锋哥原创的TensorFlow2 Python深度学习视频教程:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1X5xVz6E4w/
课程介绍
本课程主要讲解基于TensorFlow2的Python深度学习知识,包括深度学习概述,TensorFlow2框架入门知识,以及卷积神经网络(CNN),循环神经网络(RNN),生成对抗网络(GAN),模型保存与加载等。
TensorFlow2 Python深度学习 - 函数式API(Functional API)
TensorFlow 2.x 的函数式 API 允许用户以更灵活和可扩展的方式构建模型,相比于顺序模型,它能处理更复杂的结构,尤其是当你需要多个输入或输出,或者需要共享层时。
1. 函数式 API 简介
在 TensorFlow 2.x 中,函数式 API 是通过 tf.keras.Model 和 tf.keras.layers.Layer 类来实现的。它允许你定义非线性模型的多个输入和输出,不同于 Sequential API,它是层的线性堆叠。
2. 主要特点:
-
多个输入输出:适用于多个输入、多个输出的模型。
-
共享层:不同的模型部分可以共享相同的层。
-
动态结构:能够创建复杂的模型结构,如跳跃连接、残差网络(ResNet)等。
3. 函数式 API 基本用法
3.1 示例代码:单一输入单一输出
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import Input, layers, models
# 输入层
inputs = Input(shape=(32,))
# 一个全连接层
x = layers.Dense(64, activation='relu')(inputs)
# 输出层
outputs = layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
# 创建模型
model = models.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
# 查看模型结构
model.summary()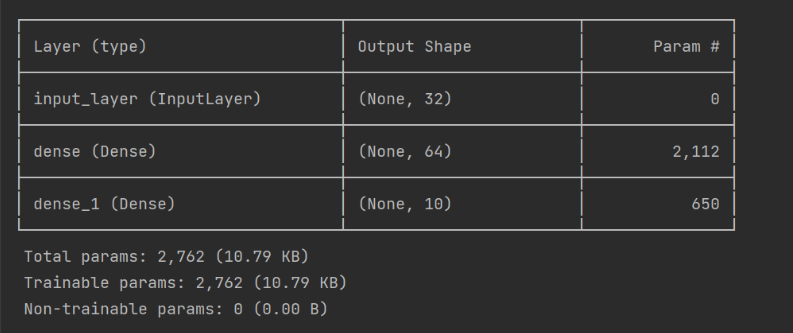
3.2 示例代码:多个输入输出
假设你有一个模型,它接收两个输入,并输出两个结果。
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import Input, layers, models
# 输入层1
input1 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(32,))
# 输入层2
input2 = tf.keras.Input(shape=(64,))
# 分别通过不同的全连接层
x1 = layers.Dense(64, activation='relu')(input1)
x2 = layers.Dense(64, activation='relu')(input2)
# 将两个中间层拼接
x = layers.concatenate([x1, x2])
# 输出层1
output1 = layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(x)
# 输出层2
output2 = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')(x)
# 创建模型
model = models.Model(inputs=[input1, input2], outputs=[output1, output2])
# 查看模型结构
model.summary()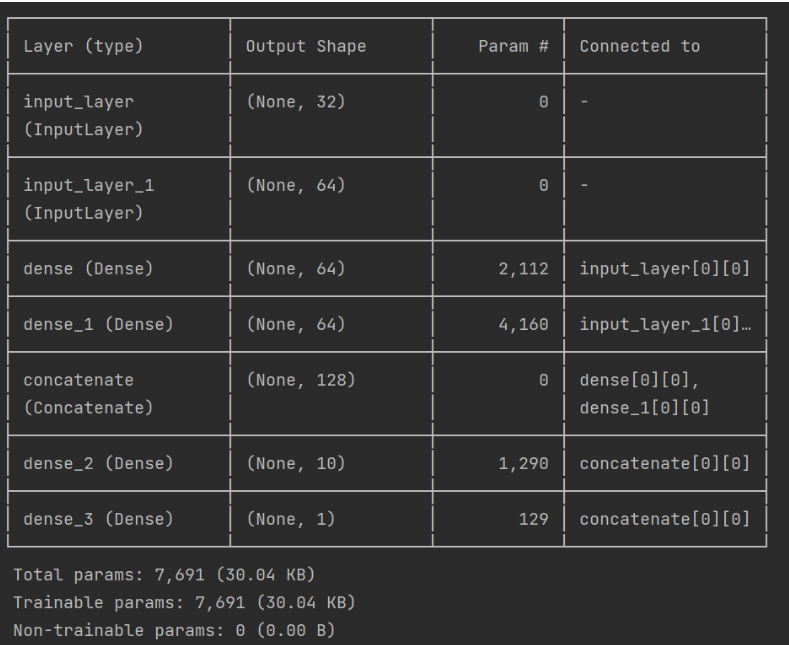
4. 总结
-
TensorFlow 2.x 的函数式 API 提供了灵活的模型定义方式,可以处理更复杂的网络结构。
-
与
SequentialAPI 相比,函数式 API 允许处理多个输入和输出,适用于更加复杂的应用场景(如共享层、跳跃连接等)。 -
通过
tf.keras.Input定义输入,通过层的函数调用将数据传递给后续层,最后通过models.Model构建整个模型。