目录
[一、什么是 CompletableFuture?](#一、什么是 CompletableFuture?)
[二、入门:创建第一个 CompletableFuture](#二、入门:创建第一个 CompletableFuture)
[1. 处理依赖任务:thenCompose](#1. 处理依赖任务:thenCompose)
[2. 处理独立任务:thenCombine](#2. 处理独立任务:thenCombine)
[3. 等待所有任务:allOf](#3. 等待所有任务:allOf)
[4. 等待任意任务:anyOf](#4. 等待任意任务:anyOf)
[1. exceptionally:捕获异常并返回默认值](#1. exceptionally:捕获异常并返回默认值)
[2. handle:同时处理正常结果和异常](#2. handle:同时处理正常结果和异常)
[六、CompletableFuture 的线程池:默认还是自定义?](#六、CompletableFuture 的线程池:默认还是自定义?)
[1. 默认线程池:ForkJoinPool.commonPool ()](#1. 默认线程池:ForkJoinPool.commonPool ())
[2. 自定义线程池:更灵活的控制](#2. 自定义线程池:更灵活的控制)
[七、CompletableFuture vs Future:到底有什么不同?](#七、CompletableFuture vs Future:到底有什么不同?)
[1. 处理结果的方式](#1. 处理结果的方式)
[2. 异常处理能力](#2. 异常处理能力)
[3. 多任务组合能力](#3. 多任务组合能力)
大家在开发中有没有遇到过这样的场景:需要同时调用好几个接口,等所有接口都返回结果后再进行下一步处理?或者某个操作依赖另一个操作的结果,但又不想让程序一直等着?
如果还用传统的多线程或者 Future 来处理,代码往往写得又复杂又难维护。今天就来给大家介绍一个 Java 8 引入的异步编程神器 ------CompletableFuture,它能让这些复杂的异步操作变得简单优雅。
一、什么是 CompletableFuture?
简单说,CompletableFuture 是一个「可以手动完成的 Future」。它不仅能像普通 Future 那样执行异步任务,还提供了一堆实用的方法,让我们可以轻松实现:
- 链式调用(上一个任务完成后自动执行下一个)
- 组合多个任务(不管是有依赖关系还是完全独立)
- 优雅处理异常(不用担心异步任务的异常被悄悄吃掉)
形象点说,普通 Future 就像寄快递,只能等快递到了自己去取;而 CompletableFuture 更像「快递上门」,不仅能自动通知你,还能帮你把快递拆开、分类,甚至直接送到指定位置。
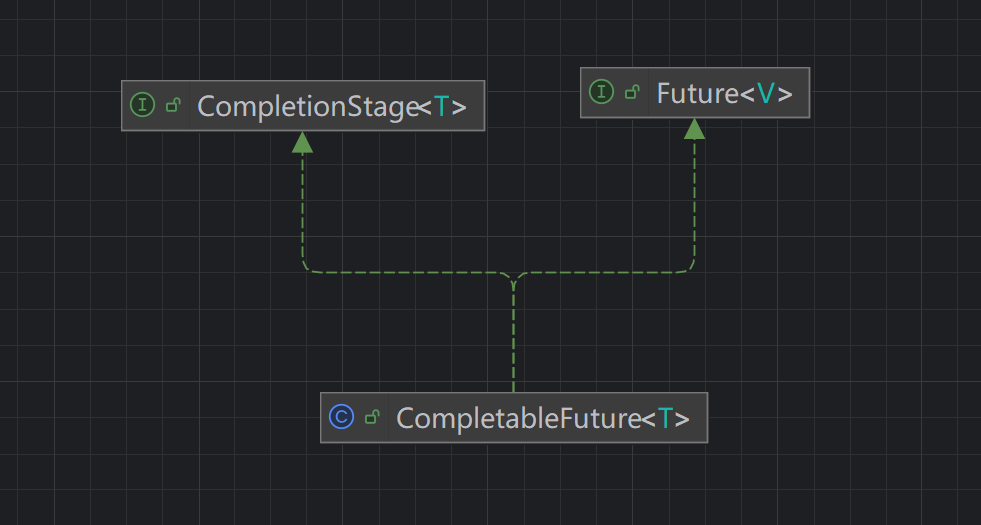
CompletableFuture 同时实现了 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口
java
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
}
二、入门:创建第一个 CompletableFuture
创建 CompletableFuture 主要靠两个静态方法,先看个简单例子:
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
public class FirstCompletableFuture {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 1. 有返回值的异步任务:supplyAsync
CompletableFuture<String> foodFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟耗时操作(比如调用接口查外卖)
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "麻辣烫"; // 任务结果
});
// 2. 无返回值的异步任务:runAsync
CompletableFuture<Void> noticeFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// 模拟耗时操作(比如发送通知)
try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
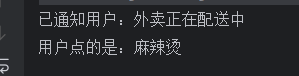
System.out.println("已通知用户:外卖正在配送中");
});
// 获取第一个任务的结果(会等任务完成)
String food = foodFuture.get();
System.out.println("用户点的是:" + food);
// 等待第二个任务完成(虽然它没返回值,但我们需要它执行完)
noticeFuture.get();
}
}运行结果:
关键点:
1.supplyAsync(带Async表示是****异步):适合有返回结果的任务(比如查数据、算结果),参数是一个 Supplier(带返回值的函数)。
java
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
//使用自定义线程池,比较推荐
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,
Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}2.runAsync:适合无返回结果的任务(比如发日志、发通知),参数是一个 Runnable(无返回值的函数)。
java
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
//使用自定义线程池,比较推荐
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,
Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
}3.两个任务是并行执行的,所以通知先完成(只等了 500ms),外卖查询后完成(等了 1000ms)。
三、进阶:链式操作,让任务像流水线一样执行
最能体现 CompletableFuture 强大的,就是它的链式操作。不用手动等待上一个任务完成,直接指定「下一个要做什么」。
比如我们要完成这样一个流程:
- 查用户 ID(耗时 1s)
- 用 ID 查用户名(耗时 0.5s)
- 打印用户名(耗时忽略)
用链式操作实现,代码会非常清爽:
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class CompletableFutureChain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 链式操作:一步接一步执行
CompletableFuture<Void> pipeline = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 第一步:查用户ID
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
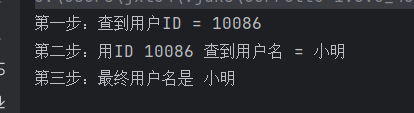
System.out.println("第一步:查到用户ID = 10086");
return 10086; // 把结果传给下一步
}).thenApply(userId -> {
// 第二步:用ID查用户名(接收上一步的结果)
try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("第二步:用ID " + userId + " 查到用户名 = 小明");
return "小明"; // 再把结果传给下一步
}).thenAccept(username -> {
// 第三步:打印用户名(接收上一步的结果,无返回值)
System.out.println("第三步:最终用户名是 " + username);
});
// 等待整个流水线完成
pipeline.get();
}
}运行结果:
常用链式方法:
thenApply:接收上一步结果,处理后返回新结果(比如「ID→用户名」的转换)。thenAccept:接收上一步结果,只处理不返回(比如打印、保存)。thenRun:不关心上一步结果,只在完成后执行(比如「不管结果如何,都记录日志」)。
就像流水线一样,上一个工序的产品自动传到下一个工序,全程无需人工干预。
四、高手篇:组合多个任务,效率翻倍
实际开发中,我们经常需要处理多个任务,有的任务之间有依赖(比如先登录才能下单),有的则完全独立(比如同时加载商品信息和用户信息)。CompletableFuture 提供了专门的方法来处理这些场景。
1. 处理依赖任务:thenCompose
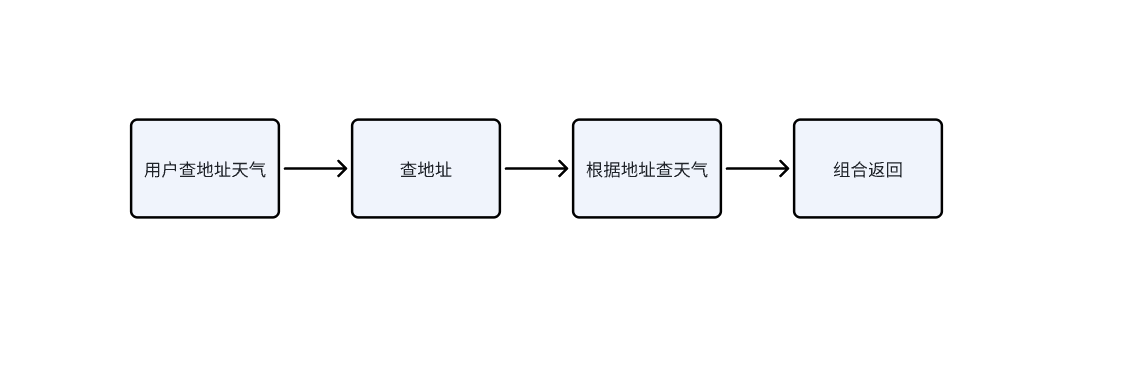
比如「先查用户地址,再根据地址查天气」,第二个任务依赖第一个的结果:
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class ThenComposeDemo {
// 模拟:查用户地址
public static CompletableFuture<String> getAddress(String username) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return username + "的地址是:北京市海淀区";
});
}
// 模拟:根据地址查天气
public static CompletableFuture<String> getWeather(String address) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(600); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return address + ",今天天气:晴,25℃";
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 组合两个依赖任务
CompletableFuture<String> result = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "小明")
.thenCompose(username -> getAddress(username)) // 先查地址
.thenCompose(address -> getWeather(address)); // 再查天气
System.out.println(result.get());
}
}运行流程如下:
运行结果:
thenCompose 就像「接力赛」,第一棒跑完了,把接力棒交给第二棒,确保任务按顺序执行。
2. 处理独立任务:thenCombine
如果两个任务毫无关系,可以并行执行,最后合并结果。比如「同时查商品价格和库存,计算总价」:
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class ThenCombineDemo {
// 查价格
public static CompletableFuture<Double> getPrice(String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(product + "的价格是:99.9元");
return 99.9;
});
}
// 查库存
public static CompletableFuture<Integer> getStock(String product) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(product + "的库存是:5件");
return 5;
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String product = "Java编程思想";
// 并行执行两个任务,然后合并结果
CompletableFuture<Double> total = getPrice(product)
.thenCombine(getStock(product), (price, stock) -> price * stock);
System.out.println("总价:" + total.get() + "元");
}
}执行流程:
执行结果:
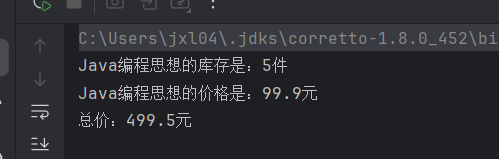
两个任务并行执行,效率大大提高!
3. 等待所有任务:allOf
如果有一堆任务,需要全部完成后再做处理(比如批量下载多个文件,全部下完后打包):
java
package com.itheima.future;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class AllOfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//计时开始
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 3个下载任务
CompletableFuture<Void> download1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("文件1下载完成");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> download2 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("文件2下载完成");
});
CompletableFuture<Void> download3 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("文件3下载完成");
});
// 等待所有任务完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(download1, download2, download3).get();
System.out.println("所有文件下载完成,开始打包...");
System.out.println("打包完成,耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "毫秒");
}
}执行流程如下:
运行结果:
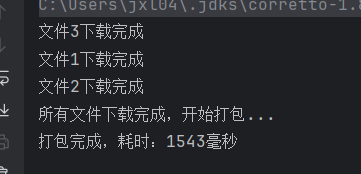
4. 等待任意任务:anyOf
如果多个任务中,只要有一个完成就可以继续**(比如查多个数据源,哪个快用哪个)**:
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class AnyOfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 3个查询任务(不同数据源)
CompletableFuture<String> fromCache = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "从缓存查到数据:Java入门";
});
CompletableFuture<String> fromDb = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "从数据库查到数据:Java入门";
});
CompletableFuture<String> fromApi = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "从API查到数据:Java入门";
});
// 只要有一个任务完成就返回
CompletableFuture<Object> result = CompletableFuture.anyOf(fromCache, fromDb, fromApi);
System.out.println("最快的结果:" + result.get());
}
}运行结果:
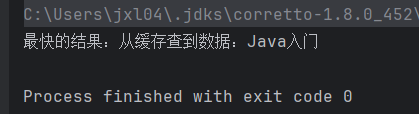
五、异常处理:别让异步任务的错误悄悄溜走
异步任务的异常很容易被忽略(比如线程池悄悄吃掉异常),CompletableFuture 提供了贴心的异常处理方法。
1. exceptionally:捕获异常并返回默认值
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class ExceptionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 模拟任务失败
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("查询失败:数据库连接超时");
}
return 100;
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
// 捕获异常,返回默认值
System.out.println("出错了:" + ex.getMessage());
return 0; // 默认值
});
System.out.println("最终结果:" + future.get()); // 输出 0
}
}执行结果:
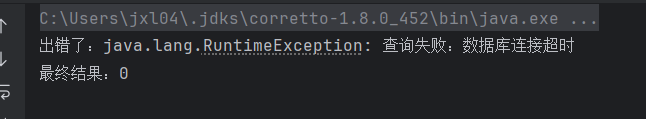
2. handle:同时处理正常结果和异常
java
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class ExceptionDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 这里可以故意抛出异常测试
return "正常结果";
}).handle((result, ex) -> {
if (ex != null) {
return "处理异常:" + ex.getMessage();
} else {
return "处理成功:" + result;
}
});
System.out.println(future.get()); // 输出 处理成功:正常结果
}
}执行结果:
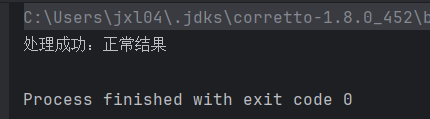
六、CompletableFuture 的线程池:默认还是自定义?
使用 CompletableFuture 时,线程池的选择非常关键,它直接影响程序的性能和稳定性。
1. 默认线程池:ForkJoinPool.commonPool ()
当我们使用无参的**supplyAsync()或runAsync()** 时,CompletableFuture 会默认使用**ForkJoinPool.commonPool()**作为线程池:
java
// 使用默认线程池
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// 任务逻辑
return "result";
});默认线程池的特点:
- 线程数量:默认等于 CPU 核心数(可以通过
-Djava.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool.common.parallelism参数调整)- 适用场景:CPU 密集型任务(如计算)
- 优点:无需手动管理线程池,简单方便
潜在问题:
- 所有使用默认线程池的任务会共享这一组线程,高并发下可能出现资源竞争
- 对于 IO 密集型任务(如网络请求、文件读写),固定的线程数可能导致效率低下
- 当有大量任务时,可能会拖慢所有依赖此线程池的任务
2. 自定义线程池:更灵活的控制
实际项目中,强烈建议使用自定义线程池,尤其是在生产环境。我们可以通过带线程池参数的方法来指定:
java
package com.itheima.future;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
public class CustomThreadPoolDemo {
// 自定义线程池(这里我暂时使用线程池包里的线程池,一般情况下要使用自定义线程池ThreadPoolExecutor)
private static final ExecutorService customExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用自定义线程池
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务在自定义线程池执行:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "处理完成";
}, customExecutor)
.thenAccept(result -> {
System.out.println("结果:" + result);
});
// 记得在程序结束时关闭线程池
customExecutor.shutdown();
}
}执行结果:
自定义线程池的优势:
- 隔离不同类型的任务(例如:查询数据库的任务用一个线程池,发送消息的任务用另一个)
- 可以根据任务类型(CPU 密集 / IO 密集)调整线程数量
- 避免默认线程池被某个耗时任务占满导致的整体阻塞
线程池配置建议:
- CPU 密集型任务:线程数 = CPU 核心数 + 1
- IO 密集型任务:线程数 = CPU 核心数 × 2(或更多,根据实际测试调整)
- 为线程池起一个有意义的名字,方便问题排查(可以通过自定义 ThreadFactory 实现)
七、CompletableFuture vs Future:到底有什么不同?
很多人会疑惑,Java 已经有了 Future,为什么还需要 CompletableFuture?它们的核心区别在哪里?
| 特性 | Future | CompletableFuture |
|---|---|---|
| 实现接口 | 仅实现 Future 接口 | 实现 Future 和 CompletionStage 接口 |
| 链式操作 | 不支持,必须阻塞获取结果后再处理 | 支持,可通过 thenApply 等方法串联多个任务 |
| 异常处理 | 无专门的 API,需要在任务内部捕获 | 提供 exceptionally、handle 等专门的异常处理方法 |
| 任务组合 | 不支持,需要手动编写同步逻辑 | 支持 thenCompose、thenCombine 等多种组合方式 |
| 手动完成 | 不支持 | 支持 complete ()、completeExceptionally () 手动设置结果或异常 |
| 阻塞获取 | 只能通过 get () 阻塞获取 | 可以阻塞获取,也可以通过回调非阻塞处理 |
具体区别举例
1. 处理结果的方式
Future 的方式(繁琐且必须阻塞):
java
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<String> future = executor.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "任务结果";
});
// 必须阻塞等待结果
String result = future.get();
// 处理结果
System.out.println("处理:" + result);
executor.shutdown();CompletableFuture 的方式(非阻塞,链式处理):
java
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "任务结果";
}).thenApply(result -> {
return "处理后:" + result;
}).thenAccept(processedResult -> {
System.out.println(processedResult);
});2. 异常处理能力
Future 的方式(异常处理麻烦):
java
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("计算失败");
}
return 100;
});
try {
Integer result = future.get(); // 异常会在这里抛出
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();CompletableFuture 的方式(专门的异常处理 API):
java
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("计算失败");
}
return 100;
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println("捕获异常:" + ex.getMessage());
return 0; // 返回默认值
}).thenAccept(result -> {
System.out.println("结果:" + result); // 输出0
});3. 多任务组合能力
Future 几乎无法优雅地组合多个任务,而 CompletableFuture 提供了丰富的组合方式,这也是它最核心的优势。
感兴趣的宝子可以关注一波,后续会更新更多有用的知识!!!
