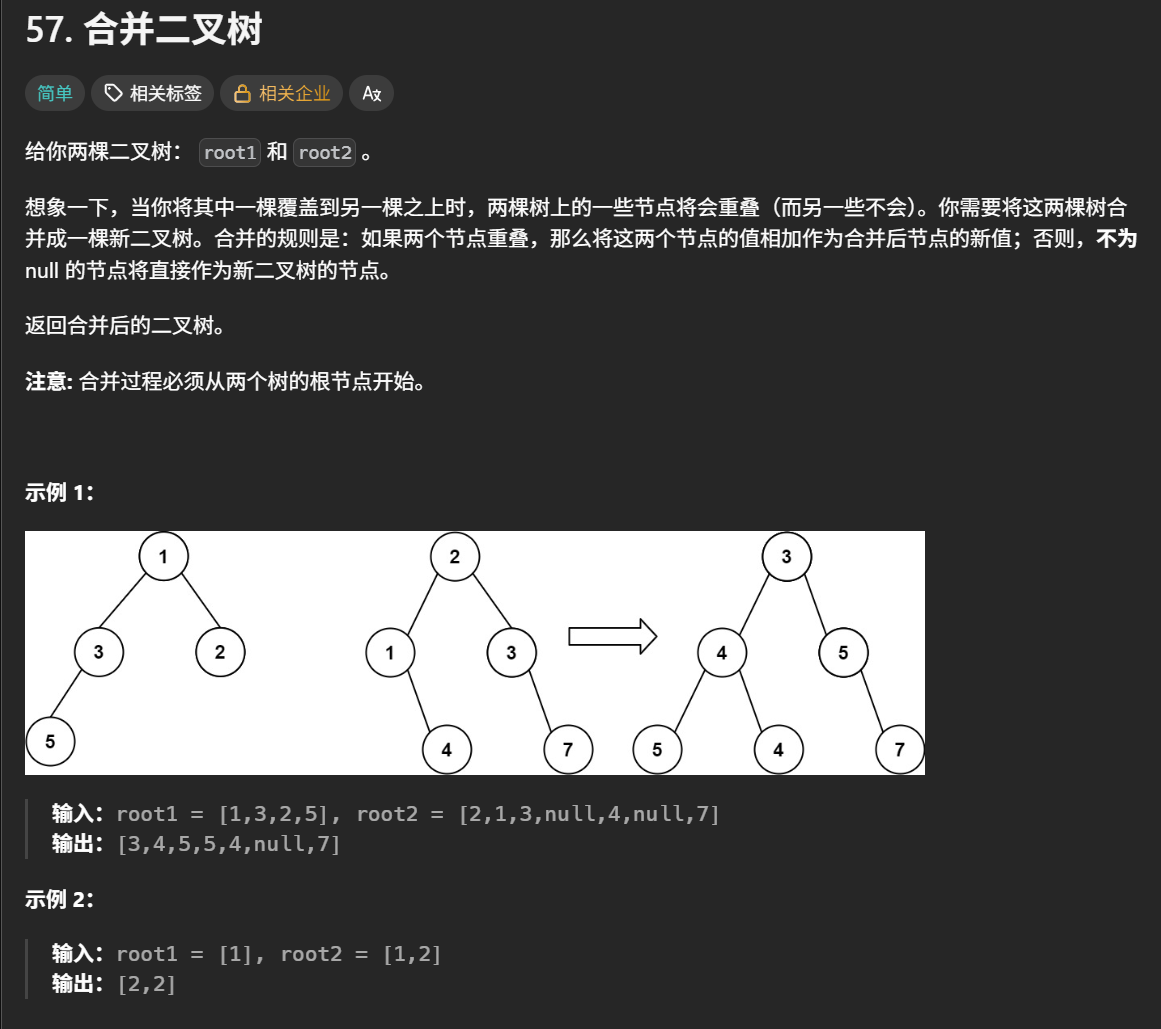
题目要求:
1.如果两个节点重叠,则两个节点值相加作为合并后节点的新值。
2.否则,不为null的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
3.合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
思路:同时遍历两个二叉树,其实和遍历一个树的逻辑是一样的,只不过需要传入两个树的节点同时操作。
方法一:前序遍历递归(使用中序、后序遍历也可)。
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:因为要合并两棵树,所以参数是两个二叉树的根节点,返回值是合并后二叉树的根节点。
java
TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2)2.确定终止条件:因为传入了两个树,那么就有两个树遍历的节点root1和root2。
(1)如果root1 == null,两个树合并之后就是root2;
(2)反过来如果root2 == null,两个树合并之后就是root1。
(3)如果两个树都是null,合并之后自然是null(可省略不写)。
java
if(root1 == null){
return root2;
}
if(root2 == null){
return root1;
}3.确定单层递归的逻辑:借助root1树存放合并后树的节点值。接下来root1的左子树就是合并root1和root2后的左子树;root1的右子树就是合并root1和root2后的右子树。最终root1就是合并后的根节点。
java
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
return root1;附代码:
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null){
return root2;
}
if(root2 == null){
return root1;
}
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
return root1;
}
}方法二:层序遍历迭代法
思路:把两个树的节点同时加入队列。
附代码:
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
queue.add(root1);
queue.add(root2);
while(queue.size() > 0){
TreeNode t1 = queue.remove();
TreeNode t2 = queue.remove();
//此时两个节点一定不为空,val值相加
t1.val += t2.val;
if(t1.left != null && t2.left != null){
queue.add(t1.left);
queue.add(t2.left);
}
if(t1.right != null && t2.right != null){
queue.add(t1.right);
queue.add(t2.right);
}
//如果t1的左节点为空,则把t2的左节点赋值过去
if(t1.left == null && t2.left != null){
t1.left = t2.left;
}
//如果t1的右节点为空,则把t2的右节点赋值过去
if(t1.right == null && t2.right != null){
t1.right = t2.right;
}
}
return root1; //返回合并后的root1
}
}