数学原理
- 线段长度的平方 = 线段两端端点组成向量与其自身的内积

- 向量外点向向量上投影的相对位置 t
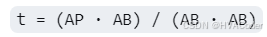
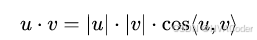
第一种情况,P向AB投影在AB中间,cosθ > 0
AP AB向量点积等于AB,AP的模以及cosθ乘积
所以 t 等于( |AP | * cosθ ) / |AB | = |AX | / |AB|
垂足X的坐标就可以根据 t, A,B坐标计算:
X = A + t * AB向量
然后得到PX向量
对PQ上每一个点 point 执行 point + PX向量,即完成平移
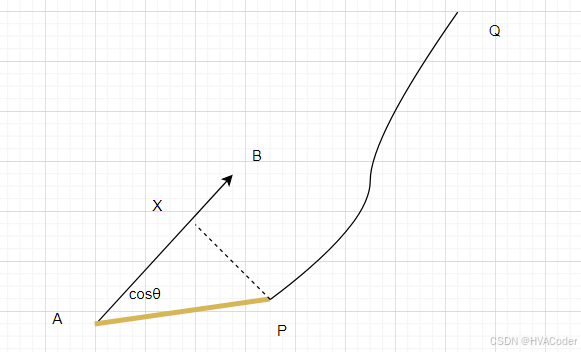
第二种情况,投影在AB外,靠近A的方向, cosθ < 0
t 为负数
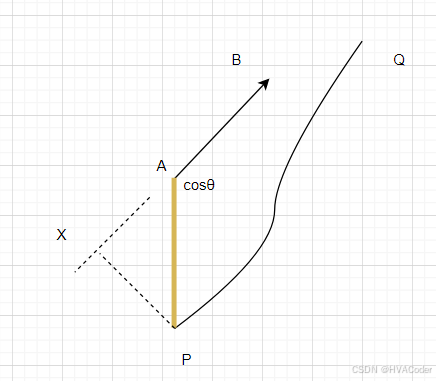
第三种情况,投影在AB外,靠近B的方向,类似的
python代码
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
def normalize_vector(v):
"""单位化向量"""
norm = np.linalg.norm(v)
if norm == 0:
return v
return v / norm
def point_to_line_distance(point, line_point1, line_point2):
"""
计算点到直线的距离
参数:
point: 点的坐标 (x,y)
line_point1, line_point2: 直线上的两个点
返回:
点到直线的距离
"""
p = np.array(point)
p1 = np.array(line_point1)
p2 = np.array(line_point2)
# 直线方向向量
line_dir = p2 - p1
line_length = np.linalg.norm(line_dir)
if line_length < 1e-10:
# 如果线段长度为零,返回点到点的距离
return np.linalg.norm(p - p1)
# 计算点到直线的距离
# 使用向量叉积公式:|(p-p1) × (p2-p1)| / |p2-p1|
distance = np.abs(np.cross(p2-p1, p-p1)) / line_length
return distance
def point_to_line_perpendicular_vector(point, line_point1, line_point2):
"""
计算点到直线的垂线向量
返回从点到直线的垂线向量(从点指向直线)
"""
p = np.array(point)
p1 = np.array(line_point1)
p2 = np.array(line_point2)
# 直线方向向量
line_dir = p2 - p1
line_length_squared = np.dot(line_dir, line_dir)
if line_length_squared < 1e-10:
return p1 - p
# 计算投影参数 t
t = np.dot(p - p1, line_dir) / line_length_squared
# 计算垂足坐标
foot_point = p1 + t * line_dir
# 垂线向量(从点指向垂足)
perpendicular_vector = foot_point - p
return perpendicular_vector
def translate_curve_by_first_point_distance(line_points, curve_points):
"""
将曲线沿着线段的垂线方向平移,平移距离等于曲线第一个点到线段的垂直距离
参数:
line_points: 线段的两个端点 [(x1,y1), (x2,y2)]
curve_points: 曲线的点集 [(x,y), ...]
返回:
平移后的曲线点集
"""
if len(curve_points) == 0:
return curve_points
# 提取线段端点和曲线第一个点
p1, p2 = np.array(line_points[0]), np.array(line_points[1])
first_point = np.array(curve_points[0])
# 计算第一个点到线段的垂线向量
perp_vector = point_to_line_perpendicular_vector(first_point, p1, p2)
# 计算垂线距离(平移距离)
distance = np.linalg.norm(perp_vector)
# 计算垂线方向单位向量
if distance > 1e-10:
unit_perp = perp_vector / distance
else:
# 如果点在直线上,使用法线方向
line_dir = p2 - p1
unit_perp = normalize_vector(np.array([line_dir[1], -line_dir[0]]))
# 平移所有曲线点
translated_points = []
for point in curve_points:
new_point = np.array(point) + unit_perp * distance
translated_points.append(new_point)
return np.array(translated_points), distance
def create_parabola(a, b, c, x_range, num_points=50):
"""创建抛物线点集"""
x = np.linspace(x_range[0], x_range[1], num_points)
y = a * x**2 + b * x + c
return list(zip(x, y))
# 可视化函数
def plot_translation_result(line_points, original_curve, translated_curve, distance, title):
"""绘制平移结果"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
chinese_fonts = [f.name for f in fm.fontManager.ttflist if 'CJK' in f.name or 'Hei' in f.name or 'YaHei' in f.name]
print("可用的中文字体:", chinese_fonts)
# 如果有可用中文字体,使用第一个
if chinese_fonts:
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = [chinese_fonts[0], 'DejaVu Sans']
else:
print("未找到中文字体,需要安装")
# 绘制原始线段
line_x = [line_points[0][0], line_points[1][0]]
line_y = [line_points[0][1], line_points[1][1]]
plt.plot(line_x, line_y, 'b-', linewidth=3, label='参考线段', marker='o', markersize=8)
# 绘制原始曲线
orig_x, orig_y = zip(*original_curve)
plt.plot(orig_x, orig_y, 'red', linewidth=2, label='原始曲线')
plt.scatter(orig_x, orig_y, c='red', s=30, alpha=0.6)
# 绘制平移后的曲线
trans_x, trans_y = zip(*translated_curve)
plt.plot(trans_x, trans_y, 'green', linewidth=2, label='平移后曲线')
plt.scatter(trans_x, trans_y, c='green', s=30, alpha=0.6)
# 标记第一个点并绘制垂线
first_point = original_curve[0]
plt.scatter(first_point[0], first_point[1], c='darkred', s=100, marker='*',
label='曲线第一个点', zorder=5)
# 计算垂足
p1, p2 = np.array(line_points[0]), np.array(line_points[1])
first_pt = np.array(first_point)
line_dir = p2 - p1
t = np.dot(first_pt - p1, line_dir) / np.dot(line_dir, line_dir)
foot_point = p1 + t * line_dir
# 绘制垂线
plt.plot([first_point[0], foot_point[0]], [first_point[1], foot_point[1]],
'purple', linestyle='--', linewidth=2, label=f'垂线 (距离: {distance:.2f})')
plt.scatter(foot_point[0], foot_point[1], c='blue', s=80, marker='s', label='垂足')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.axis('equal')
plt.legend()
plt.title(f'{title}\n平移距离: {distance:.2f}')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.show()
# 示例使用
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=== 自适应平移距离测试 ===\n")
# 测试1: 水平线段 + 抛物线
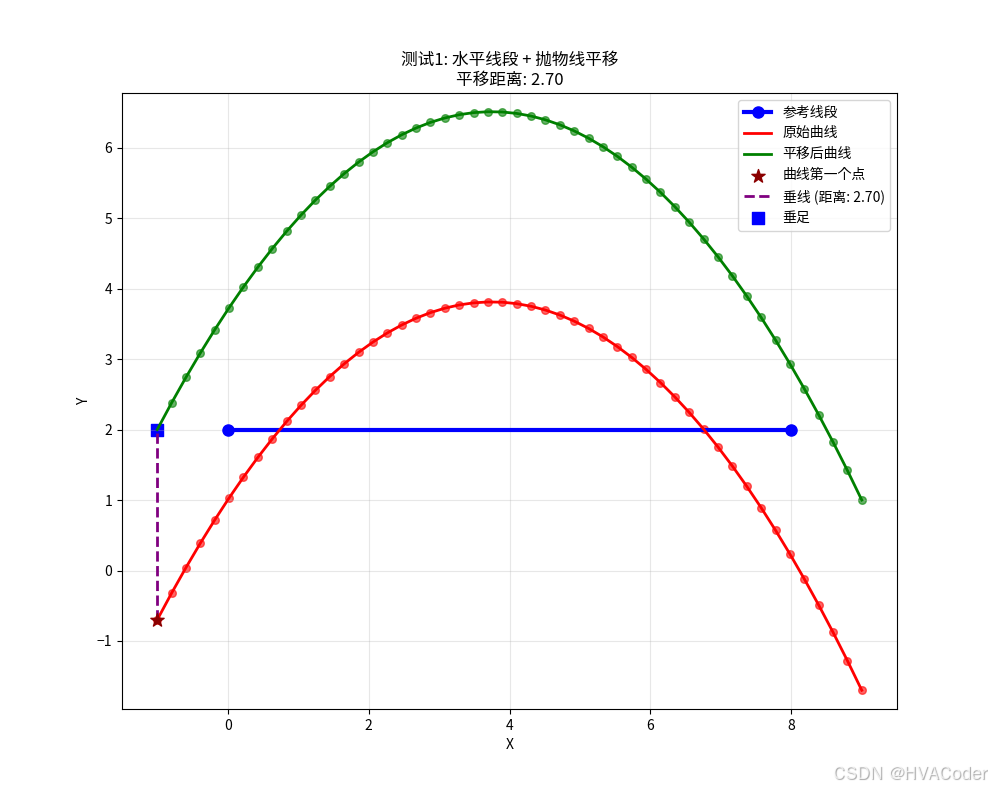
print("测试1: 水平线段 + 抛物线")
line_segment1 = [(0, 2), (8, 2)] # 水平线段
parabola1 = create_parabola(a=-0.2, b=1.5, c=1, x_range=(-1, 9))
translated_parabola1, distance1 = translate_curve_by_first_point_distance(line_segment1, parabola1)
plot_translation_result(line_segment1, parabola1, translated_parabola1, distance1,
"测试1: 水平线段 + 抛物线平移")
# 测试2: 斜线段 + 倒抛物线
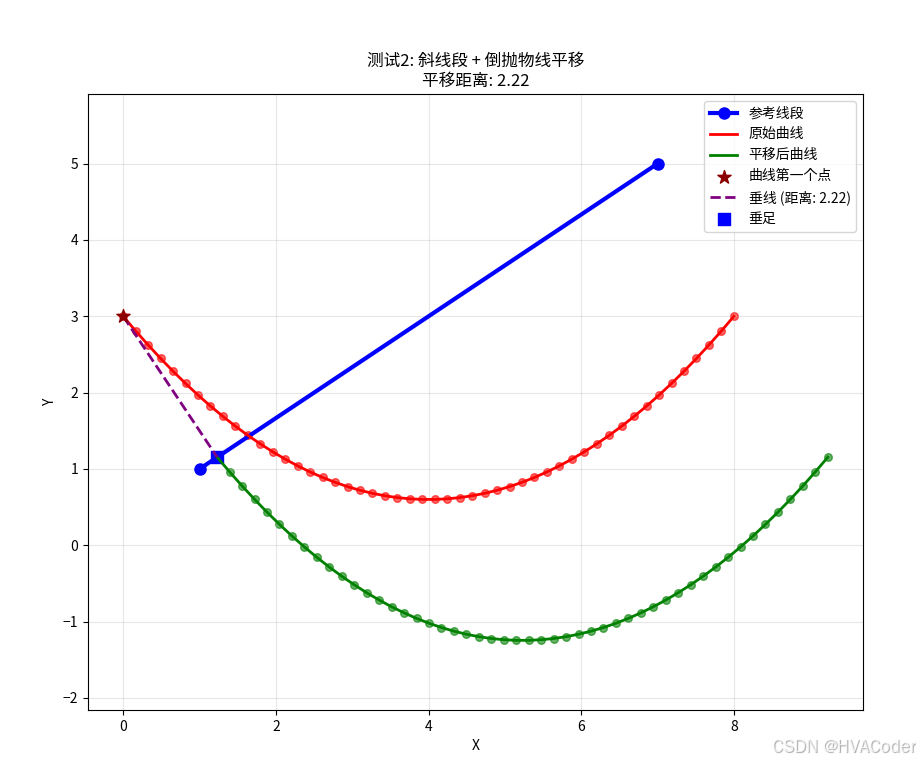
print("测试2: 斜线段 + 倒抛物线")
line_segment2 = [(1, 1), (7, 5)] # 斜线段
parabola2 = create_parabola(a=0.15, b=-1.2, c=3, x_range=(0, 8))
translated_parabola2, distance2 = translate_curve_by_first_point_distance(line_segment2, parabola2)
plot_translation_result(line_segment2, parabola2, translated_parabola2, distance2,
"测试2: 斜线段 + 倒抛物线平移")
# 测试3: 垂直线段 + 宽抛物线
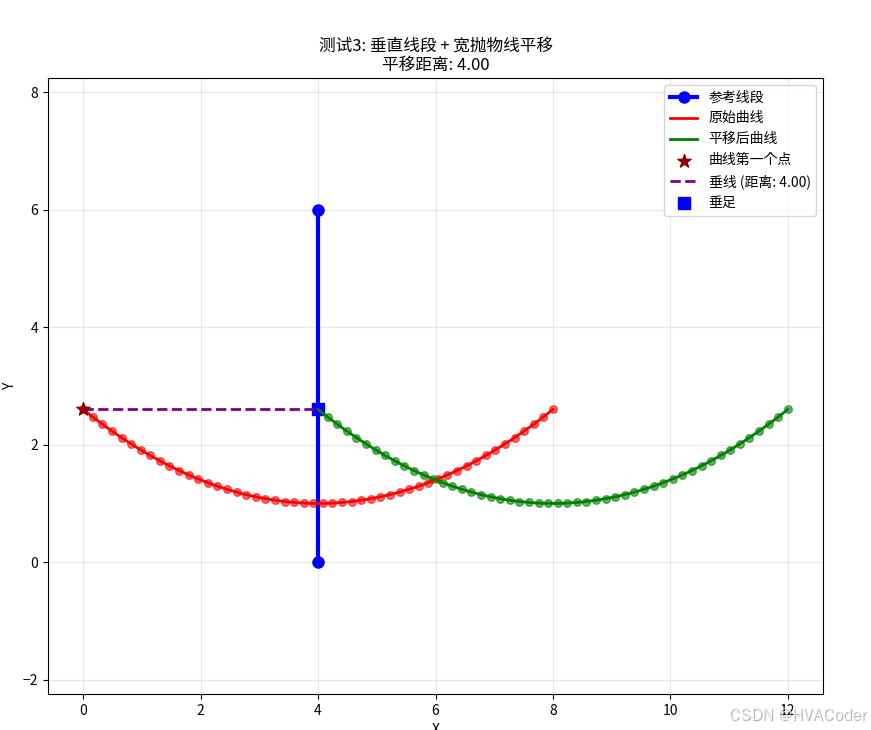
print("测试3: 垂直线段 + 宽抛物线")
line_segment3 = [(4, 0), (4, 6)] # 垂直线段
x3 = np.linspace(0, 8, 50)
y3 = 0.1 * (x3 - 4)**2 + 1
parabola3 = list(zip(x3, y3))
translated_parabola3, distance3 = translate_curve_by_first_point_distance(line_segment3, parabola3)
plot_translation_result(line_segment3, parabola3, translated_parabola3, distance3,
"测试3: 垂直线段 + 宽抛物线平移")
# 测试4: 验证平移精度
print("测试4: 验证平移精度")
line_segment4 = [(2, 2), (6, 4)] # 斜线段
parabola4 = create_parabola(a=0.1, b=-0.5, c=3, x_range=(1, 7))
translated_parabola4, distance4 = translate_curve_by_first_point_distance(line_segment4, parabola4)
# 验证平移后第一个点到线段的距离应该接近0
first_point_after = translated_parabola4[0]
new_distance = point_to_line_distance(first_point_after, line_segment4[0], line_segment4[1])
print(f"原始第一个点到线段距离: {distance4:.6f}")
print(f"平移后第一个点到线段距离: {new_distance:.6f}")
print(f"平移精度误差: {abs(new_distance):.6f}")
plot_translation_result(line_segment4, parabola4, translated_parabola4, distance4,
"测试4: 平移精度验证")
print("\n=== 所有测试完成 ===")效果可视化