 计算连接线路径](#2. 计算连接线路径)
- [3. 渲染连接线](#3. 渲染连接线)
- [4. 添加交互效果](#4. 添加交互效果)
- [5. 响应窗口变化和滚动](#5. 响应窗口变化和滚动)
- [6. 优化路径计算(曲线路径)](#6. 优化路径计算(曲线路径))
- 二、核心知识点解析
-
- [1. DOM位置获取](#1. DOM位置获取)
- [2. SVG路径绘制](#2. SVG路径绘制)
- [3. React Refs系统](#3. React Refs系统)
- [4. 事件处理](#4. 事件处理)
- [5. 性能优化](#5. 性能优化)
- [三、完整组件示例 + 运行效果](#三、完整组件示例 + 运行效果)
- 四、高级优化技巧
-
- [1. 性能优化](#1. 性能优化)
- [2. 动画效果](#2. 动画效果)
- [3. 响应设计](#3. 响应设计)
- [4. 虚拟化渲染](#4. 虚拟化渲染)
前言
本文基于React 18 + TypeScript环境,详细讲解如何在SVG图形和按钮之间实现动态连接线。这种连接线不是通过拖拽改变,而是基于数据配置自动生成。
核心在于根据用户在配置弹窗中的选择,动态生成并渲染图标与按钮之间的连接线。
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、实现步骤
实现SVG连接线的关键步骤:
(1)准备DOM引用:为端口和出口创建Ref
(2)计算路径:基于元素位置计算SVG路径
(3)渲染连线:使用SVG 元素
(4)添加交互:实现悬停高亮效果
(5)响应变化:监听窗口大小和滚动事件
1. 准备DOM引用
首先需要为每个端口和出口创建DOM引用,以便获取它们的位置信息:
typescript
// 创建Refs存储端口和出口的DOM元素
const portNodeRefs = useRef<Record<string, HTMLElement | null>>({});
const exitNodeRefs = useRef<Record<string, HTMLElement | null>>({});
const containerRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement | null>(null);
// 在渲染函数中绑定Ref
{ports.map((port) => (
<div
key={port.name}
ref={(el) => (portNodeRefs.current[port.name] = el)}
// ...其他属性
>
{/* 端口图标 */}
</div>
))}
{landingOptions.map((option) => (
<div
key={option.value}
ref={(el) => (exitNodeRefs.current[option.value] = el)}
// ...其他属性
>
{/* 出口按钮 */}
</div>
))}2. 计算连接线路径
这是核心步骤,需要计算每个端口到其分配出口的连线路径:
typescript
const recomputeLines = () => {
const container = containerRef.current;
if (!container) return;
const containerRect = container.getBoundingClientRect();
const newLines: { path: string; port: string; exit: string }[] = [];
// 遍历所有端口和其分配的出口
Object.entries(portLandingMap).forEach(([portName, exits]) => {
exits?.forEach((exitVal) => {
const portEl = portNodeRefs.current[portName];
const exitEl = exitNodeRefs.current[exitVal];
if (!portEl || !exitEl) return;
// 获取端口和出口的位置
const portRect = portEl.getBoundingClientRect();
const exitRect = exitEl.getBoundingClientRect();
// 计算相对容器的坐标
const startX = portRect.left - containerRect.left + portRect.width / 2;
const startY = portRect.bottom - containerRect.top;
const endX = exitRect.left - containerRect.left + exitRect.width / 2;
const endY = exitRect.top - containerRect.top;
// 计算路径(这里使用简单的折线,实际可优化为曲线)
const path = `M ${startX} ${startY} L ${endX} ${endY}`;
newLines.push({ path, port: portName, exit: exitVal });
});
});
setLines(newLines);
};3. 渲染连接线
在组件中渲染SVG路径:
typescript
<div ref={containerRef} style={{ position: 'relative' }}>
{/* 端口和出口的渲染 */}
{/* SVG容器用于绘制连接线 */}
<svg
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: '100%',
height: '100%',
pointerEvents: 'none', // 避免连线拦截鼠标事件
}}
>
{lines.map((line, index) => (
<path
key={index}
d={line.path}
stroke="#1f78ff" // 线条颜色
strokeWidth="2" // 线条宽度
fill="none"
/>
))}
</svg>
</div>4. 添加交互效果
实现鼠标悬停时高亮相关连线的效果:
typescript
// 状态记录当前悬停的连线
const [hoverLineKey, setHoverLineKey] = useState<string | null>(null);
// 在渲染连线时添加交互
{lines.map((line, index) => {
const lineKey = `${line.port}-${line.exit}`;
return (
<path
key={index}
d={line.path}
stroke={hoverLineKey === lineKey ? '#ff0000' : '#1f78ff'}
strokeWidth={hoverLineKey === lineKey ? 3 : 2}
fill="none"
onMouseEnter={() => setHoverLineKey(lineKey)}
onMouseLeave={() => setHoverLineKey(null)}
/>
);
})}5. 响应窗口变化和滚动
确保在窗口大小变化或容器滚动时重新计算连线位置:
typescript
useEffect(() => {
const handleResize = () => recomputeLines();
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
const container = containerRef.current;
if (container) {
container.addEventListener('scroll', recomputeLines);
}
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
if (container) {
container.removeEventListener('scroll', recomputeLines);
}
};
}, []);6. 优化路径计算(曲线路径)
更美观的贝塞尔曲线实现:
typescript
// 计算曲线路径
const controlPointY = (startY + endY) / 2;
const path = `M ${startX} ${startY}
C ${startX} ${controlPointY},
${endX} ${controlPointY},
${endX} ${endY}`;二、核心知识点解析
1. DOM位置获取
使用getBoundingClientRect()获取元素位置和尺寸:
typescript
// 关键计算步骤:
const containerRect = container.getBoundingClientRect();
const portRect = portEl.getBoundingClientRect();
// 计算相对容器位置的坐标
const px = portRect.left - containerRect.left + portRect.width / 2;
const py = portRect.bottom - containerRect.top;2. SVG路径绘制
SVG 元素的d属性定义路径:
M x y:移动到指定坐标
L x y:画直线到指定坐标
C x1 y1, x2 y2, x y:三次贝塞尔曲线
typescript
// SVG路径命令:
// M = moveto (起点)
// L = lineto (直线)
// C = curveto (贝塞尔曲线)
// Z = closepath (闭合路径)
const path = `M ${startX} ${startY} L ${midX} ${midY} L ${endX} ${endY}`;3. React Refs系统
三种Ref使用场景:
DOM元素引用:useRef(null)+ ref={ref}
存储可变值:替代类组件的实例变量
转发Refs:forwardRef访问子组件DOM
typescript
// 动态ref管理模式
const refs = useRef<Record<string, HTMLElement | null>>({});
// 在渲染循环中绑定
{elements.map(item => (
<div
key={item.id}
ref={(el) => {
refs.current[item.id] = el;
}}
/>
))}4. 事件处理
React合成事件系统:
使用onMouseEnter/onMouseLeave代替原生事件
事件委托提高性能
使用useEffect清理事件监听器
5. 性能优化
typescript
// 1. 使用useLayoutEffect避免闪烁
useLayoutEffect(() => {
recomputeLines();
}, [dependencies]);
// 2. 防抖处理
const debouncedRecompute = useMemo(
() => debounce(recomputeLines, 100),
[]
);
// 3. 条件重计算
const shouldRecompute = useMemo(() => {
return JSON.stringify(portLandingMap) !== lastMappingRef.current;
}, [portLandingMap]);三、完整组件示例 + 运行效果
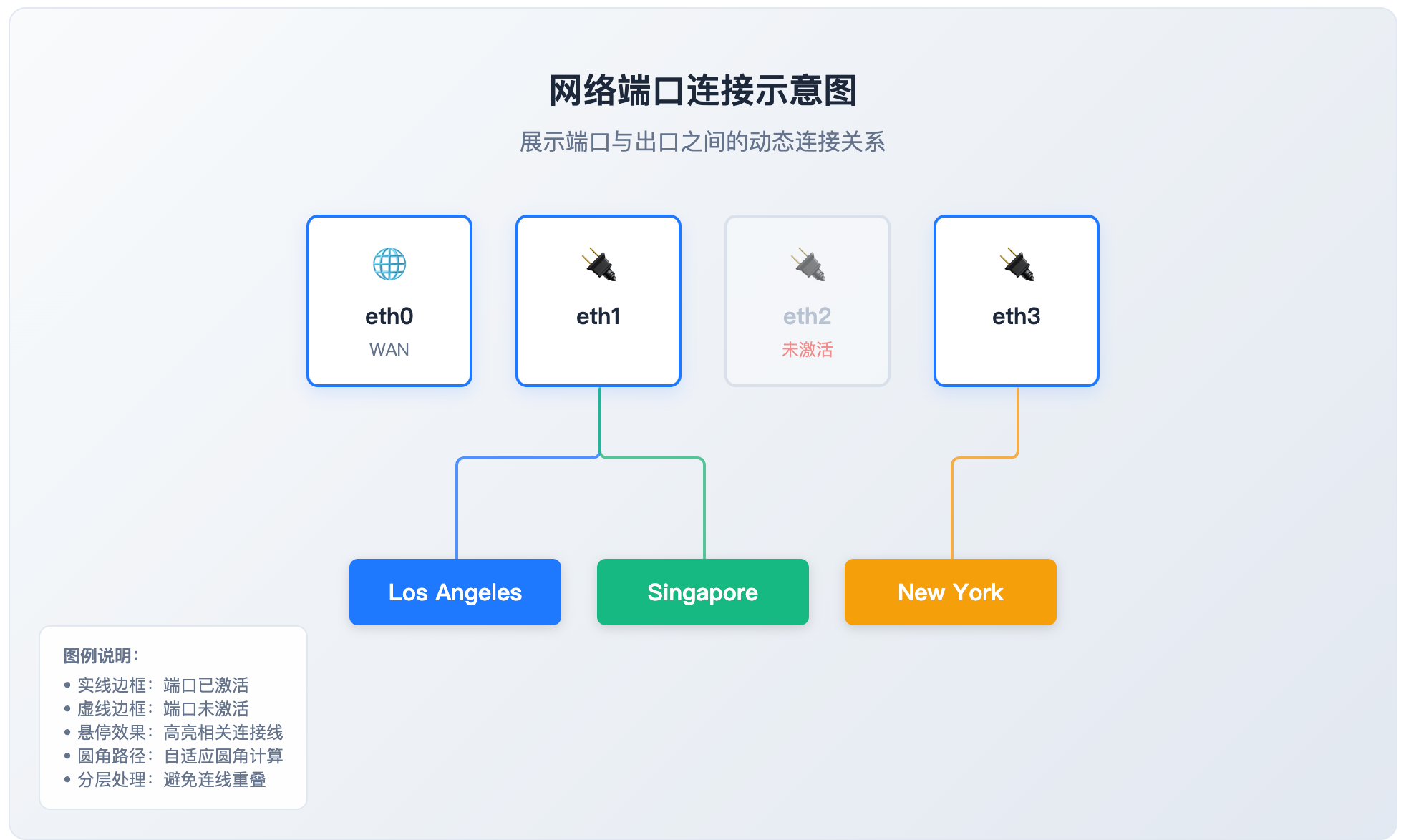
📢注意:我现在给的这个套完整示例,仅作为参考,跟上面的步骤还是不太一样的,比如缺少编辑弹窗等,但是为了方便直接运行,看到连线效果,改动后如下:
typescript
// App.tsx
import React, { useRef, useState, useLayoutEffect, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
interface Port {
name: string;
isWan?: boolean;
active?: boolean;
}
interface LandingOption {
value: string;
label: string;
}
interface ConnectionLine {
path: string;
port: string;
exit: string;
}
const PortConnectionDemo: React.FC = () => {
// 状态管理
const [ports] = useState<Port[]>([
{ name: 'eth0', isWan: true, active: true },
{ name: 'eth1', isWan: false, active: true },
{ name: 'eth2', isWan: false, active: false },
{ name: 'eth3', isWan: false, active: true },
]);
const [landingOptions] = useState<LandingOption[]>([
{ value: 'LA', label: 'Los Angeles' },
{ value: 'SG', label: 'Singapore' },
{ value: 'NY', label: 'New York' },
]);
const [portLandingMap] = useState<Record<string, string[]>>({
eth1: ['LA', 'SG'],
eth3: ['NY'],
});
// DOM引用
const portNodeRefs = useRef<Record<string, HTMLDivElement | null>>({});
const exitNodeRefs = useRef<Record<string, HTMLDivElement | null>>({});
const containerRef = useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const linesSvgRef = useRef<SVGSVGElement>(null);
// 连线状态
const [lines, setLines] = useState<ConnectionLine[]>([]);
const [hoverLineKey, setHoverLineKey] = useState<string | null>(null);
// 核心连线计算函数
const recomputeLines = useCallback(() => {
const container = containerRef.current;
if (!container) {
if (lines.length) setLines([]);
return;
}
const containerRect = container.getBoundingClientRect();
const basePortRadius = 5;
const minExitRadius = 4;
const exitRadiusCache: Record<string, number> = {};
const newLines: ConnectionLine[] = [];
const exitBusYCache: Record<string, number> = {};
const exitConnections: Record<string, string[]> = {};
// 建立出口连接关系映射
Object.keys(portLandingMap).forEach((portName) => {
const exits = portLandingMap[portName];
exits?.forEach((exitVal) => {
if (!exitConnections[exitVal]) exitConnections[exitVal] = [];
exitConnections[exitVal].push(portName);
});
});
// 计算每个出口的总线Y坐标
const getBusYForExit = (exitVal: string): number => {
if (exitBusYCache[exitVal] !== undefined) return exitBusYCache[exitVal];
const exitEl = exitNodeRefs.current[exitVal];
const eyTop = exitEl ? exitEl.getBoundingClientRect().top - containerRect.top : 0;
const connectedPorts = Object.keys(portLandingMap).filter((portName) =>
portLandingMap[portName]?.includes(exitVal)
);
const portBottoms: number[] = [];
connectedPorts.forEach((portName) => {
const portEl = portNodeRefs.current[portName];
if (portEl) {
portBottoms.push(portEl.getBoundingClientRect().bottom - containerRect.top);
}
});
const avgPortBottom = portBottoms.length
? portBottoms.reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0) / portBottoms.length
: eyTop - 50;
// 40% 靠上位置,避免总线过低
const busY = Math.round(avgPortBottom + (eyTop - avgPortBottom) * 0.4);
exitBusYCache[exitVal] = busY;
return busY;
};
// 为每个端口到出口计算路径
for (const portName of Object.keys(portLandingMap)) {
const exits = portLandingMap[portName];
if (!exits || exits.length === 0) continue;
const portEl = portNodeRefs.current[portName];
if (!portEl) continue;
const portRect = portEl.getBoundingClientRect();
const startX = portRect.left - containerRect.left + portRect.width / 2;
const startY = portRect.bottom - containerRect.top;
// 检查端口是否在容器可见范围内
if (startX < 0 || startX > containerRect.width) continue;
for (const exitVal of exits) {
const exitEl = exitNodeRefs.current[exitVal];
if (!exitEl) continue;
const exitRect = exitEl.getBoundingClientRect();
const endX = exitRect.left - containerRect.left + exitRect.width / 2;
const endY = exitRect.top - containerRect.top;
// 检查出口是否在容器可见范围内
if (endX < 0 || endX > containerRect.width) continue;
const direction = endX >= startX ? 1 : -1;
const busY = getBusYForExit(exitVal);
// 计算分层偏移,避免重叠
const connectedPorts = exitConnections[exitVal] || [];
const laneIndex = connectedPorts.indexOf(portName);
const laneCount = connectedPorts.length || 1;
const laneSpread = Math.min(26, Math.max(8, laneCount * 5));
const laneOffset = laneCount === 1 ? 0 : (laneIndex / (laneCount - 1) - 0.5) * laneSpread;
const laneBusY = busY + laneOffset;
// 计算圆角半径
const downSpace = laneBusY - startY;
const upSpace = endY - laneBusY;
let portRadius = Math.min(
basePortRadius,
Math.max(3, Math.floor(Math.min(downSpace, upSpace) * 0.55))
);
if (Math.min(downSpace, upSpace) < basePortRadius * 1.6) {
portRadius = Math.min(portRadius, Math.max(2, Math.floor(Math.min(downSpace, upSpace) * 0.45)));
}
const canUsePortArc = downSpace > portRadius * 1.8 && portRadius >= 2;
const portVertEndY = Math.max(startY + 4, laneBusY - portRadius);
const sweep1 = direction > 0 ? 0 : 1;
const sweep2 = direction > 0 ? 1 : 0;
// 出口侧圆角计算
if (exitRadiusCache[exitVal] === undefined) {
const upSpaceAtExit = endY - busY;
let exitRadius = Math.min(Math.max(minExitRadius, portRadius), Math.floor(upSpaceAtExit * 0.55));
if (upSpaceAtExit < portRadius * 1.6) {
exitRadius = Math.min(exitRadius, Math.max(minExitRadius, Math.floor(upSpaceAtExit * 0.45)));
}
// 协调端口和出口圆角
if (Math.abs(exitRadius - portRadius) > 3) {
exitRadius = exitRadius > portRadius ? portRadius + 3 : exitRadius;
}
exitRadiusCache[exitVal] = Math.max(minExitRadius, exitRadius);
}
let exitRadius = exitRadiusCache[exitVal];
const exitLaneUpSpace = endY - laneBusY;
if (exitLaneUpSpace < exitRadius + 6) {
const availableSpace = exitLaneUpSpace - 4;
exitRadius = availableSpace >= minExitRadius ? Math.min(exitRadius, availableSpace) : 0;
}
const canUseExitArc = exitRadius >= minExitRadius;
const midStartX = startX + direction * portRadius;
const midEndX = endX - direction * (canUseExitArc ? exitRadius : 0);
let useSimple = false;
if (Math.abs(midEndX - midStartX) < portRadius * 2.2) {
useSimple = true;
}
let path: string;
if (useSimple) {
const arcY = (startY + endY) / 2;
if (canUsePortArc && canUseExitArc) {
path = [
`M ${startX} ${startY}`,
`V ${arcY - portRadius}`,
`A ${portRadius} ${portRadius} 0 0 ${sweep1} ${startX + direction * portRadius} ${arcY}`,
`H ${endX - direction * exitRadius}`,
`A ${exitRadius} ${exitRadius} 0 0 ${sweep2} ${endX} ${arcY + exitRadius}`,
`V ${endY}`,
].join(' ');
} else {
// 简化路径:直线连接
path = `M ${startX} ${startY} V ${arcY} H ${endX} V ${endY}`;
}
} else {
// 标准路径:带圆角的折线
const arc1EndY = laneBusY;
if (canUsePortArc && canUseExitArc) {
path = [
`M ${startX} ${startY}`,
`V ${portVertEndY}`,
`A ${portRadius} ${portRadius} 0 0 ${sweep1} ${startX + direction * portRadius} ${arc1EndY}`,
`H ${midEndX}`,
`A ${exitRadius} ${exitRadius} 0 0 ${sweep2} ${endX} ${laneBusY + exitRadius}`,
`V ${endY}`,
].join(' ');
} else {
// 降级为直角折线
path = `M ${startX} ${startY} V ${laneBusY} H ${endX} V ${endY}`;
}
}
newLines.push({ path, port: portName, exit: exitVal });
}
}
// 只有当连线确实变化时才更新状态
const sameLength = newLines.length === lines.length;
let sameContent = sameLength;
if (sameLength) {
for (let i = 0; i < newLines.length; i++) {
if (newLines[i].path !== lines[i].path) {
sameContent = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (!sameContent) {
setLines(newLines);
}
}, [lines, portLandingMap]);
// 初始化和响应式更新
useLayoutEffect(() => {
recomputeLines();
}, [recomputeLines]);
// 窗口大小变化监听
useLayoutEffect(() => {
const handleResize = () => {
recomputeLines();
};
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize);
};
}, [recomputeLines]);
// 颜色映射
const exitColorMap = useMemo(() => {
const baseColors = ['#1f78ff', '#10b981', '#f59e0b', '#6366f1', '#ef4444'];
const map: Record<string, string> = {};
landingOptions.forEach((opt, idx) => {
map[opt.value] = baseColors[idx % baseColors.length];
});
return map;
}, [landingOptions]);
// 处理鼠标悬停
const handlePortMouseEnter = useCallback((portName: string) => {
setHoverLineKey(`${portName}::ALL`);
}, []);
const handlePortMouseLeave = useCallback(() => {
setHoverLineKey(null);
}, []);
const handleExitMouseEnter = useCallback((exitVal: string) => {
setHoverLineKey(`ANY::${exitVal}`);
}, []);
const handleExitMouseLeave = useCallback(() => {
setHoverLineKey(null);
}, []);
const handleLineMouseEnter = useCallback((port: string, exit: string) => {
setHoverLineKey(`${port}::${exit}`);
}, []);
const handleLineMouseLeave = useCallback(() => {
setHoverLineKey(null);
}, []);
return (
<div
ref={containerRef}
style={{
position: 'relative',
padding: '40px 20px',
background: 'linear-gradient(135deg, #f8fafc 0%, #e2e8f0 100%)',
minHeight: '500px',
borderRadius: '12px',
border: '1px solid #e2e8f0'
}}
>
{/* 标题 */}
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', marginBottom: '40px' }}>
<h2 style={{ color: '#1e293b', margin: 0 }}>网络端口连接示意图</h2>
<p style={{ color: '#64748b', margin: '8px 0 0 0' }}>
展示端口与出口之间的动态连接关系
</p>
</div>
{/* 端口区域 */}
<div style={{
display: 'flex',
justifyContent: 'center',
gap: '30px',
marginBottom: '120px',
flexWrap: 'wrap' as const
}}>
{ports.map((port) => (
<div
key={port.name}
ref={(el) => {
if (el) portNodeRefs.current[port.name] = el;
}}
style={{
padding: '16px',
border: `2px solid ${port.active ? '#1f78ff' : '#cbd5e1'}`,
borderRadius: '8px',
background: port.active ? '#ffffff' : '#f8fafc',
boxShadow: port.active ? '0 4px 12px rgba(31, 120, 255, 0.15)' : 'none',
textAlign: 'center',
minWidth: '80px',
transition: 'all 0.3s ease',
opacity: port.active ? 1 : 0.6,
cursor: 'pointer'
}}
onMouseEnter={() => handlePortMouseEnter(port.name)}
onMouseLeave={handlePortMouseLeave}
>
<div style={{
fontSize: '24px',
marginBottom: '8px',
color: port.active ? '#1f78ff' : '#94a3b8'
}}>
{port.isWan ? '🌐' : '🔌'}
</div>
<div style={{
fontWeight: '600',
color: port.active ? '#1e293b' : '#94a3b8'
}}>
{port.name}
</div>
{port.isWan && (
<div style={{
fontSize: '12px',
color: '#64748b',
marginTop: '4px'
}}>
WAN
</div>
)}
{!port.active && (
<div style={{
fontSize: '12px',
color: '#ef4444',
marginTop: '4px'
}}>
未激活
</div>
)}
</div>
))}
</div>
{/* 出口区域 */}
<div style={{
display: 'flex',
justifyContent: 'center',
gap: '25px',
flexWrap: 'wrap' as const
}}>
{landingOptions.map((option) => (
<div
key={option.value}
ref={(el) => {
if (el) exitNodeRefs.current[option.value] = el;
}}
style={{
padding: '12px 24px',
background: exitColorMap[option.value],
color: 'white',
borderRadius: '6px',
fontWeight: '600',
boxShadow: '0 2px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15)',
cursor: 'pointer',
transition: 'all 0.3s ease',
minWidth: '100px',
textAlign: 'center'
}}
onMouseEnter={() => handleExitMouseEnter(option.value)}
onMouseLeave={handleExitMouseLeave}
>
{option.label}
</div>
))}
</div>
{/* SVG连接线容器 */}
<svg
ref={linesSvgRef}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: '100%',
height: '100%',
pointerEvents: 'none',
zIndex: 1
}}
>
{lines.map((line, index) => {
const lineKey = `${line.port}::${line.exit}`;
const isHovered =
hoverLineKey === lineKey ||
hoverLineKey === `${line.port}::ALL` ||
hoverLineKey === `ANY::${line.exit}`;
const baseColor = exitColorMap[line.exit] || '#1f78ff';
return (
<path
key={index}
d={line.path}
stroke={baseColor}
strokeWidth={isHovered ? 3 : 2}
fill="none"
strokeLinecap="round"
strokeLinejoin="round"
style={{
opacity: isHovered ? 1 : 0.8,
filter: isHovered ? 'drop-shadow(0 0 6px rgba(0,0,0,0.3))' : 'none',
transition: 'all 0.3s ease',
pointerEvents: 'stroke' as const
}}
onMouseEnter={() => handleLineMouseEnter(line.port, line.exit)}
onMouseLeave={handleLineMouseLeave}
/>
);
})}
</svg>
{/* 图例说明 */}
<div style={{
position: 'absolute',
bottom: '20px',
left: '20px',
background: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.9)',
padding: '12px 16px',
borderRadius: '8px',
border: '1px solid #e2e8f0',
fontSize: '12px',
color: '#64748b'
}}>
<div style={{ fontWeight: '600', marginBottom: '4px' }}>图例说明:</div>
<div>• 实线边框:端口已激活</div>
<div>• 虚线边框:端口未激活</div>
<div>• 悬停效果:高亮相关连接线</div>
<div>• 圆角路径:自适应圆角计算</div>
<div>• 分层处理:避免连线重叠</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default PortConnectionDemo;四、高级优化技巧
1. 性能优化
typescript
// 使用防抖避免频繁重计算
const recomputeLines = useCallback(debounce(() => {
// 计算逻辑...
}, 100), [portLandingMap, landingOptions]);
// 使用React.memo避免不必要重渲染
const PortIcon = React.memo(({ port }) => {
// 渲染逻辑
});2. 动画效果
typescript
// 使用react-spring添加动画
import { useSpring, animated } from 'react-spring';
const AnimatedPath = animated.path;
// 在组件中使用
<AnimatedPath
d={line.path}
style={{
stroke: colorSpring,
strokeWidth: widthSpring
}}
/>3. 响应设计
typescript
/* 使用CSS媒体查询适应不同屏幕 */
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.port-container {
flex-direction: column;
}
.exit-container {
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
}4. 虚拟化渲染
对于大量连线的情况,使用虚拟化技术:
typescript
import { useVirtual } from 'react-virtual';
const virtualizer = useVirtual({
size: lines.length,
parentRef: containerRef,
estimateSize: useCallback(() => 20, []),
});
{virtualizer.virtualItems.map((virtualRow) => (
<path
key={virtualRow.index}
d={lines[virtualRow.index].path}
// ...其他属性
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: 0,
left: 0,
width: '100%',
height: `${virtualRow.size}px`,
transform: `translateY(${virtualRow.start}px)`
}}
/>
))}