写在前面:
写本系列**(自用)**的目的是回顾已经学过的知识、记录新学习的知识或是记录心得理解,方便自己以后快速复习,减少遗忘。
一、Json文件格式
1、基本语法
(1)注释方法
Json文件的注释方法和C#相同,//表示单行注释,/* */可以进行多行注释:
cs
//注释内容
/*hdfsf
dfef
*/(2)语法规则
{ } :大括号包裹的就代表一个对象
\]:中括号代表数组
: :冒号代表的是键值对的对应关系。键值对表示,"键名":值内容
,:逗号代表的就是分割成员变量的间隔符
" ":Json当中的键一定要用双引号包裹,字符串也需要被双引号包裹,除此之外,字典的键也会被双引号包裹。
将下图的类按以上规则存储在Json中,如下所示
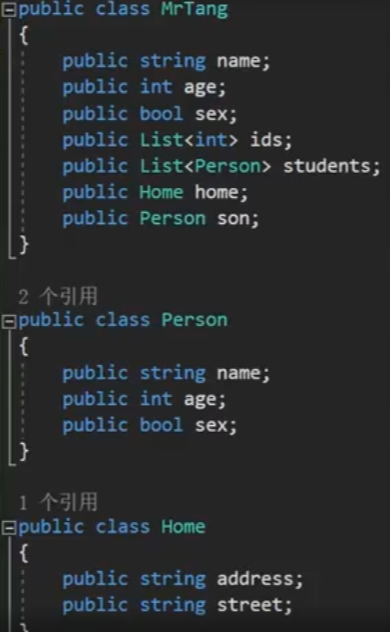
```cs
//大括号包裹的就代表一个对象
{
//冒号代表的是键值对的对应关系
//逗号代表的就是分割成员变量的间隔符
//Json当中的键一定要用双引号包裹
"name":"Alice",
"age":18,
"sex":false,
"height":173.5,
//中括号代表数组
"ids":[1,2,3,4],
"students":[{"name":"Max","age":10,"sex":false},
{"name":"Jack","age":10,"sex":true}],
"home":{"address":"上海","stress":"南京路"},
"son":null,
//字典的键会被双引号包裹
"dic":{"1":"123","2":"234"}
}
```
## 二、JsonUtlity序列化和反序列化
### 1、在文件中存读字符串
在文件中存字符串到指定路径文件中使用的API是File.WriteAllText(),传入的第一个参数为存储的路径,第二个参数为存储的字符串内容。
在指定路径文件中读取字符串使用的API是File.ReadAllText(),在括号中传入读取的路径即可。
```cs
void Start()
{
File.WriteAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Test.json", "存储的json文件");
string str = File.ReadAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Test.json");
print(str);
}
```
### 2、使用JsonUtlity进行序列化
为便于后续讨论,这里先初始化一个类并为其初始化,后续默认使用该类:
```cs
[System.Serializable]
public class Student
{
public int age;
public string name;
public Student(int age, string name)
{
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Teacher
{
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
public float testF;
public double testD;
public int[] ids;
public List
此外,JsonUtlity不支持 字典,JsonUtlity存储的null对象不会是null,而是默认的数值,例如int是0。在序列化float时看起来会有些误差,但反序列化出来后是没有误差的,因此不用在意。
(2)序列化
序列化使用的API是:JsonUtility.ToJson(),括号中传入希望序列化的对象,JsonUtility可以把该类对象序列化为json字符串。之后直接调用File.WriteAllText()存储字符串即可。
cs
public class lession1 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
string jsonStr = JsonUtility.ToJson(t);
File.WriteAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Teacher.json", jsonStr);
}3、反序列化
首先直接调用File.ReadAllText()读取存储的字符串,然后使用JsonUtility的JsonUtility.FromJson即可将字符串转为对应的对象。有两种调用方式,如下,一般习惯使用第二种。
cs
public class lession1 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Teacher.json");
Teacher t2 = JsonUtility.FromJson(jsonStr, typeof(Teacher)) as Teacher;
Teacher t3 = JsonUtility.FromJson<Teacher>(jsonStr);
}三、LitJson序列化和反序列化
LitJson是一个第三方库,用于处理Json的序列化和反序列化。LitJson是C#编写的,体积小,速度快,易于使用。只需要将LitJson代码拷贝到工程中即可。
相比于JsonUtlity,JsonUtlity不能直接存读数值类型,例如数组字典等,需要用类进行包裹,这不是很方便,LitJson可以直接存读数值类型。
1、序列化
同样的,便于讨论,先给出需要进行序列化和反序列化的对象:
cs
public class Student2
{
public int age;
public string name;
public Student2() { }
public Student2(int age, string name)
{
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Teacher2
{
public string name;
public int age;
public bool sex;
public float testF;
public double testD;
public int[] ids;
public List<int> ids2;
public Dictionary<string, string> dic2;
public Student2 s1;
public List<Student2> s2s;
private int privateI = 1;
protected int protectedI = 2;
}
public class lession2 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
Teacher2 t = new Teacher2();
t.name = "MrTang";
t.age = 18;
t.sex = true;
t.testF = 1.4f;
t.testD = 1.4;
t.ids = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
t.ids2 = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3 };
t.dic2 = new Dictionary<string, string>() { { "1", "123" }, { "2", "234" } };
t.s1 = new Student2(10, "Max");
t.s2s = new List<Student2>() { new Student2(9, "Jack"), new Student2(10, "Lucy");
}
}(1)注意点
需要注意的是,相对于JsonUtlity,LitJson不需要加特性。
LitJson不能序列化私有变量。
LitJson支持字典类型,但是字典的键不能是整形,是整形后续反序列化就会报错。
LitJson可以准确的保存null类型。
(2)代码
LitJson序列化的代码很简单,使用JsonMapper.ToJson(),括号内传入需要序列化的对象即可,其余操作和JsonUtlity一样。
cs
public class lession2 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
string jsonStr = JsonMapper.ToJson(t);
File.WriteAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Teacher2.json", jsonStr);
}
}2、反序列化
(1)注意点
类结构需要无参构造函数,否则反序列化时会报错。我们在Student2类中定义了有参构造函数,这顶掉了无参构造函数。为了正常进行反序列化,我们需要重新写无参构造函数。
字典结构虽然支持,但是在键为数值时会有问题,需要用字符串类型。
(2)代码
反序列化使用的是JsonMapper.ToObject(),括号内传入需要反序列化的字符串。
有两种常用的重载,第一种是直接使用JsonMapper.ToObject(),接受返回的JsonData型返回值,该返回值类型会以键值对的形式存储数值。可以以data["name"]的方式获得里面的内容,但这种方式显然不太方便。
第二种方式是使用泛型:JsonMapper.ToObject<Teacher2>(jsonStr)例如这样,就可以直接返回我们需要的类型。
cs
public class lession2 : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
jsonStr = File.ReadAllText(Application.persistentDataPath + "/Teacher2.json");
JsonData data = JsonMapper.ToObject(jsonStr);
print(data["name"]);
print(data["age"]);
Teacher2 t2 = JsonMapper.ToObject<Teacher2>(jsonStr);
}
}