一、多窗口通信方式
C# WinForms 多窗口通信的方式有:
- 构造函数传递
- 属性传递
- 接口
- 事件通信
- 委托回调
- 静态消息中心
二、示例代码
C# WinForms中多窗口之间各种通信方式的示例。示例包含一个主窗口和多个子窗口,测试开发中常用的几种通信方式。
项目结构如下:
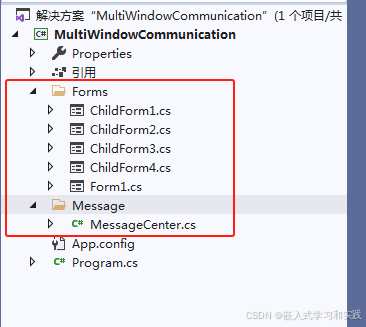
2.1 MessageCenter.cs 代码
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Message
{
//class MessageCenter
//{
//}
// 4. 使用静态类作为消息中心
public static class MessageCenter
{
// 定义消息接收事件
public static event Action<string, string> MessageReceived;
// 发送消息的方法
public static void SendMessage(string sender, string message)
{
// 触发所有订阅者的事件
MessageReceived?.Invoke(sender, message);
}
}
}2.2 ChildForm1.cs 代码
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
// 定义接口用于子窗口向主窗口通信
public interface IMainForm
{
void ReceiveMessageFromChild1(string message);
}
public partial class ChildForm1 : Form
{
public ChildForm1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 2. 使用属性传递数据
private string _receivedMessage;
public string ReceivedMessage
{
get => _receivedMessage;
set
{
_receivedMessage = value;
txtReceived.Text = $"收到主窗口消息: {value}";
}
}
// 保存主窗口引用
private readonly IMainForm _mainForm;
// 1. 使用构造函数传递数据
public ChildForm1(string initialMessage, IMainForm mainForm)
{
InitializeComponent();
_mainForm = mainForm;
txtReceived.Text = initialMessage;
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text) && _mainForm != null)
{
// 通过接口向主窗口发送消息
_mainForm.ReceiveMessageFromChild1(txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.3 ChildForm2.cs 代码
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm2 : Form
{
// 定义事件用于向主窗口发送消息
public event EventHandler<string> SendMessageToMain;
public ChildForm2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 供主窗口调用的方法,接收主窗口消息
public void ReceiveMessage(string message)
{
txtReceived.Text = $"收到主窗口消息: {message}";
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text))
{
// 触发事件,向主窗口发送消息
SendMessageToMain?.Invoke(this, txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.4 ChildForm3.cs 代码
csharp
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm3 : Form
{
// 定义委托
private Action<string> _callback;
public ChildForm3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
// 设置回调函数
public void SetCallback(Action<string> callback)
{
_callback = callback;
}
private void btnSendToMain_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text) && _callback != null)
{
// 通过委托向主窗口发送消息
_callback(txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
}
}2.5 ChildForm4.cs 代码
csharp
using MultiWindowCommunication.Message;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication.Forms
{
public partial class ChildForm4 : Form
{
public ChildForm4()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 订阅消息中心事件
MessageCenter.MessageReceived += OnMessageReceived;
}
private void btnSendToAll_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtMessage.Text))
{
// 通过消息中心发送消息
MessageCenter.SendMessage("ChildForm4", txtMessage.Text);
txtMessage.Clear();
}
}
// 接收消息中心的消息
private void OnMessageReceived(string sender, string message)
{
// 过滤掉自己发送的消息
if (sender != "ChildForm4")
{
txtReceived.Text = $"从{sender}收到消息: {message}";
}
}
private void ChildForm4_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// 取消订阅
MessageCenter.MessageReceived -= OnMessageReceived;
}
}
}2.6 MainForm.cs 代码
csharp
using MultiWindowCommunication.Forms;
using MultiWindowCommunication.Message;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MultiWindowCommunication
{
public partial class MainForm : Form, IMainForm
{
// 子窗口实例
private ChildForm1 _childForm1;
private ChildForm2 _childForm2;
private ChildForm3 _childForm3;
private ChildForm4 _childForm4;
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponent();
// 初始化消息中心事件
MessageCenter.MessageReceived += OnMessageFromMessageCenter;
}
#region 打开子窗口的方法
private void btnOpenForm1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm1 == null || _childForm1.IsDisposed)
{
// 1. 使用构造函数传递数据
_childForm1 = new ChildForm1("来自主窗口的初始消息", this);//(IMainForm)this
_childForm1.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm1.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm2 == null || _childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
_childForm2 = new ChildForm2();
// 2. 使用事件进行通信(子窗口到主窗口)
_childForm2.SendMessageToMain += OnMessageFromChildForm2;
_childForm2.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm2.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm3 == null || _childForm3.IsDisposed)
{
// 3. 使用委托进行通信(子窗口回调主窗口)
_childForm3 = new ChildForm3();
_childForm3.SetCallback(OnMessageFromChildForm3);
_childForm3.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm3.BringToFront();
}
}
private void btnOpenForm4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm4 == null || _childForm4.IsDisposed)
{
// 4. 使用静态类消息中心进行通信
_childForm4 = new ChildForm4();
_childForm4.Show();
}
else
{
_childForm4.BringToFront();
}
}
#endregion
#region 接收来自子窗口的消息
// 处理来自ChildForm1的消息(通过接口)
public void ReceiveMessageFromChild1(string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"从ChildForm1收到: {message}");
}
// 处理来自ChildForm2的消息(通过事件)
private void OnMessageFromChildForm2(object sender, string e)
{
AddMessageToLog($"从ChildForm2收到: {e}");
}
// 处理来自ChildForm3的消息(通过委托)
private void OnMessageFromChildForm3(string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"从ChildForm3收到: {message}");
}
// 处理来自消息中心的消息
private void OnMessageFromMessageCenter(string sender, string message)
{
AddMessageToLog($"从{sender}通过消息中心收到: {message}");
}
#endregion
#region 向子窗口发送消息
private void btnSendToForm1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm1 != null && !_childForm1.IsDisposed)
{
// 使用属性传递数据(主窗口到子窗口)
_childForm1.ReceivedMessage = txtMessage.Text;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("请先打开ChildForm1");
}
}
private void btnSendToForm2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (_childForm2 != null && !_childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
// 直接调用子窗口方法
_childForm2.ReceiveMessage(txtMessage.Text);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("请先打开ChildForm2");
}
}
private void btnSendToALL_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// 通过消息中心向所有窗口广播消息
MessageCenter.SendMessage("MainForm", txtMessage.Text);
}
#endregion
// 添加消息到日志
private void AddMessageToLog(string message)
{
txtLog.AppendText($"[{DateTime.Now:HH:mm:ss}] {message}{Environment.NewLine}");
txtLog.ScrollToCaret();
}
private void MainForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// 清理事件订阅
MessageCenter.MessageReceived -= OnMessageFromMessageCenter;
// 关闭所有子窗口
if (_childForm1 != null && !_childForm1.IsDisposed)
_childForm1.Close();
if (_childForm2 != null && !_childForm2.IsDisposed)
{
_childForm2.SendMessageToMain -= OnMessageFromChildForm2;
_childForm2.Close();
}
if (_childForm3 != null && !_childForm3.IsDisposed)
_childForm3.Close();
if (_childForm4 != null && !_childForm4.IsDisposed)
_childForm4.Close();
}
}
}2.7 通信方式详解
WinForms中的几种常用的多窗口通信方式:
-
构造函数传递(ChildForm1)
- 适用于初始化时需要传递数据的场景
- 优点:简单直接,适合初始化数据
- 缺点:只能在创建窗口时传递一次
-
属性传递(ChildForm1)
- 适用于需要多次传递数据的场景
- 优点:可以在窗口生命周期内随时设置
- 缺点:需要手动检查窗口是否已释放
-
事件通信(ChildForm2)
- 适用于子窗口主动向父窗口发送消息
- 优点:解耦性好,子窗口不需要知道父窗口具体类型
- 缺点:需要手动管理事件订阅和取消订阅
-
委托回调(ChildForm3)
- 适用于父窗口需要对子窗口消息做出响应的场景
- 优点:灵活,可以传递复杂参数
- 缺点:需要维护委托引用
-
静态消息中心(ChildForm4)
- 适用于多个窗口之间需要互相通信的复杂场景
- 优点:完全解耦,任意窗口间可通信
- 缺点:需要管理事件订阅,可能导致内存泄漏
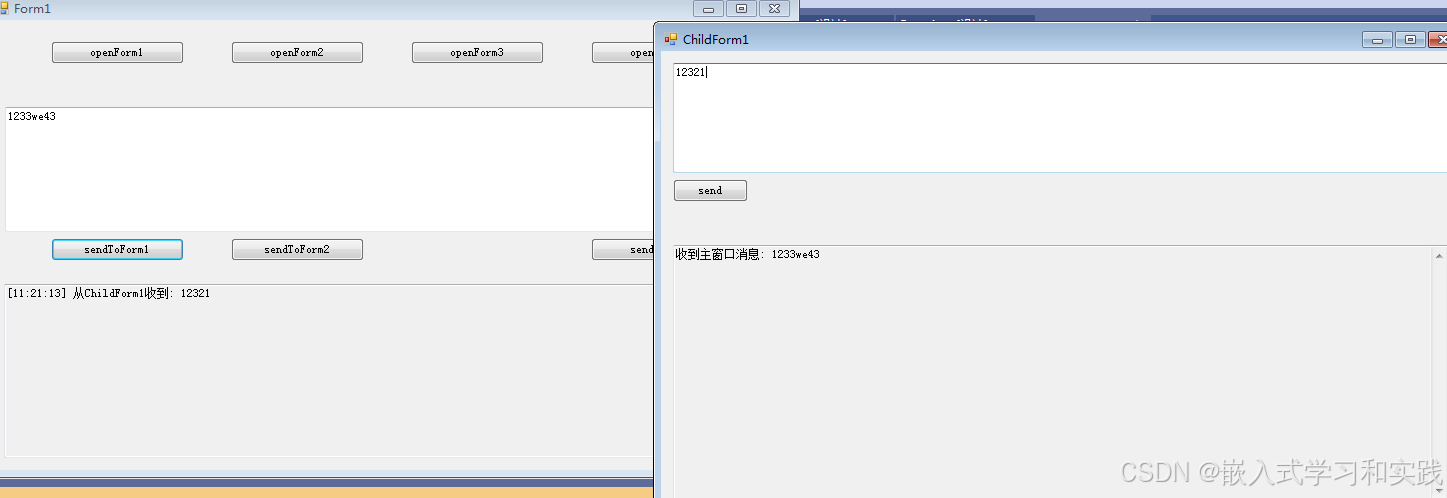
三、测试结果
四、建议
- 简单的父子窗口通信,优先使用事件 或委托
- 初始化数据传递,使用构造函数
- 复杂的多窗口通信场景,使用静态消息中心
- 无论使用哪种方式,都要注意在窗口关闭时清理事件订阅,避免内存泄漏
可以根据实际项目需求选择合适的通信方式,也可以结合多种方式使用。