一、倍增思想
倍增,顾名思义就是翻倍。它能够使线性的处理转化为对数级的处理,极大地优化了时间复杂度。
1.1 【模板】快速幂
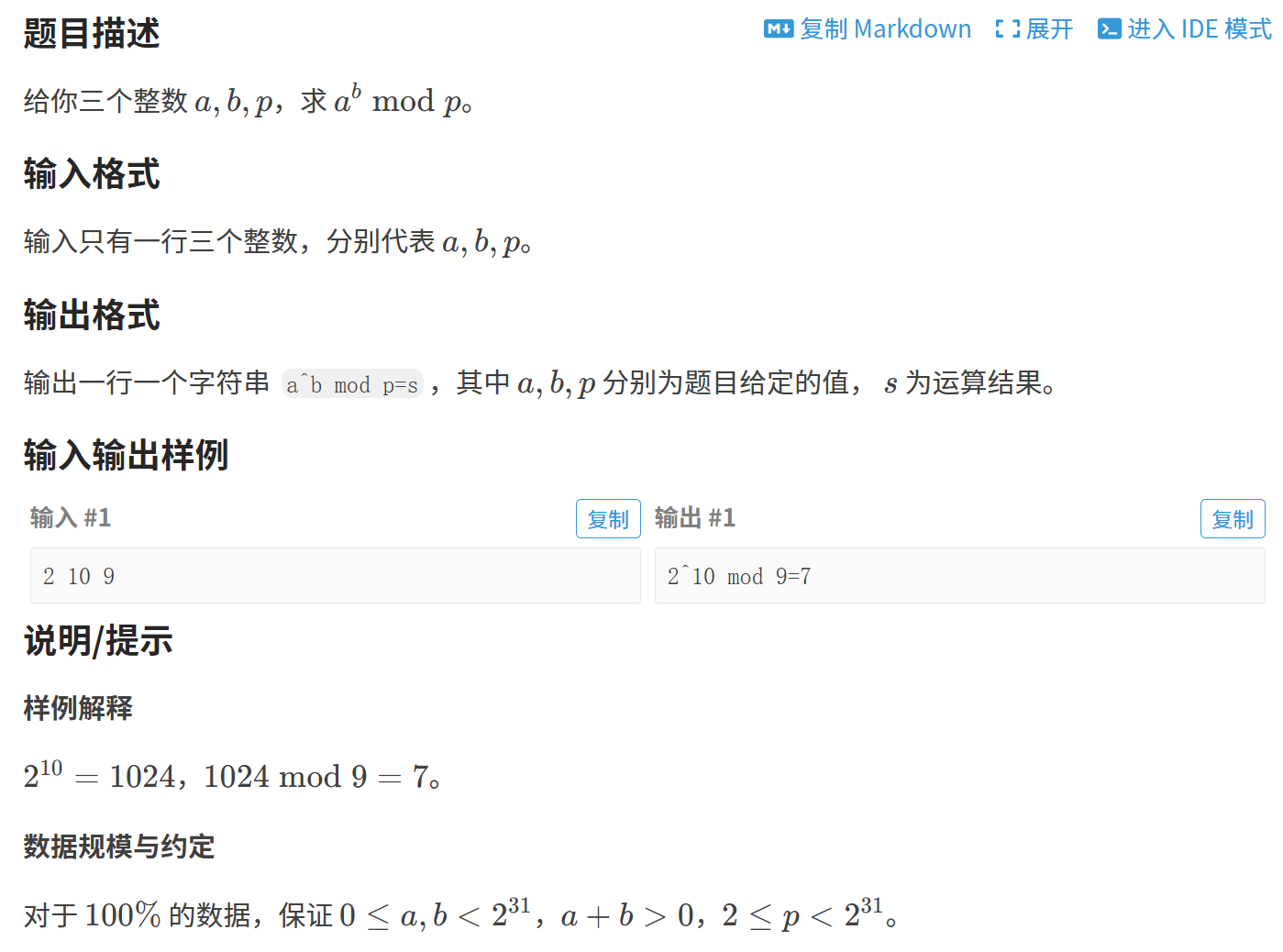
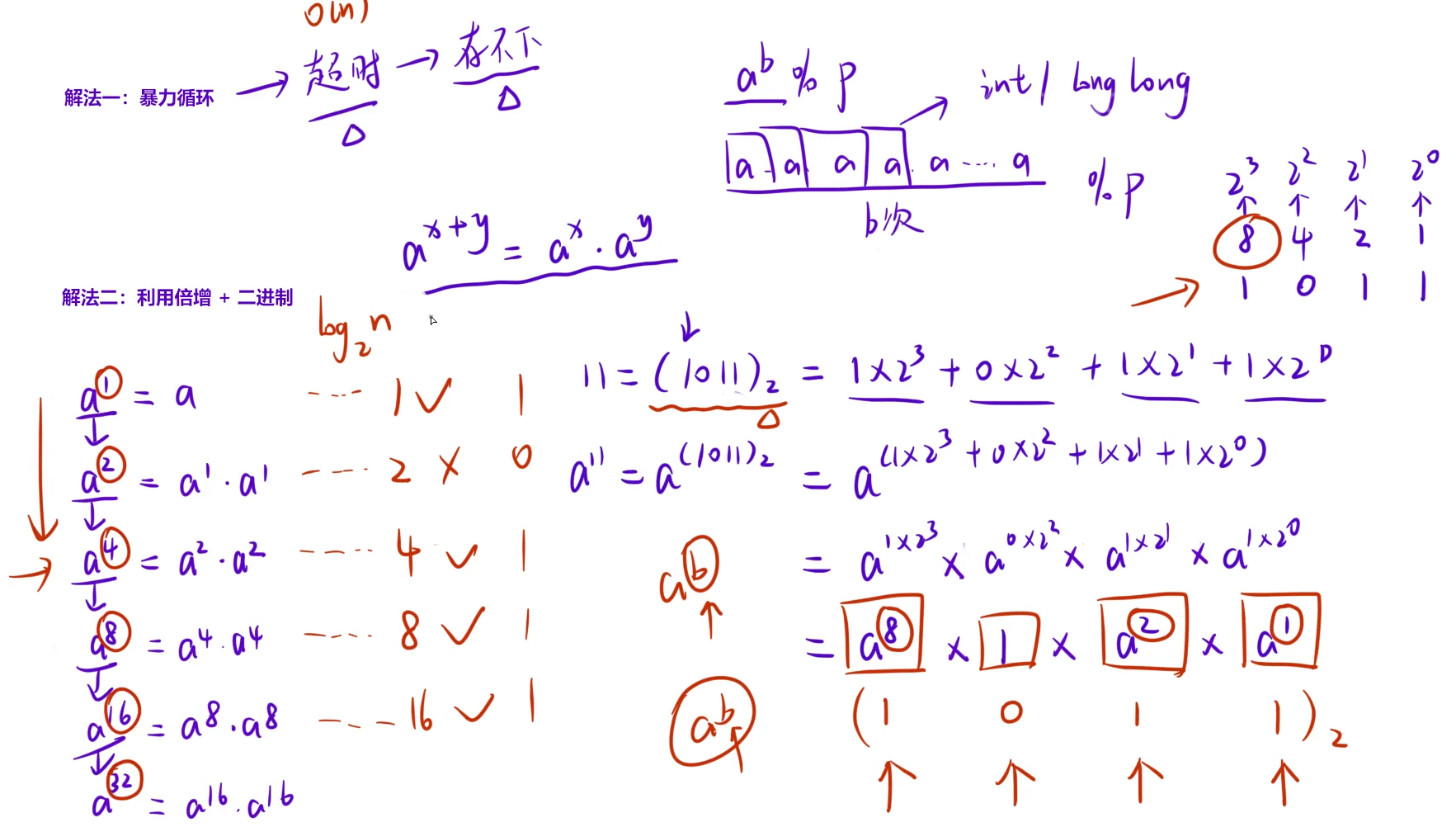

注:如果计算过程中存在除法时,取模会造成结果错误,这时候就需要"求逆元",关于如何求逆元,在后续章节中会有所讲解。
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a, b, p;
// 快速幂的模板
LL qpow(LL a, LL b, LL p)
{
LL ret = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
ret = ret * a % p;
a = a * a % p;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> a >> b >> p;
printf("%lld^%lld mod %lld=%lld", a, b, p, qpow(a, b, p));
return 0;
}1.2 【练习】64位整数乘法
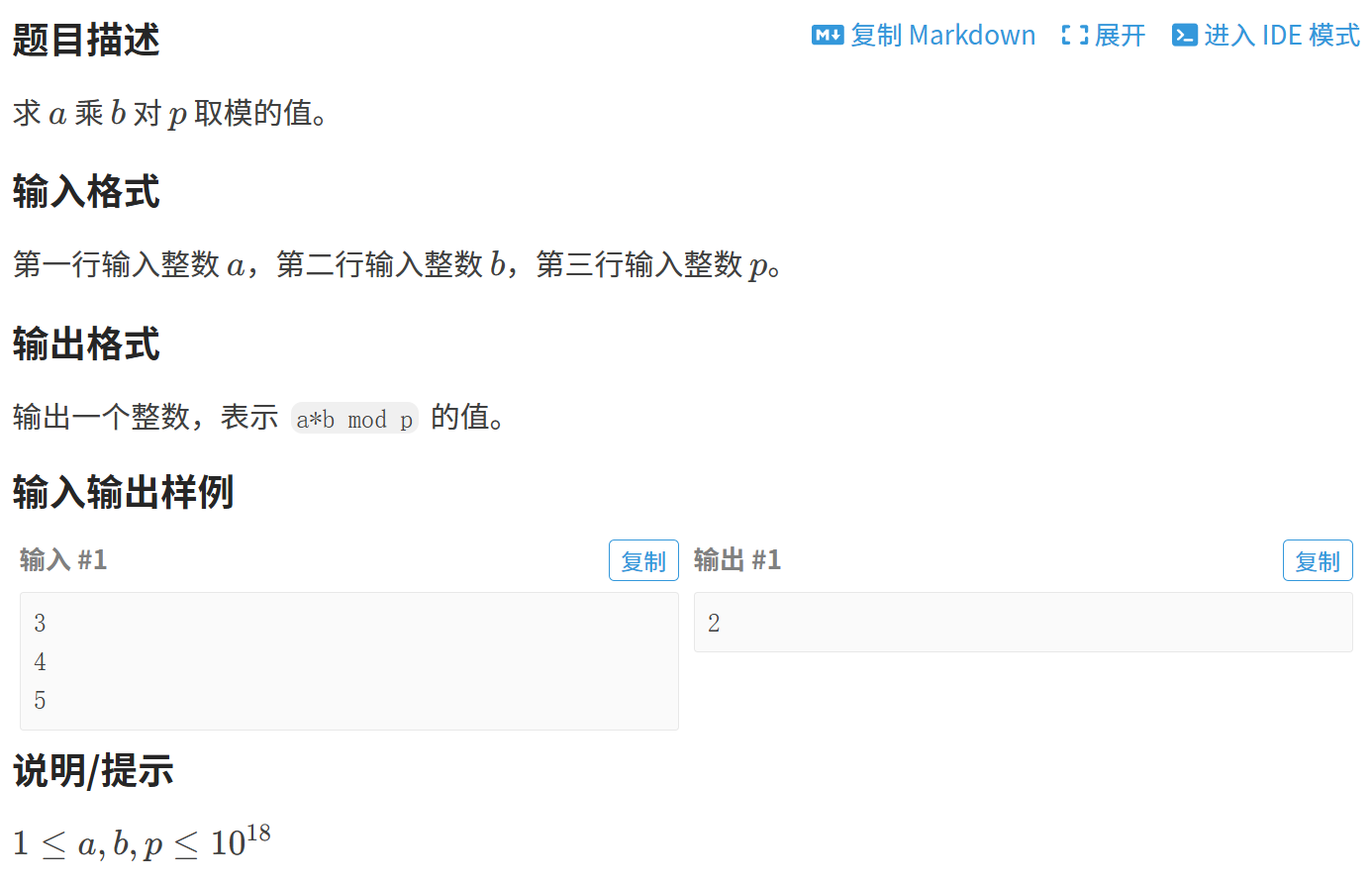
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a, b, p;
// 快速乘的模板
LL qmul(LL a, LL b, LL p)
{
LL sum = 0;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
sum = (sum + a) % p;
a = (a + a) % p;
b >>= 1;
}
return sum;
}
int main()
{
cin >> a >> b >> p;
cout << qmul(a, b, p) << endl;
return 0;
}二、离散化
当题目中数据范围很大,但是数据总量不是很大。此时如果需要用数据的值来映射数组的下标时,就可以用离散化的思想预处理一下所有的数据,使得每一个数据都映射成一个较小的值,之后再用离散化之后的数去处理问题。
【离散化模板1】排序+去重+二分查找离散化之后的结果
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
int pos; //标记去重之后的元素个数
int disc[N]; //帮助离散化
//二分x的位置
int find(int x)
{
int l = 1, r = pos;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (disc[mid] >= x)
r = mid;
else
l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
disc[++pos] = a[i];
}
//离散化
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos); //排序
pos = unique(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos) - (disc + 1); //去重
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cout << a[i] << "离散化之后:" << find(a[i]) << endl;
}
return 0;
}【离散化模板2】排序+哈希表去重以及记录最终位置
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n;
int a[N];
int pos;
int disc[N];
unordered_map<int, int> id; //<原始值, 离散之后的值>
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
disc[++pos] = a[i];
}
//离散化
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos); //排序
int cnt = 1; //当前这个值是第几号元素
for (int i = 1;i <= pos;i++)
{
int x = disc[i];
if (id.count(x))
continue;
id[x] = cnt;
cnt++;
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cout << a[i] << "离散化之后的值:" << id[a[i]] << endl;
}
return 0;
}【练习1】火烧赤壁
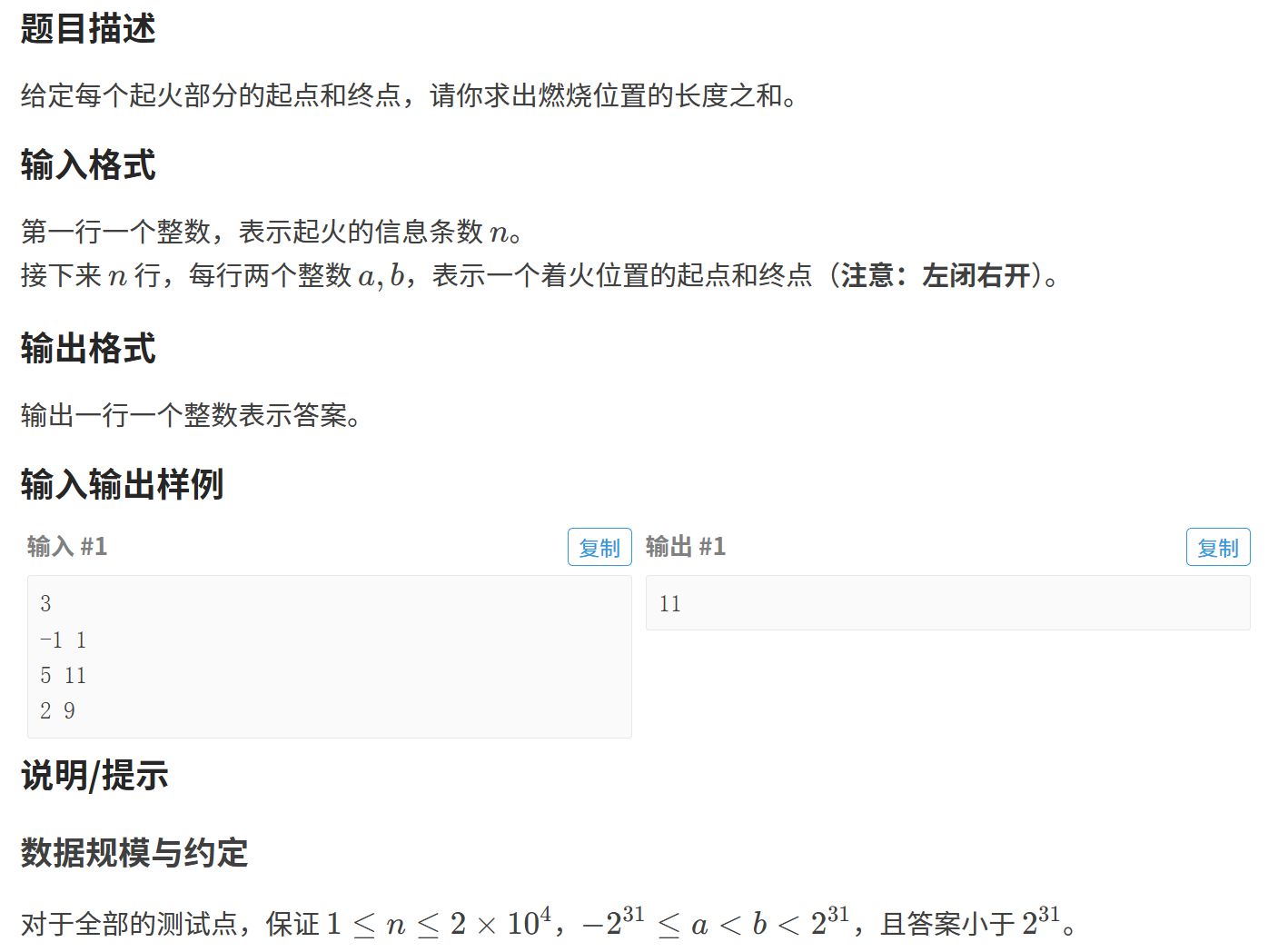
如果不看数据范围的话,这道题就是一道典型的差分问题。对着火区间内的所有元素统一加上1,处理完差分数组之后还原原数组,原数组中大于0的区间就是所有的着火区间。但是,最大的问题就是题目的数据范围太大,是创建不出来我们所需要的差分数组的。所以这道题要先进行离散化之后,再差分。
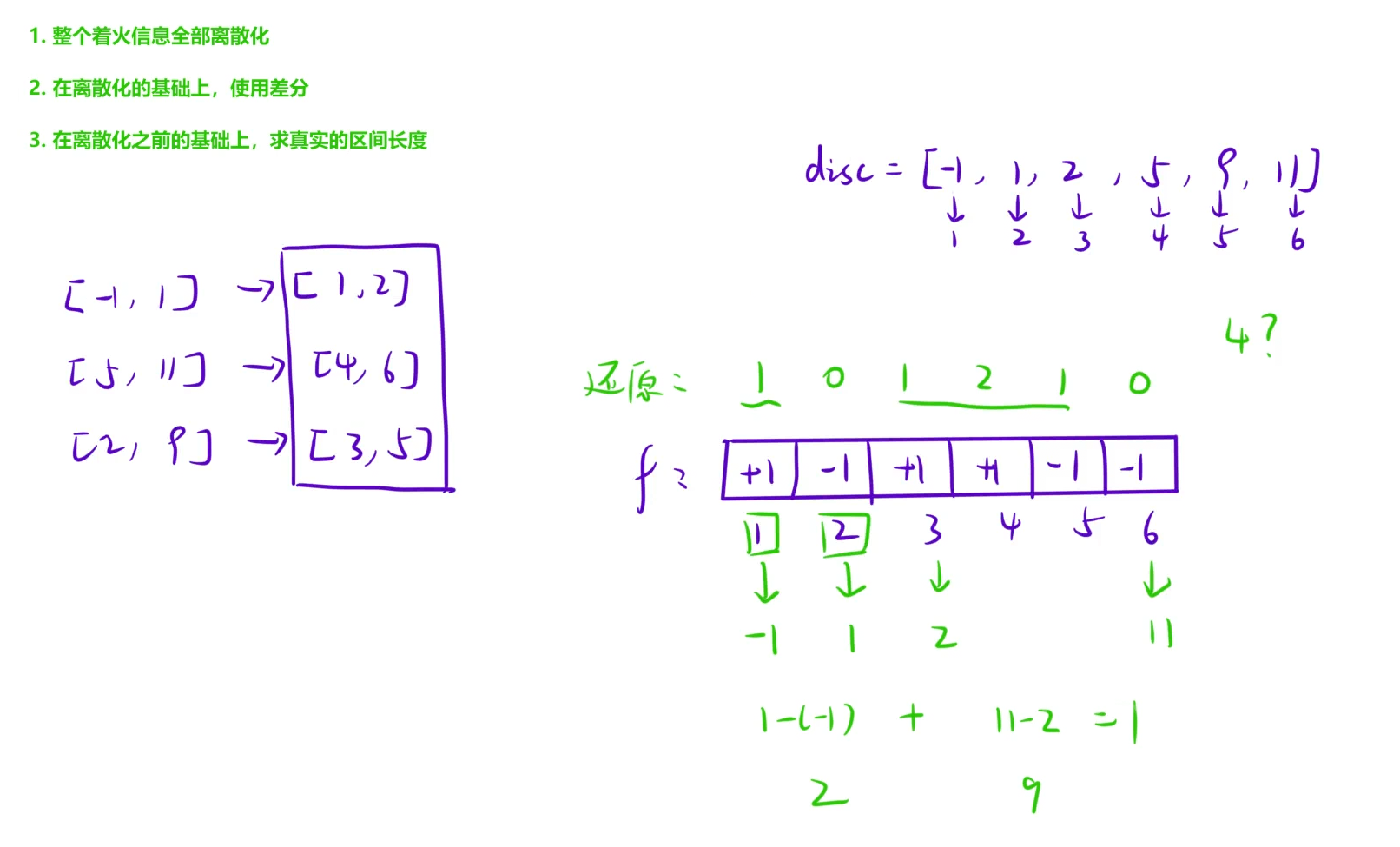
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e4 + 10;
int n;
int a[N], b[N];
int pos;
int disc[2 * N];
unordered_map<int, int> id;
int f[N * 2]; //差分数组
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
disc[++pos] = a[i];
disc[++pos] = b[i];
}
//离散化
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos);
pos = unique(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos) - (disc + 1);
for (int i = 1;i <= pos;i++)
{
int x = disc[i];
id[x] = i;
}
//离散化的基础上做差分
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
// a[i]~b[i]
int l = id[a[i]];
int r = id[b[i]];
f[l] += 1;
f[r] -= 1;
}
//还原数组
for (int i = 1;i <= pos;i++)
{
f[i] = f[i - 1] + f[i];
}
//统计结果
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= pos;i++)
{
int j = i;
while (j <= pos && f[j] > 0)
j++;
//i ~ j
ret += disc[j] - disc[i];
i = j;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}【练习2】贴海报

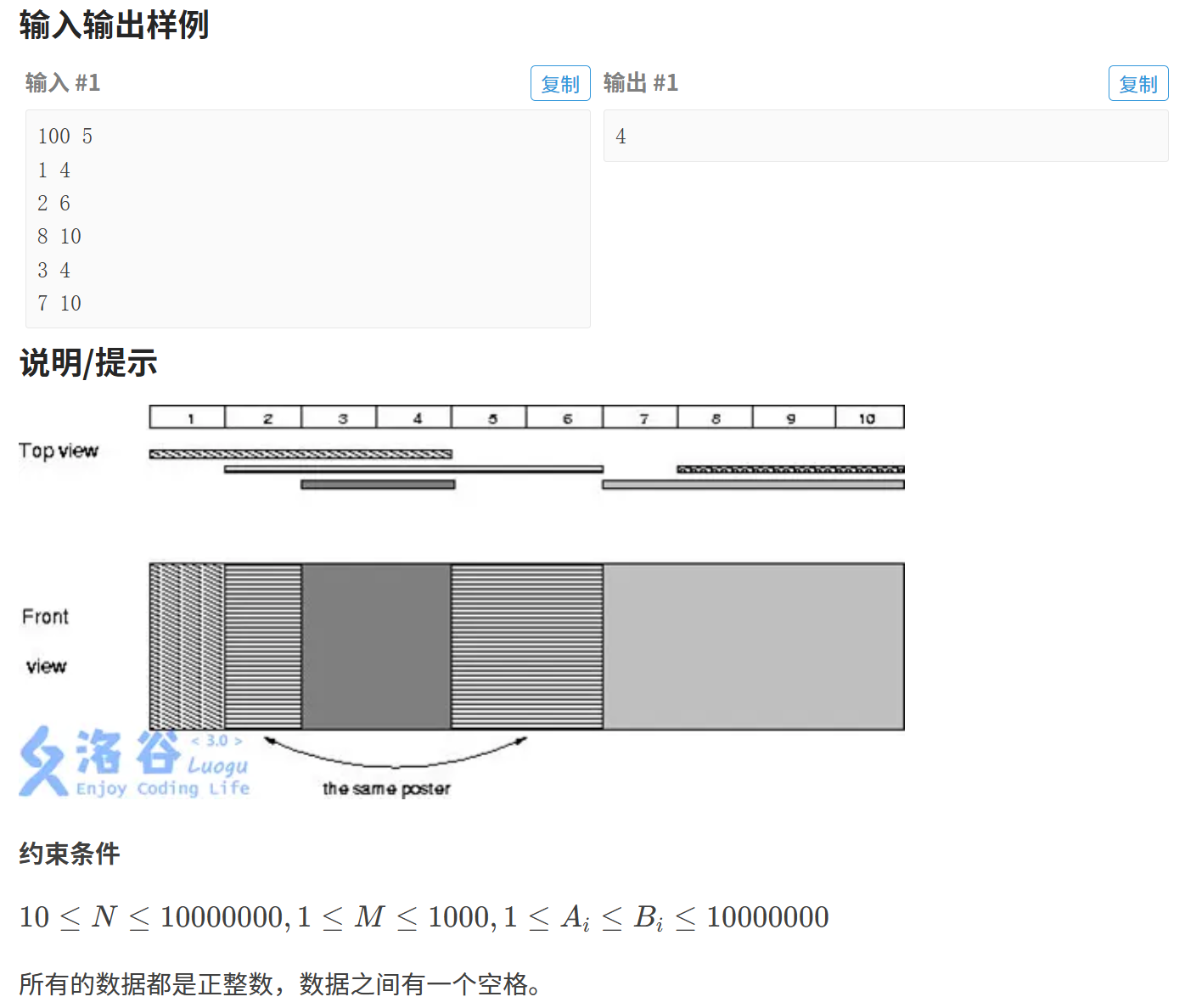
这道题的解法很简单,就是模拟整个流程,然后看数组中有多少种不同的数即可。但是和上道题一样,数据范围很大,但是数据个数较少,所以要先离散化,再进行模拟。
但是直接这样做又会导致一个问题,我们在离散化时,会把有的区间缩小,此时在做区间覆盖 问题的时候,会把缩小的区间完全覆盖掉,这样可能会导致计算出的结果不对。该如何解决这个问题呢?我们需要在离散化[x, y]的时候,把x+1 和 y+1 这两个数也离散化进去。
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int a[N], b[N];
int pos;
int disc[N * 4];
unordered_map<int, int> id;
int w[N * 4]; //海报墙
bool st[N * 4]; //标记哪些数字已经出现过
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++)
{
cin >> a[i] >> b[i];
disc[++pos] = a[i];
disc[++pos] = a[i] + 1;
disc[++pos] = b[i];
disc[++pos] = b[i] + 1;
}
//离散化
sort(disc + 1, disc + 1 + pos);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= pos;i++)
{
int x = disc[i];
if (id.count(x))
continue;
++cnt;
id[x] = cnt;
}
//在离散化的基础上,模拟贴海报的过程
for (int i = 1;i <= m;i++)
{
for (int j = id[a[i]];j <= id[b[i]];j++)
{
w[j] = i;
}
}
//统计结果------数组中有多少个不同的数
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1;i <= cnt;i++)
{
int x = w[i];
if (x == 0 || st[x])
continue;
ret++;
st[x] = true;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}