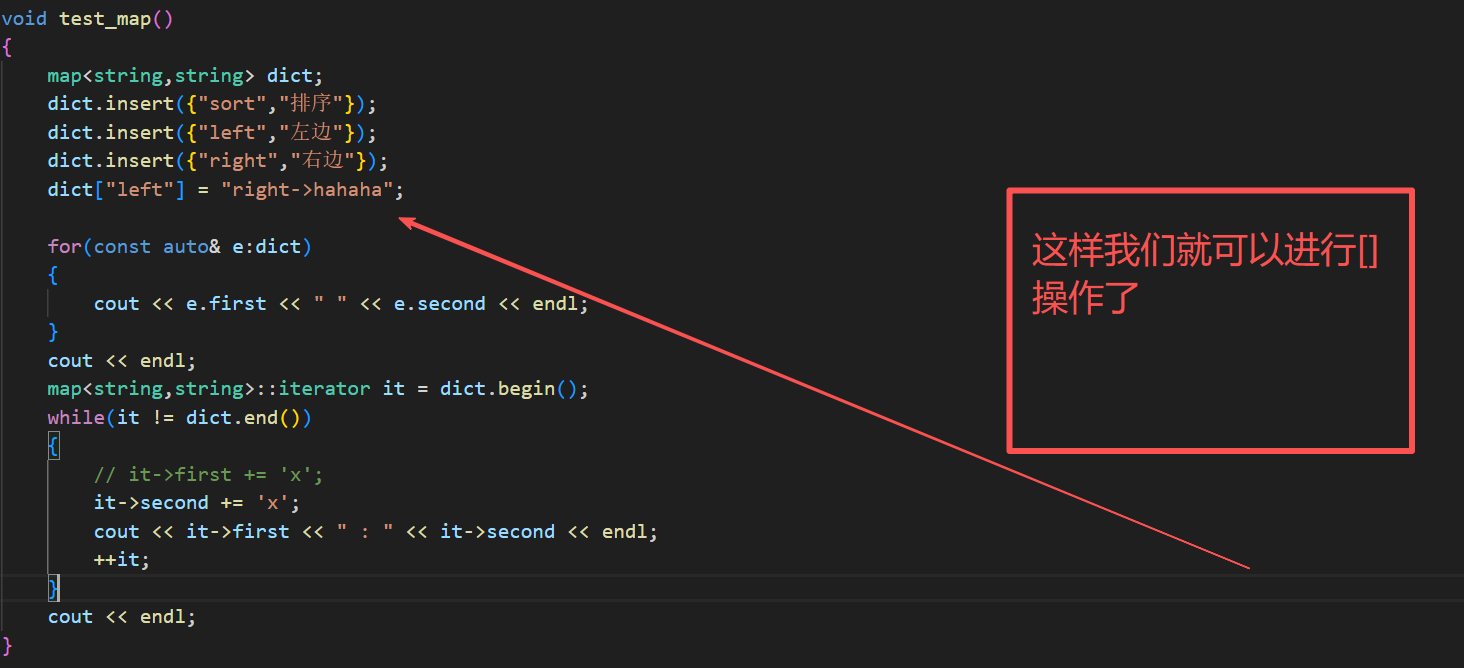
总的代码会放在最后面
一.set和map源码分析
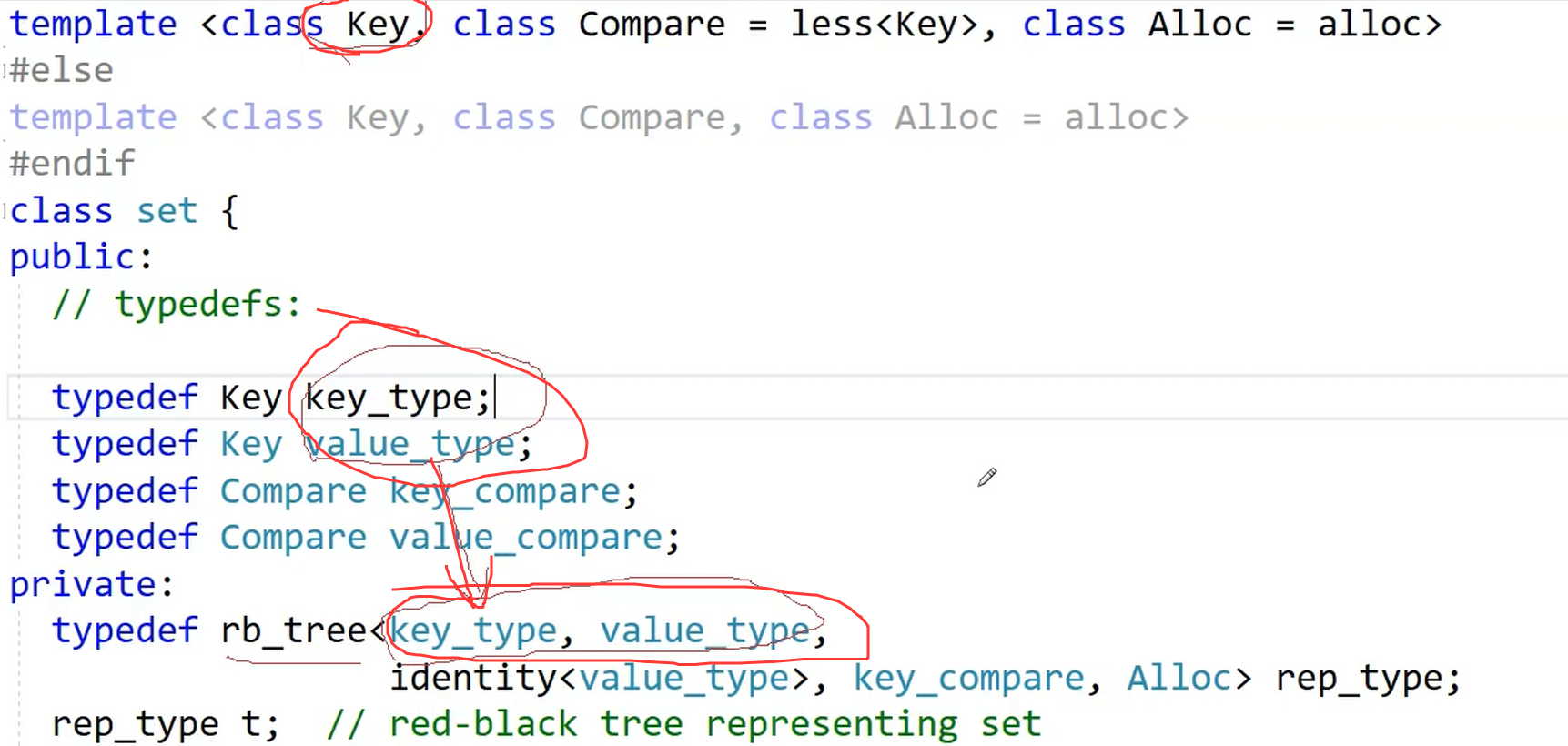
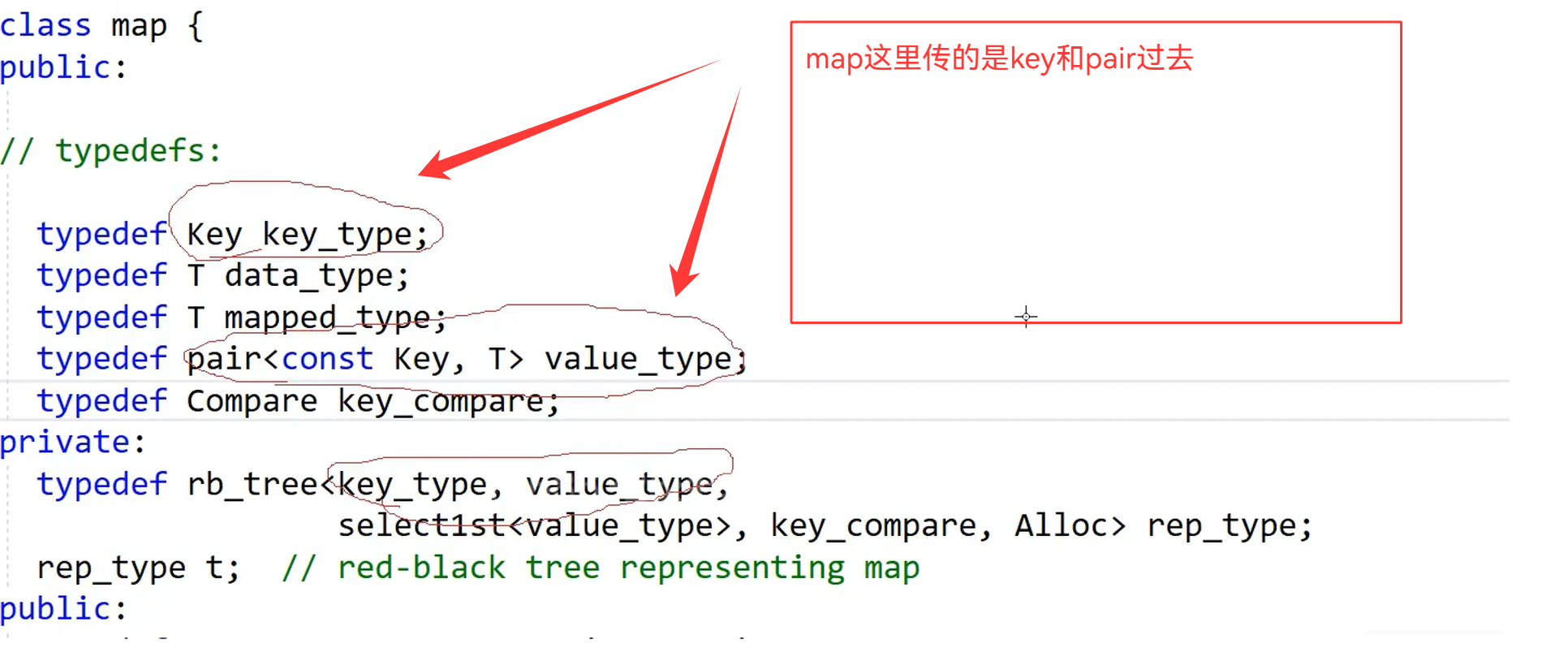
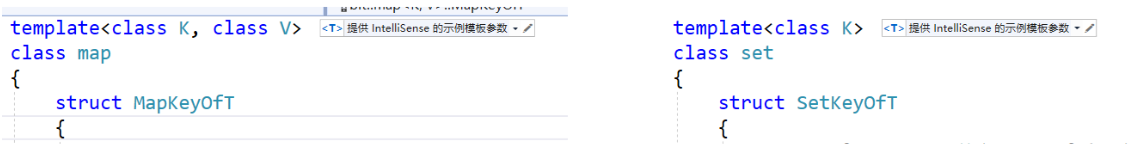
我们根据这里的map和set发现,他们传入的要么是(key,key)或者是(key,pair(key,T))
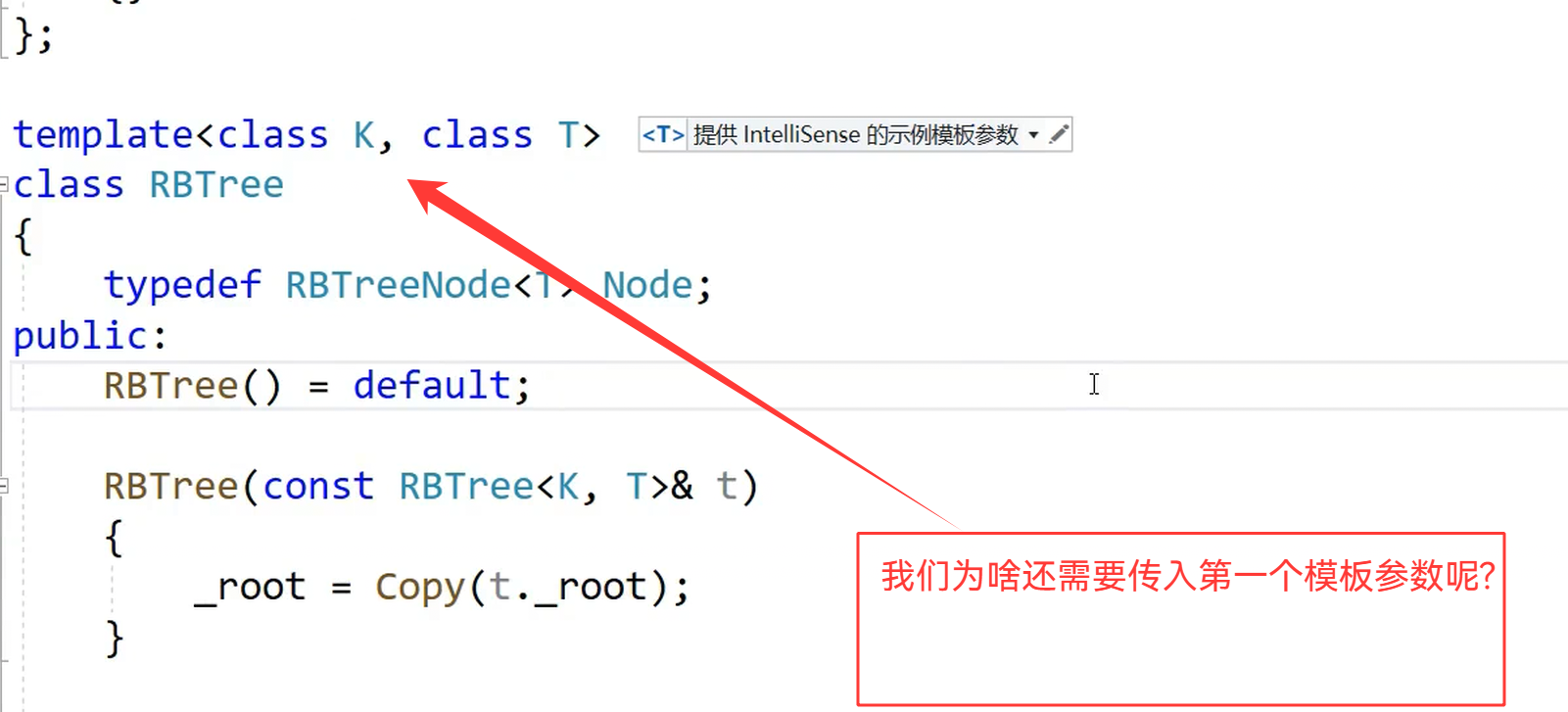
第一个模板参数传入的都是key,就第二个模板参数有问题(这个地方是关键)
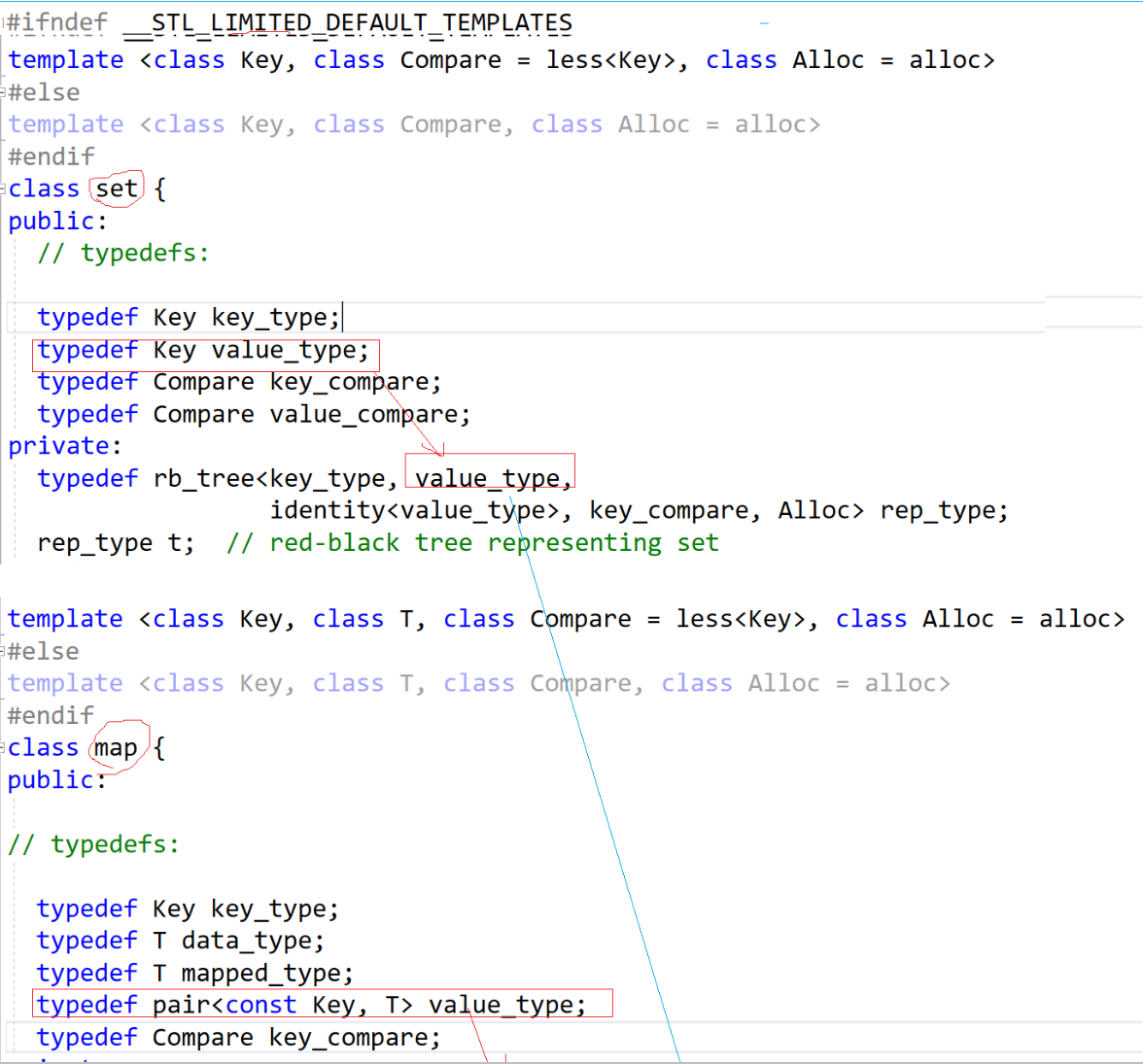
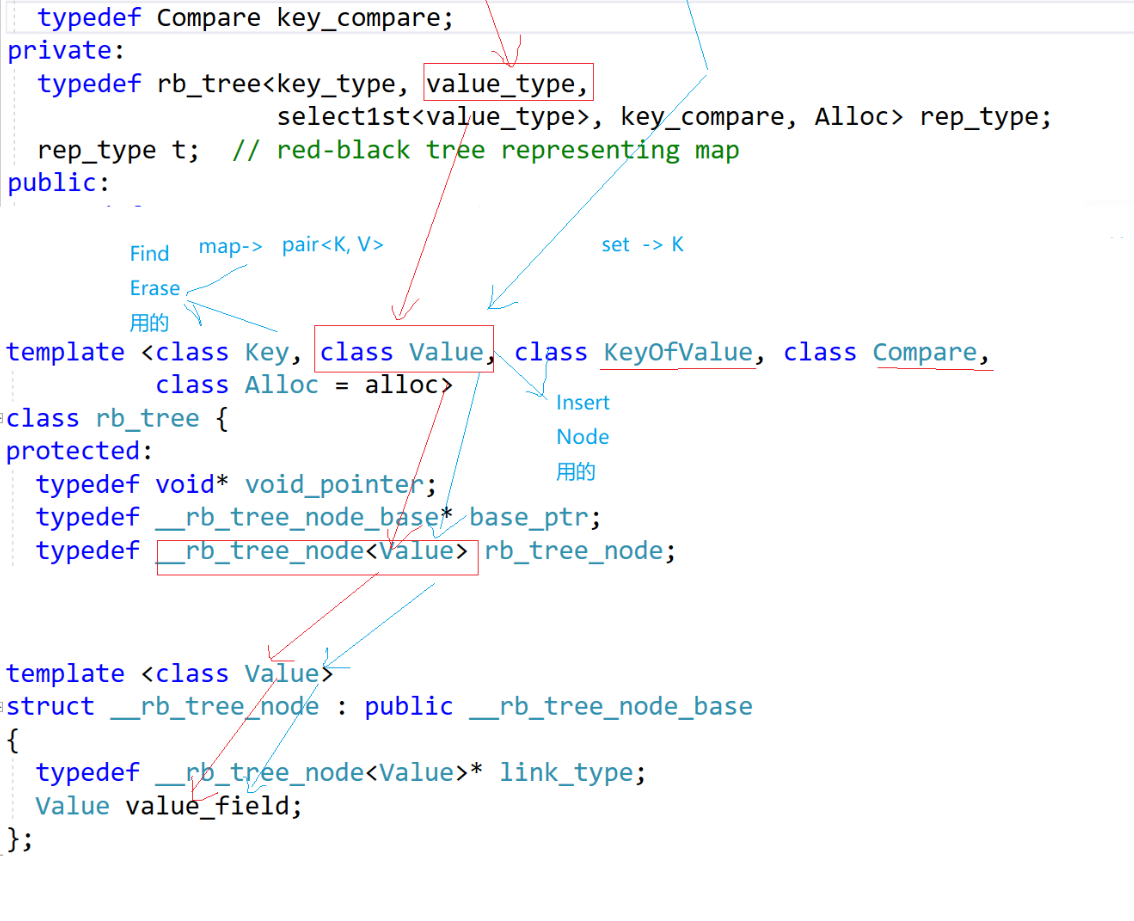
我们可以发现这个地方和我们写的不一样,这里他用的是一个RBTree进行使用,set和map是通过模板参数进行使用
一个传入的是(key,key) , 另一个传入的是(key,pair<key,T>)

所以说,第一个参数是给find和erase使用的
二.实现set和map的框架
cpp
"set实现"
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K>
class set
{
private:
RBTree<K,K> _t;
};
}
cpp
"map实现"
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>> _t;
};
} 三.插入的复用
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K>
class set
{
public:
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
_t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K,K> _t;
};
}
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
_t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>> _t;
};
}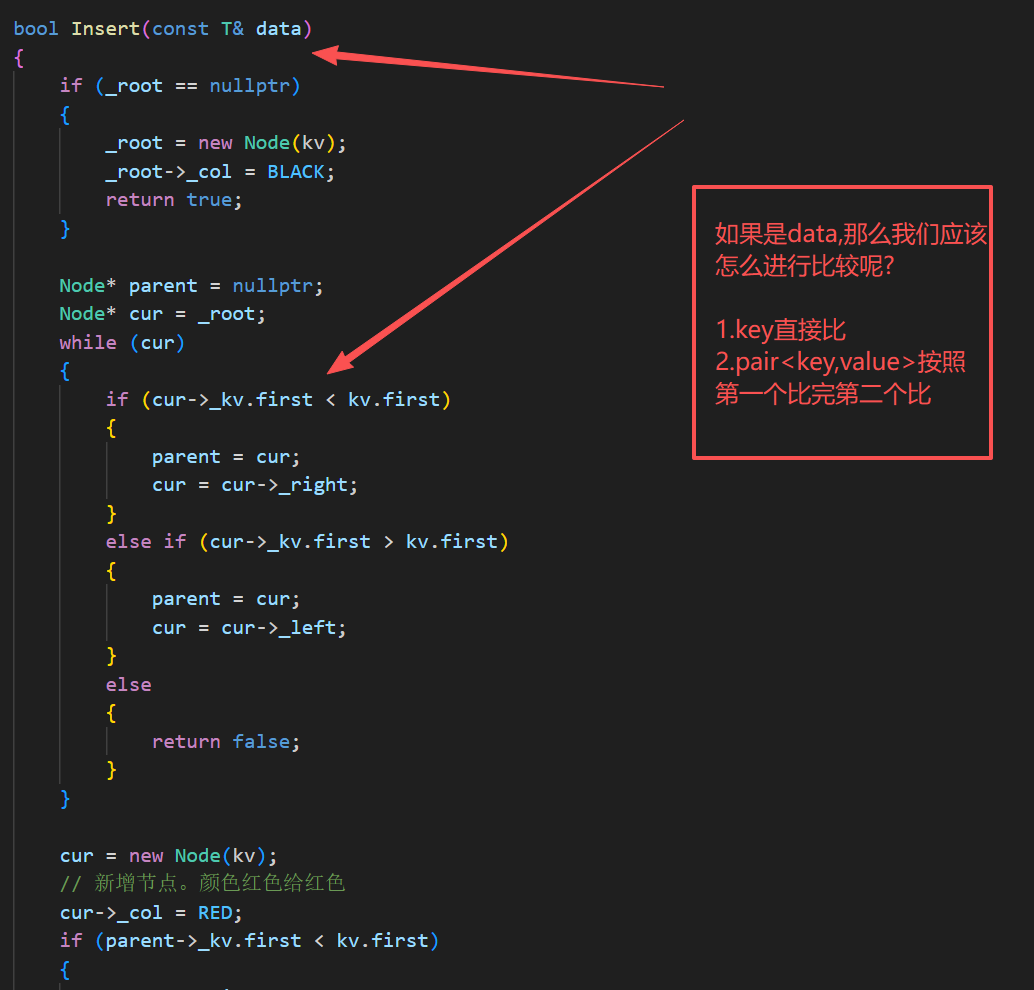
但是这里我们只要第一个进行比较
所以对于红黑树这一层,我们不知道,传入的到底是key还是pair<>,但是我们的上层知道啊
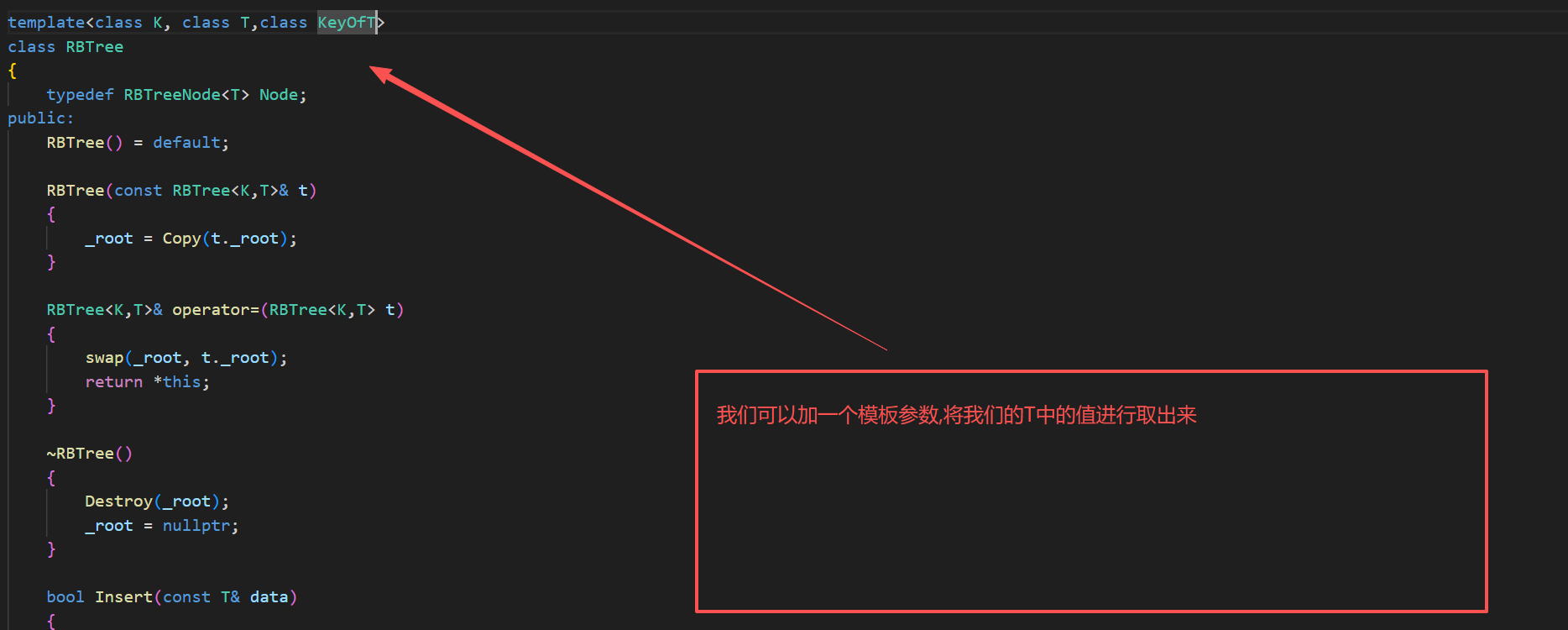
我们通过传入我们的模板参数,然后进行实例化,拿到值即可
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
bool Insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
_t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>,MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
_t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K,K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}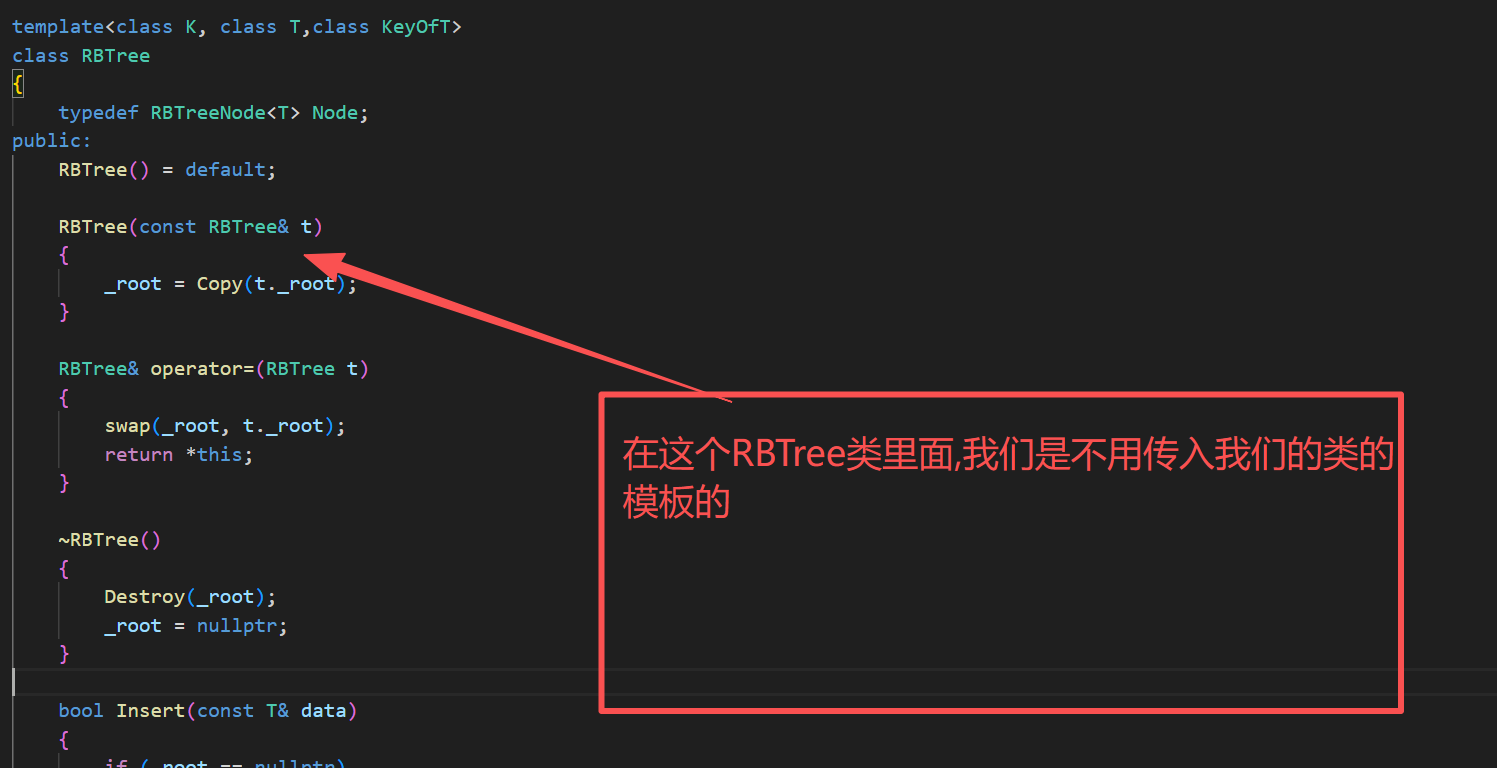
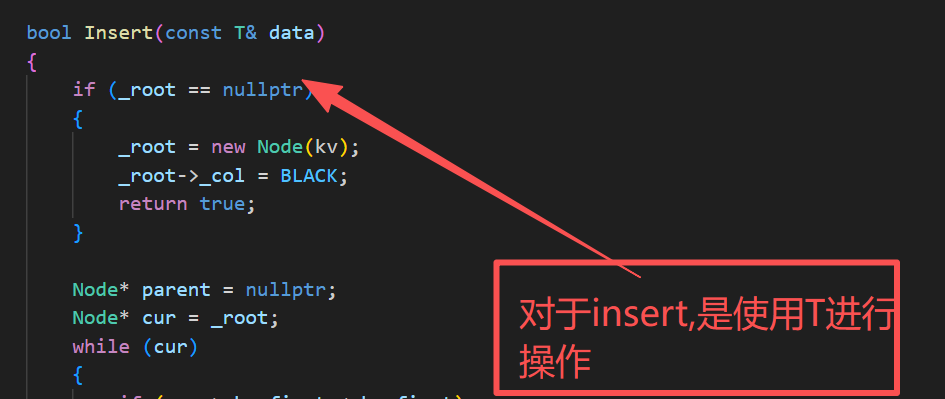
Insert的实现如下:
cpp
bool Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
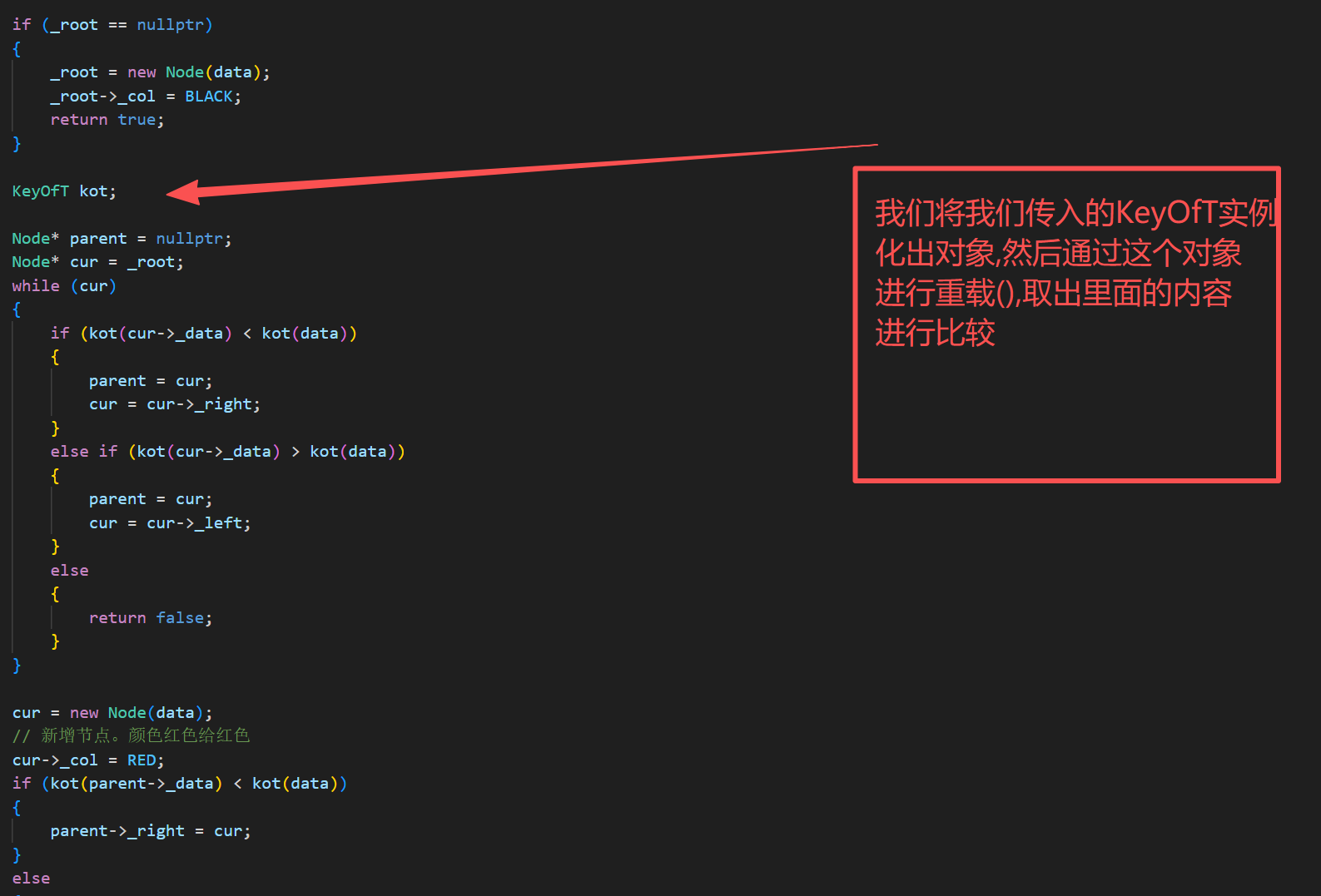
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
// 新增节点。颜色红色给红色
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while(parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
// p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//叔叔存在且为红 -> 变色+向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔存在且为黑/不存在 -> 变色+向上处理
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
// c
// 单旋
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
//双旋
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//叔叔存在且为红 -> 变色+向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔存在且为黑/不存在 -> 变色+向上处理
if(cur == parent->_right)
{
// g
// u p
// c
// 单旋
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
//双旋
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return true;
}
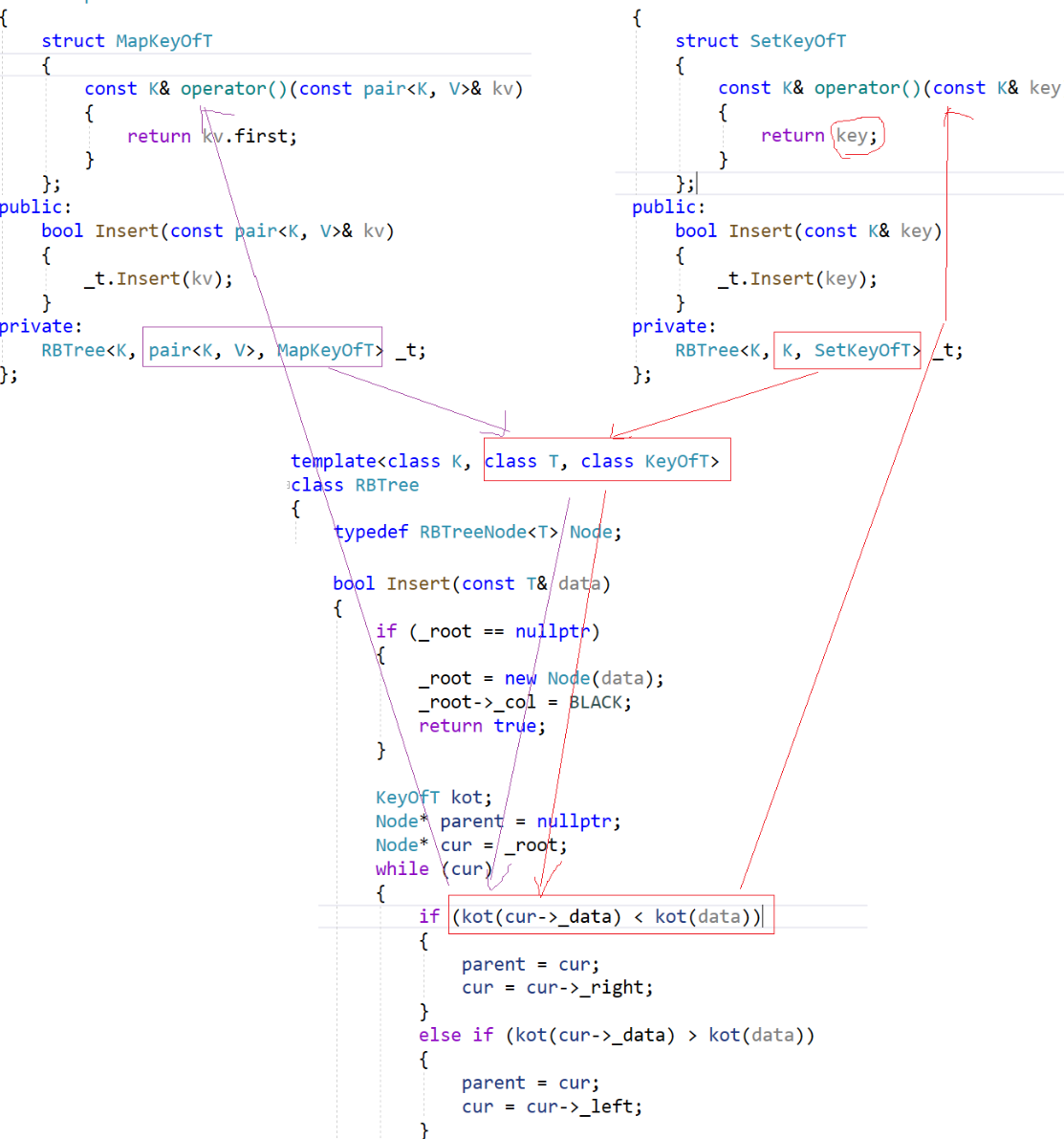
本质上就是回调
四.测试代码
cpp
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = {4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14};
for(auto e:a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
}我们插入一点数据进行测试一下,发现没有报错,那么说明我们模板部分没有写错
五.红黑树迭代器的实现
1.简单 *, !=等操作符 的实现
cpp
template <class K,class T>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<K,T> Self;
Node* _node;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};这些简单的部分,我们就不做过多的介绍了
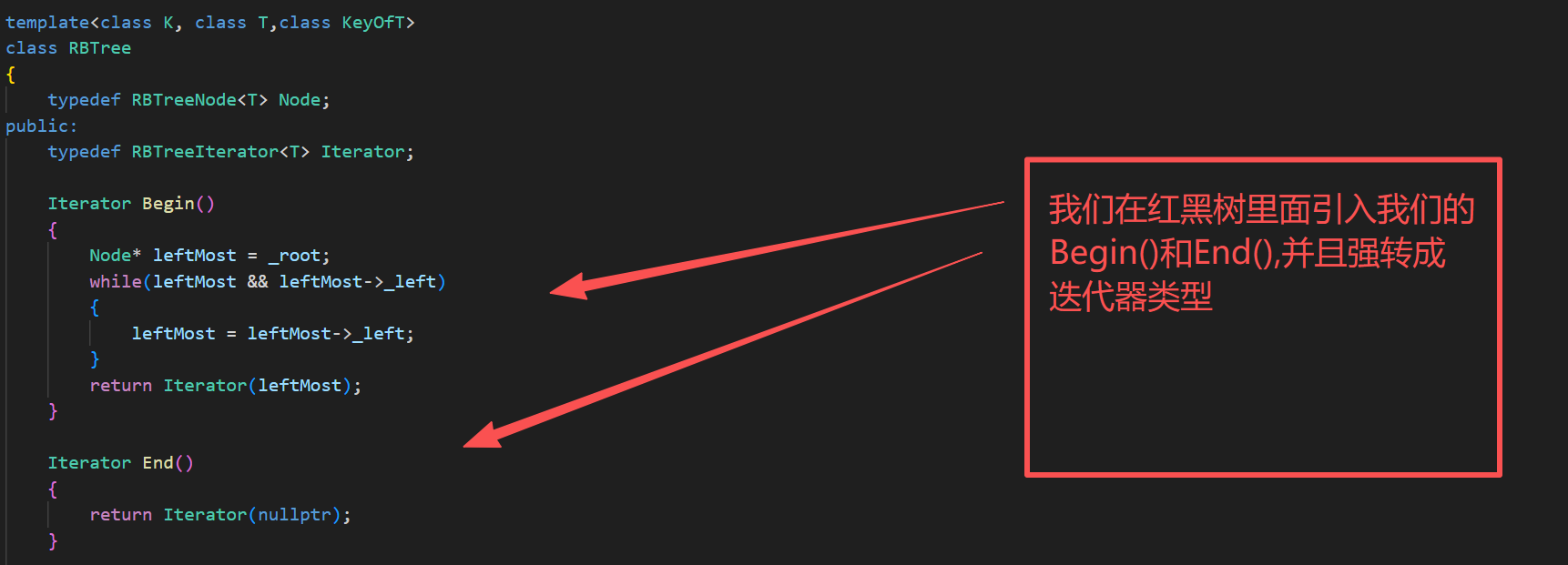
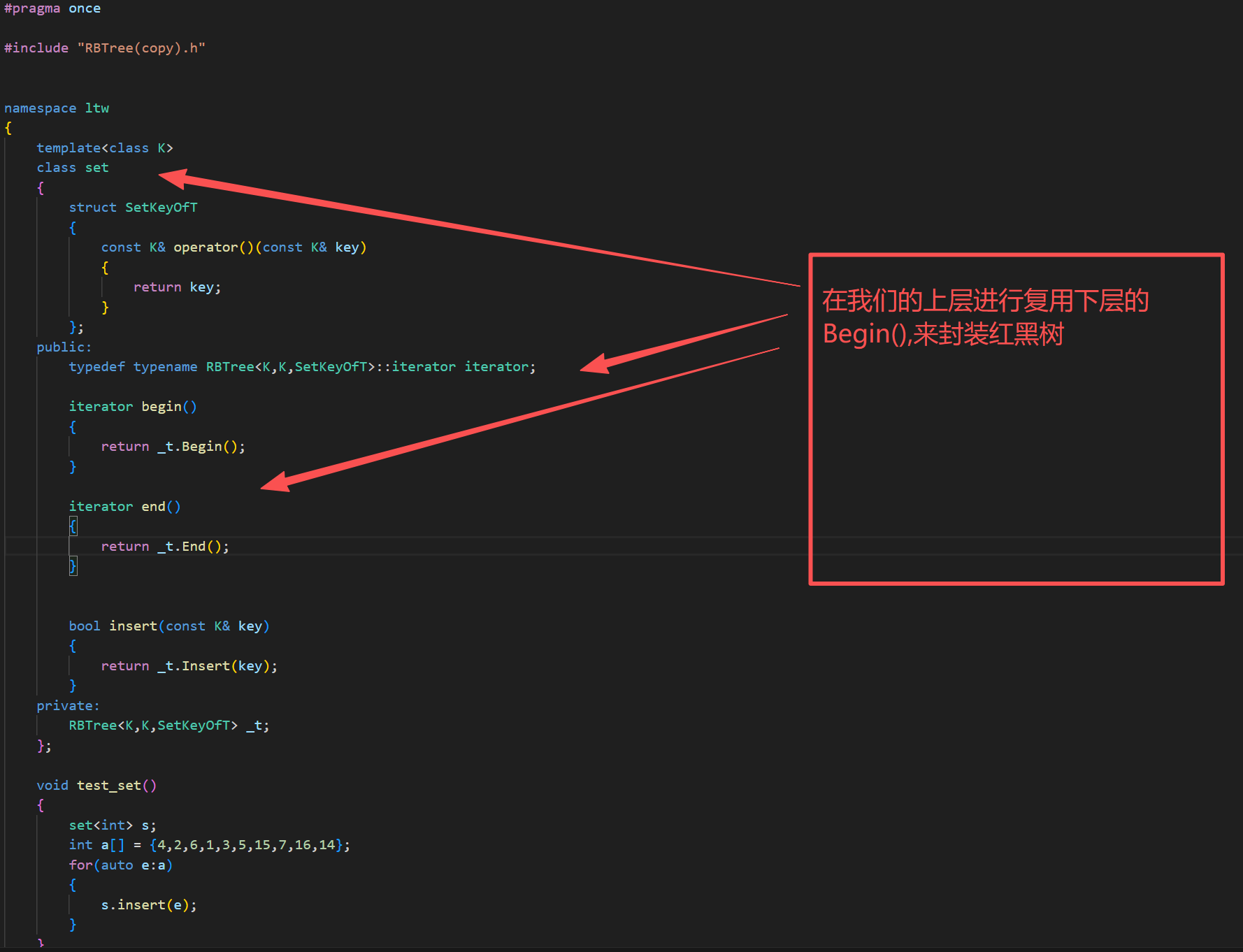
2.把迭代器加入到红黑树里面
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K,K,SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
bool insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K,K,SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = {4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14};
for(auto e:a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
}
}
cpp
#pragma once
#include "RBTree(copy).h"
namespace ltw
{
template<class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K,pair<K,V>,MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
bool insert(const pair<K,V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<K,V>,MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}3.operator++的重载
我们想一想,红黑树的迭代器进行++,是如何进行++的?
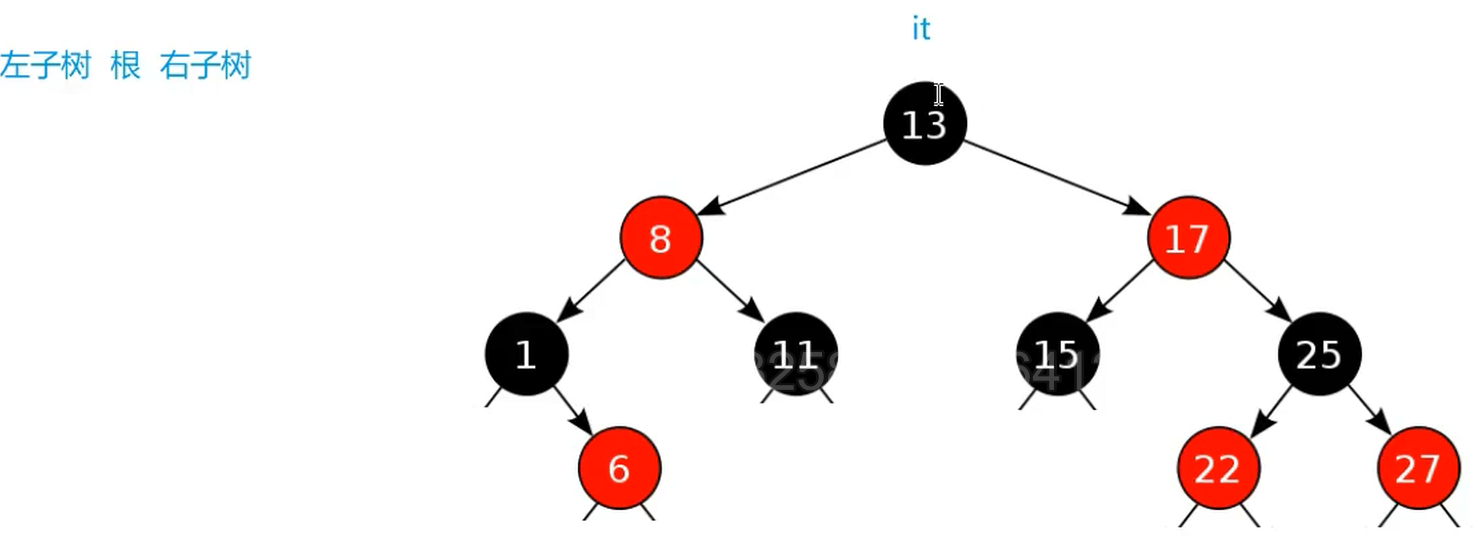
++本质上是在进行中序遍历
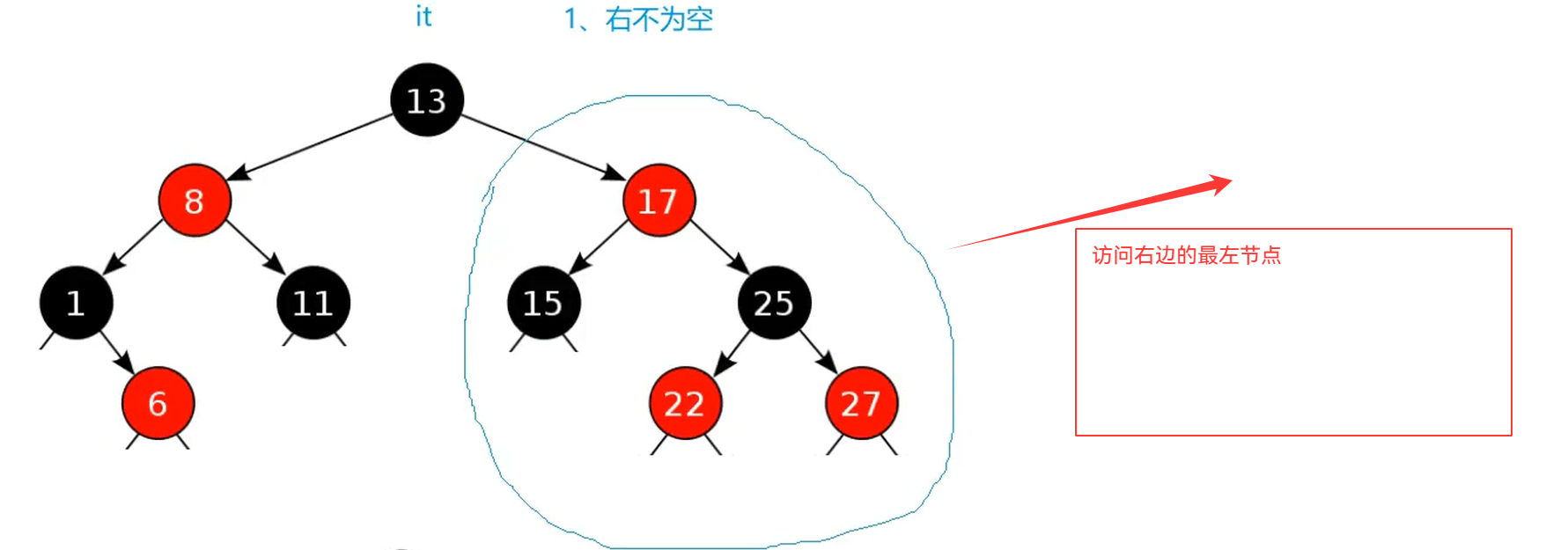
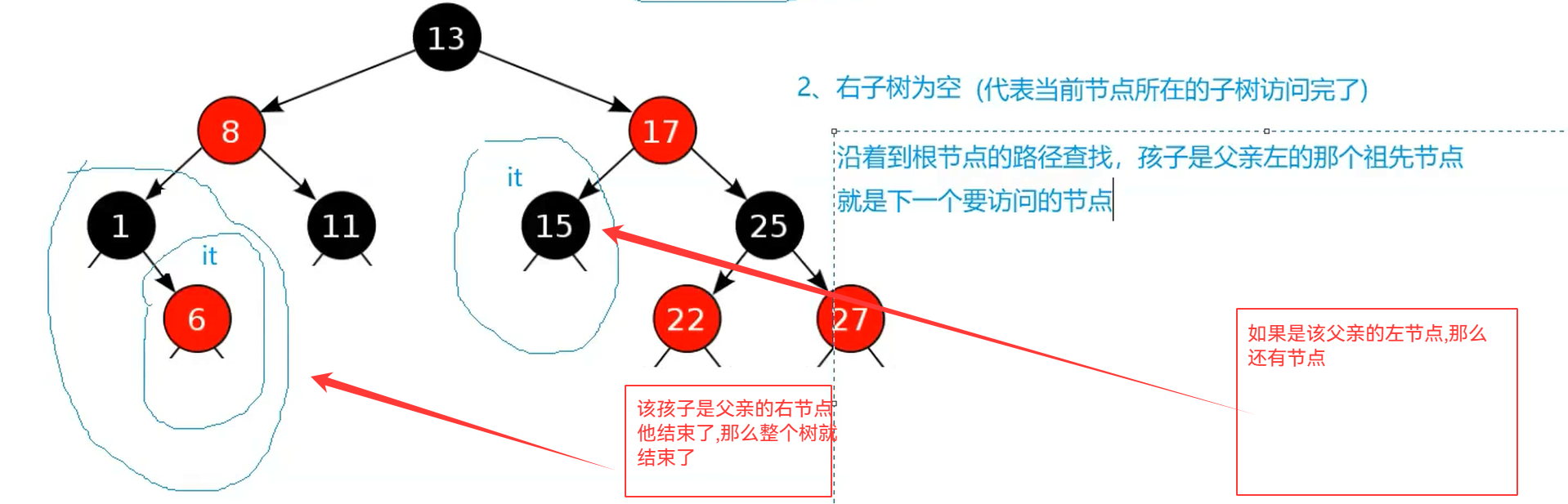
cpp
Self& operator++()
{
if(_node->_right)
{
//右不为空,右子树最左节点就是中序的下一个
Node* leftMost = _node->_right;
while(leftMost&&leftMost->_left)
{
leftMost = leftMost->_left;
}
_node = leftMost;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}这个地方我们的_parent提供了遍历
4.begin()和end()的实现
为了实现范围for,我们还要提供我们的begin()和end()
因为begin()本质上是在找我们中序遍历的第一个,就是最左节点
cpp
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* leftMost = _root;
while(leftMost && leftMost->_left)
{
leftMost = leftMost->_left;
}
return Iterator(leftMost);
}
end()的实现:


这里能跑很明显就能看到是中序遍历,符合我们二叉树的性质
cpp
void test_map()
{
map<int,int> s;
int a[] = {4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14};
for(auto e:a)
{
s.insert({e,e});
}
for(const auto& e:s)
{
cout << e.first << " " << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
我们看源码这个地方,是增加了一个哨兵位的头节点
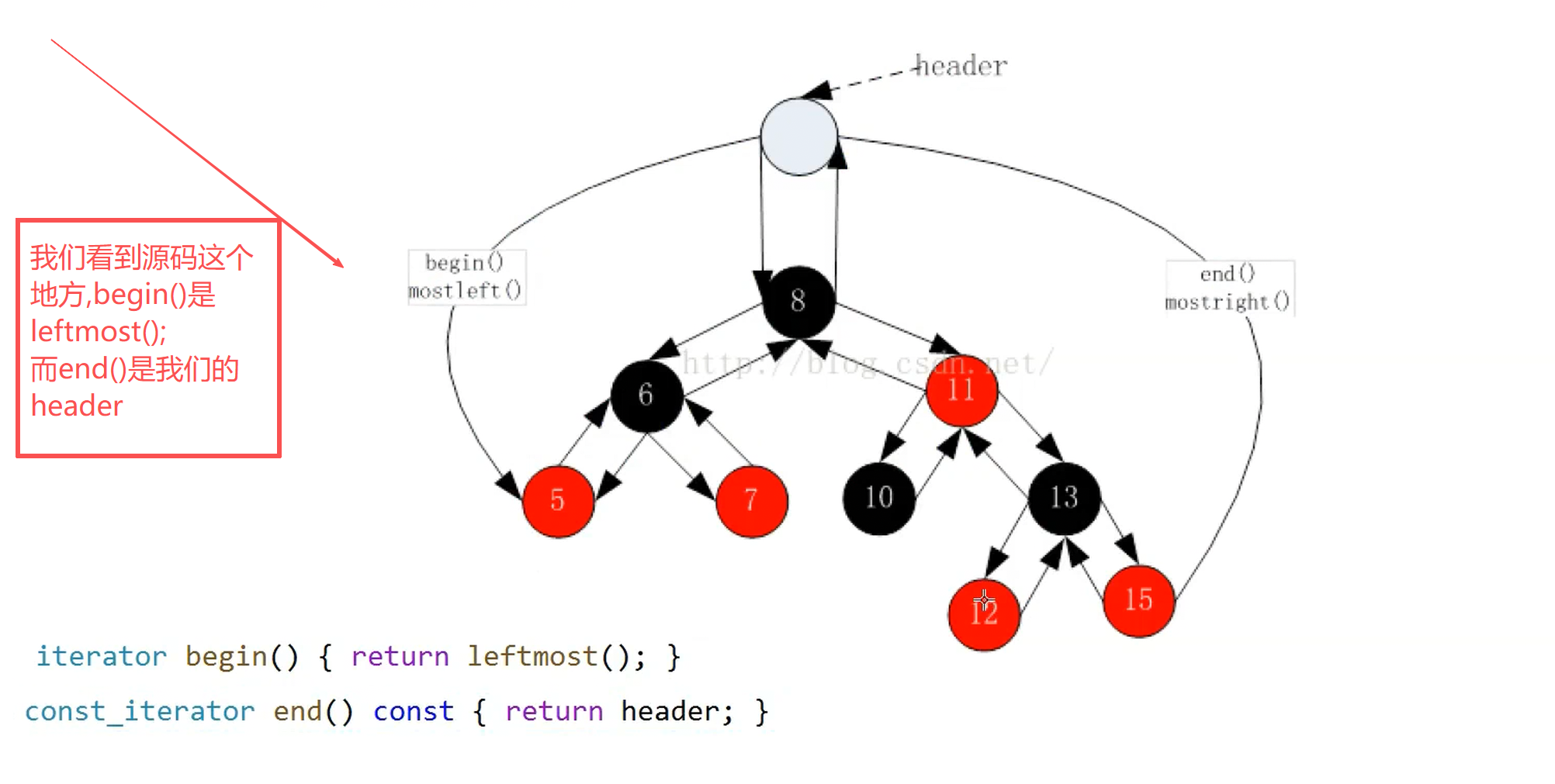
这里设计的header的好处是,header和root是互为父子的,这样判断end()的时候,会更加方便
而且,支持反向迭代器更合理一点

5.operator--的实现
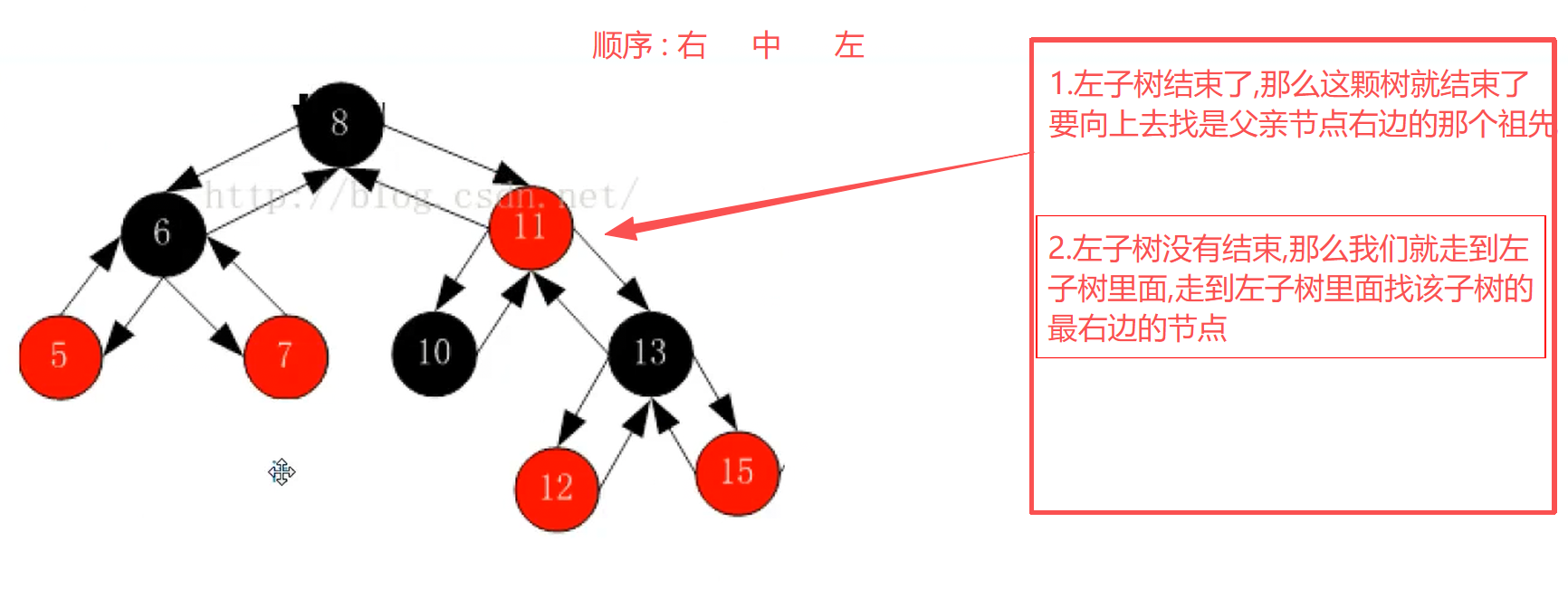
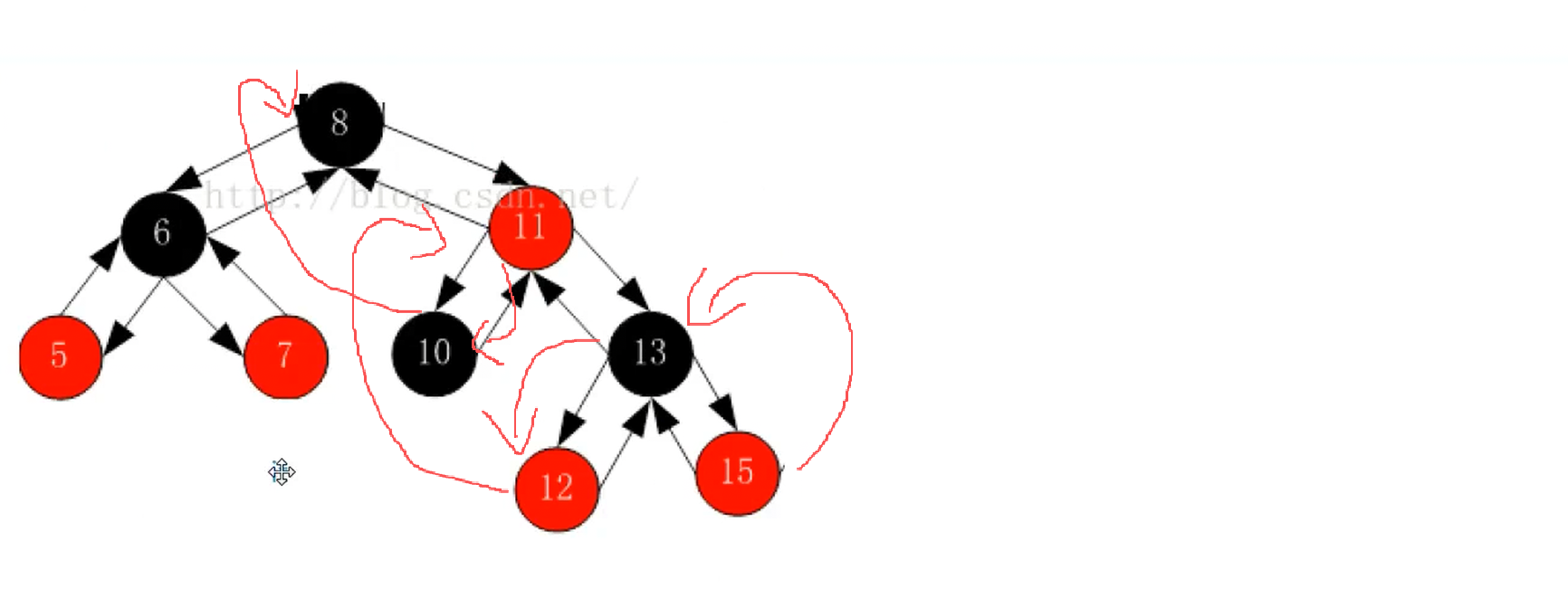
cpp
operator-- 代码实现
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node->_left)
{
Node* rightMost = _node->_left;
while(rightMost&&rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else
{
//找孩子是父亲右边的那个
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
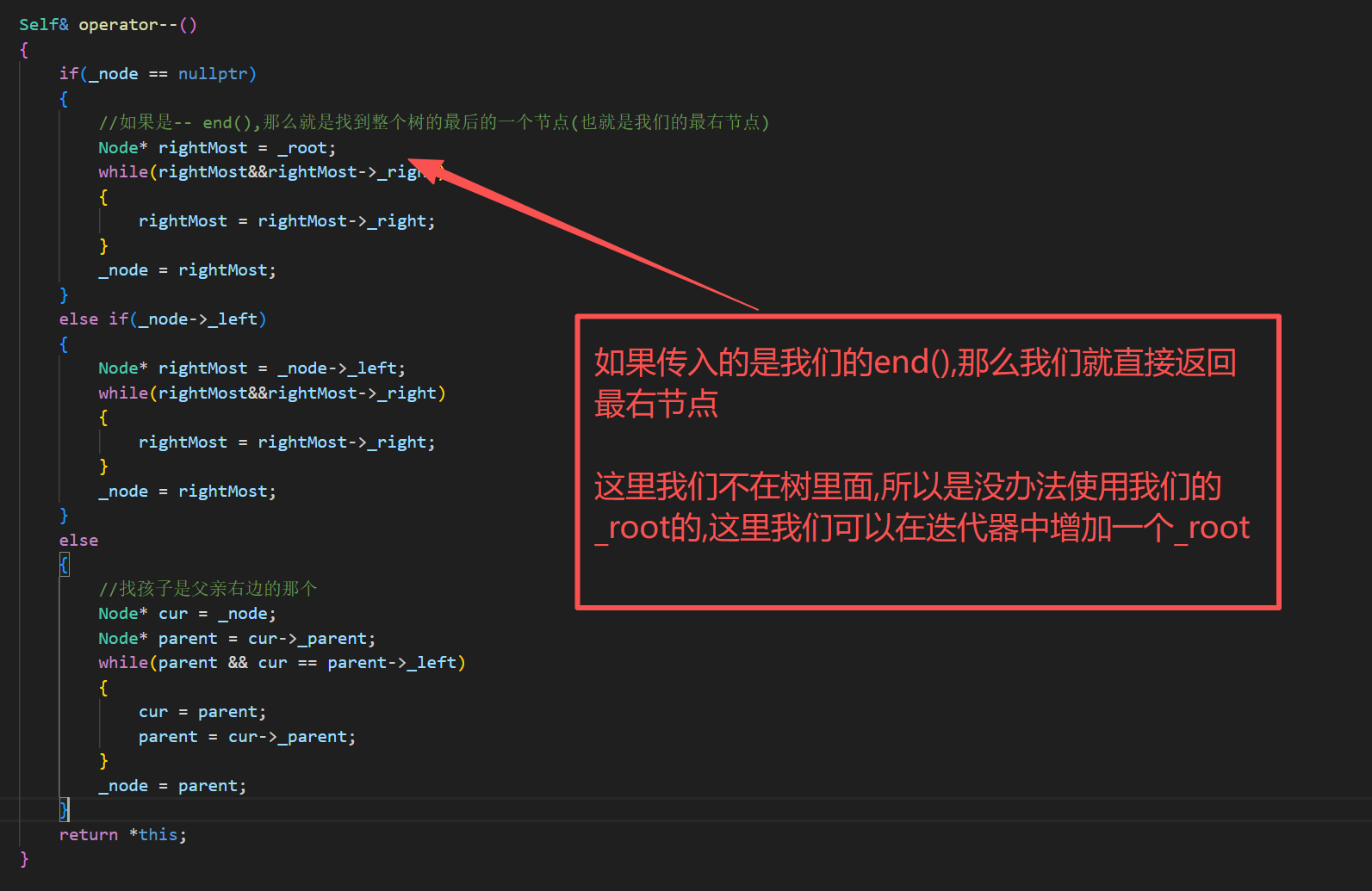
}但是我们这里的如果是end() (nullptr)传入--,那么就直接奔溃了,所以我们就要做特殊处理
cpp
Self& operator--()
{
if(_node == nullptr)
{
//如果是-- end(),那么就是找到整个树的最后的一个节点(也就是我们的最右节点)
Node* rightMost = _root;
while(rightMost&&rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else if(_node->_left)
{
Node* rightMost = _node->_left;
while(rightMost&&rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else
{
//找孩子是父亲右边的那个
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while(parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
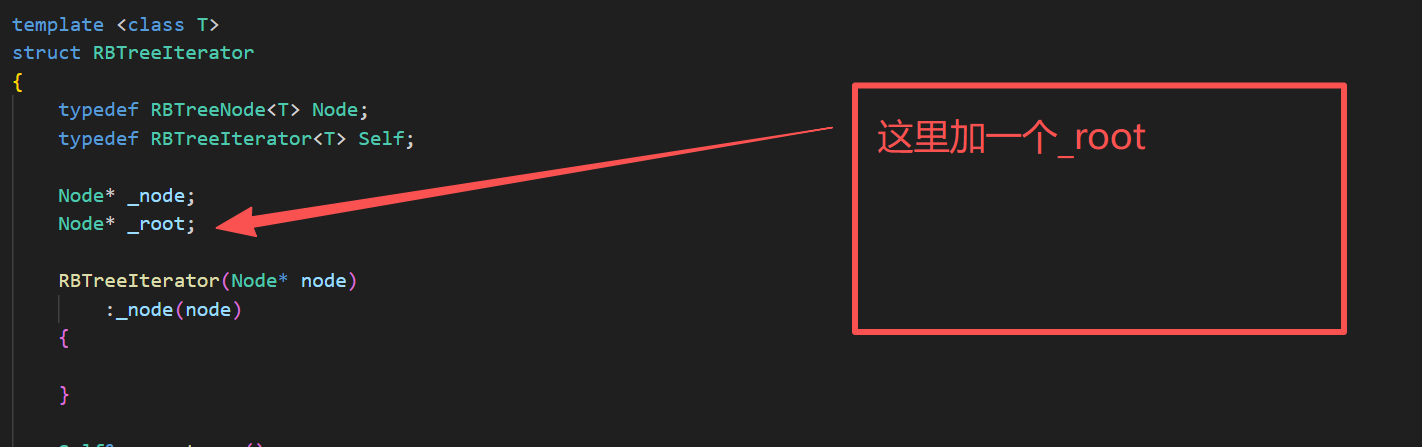

但是,这样实现还是有缺陷的,这样会面临迭代器失效(这块是一个大坑),这里我们可以采取库里面的方式设计
我们这样也能实现set的反向遍历
cpp
set<int>::iterator it = s.end();
while(it != s.begin())
{
--it;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;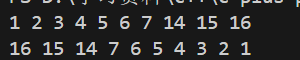
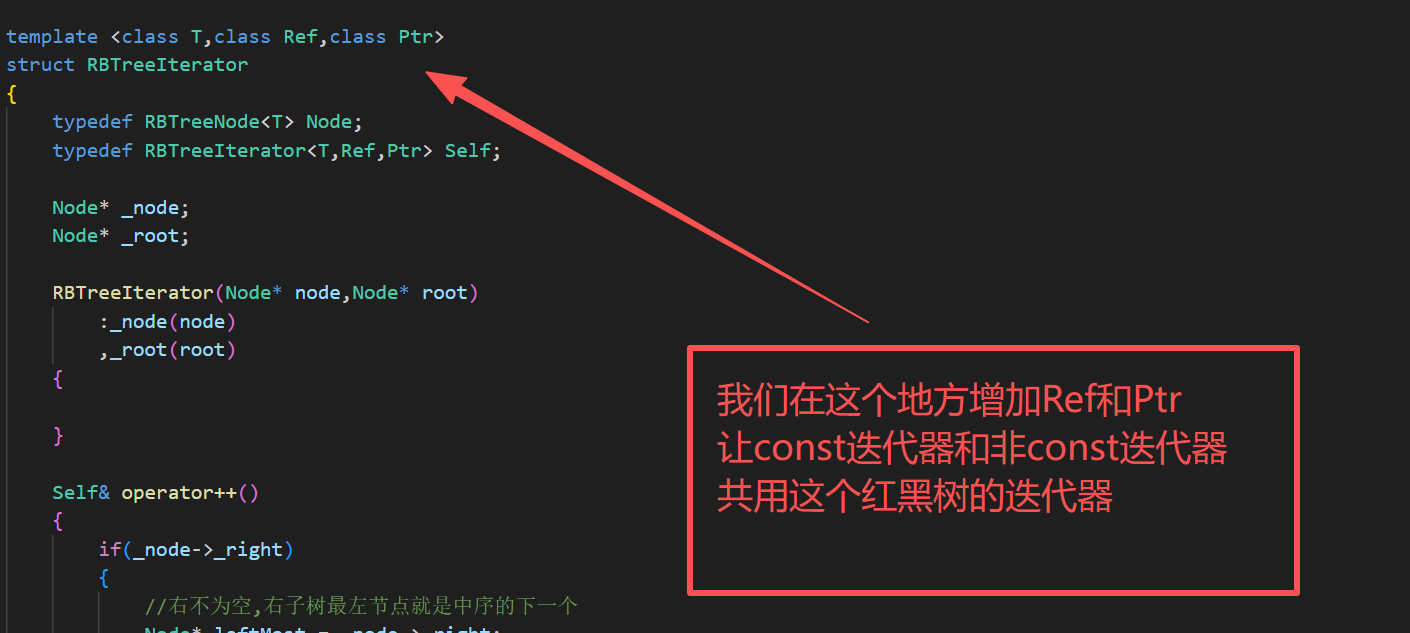
这里再讲一下我们的迭代器优势(迭代器模式):
6.const迭代器的实现
这里加const迭代器,我们采用的是以前链表的实现方式,代码链接如下:
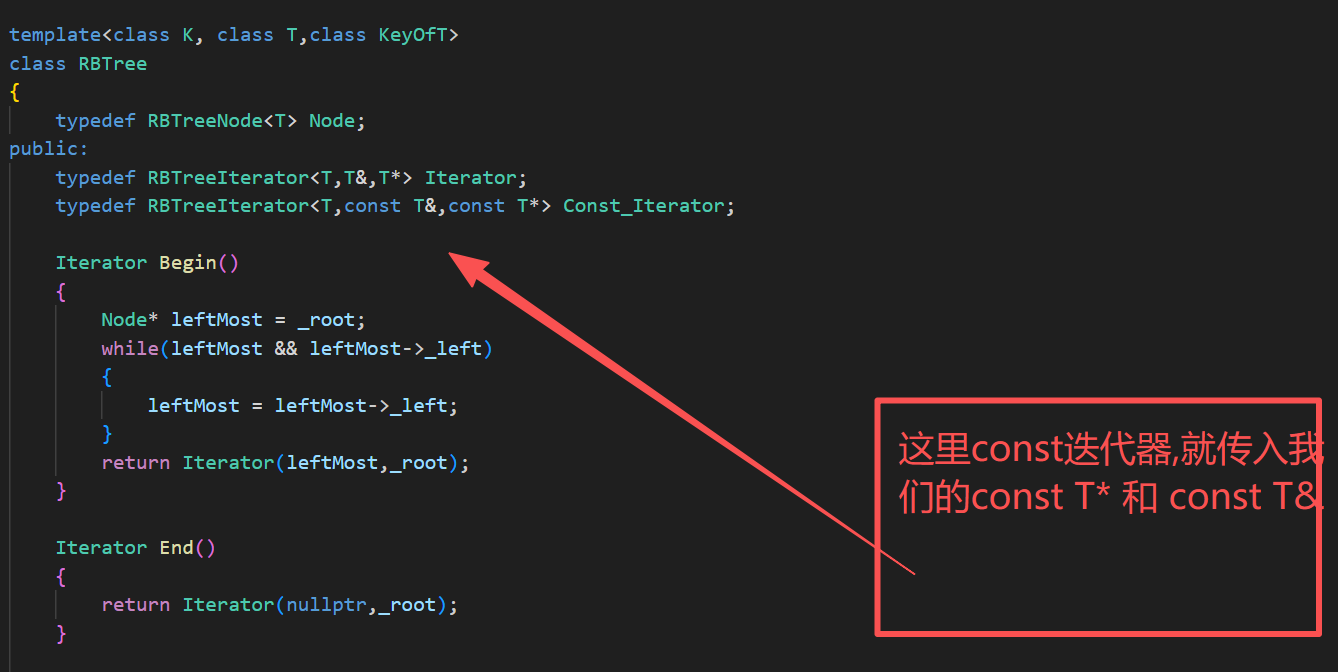
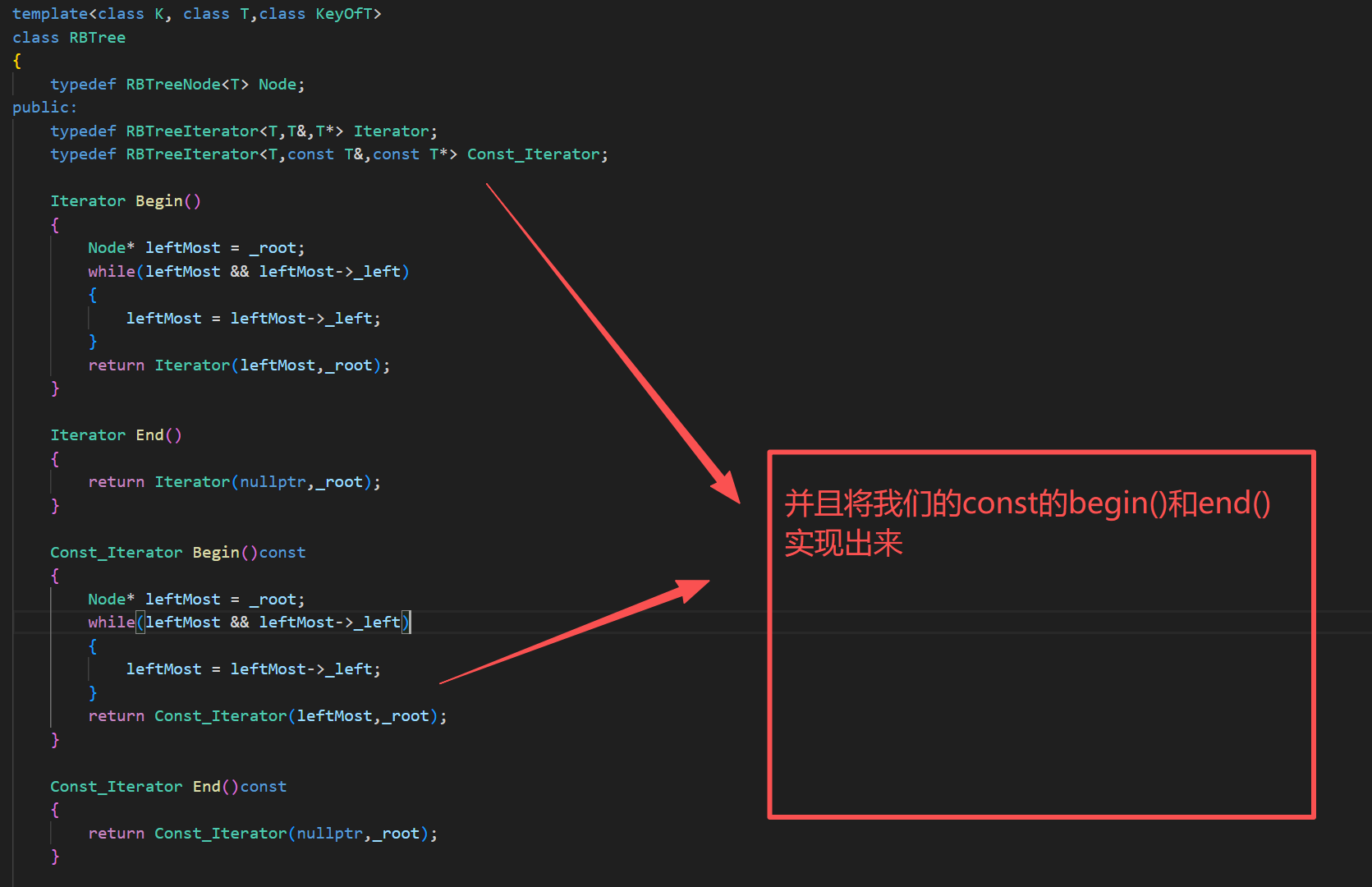
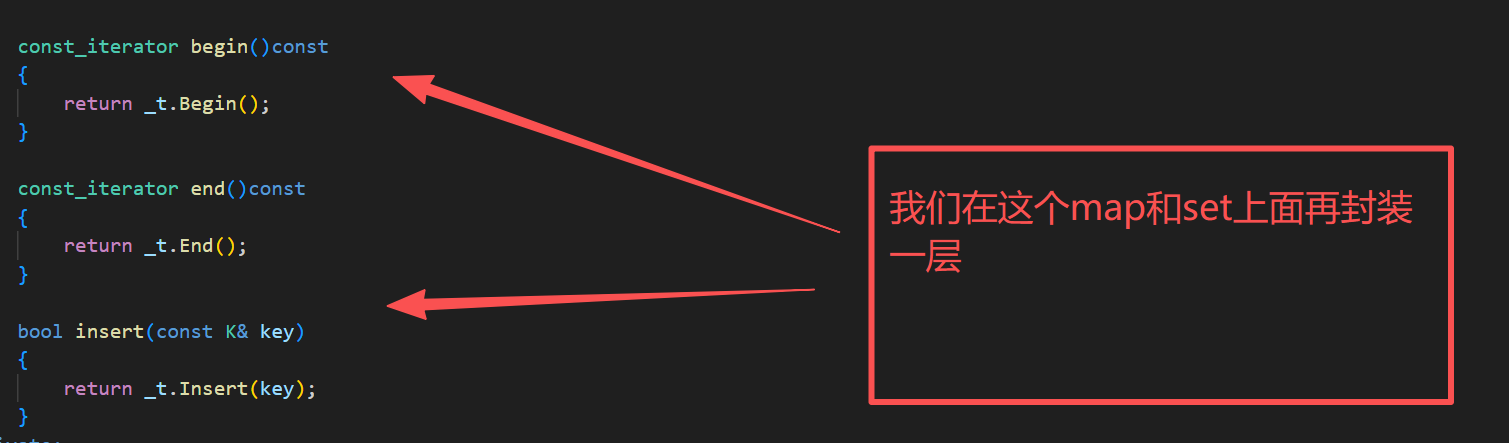
测试代码:
cpp
void Print(const set<int>& s)
{
set<int>::const_iterator it = s.end();
while(it != s.begin())
{
--it;
cout << *it << " ";
}
}
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = {4,2,6,1,3,5,15,7,16,14};
for(auto e:a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
for(const auto& e:s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<int>::iterator it = s.end();
while(it != s.begin())
{
--it;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
Print(s);
}

毕竟是树形的结构,如果改变一个节点的值就不一定是搜索树了

,还有一点,就是map的first是不支持修改的,但是map的second是支持修改的,所以我们在这个代码不能直接使用const迭代器

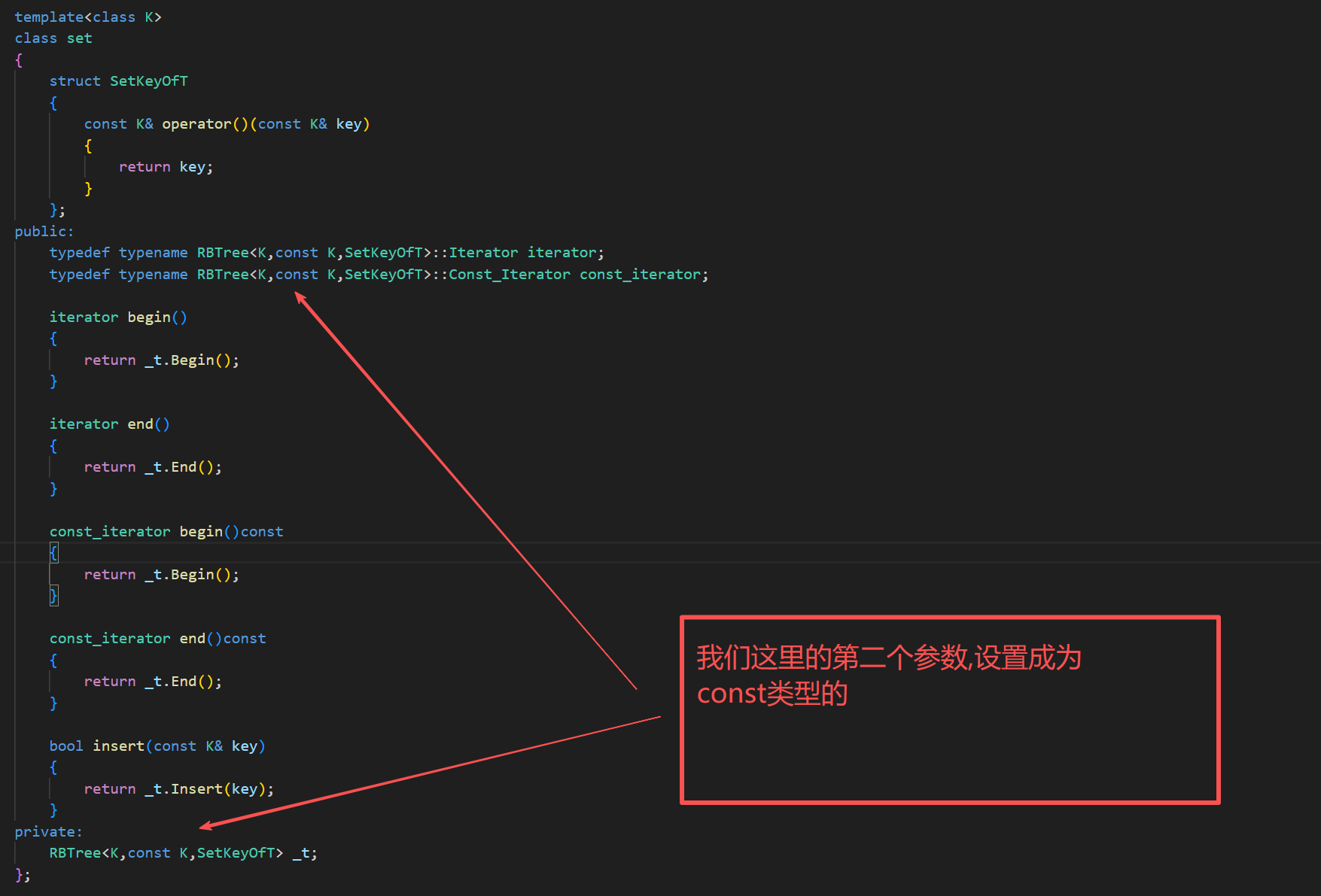
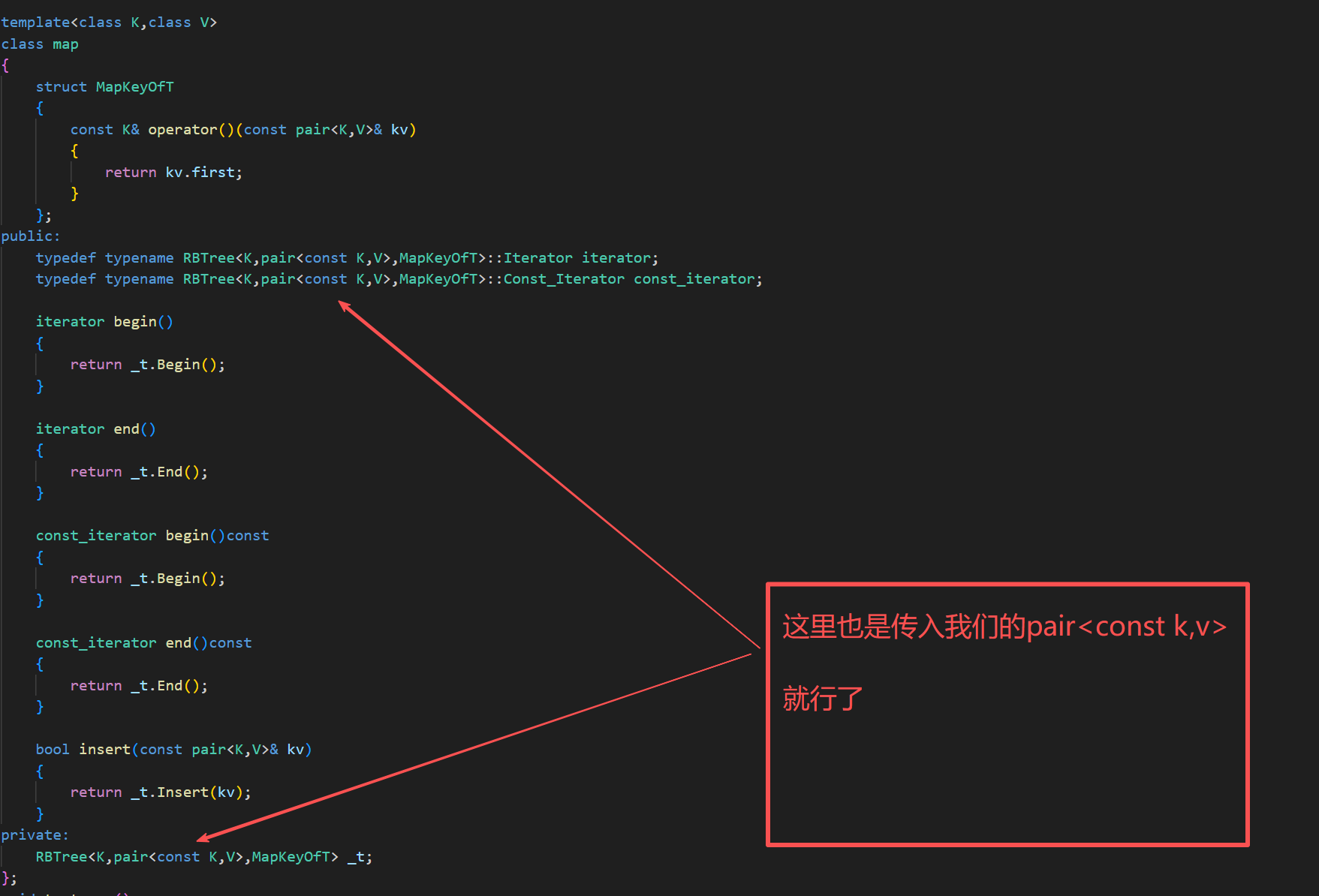
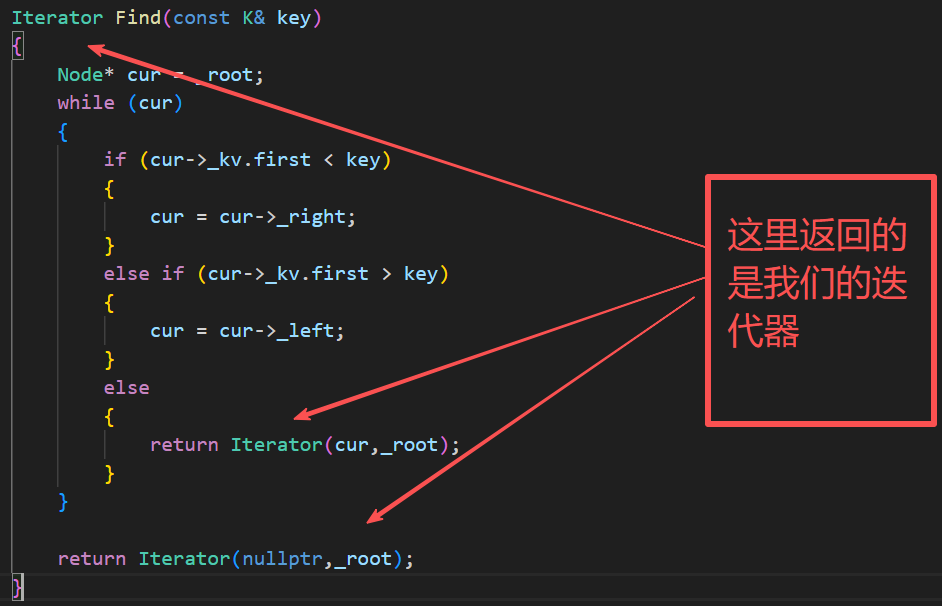
7.Find的实现
cpp
Iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return Iterator(cur,_root);
}
}
return Iterator(nullptr,_root);
}
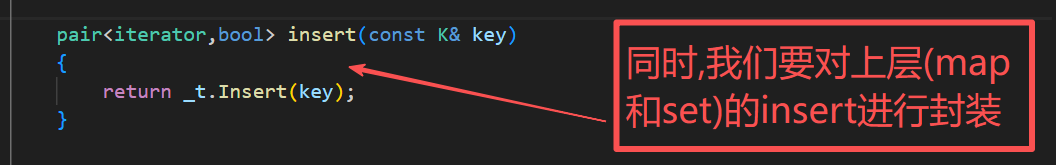
8.map实现我们的operator[]
map的[]实现,应该依赖我们的insert
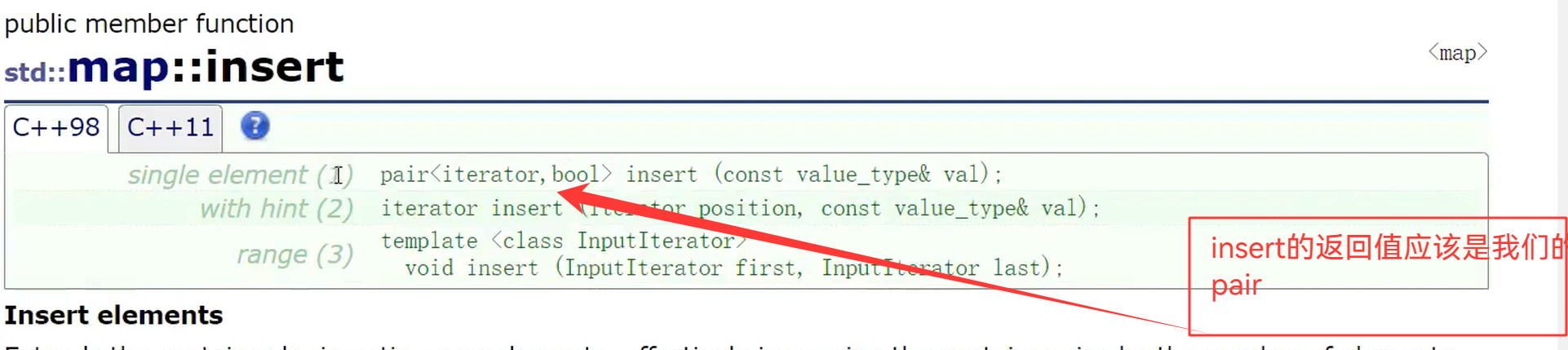
所以,我们要进行修改插入函数
cpp
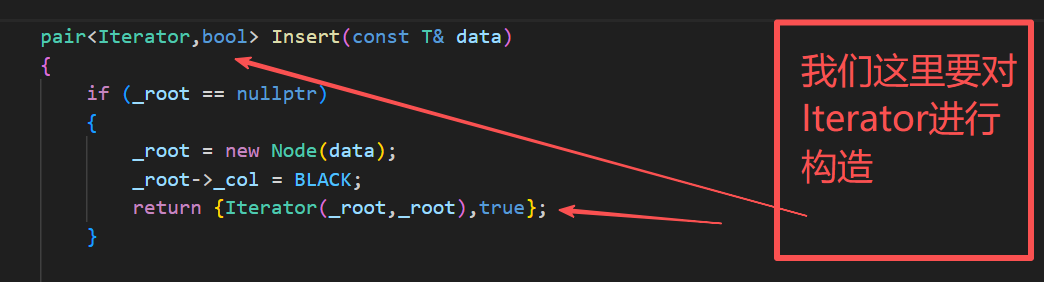
pair<Iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return {Iterator(_root,_root),true};
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return {Iterator(cur,_root),false};
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
// 新增节点。颜色红色给红色
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while(parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if(parent == grandfather->_left)
{
// g
// p u
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//叔叔存在且为红 -> 变色+向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔存在且为黑/不存在 -> 变色+向上处理
if(cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
// c
// 单旋
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
//双旋
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if(uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//叔叔存在且为红 -> 变色+向上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//叔叔存在且为黑/不存在 -> 变色+向上处理
if(cur == parent->_right)
{
// g
// u p
// c
// 单旋
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
//双旋
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return {Iterator(newnode,_root),true};
}
cpp
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator,bool> ret = insert({key,V()});
return ret.first->second;
}