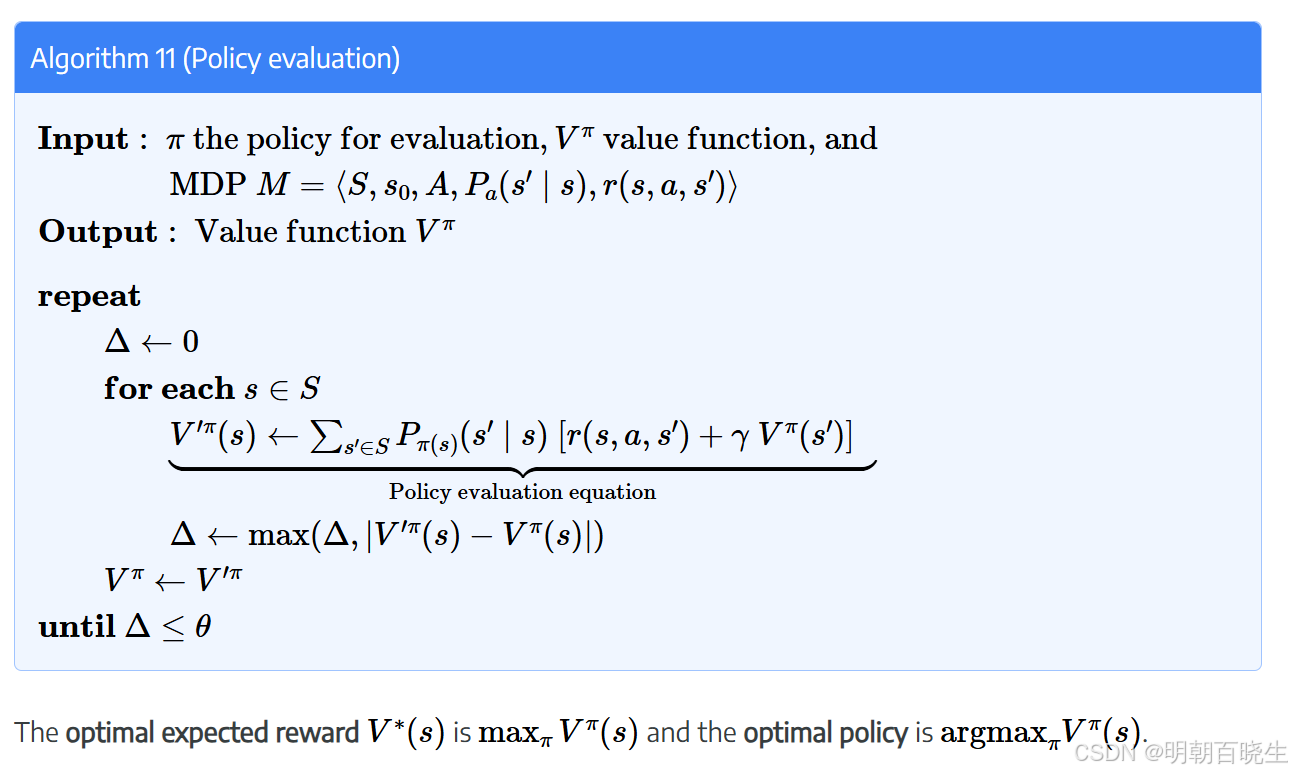
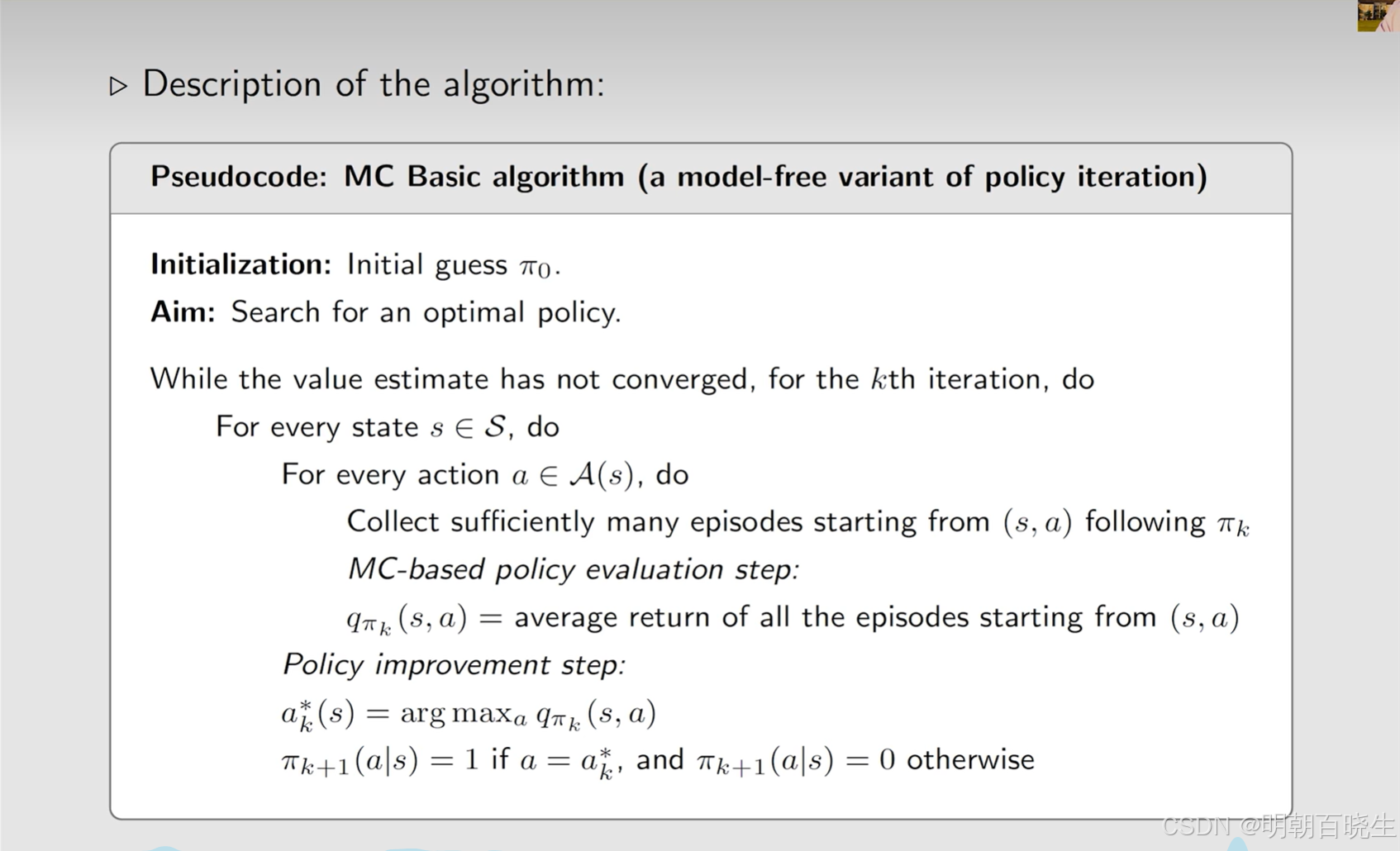
前文介绍了基于模型的(model-based)强化学习的两种方法:
值迭代(value-iteration)和策略迭代(policy iteration)。
当环境中状态转移概率未知时,就需要采用无模型(model-free)的强化学习方法。在此,我们介绍一种经典的无模型强化学习方法------蒙特卡洛学习(Monte Carlo Learning),该方法主要包含三种算法:
蒙特卡洛基本算法(MC Basic)
蒙特卡洛起始探索算法(MC Exploring starts)
蒙特卡洛 ε-贪婪算法(MC ε-greedy)
简介
-
Monte Carlo Policy Evaluation
-
Policy Imporve
-
python 代码实现
一 简介:
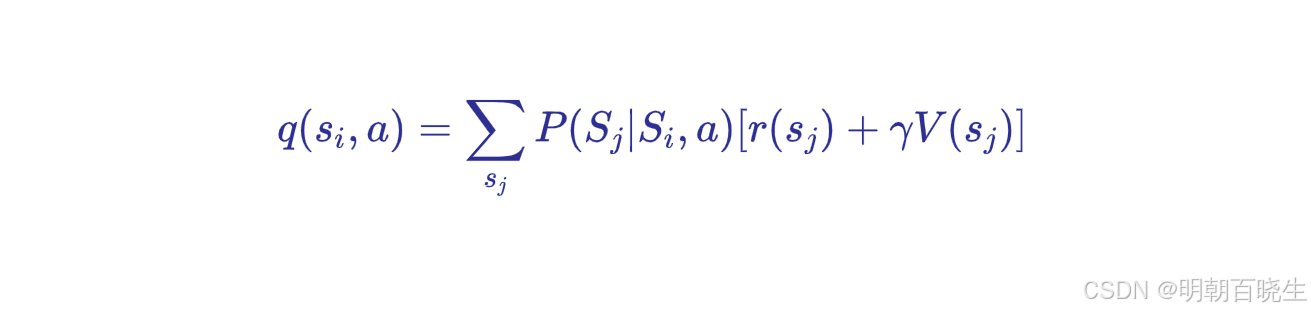
在使用基于模型(model-based)的强化学习方法,特别是进行策略迭代时,我们通常会通过上述公式来求解 状态-动作累积奖赏的数学期望 q。然而,状态转移概率往往是未知的,在这种情况下,我们通常会采用蒙特卡洛(Monte Carlo)方法进行求解(该方法本质上是通过大数定律来计算数学期望)。
二 MC-Basic 算法
该算法和Policy iteration 流程是一样的,主要是Policy evaluation更换成了Monte Carlo Polciy Evaluation
- Policy evaluation(Monte Carlo Polciy Evaluation)
- policy improvement
2.1 Policy iteration(model-based)
其中 Policy evaluation
在policy iteratoin ,利用了状态转移概率计算了state value
2.2 Monte Carlo Policy Evaluation(model-free)
在 Policy iteration 的时候计算了 state-action 的均值(大数定律里面的切比雪夫不等式)
但是不实用,效率低
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Oct 17 16:42:46 2025
@author: chengxf2
"""
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
蒙特卡洛学习在网格世界环境中的实现
Created on Mon Sep 29 21:37:49 2025
@author: cxf
"""
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
import random
from matplotlib import rcParams
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
# 添加中文字体支持
rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 添加多个备选中文字体,确保跨平台兼容性
chinese_fonts = ['SimHei', 'Microsoft YaHei', 'WenQuanYi Micro Hei', 'Source Han Sans CN']
available_fonts = [font.name for font in fm.fontManager.ttflist]
valid_fonts = [f for f in chinese_fonts if f in available_fonts]
if valid_fonts:
rcParams['font.family'] = valid_fonts[0]
else:
print("警告:未找到合适的中文字体,中文显示可能异常")
class Gridworld:
"""网格世界环境,用于蒙特卡洛学习"""
def __init__(self, grid, rewards):
"""
初始化网格世界环境
参数:
grid: 表示网格世界的二维数组
rewards: 映射状态类型到奖励值的字典
"""
self.grid = np.array(grid)
self.rewards = rewards
self.rows, self.cols = self.grid.shape
self.actions = ['up', 'down', 'left', 'right']
self.action_effects = {
'up': (-1, 0), # 向上移动
'down': (1, 0), # 向下移动
'left': (0, -1), # 向左移动
'right': (0, 1) # 向右移动
}
# 初始化特殊状态位置
self.start_state = None # 起始状态
self.goal_states = [] # 目标状态列表
self.hole_states = [] # 陷阱状态列表
self._find_special_states()
def _find_special_states(self):
"""在网格中识别起始状态、目标状态和陷阱状态"""
for row in range(self.rows):
for col in range(self.cols):
state_type = self.grid[row, col]
state_position = (row, col)
if state_type == 'S':
self.start_state = state_position
elif state_type == 'G':
self.goal_states.append(state_position)
elif state_type == 'H':
self.hole_states.append(state_position)
def reset(self):
"""重置环境到起始状态"""
return self.start_state
def step(self, state, action):
"""
在环境中执行一步动作
参数:
state: 当前状态 (行, 列)
action: 要执行的动作
返回:
next_state: 执行动作后的下一个状态
reward: 转移的奖励值
done: 是否终止回合
"""
current_row, current_col = state
row_change, col_change = self.action_effects[action]
# 计算新位置,确保不超出边界
new_row = max(0, min(self.rows - 1, current_row + row_change))
new_col = max(0, min(self.cols - 1, current_col + col_change))
next_state = (new_row, new_col)
# 根据下一个状态类型获取奖励
state_type = self.grid[next_state]
reward = self.rewards[state_type]
# 检查回合是否终止(到达目标、陷阱或无法移动)
reached_terminal = state_type in ['G', 'H']
stuck_in_position = (current_row == new_row and current_col == new_col)
done = reached_terminal or stuck_in_position
return next_state, reward, done
def get_state_type(self, state):
"""获取状态的类型"""
row, col = state
return self.grid[row, col]
def is_terminal(self, state):
"""检查状态是否为终止状态(目标或陷阱)"""
return self.get_state_type(state) in ['G', 'H']
def render(self, values=None, policy=None, title=None):
"""
可视化网格世界,可选显示价值函数和策略
参数:
values: 状态价值的二维数组(可选)
policy: 策略的二维数组(可选)
title: 图表标题(可选)
"""
figure, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
# 创建网格的颜色映射
color_map = ListedColormap(['white', 'lightblue', 'lightcoral', 'lightgreen'])
# 创建可视化矩阵
visualization_grid = np.zeros_like(self.grid, dtype=float)
for row in range(self.rows):
for col in range(self.cols):
state_type = self.grid[row, col]
visualization_grid[row, col] = self._get_state_color_value(state_type)
# 显示网格
axes.imshow(visualization_grid, cmap=color_map)
# 添加文本和策略箭头
self._add_grid_annotations(axes, values, policy)
# 配置图表外观
self._configure_plot_appearance(axes)
if title:
# 使用本地处理的标题变量确保中文字符正确显示
local_title = title
try:
axes.set_title(local_title, fontsize=16)
except Exception as e:
print(f"标题设置失败: {e}")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
#plt.savefig('gridworld_visualization.png') # 保存为文件确保中文正确显示
#plt.close() # 关闭图形以避免内存泄漏
def _get_state_color_value(self, state_type):
"""获取状态类型对应的颜色值"""
color_mapping = {
'S': 0.0, # 白色 - 起始状态
'F': 0.33, # 浅蓝色 - 自由状态
'H': 0.66, # 浅珊瑚色 - 陷阱状态
'G': 1.0 # 浅绿色 - 目标状态
}
return color_mapping.get(state_type, 0.0)
def _add_grid_annotations(self, axes, values, policy):
"""向网格可视化添加文本和箭头"""
for row in range(self.rows):
for col in range(self.cols):
state_type = self.grid[row, col]
text = state_type
# 如果提供了价值函数,添加价值信息
if values is not None:
# 使用格式化字符串确保数值显示正确
text += f'\n{values[row, col]:.2f}'
# 尝试使用中文字体添加文本
try:
axes.text(col, row, text, ha='center', va='center',
fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
except Exception as e:
print(f"文本添加失败: {e}")
# 如果提供了策略,添加策略箭头
if policy is not None and not self.is_terminal((row, col)):
self._draw_policy_arrow(axes, row, col, policy[row, col])
def _draw_policy_arrow(self, axes, row, col, action):
"""绘制表示策略动作的箭头"""
arrow_vectors = {
'up': (0, -0.3), # 向上箭头
'down': (0, 0.3), # 向下箭头
'left': (-0.3, 0), # 向左箭头
'right': (0.3, 0) # 向右箭头
}
if action in arrow_vectors:
dx, dy = arrow_vectors[action]
try:
axes.arrow(col, row, dx, dy, head_width=0.2, head_length=0.1,
fc='black', ec='black')
except Exception as e:
print(f"箭头绘制失败: {e}")
def _configure_plot_appearance(self, axes):
"""配置图表的视觉外观"""
# 添加网格线
axes.set_xticks(np.arange(-0.5, self.cols, 1), minor=True)
axes.set_yticks(np.arange(-0.5, self.rows, 1), minor=True)
axes.grid(which="minor", color="gray", linestyle='-', linewidth=2)
axes.tick_params(which="minor", size=0)
# 移除主刻度
axes.set_xticks([])
axes.set_yticks([])
class MonteCarloBasicAgent:
"""蒙特卡洛基础学习智能体"""
def __init__(self, environment, discount_factor=0.9):
"""
初始化蒙特卡洛基础智能体
参数:
environment: 网格世界环境
discount_factor: 未来奖励的折扣因子
"""
self.environment = environment
self.discount_factor = discount_factor
self.actions = environment.actions
# 初始化数据结构
self.q_values = {} # 状态 -> 动作价值列表
self.returns_data = {} # (状态, 动作) -> 回报列表
self.policy = {} # 策略:状态 -> 动作
self._initialize_policy()
def _initialize_policy(self):
"""为所有非终止状态初始化随机策略"""
for row in range(self.environment.rows):
for col in range(self.environment.cols):
state = (row, col)
if not self.environment.is_terminal(state):
self.policy[state] = random.choice(self.actions)
def _ensure_state_in_q_values(self, state):
"""确保状态存在于Q值字典中,并用零值初始化"""
if state not in self.q_values:
self.q_values[state] = [0.0] * len(self.actions)
def _ensure_state_action_in_returns(self, state, action):
"""确保状态-动作对存在于回报字典中"""
state_action = (state, action)
if state_action not in self.returns_data:
self.returns_data[state_action] = []
def get_q_value(self, state, action):
"""获取状态-动作对的Q值"""
self._ensure_state_in_q_values(state)
action_index = self.actions.index(action)
return self.q_values[state][action_index]
def update_q_value(self, state, action, new_value):
"""更新状态-动作对的Q值"""
self._ensure_state_in_q_values(state)
action_index = self.actions.index(action)
self.q_values[state][action_index] = new_value
def add_return_data(self, state, action, return_value):
"""为状态-动作对添加回报值"""
self._ensure_state_action_in_returns(state, action)
self.returns_data[(state, action)].append(return_value)
def get_average_return(self, state, action):
"""计算状态-动作对的平均回报"""
self._ensure_state_action_in_returns(state, action)
returns = self.returns_data[(state, action)]
if not returns:
return 0.0
return sum(returns) / len(returns)
def _generate_episode_from_state_action(self, start_state, start_action):
"""
从特定的状态-动作对生成一个回合
参数:
start_state: 起始状态 (行, 列)
start_action: 起始动作
返回:
episode: (状态, 动作, 奖励) 元组列表
"""
episode = []
current_state = start_state
# 第一步:执行指定的动作
next_state, reward, done = self.environment.step(current_state, start_action)
episode.append((current_state, start_action, reward))
#print("\n s1",start_state, start_action, "done",done)
if done:
#print("\n s2",start_state, start_action, "done",done)
return episode
current_state = next_state
iter_num = 0
max_iter = 50
# 后续步骤使用当前策略继续
while True:
if self.environment.is_terminal(current_state):
break
iter_num +=1
action = self.policy[current_state]
next_state, reward, done = self.environment.step(current_state, action)
episode.append((current_state, action, reward))
#print("\n s3",next_state, "done",done)
if done or iter_num>max_iter:
break
current_state = next_state
return episode
def update_policy(self):
"""更新策略为基于Q值的贪婪策略"""
for state in self.policy:
if not self.environment.is_terminal(state):
self._ensure_state_in_q_values(state)
state_q_values = self.q_values[state]
# 找到最佳动作
best_action_index = self._find_best_action_index(state_q_values)
self.policy[state] = self.actions[best_action_index]
def _find_best_action_index(self, q_values):
"""找到具有最大Q值的动作索引"""
best_index = 0
best_value = q_values[0]
for index in range(1, len(q_values)):
if q_values[index] > best_value:
best_value = q_values[index]
best_index = index
return best_index
def learn(self, num_iterations=20, episodes_per_state_action=5):
"""
蒙特卡洛基础算法
参数:
num_iterations: 策略迭代步数
episodes_per_state_action: 每个状态-动作对生成的回合数
"""
for iteration in range(num_iterations):
print(f"第 {iteration + 1}/{num_iterations} 次迭代")
# 策略评估:估计当前策略的Q值
# 访问所有状态-动作对
state_action_count = 0
total_state_actions = 0
n = len(self.actions)
for row in range(self.environment.rows):
for col in range(self.environment.cols):
total_state_actions += n
for row in range(self.environment.rows):
for col in range(self.environment.cols):
state = (row, col)
# 跳过终止状态
if self.environment.is_terminal(state):
continue
# 评估该状态的每个动作
print(f"处理状态 ({row},{col})")
for action in self.actions:
state_action_count += 1
if state_action_count % 20 == 0:
print(f" 处理状态-动作对 {state_action_count}/{total_state_actions}")
# 从(状态, 动作)开始生成多个回合
for episode_count in range(episodes_per_state_action):
episode = self._generate_episode_from_state_action(state, action)
self._process_episode_for_state_action(episode, state, action)
# 策略改进:更新为基于Q值的贪婪策略
self.update_policy()
# 打印进度
if (iteration + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f" 已完成 {iteration + 1} 次迭代")
# 显示当前价值函数
current_values = self.get_value_function()
print("当前价值函数:")
print(current_values)
def _process_episode_for_state_action(self, episode, target_state, target_action):
"""
处理回合以更新特定状态-动作对的Q值
参数:
episode: (状态, 动作, 奖励) 元组列表
target_state: 要评估的目标状态
target_action: 要评估的目标动作
"""
total_return = 0.0
found_target = False
# 反向处理回合以计算回报
for step in reversed(range(len(episode))):
state, action, reward = episode[step]
total_return = self.discount_factor * total_return + reward
# 检查这是否是我们的目标状态-动作对
if state == target_state and action == target_action:
found_target = True
break
# 只有在回合中找到目标状态-动作对时才更新
if found_target:
self.add_return_data(target_state, target_action, total_return)
average_return = self.get_average_return(target_state, target_action)
self.update_q_value(target_state, target_action, average_return)
def get_value_function(self):
"""从Q值获取价值函数"""
value_function = np.zeros((self.environment.rows, self.environment.cols))
for row in range(self.environment.rows):
for col in range(self.environment.cols):
state = (row, col)
if not self.environment.is_terminal(state):
if state in self.q_values:
value_function[row, col] = max(self.q_values[state])
else:
value_function[row, col] = 0.0
return value_function
def get_policy_matrix(self):
"""获取策略的二维矩阵用于可视化"""
policy_matrix = np.empty((self.environment.rows, self.environment.cols),
dtype=object)
for row in range(self.environment.rows):
for col in range(self.environment.cols):
state = (row, col)
if self.environment.is_terminal(state):
policy_matrix[row, col] = ''
else:
policy_matrix[row, col] = self.policy[state]
return policy_matrix
def main():
"""主函数:演示网格世界中的蒙特卡洛基础学习"""
# 定义网格世界布局
grid_layout = [
['S', 'F', 'F', 'F'],
['F', 'H', 'F', 'H'],
['F', 'F', 'F', 'H'],
['H', 'F', 'F', 'G']
]
# 定义每个状态类型的奖励
state_rewards = {
'S': 0, # 起始状态
'G': 1, # 目标状态
'H': -1, # 陷阱状态
'F': 0 # 自由状态
}
# 创建环境
environment = Gridworld(grid_layout, state_rewards)
# 显示初始网格世界
print("第一步:初始网格世界:")
environment.render(title="初始网格世界")
# 创建智能体
agent = MonteCarloBasicAgent(environment, discount_factor=0.9)
# 运行蒙特卡洛基础算法
print("第二步:运行蒙特卡洛基础算法...")
agent.learn(num_iterations=10, episodes_per_state_action=3)
# 获取价值函数和策略用于可视化
value_function = agent.get_value_function()
policy_matrix = agent.get_policy_matrix()
# 显示结果
print("第三步:蒙特卡洛基础算法后的价值函数:")
environment.render(values=value_function,
title="MC基础算法后的价值函数")
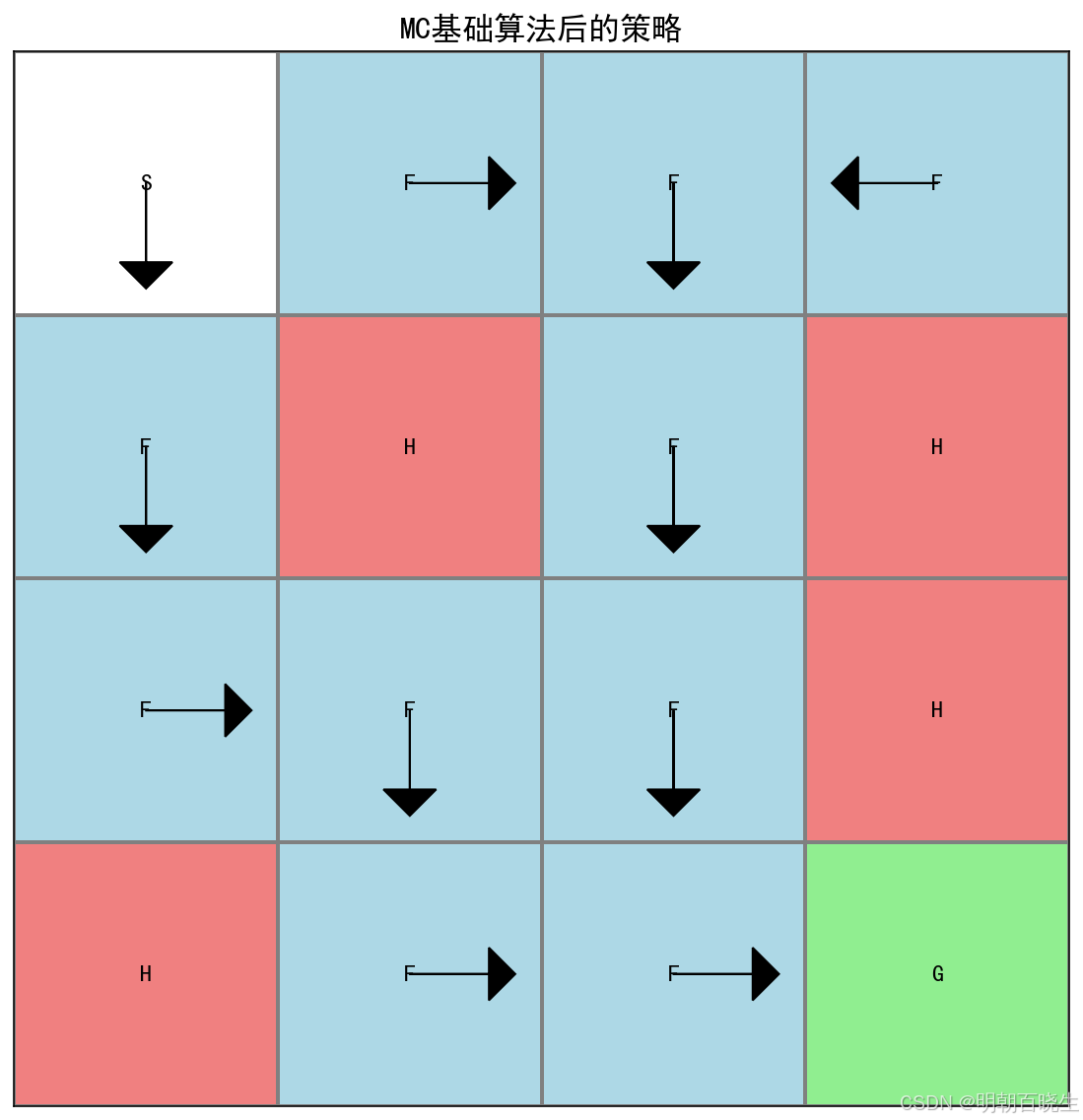
print("第四步:蒙特卡洛基础算法后的策略:")
environment.render(policy=policy_matrix,
title="MC基础算法后的策略")
# 打印样本Q值用于检查
print("\n第五步:样本Q值:")
for row in range(environment.rows):
for col in range(environment.cols):
state = (row, col)
if not environment.is_terminal(state):
state_q_values = agent.q_values.get(state, [0.0] * len(agent.actions))
q_value_dict = dict(zip(agent.actions, state_q_values))
print(f"状态 ({row},{col}): {q_value_dict}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()