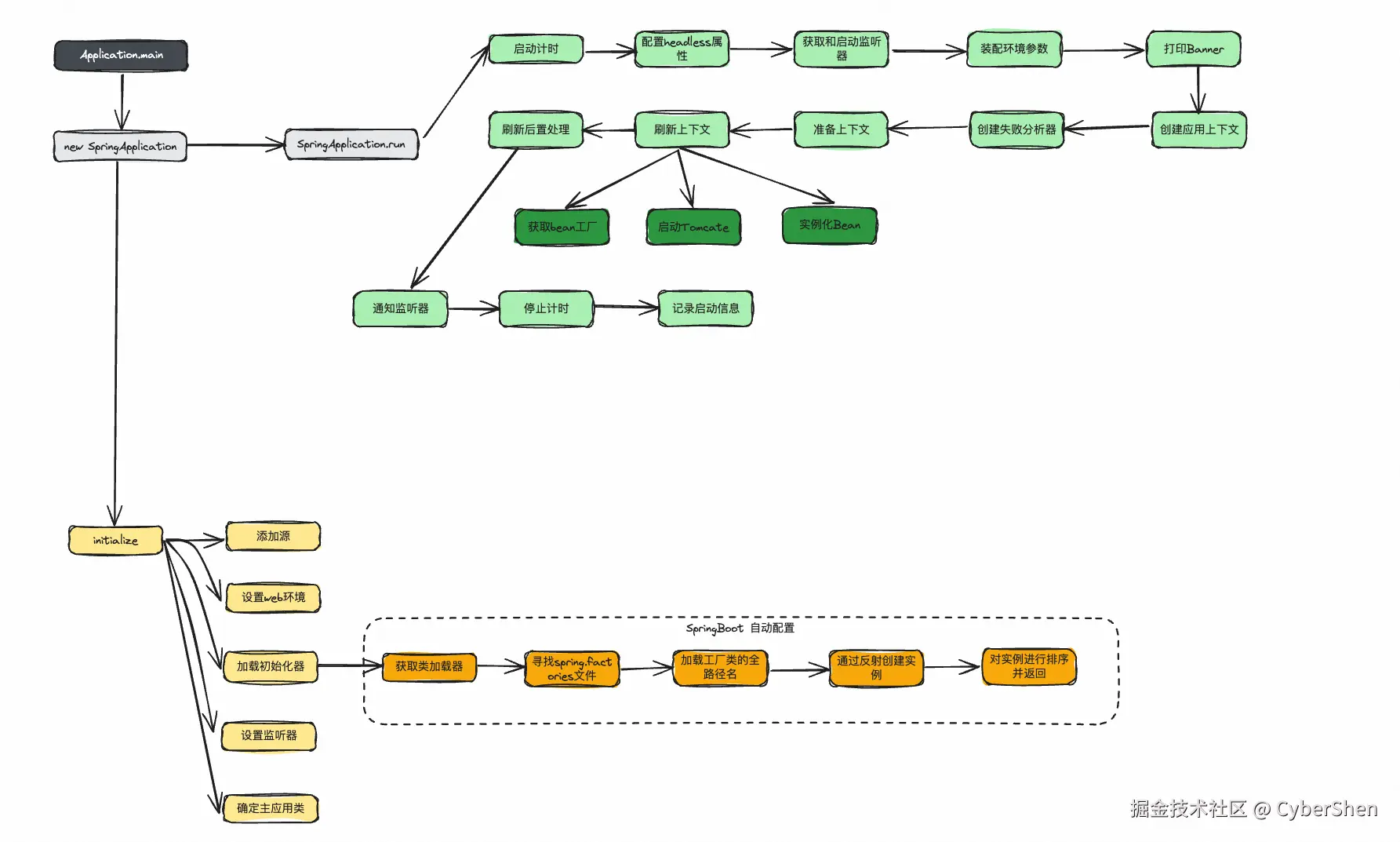
一、启动类入口
SpringBoot的启动很简单,通用的代码如下:
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}在启动类中需要关注的是
- @SpringBootApplication
- SpringApplication.run()
关于@SpringBootApplication注解,可以查看SpringBoot自动装配。重点关注的就是SpringApplication.run()方法。
查看run()方法的实现,如下面代码所示,我们发现其实其首先是创建了SpringApplication的实例,然后调用了SpringApplication的run()方法,那我们关注的就是SpringApplication创建实例的过程。
SpringApplication.run方法实际执行的方法如下:
java
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}二、初始化SpringApplication
SpringApplication的构造函数中调用了initialize方法来初始化SpringApplication:
java
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
initialize(sources);
}
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
// 添加源:如果sources不为空且长度大于0,则将它们添加到应用的源列表中
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
// 设置web环境:推断并设置Web环境(例如,检查应用是否应该运行在Web环境中)
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
// 加载初始化器:设置ApplicationContext的初始化器,
// 从spring.factories文件中加载ApplicationContextInitializer实现
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 设置监听器:从spring.factories文件中加载ApplicationListener实现
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 确定主应用类:通常是包含main方法的类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}2.1 添加sources
将提供的源(通常是配置类)添加到应用的源列表中。
2.2 设置web环境
java
private static final String[] WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES = new String[]{"javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"};
private boolean deduceWebEnvironment() {
String[] var1 = WEB_ENVIRONMENT_CLASSES;
int var2 = var1.length;
for(int var3 = 0; var3 < var2; ++var3) {
String className = var1[var3];
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, (ClassLoader)null)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}调用deduceWebEnvironment来判断当前的应用是否是web应用,并设置到webEnvironment属性中。deduceWebEnvironment方法通过获取
java
javax.servlet.Servlet
org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext这两个类来判断,如果能获得这两个类则说明是web应用,否则不是。
2.3 加载初始化器
调用getSpringFactoriesInstances从spring.factories文件中找出key为ApplicationContextInitializer的类并实例化,然后调用setInitializers方法设置到SpringApplication的initializers属性中。这个过程就是找出所有的应用程序初始化器。
java
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 读取ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 实例化ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法获取ApplicationContextInitializer接口实现的类:
java
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 获取接口类的名称
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
try {
// 获取FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION(META-INF/spring.factories)的多个位置
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
/**
* urls有
* spring-boot/META-INF/spring.factories
* spring-beans/META-INF/spring.factories
* spring-boot-autoconfigure/META-INF/spring.factories
*
*/
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// 从META-INF/spring.factories文件中加载配置
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
// 从配置中读取ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
}
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
"] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}当前的初始化器有如下几个:
java
DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer
ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer
ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer
ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer
AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer2.4 设置监听器
调用getSpringFactoriesInstances从spring.factories文件中找出key为ApplicationListener的类并实例化,然后调用setListeners方法设置到SpringApplication的listeners属性中。这个过程就是找出所有的应用程序事件监听器。
获取监听器的方法与获取初始化器的方法一致,唯一的区别在于获取
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener接口的实现类。
当前的事件监听器有如下几个:
java
ConfigFileApplicationListener
AnsiOutputApplicationListener
LoggingApplicationListener
ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener
BackgroundPreinitializer
DelegatingApplicationListener
ParentContextCloserApplicationListener
ClearCachesApplicationListener
FileEncodingApplicationListener
LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener2.5 设置主类
java
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = (new RuntimeException()).getStackTrace();
StackTraceElement[] var2 = stackTrace;
int var3 = stackTrace.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = var2[var4];
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var6) {
}
return null;
}调用deduceMainApplicationClass方法找出main类,就是这里的SpringBootDemoApplication类
三、运行SpringApplication
3.1 run方法
初始化SpringApplication完成之后,调用run方法运行:
java
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//1. 开启计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); // 构造一个任务执行观察者
stopWatch.start(); // 开始执行,记录开始时间
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
//2. 设置系统属性
configureHeadlessProperty();
//3. 获取并启用监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 封装成SpringApplicationEvent事件然后广播出去给SpringApplication中的listeners所监听
// 这里接受ApplicationStartedEvent事件的listener会执行相应的操作
listeners.starting();
try {
// 构造一个应用程序参数持有类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//4. 准备并配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//5. 打印banner图形
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//6. 创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
//7. 准备上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//8. 刷新上下文
refreshContext(context);
//9. 刷新上下文后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 调用监听器,广播Spring启动结束的事件
listeners.finished(context, null);
// 停止任务执行观察者
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}run方法执行完成之后,Spring容器也已经初始化完成,各种监听器和初始化器也做了相应的工作。具体步骤的分析见下文。
3.2 获取事件监听器
首先看getRunListeners方法:
java
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}可以看到通过调用构造函数来实例化SpringApplicationRunListeners,传入的参数有logger以及调用getSpringFactoriesInstance获得的SpringApplicationRunListener集合。
再看getSpringFactoriesInstance方法,它和获取初始化器的方法一样,获取的接口类型是org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener。获取到的实现类为org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishRunListener。
3.3 事件管理生命周期
java
class SpringApplicationRunListeners {
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
private final ApplicationStartup applicationStartup;
}SpringApplicationRunListeners内部持有SpringApplicationRunListener集合和1个Log日志类。用于SpringApplicationRunListener监听器的批量执行。
java
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
default void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
}
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
}
default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
}
}SpringApplicationRunListener用于监听SpringApplication的run方法的执行,它定义了5个步骤:
- starting:
run方法执行的时候立马执行,对应的事件类型是ApplicationStartedEvent - environmentPrepared:
ApplicationContext创建之前并且环境信息准备好的时候调用,对应的事件类型是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent - contextPrepared:
ApplicationContext创建好并且在source加载之前调用一次,没有具体的对应事件 - contextLoaded:
ApplicationContext创建并加载之后并在refresh之前调用,对应的事件类型是ApplicationPreparedEvent - finished:
run方法结束之前调用,对应事件的类型是ApplicationReadyEvent或ApplicationFailedEvent
SpringApplicationRunListener目前只有一个实现类EventPublishingRunListener,它把监听的过程封装成了SpringApplicationEvent事件并让内部属性ApplicationEventMulticaster接口的实现类SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster广播出去,广播出去的事件对象会被SpringApplication中的listeners属性进行处理。
所以说SpringApplicationRunListener和ApplicationListener之间的关系是通过ApplicationEventMulticaster广播出去的SpringApplicationEvent所联系起来的。
3.4 事件监听器的工作原理
以启动过程中的listeners.starting()方法为例:
java
public void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}this.listeners中只有一个元素:EventPublishingRunListener。它的starting方法如下:
java
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args));
}其中this.initialMulticaster是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的实例。multicastEvent方法如下:
java
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}首先调用getApplicationListeners方法,根据event的type获得ApplicationListener列表,其中type为ApplicationStartedEvent。getApplicationListeners方法中调用retrieveApplicationListeners获取支持eventType的listener:
java
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType, ListenerRetriever retriever) {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// 获取所有的listener
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
// 遍历listeners,调用supportsEvent判断listener是否支持eventType
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
// 遍历listenerBeans,调用supportsEvent判断listener是否支持eventType
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
Class<?> listenerType = beanFactory.getType(listenerBeanName);
if (listenerType == null || supportsEvent(listenerType, eventType)) {
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}ApplicationStartedEvent事件返回的是4个listener:
- LoggingApplicationListener
- BackgroundPreinitializer
- DelegatingApplicationListener
- LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
回到multicastEvent方法,调用getTaskExecutor获取executor。executor为空,调用invokeListener:
java
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}获取errorHandler,errorHandler为空,调用doInvokeListener方法:
java
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || msg.startsWith(event.getClass().getName())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}可以看到,doInvokeListener方法直接调用了listener的onApplicationEvent方法。
四、启动过程
4.1 开启计时器
程序运行到这里,就已经进入了run方法的主体了,第一步调用的run方法是静态方法,那个时候还没实例化SpringApplication对象,现在调用的run方法是非静态的,是需要实例化后才可以调用的,进来后首先会开启计时器,这个计时器有什么作用呢?顾名思义就使用来计时的嘛,计算springboot启动花了多长时间;
java
[2022-11-18 09:00:05.789][INFO][main] com.test.SpringBootDemoApplication: Started SpringBootDemoApplication in 6.666 seconds (JVM running for 7.789)4.2 设置系统属性
方法主体如下:
java
private void configureHeadlessProperty() {
System.setProperty("java.awt.headless", System.getProperty("java.awt.headless",
Boolean.toString(this.headless)));
}这里将java.awt.headless设置为true,表示运行在服务器端,在没有显示器器和鼠标键盘的模式下照样可以工作,模拟输入输出设备功能。
做了这样的操作后,
SpringBoot想干什么呢?其实是想设置该应用程序,即使没有检测到显示器,也允许其启动。对于服务器来说,是不需要显示器的,所以要这样设置。
通过方法可以看到,setProperty()方法里面又有个getProperty();这不多此一举吗?其实getProperty()方法里面有2个参数, 第一个key值,第二个是默认值,意思是通过key值查找属性值,如果属性值为空,则返回默认值true;保证了一定有值的情况。
4.3 获取并启用监听器
这一步通过监听器来实现初始化的的基本操作,这一步做了2件事情
- 创建所有Spring运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
- 启用监听器
具体可以看上文的《3.2 获取事件监听器》。
4.4 配置并准备环境
将执行run方法时传入的参数封装成一个对象
java
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 创建应用程序的环境信息。
// 如果是web程序,创建StandardServletEnvironment;否则,创建StandardEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境信息。比如profile,命令行参数
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 广播出ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件给相应的监听器执行
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 环境信息的校对
if (!this.webEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
return environment;
}4.5 打印banner信息
这一步的作用很简单,就是在控制台打印应用的启动横幅Banner。如以下内容:
java
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )___ | '_ | '_| | '_ / _` | \ \ \ \
\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |___, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v3.1.5)resources目录下添加banner.txt文件即可替换,其他什么都不需要。
4.6 创建应用上下文
java
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
// 判断是否是web应用,
// 如果是创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext,否则创建AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment
? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}4.7 配置上下文
这一步非常关键,很多核心操作都是在这一步完成的:
java
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置Spring容器上下文的环境信息
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// Spring容器创建之后做一些额外的事
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// SpringApplication的初始化器开始工作
applyInitializers(context);
// 遍历调用SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared方法。目前只是将这个事件广播器注册到Spring容器中
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// 把应用程序参数持有类注册到Spring容器中,并且是一个单例
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
// 加载sources,sources是main方法所在的类
Set<Object> sources = getSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 将sources加载到应用上下文中。最终调用的是AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader.registerBean方法
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[sources.size()]));
// 广播出ApplicationPreparedEvent事件给相应的监听器执行
// 执行EventPublishingRunListener.contextLoaded方法
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}Spring容器创建之后回调方法postProcessApplicationContext
java
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 如果SpringApplication设置了实例命名生成器,则注册到Spring容器中
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(
AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
this.beanNameGenerator);
}
// 如果SpringApplication设置了资源加载器,设置到Spring容器中
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext) context)
.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader) context)
.setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
}初始化器开始工作:
java
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 遍历每个初始化器,调用对应的initialize方法
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(
initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}首先调用getInitializers方法获取之前取得的初始化器。之后调用初始化器的initialize方法。
4.8 刷新上下文
这一步,是Spring启动的核心步骤了,这一步骤包括了实例化所有的Bean、设置它们之间的依赖关系以及执行其他的初始化任务。
java
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
this.refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
} catch (AccessControlException var3) {
}
}
}
java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 为刷新操作准备此上下文
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部 bean 工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 为在此上下文中使用做好 bean 工厂的准备工作
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对 bean 工厂进行后处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用在上下文中注册为 bean 的工厂处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截 bean 创建的 bean 处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化此上下文的消息源
initMessageSource();
// 初始化此上下文的事件多播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 在特定上下文子类中初始化其他特殊 bean
onRefresh();
// 检查监听器 bean 并注册它们
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余的(非懒加载)单例
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后一步:发布相应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 销毁已经创建的单例以避免悬挂资源
destroyBeans();
// 重置"激活"标志
cancelRefresh(ex);
// 将异常传播给调用者
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 在 Spring 的核心中重置常见的内省缓存,因为我们可能不再需要单例 bean 的元数据...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}所以,这一步中,主要就是创建BeanFactory,然后再通过BeanFactory来实例化Bean。
在refresh -> onRefresh中,这里会调用到AbstractApplicationContext的onRefresh中,然后调用web容器的OnRefresh方法。
OnRefresh方法就是Web容器启动的入口,具体的启动流程可以参考Tomcat的启动流程。
4.9 刷新上下文后置处理
java
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ApplicationArguments args) {
callRunners(context, args);
}
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<Object>();
// 找出Spring容器中ApplicationRunner接口的实现类
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
// 找出Spring容器中CommandLineRunner接口的实现类
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
// 对runners进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
// 遍历runners依次执行
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<Object>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}最后,SpringBoot的启动过程主要流程如下: