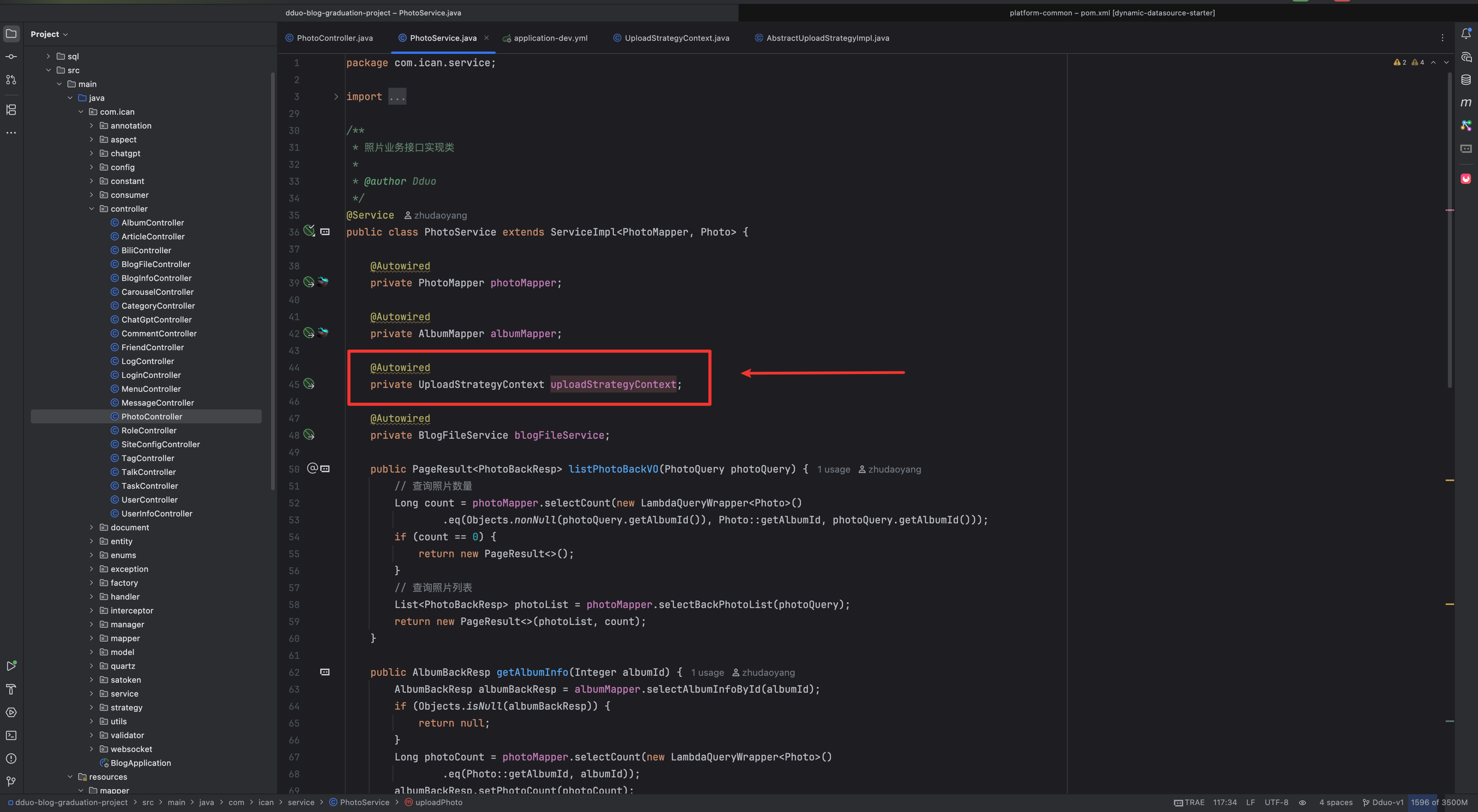
service 里面是注入的策略上下文
我们用策略上下文去调对应的方法
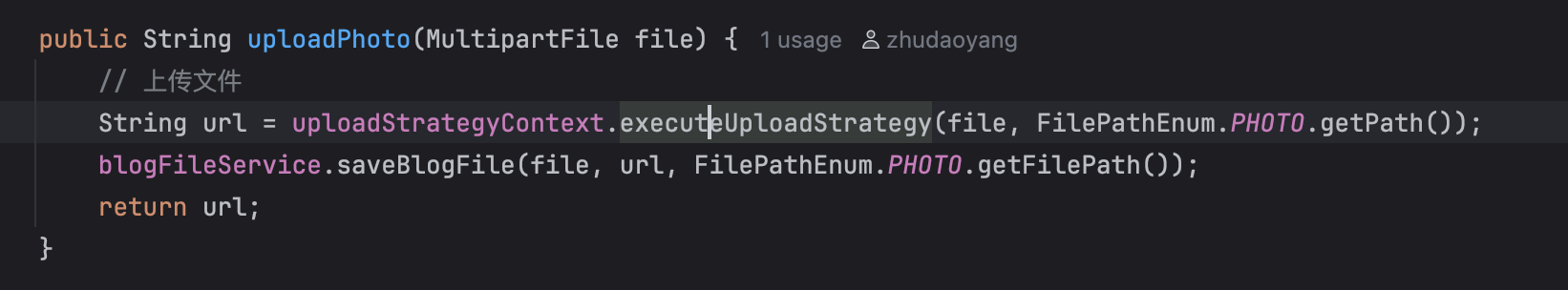
public String uploadPhoto(MultipartFile file) {
// 上传文件
String url = uploadStrategyContext.executeUploadStrategy(file, FilePathEnum.PHOTO.getPath());
blogFileService.saveBlogFile(file, url, FilePathEnum.PHOTO.getFilePath());
return url;
}策略上下文(StrategyContext)中我们把策略定义成常量,从配置中装载
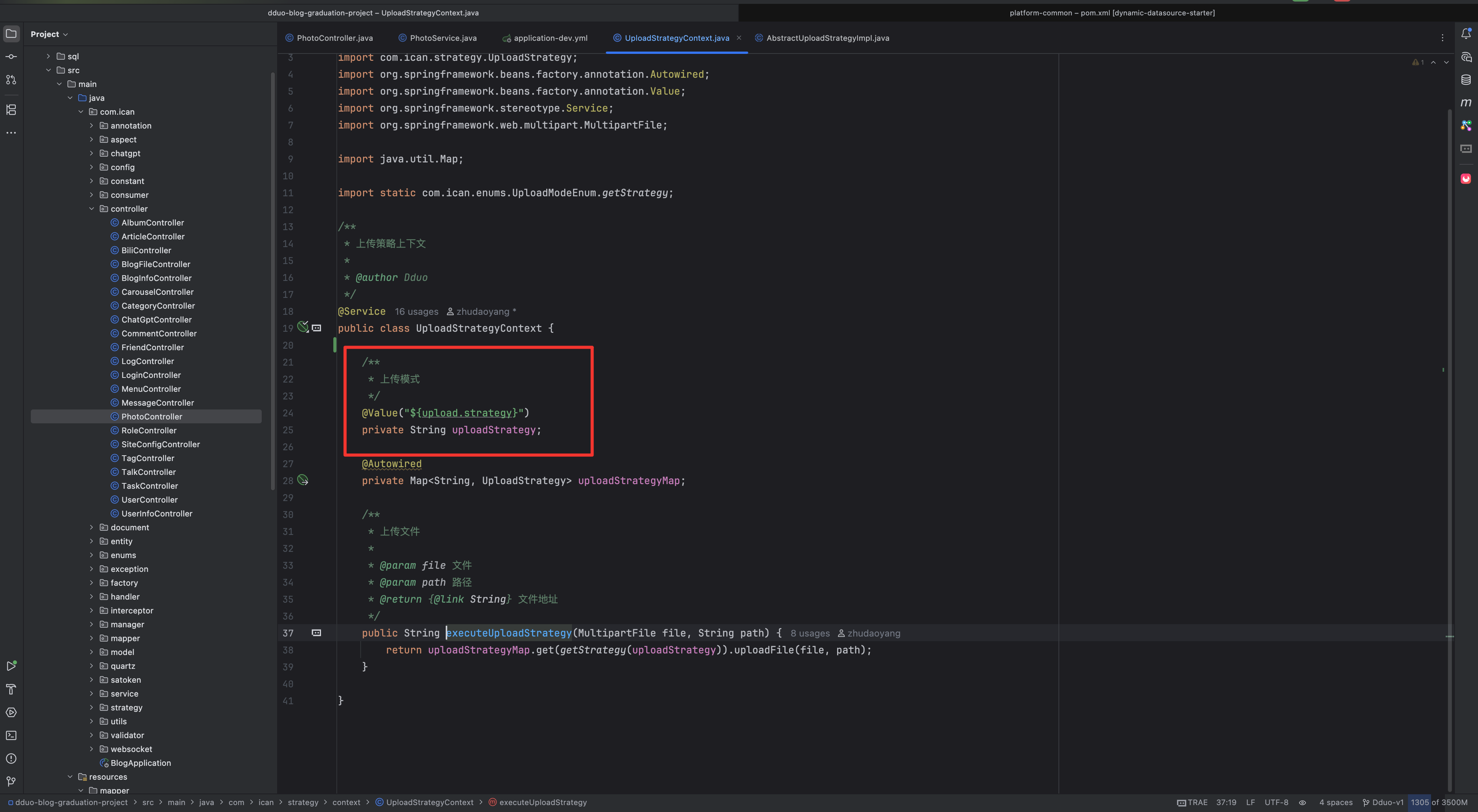
这个是我们在 yml 里面定义的常量
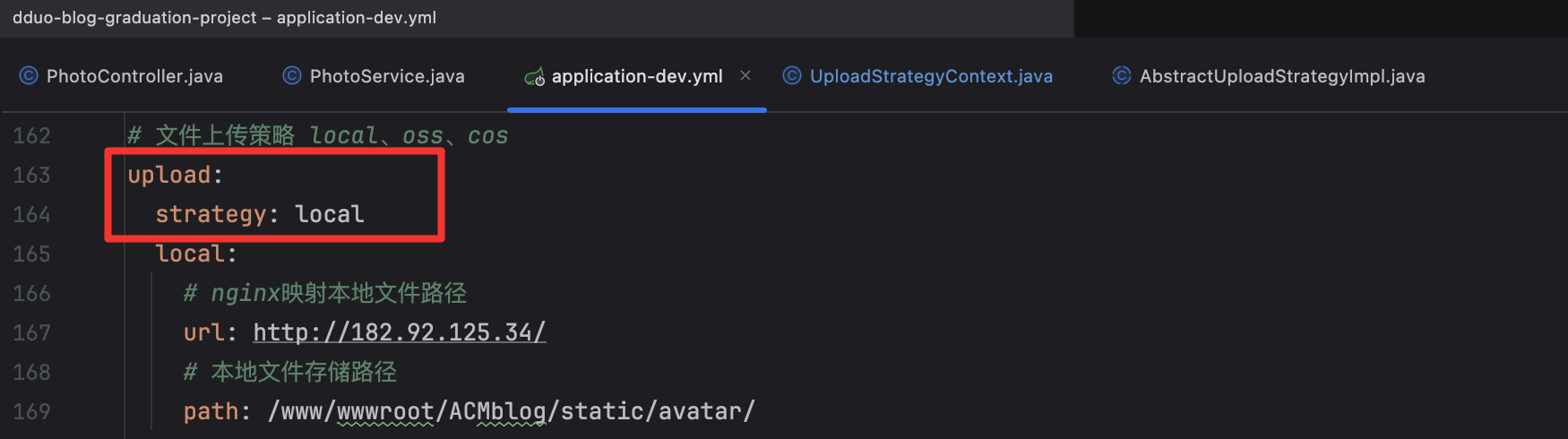
除了这个常量,策略上下文里面还有一个 map
这个 map 的 key 是 string 策略名称,value 是对应的下载策略
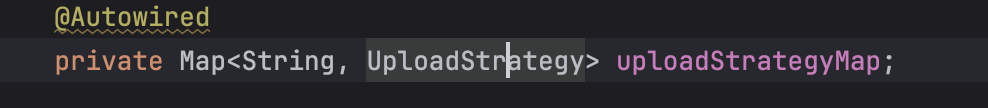
我们通过 我们写在配置文件里面的配置去 map 去调对应的策略
UploadStrategy 是一个接口
这边采用模版方法设计模式
即采用接口+抽象类的方式
我们在接口中定义统一规范
应对当前上传业务,我们只需要一个 uploadFile 方法即可
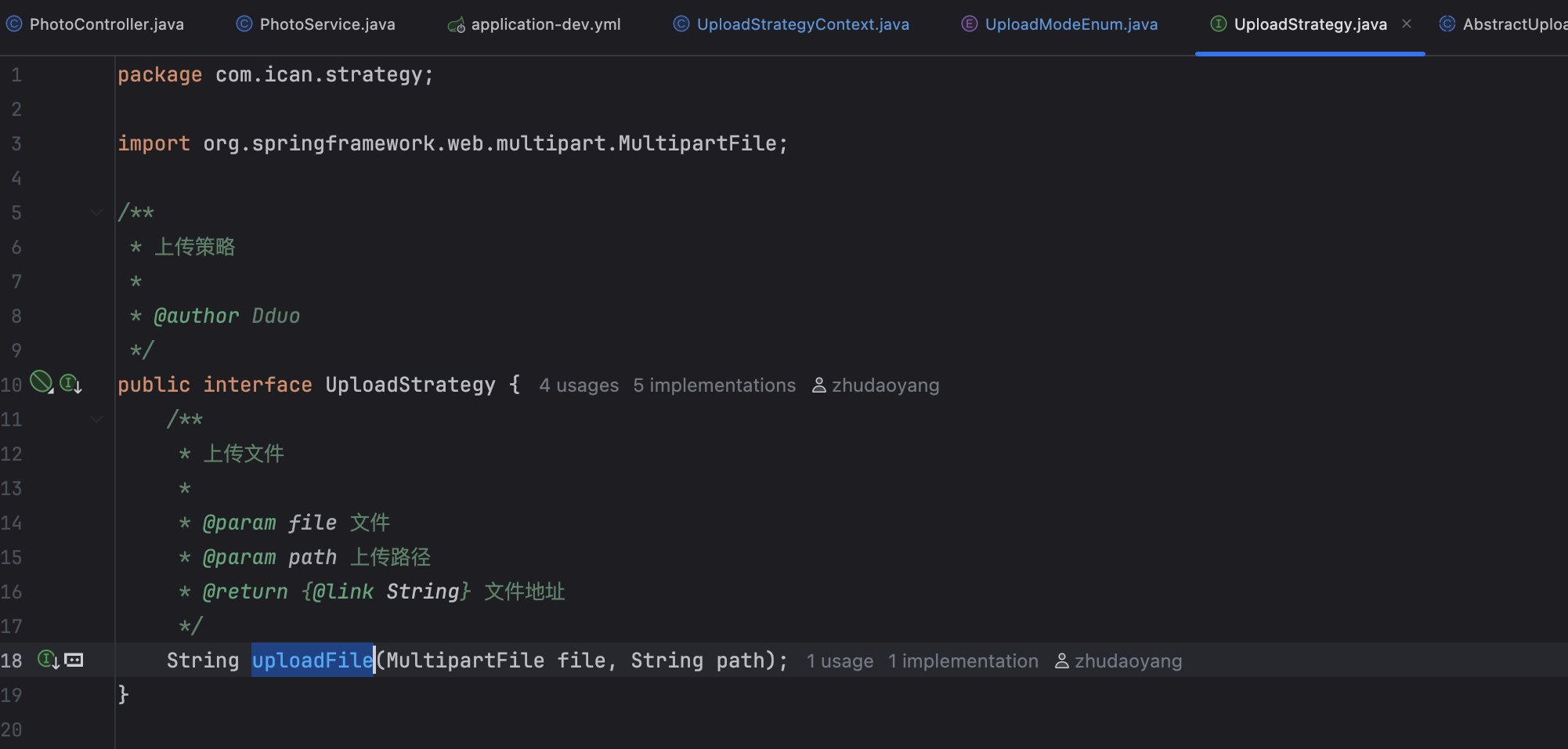
接着是模版
我们想一下我们的模版应该怎么去写
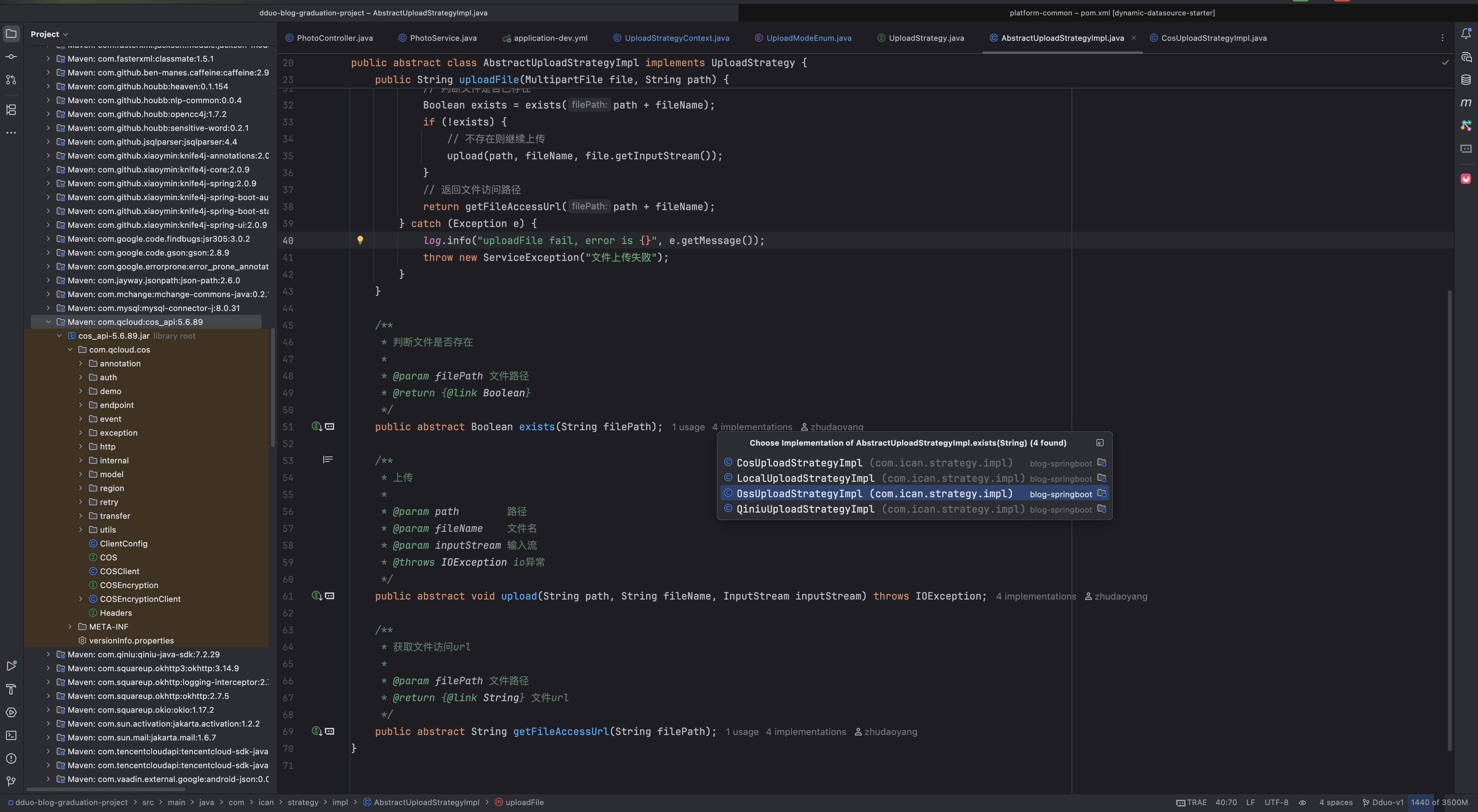
我们想到每一个实现类,都要写一个上传方法
这对应着我们调不同的客户端去执行相应的方法,uploadFile()这个方法里面会调取这个方法
然后我们就应该能想到,还有一个检查文件是否存在的方法
接着我们还要有一个出口,就是获取文件的路径
毕竟客户端的自己实现逻辑都不同,所以我们都要进行重写
package com.ican.strategy.impl;
import com.ican.exception.ServiceException;
import com.ican.strategy.UploadStrategy;
import com.ican.utils.FileUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 抽象上传模板
*
* @author Dduo
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public abstract class AbstractUploadStrategyImpl implements UploadStrategy {
@Override
public String uploadFile(MultipartFile file, String path) {
try {
// 获取文件md5值
String md5 = FileUtils.getMd5(file.getInputStream());
// 获取文件扩展名
String extName = FileUtils.getExtension(file);
// 重新生成文件名
String fileName = md5 + "." + extName;
// 判断文件是否已存在
Boolean exists = exists(path + fileName);
if (!exists) {
// 不存在则继续上传
upload(path, fileName, file.getInputStream());
}
// 返回文件访问路径
return getFileAccessUrl(path + fileName);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("uploadFile fail, error is {}", e.getMessage());
throw new ServiceException("文件上传失败");
}
}
/**
* 判断文件是否存在
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @return {@link Boolean}
*/
public abstract Boolean exists(String filePath);
/**
* 上传
*
* @param path 路径
* @param fileName 文件名
* @param inputStream 输入流
* @throws IOException io异常
*/
public abstract void upload(String path, String fileName, InputStream inputStream) throws IOException;
/**
* 获取文件访问url
*
* @param filePath 文件路径
* @return {@link String} 文件url
*/
public abstract String getFileAccessUrl(String filePath);
}这边有一个 cos 实现逻辑
仅仅供参考
package com.ican.strategy.impl;
import com.ican.config.properties.CosProperties;
import com.qcloud.cos.COSClient;
import com.qcloud.cos.ClientConfig;
import com.qcloud.cos.auth.BasicCOSCredentials;
import com.qcloud.cos.auth.COSCredentials;
import com.qcloud.cos.exception.CosClientException;
import com.qcloud.cos.exception.CosServiceException;
import com.qcloud.cos.http.HttpProtocol;
import com.qcloud.cos.model.ObjectMetadata;
import com.qcloud.cos.region.Region;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* cos上传策略
*
* @author Dduo
*/
@Slf4j
@Service("cosUploadStrategyImpl")
public class CosUploadStrategyImpl extends AbstractUploadStrategyImpl {
@Autowired
private CosProperties cosProperties;
@Override
public Boolean exists(String filePath) {
return getCosClient().doesObjectExist(cosProperties.getBucketName(), filePath);
}
@Override
public void upload(String path, String fileName, InputStream inputStream) {
COSClient cosClient = getCosClient();
try {
ObjectMetadata objectMetadata = new ObjectMetadata();
// 上传的流如果能够获取准确的流长度,则推荐一定填写 content-length
objectMetadata.setContentLength(inputStream.available());
// 调用cos方法上传
cosClient.putObject(cosProperties.getBucketName(), path + fileName, inputStream, objectMetadata);
} catch (CosServiceException e) {
log.error("Error Message:" + e.getErrorMessage());
log.error("Error Code:" + e.getErrorCode());
log.info("Request ID:" + e.getRequestId());
} catch (CosClientException e) {
log.error("Caught an CosClientException, Error Message:" + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("Caught an IOException, Error Message:" + e.getMessage());
} finally {
cosClient.shutdown();
}
}
@Override
public String getFileAccessUrl(String filePath) {
return cosProperties.getUrl() + filePath;
}
/**
* 获取cosClient
*
* @return {@link COSClient} cosClient
*/
private COSClient getCosClient() {
// 1 初始化用户身份信息(secretId, secretKey)。
COSCredentials cred = new BasicCOSCredentials(cosProperties.getSecretId(), cosProperties.getSecretKey());
// 2 设置 bucket 的地域, COS 地域的简称请参照 https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/436/6224
Region region = new Region(cosProperties.getRegion());
ClientConfig clientConfig = new ClientConfig(region);
// 这里建议设置使用 https 协议
// 从 5.6.54 版本开始,默认使用了 https
clientConfig.setHttpProtocol(HttpProtocol.https);
// 3 生成 cos 客户端。
return new COSClient(cred, clientConfig);
}
}