二叉搜索树
✨前言: 二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST)是一种基础且高效的数据结构,用于实现快速的查找、插入和删除操作。它通过在节点间保持有序关系,使得数据的组织更加灵活高效。本文将从概念出发,结合示意图与完整代码,带你深入理解二叉搜索树的构建原理与应用场景。
📖专栏 :【数据结构】
目录
- 二叉搜索树
-
- 一、二叉搜索树的概念
- 二、二叉搜索树的性能分析
- 三、二叉搜索树的插入
- 四、二叉搜索树的查找
- 五、二叉搜索树的删除
- 六、二叉搜索树的实现代码
- 七、二叉搜索树key和key/value使用场景
-
- [7.1 key说明与使用](#7.1 key说明与使用)
- [7.2 key/value说明与使用](#7.2 key/value说明与使用)
- 总结
一、二叉搜索树的概念
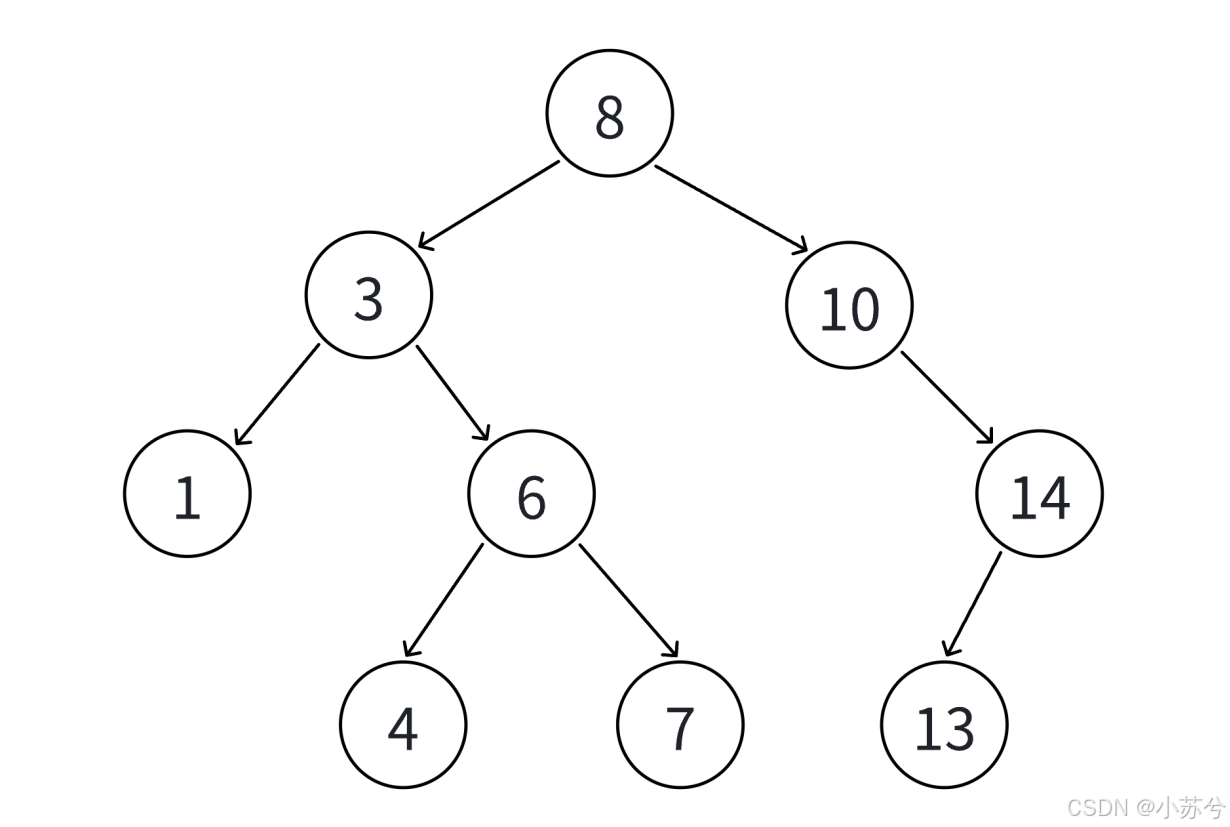
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
- 左子树性质:若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有结点的值都小于等于根结点的值
- 右子树性质:若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有结点的值都大于等于根结点的值
- 递归性质:它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
- 二叉搜索树中可以支持插入相等的值,也可以不支持插入相等的值,具体看使用场景定义,下篇我们学习map/set/multimap/multiset系列容器底层就是二叉搜索树,其中map/set不支持插入相等值,multimap/multiset支持插入相等值。
二、二叉搜索树的性能分析
-
时间复杂度分析
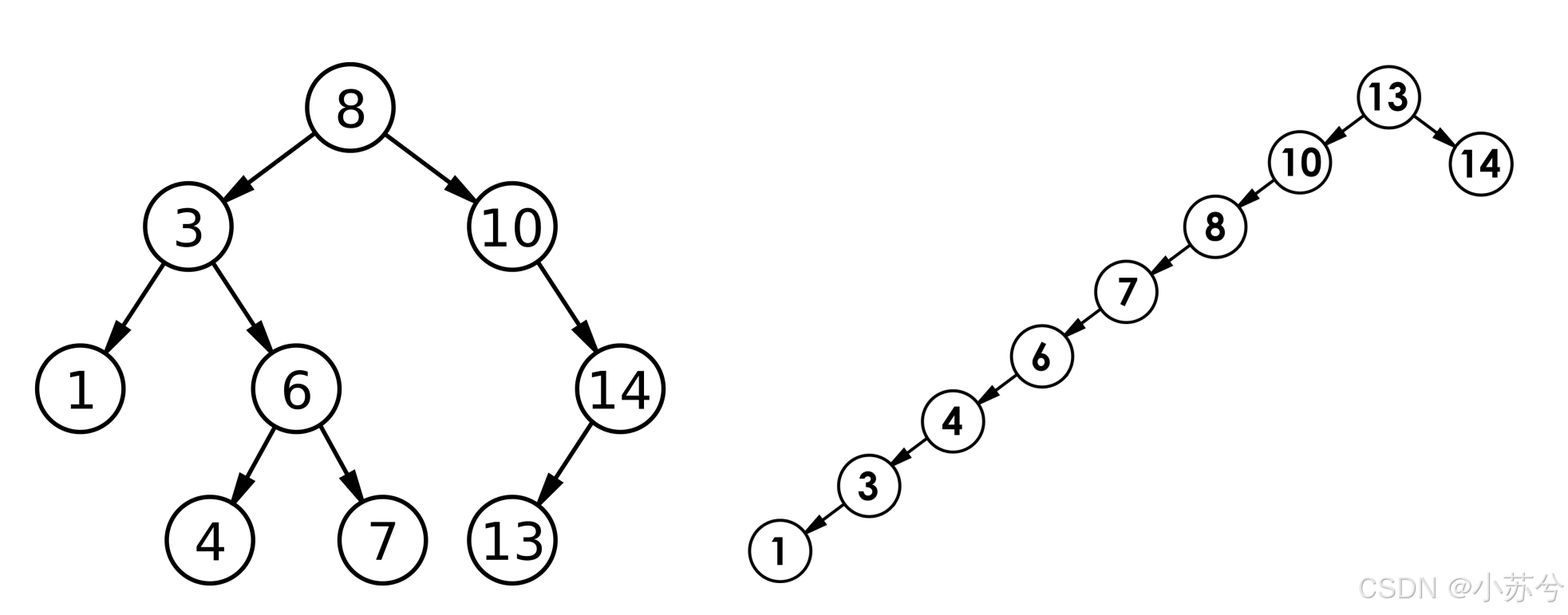
最优情况 :二叉搜索树为完全二叉树(或接近完全二叉树)- 其高度为: log 2 N \log_2 N log2N
最差情况 :- 二叉搜索树退化为单支树(或类似单支) 其高度为: N N N
综合时间复杂度 :二叉搜索树增删查改时间复杂度为: O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
-
二叉搜索树的局限性:这样的效率显然无法满足我们的需求,因此需要学习二叉搜索树的变形:
平衡二叉搜索树 AVL 树
红黑树这些数据结构才能适用于我们在内存中存储和搜索数据的需求。
- 与二分查找的比较
二分查找也可以实现 O ( log 2 N ) O(\log_2 N) O(log2N) 级别的查找效率,但是有两大缺陷:
- 存储结构限制:需要存储在支持下标随机访问的结构中,并且有序
- 插入删除效率低:存储在下标随机访问的结构中,插入和删除数据一般需要挪动数据
这里就体现出了平衡二叉搜索树的价值------它既保持了二叉搜索树的动态操作优势,又通过平衡机制保证了 O(\\log N) 的操作效率。
在此基础上,我们就可以对二叉搜索树的框架进行代码描述了,二叉搜索树本质还是一颗二叉树嘛:
cpp
//结点类型
struct BSTreeNode
{
K _key;
BSTreeNode<K>* _leftchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode<K>* _rightchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_key(key)
{}
};
//主框架
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};三、二叉搜索树的插入
对于插入,还是较为简单的,插入的具体过程如下:
- 树为空,则直接新增结点,赋值给root指针;
- 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质,插入值比当前结点大往右走,插入值比当前结点小往左走,找到空位置,插入新结点。
- 如果支持插入相等的值,插入值跟当前结点相等的值可以往右走,也可以往左走,找到空位置,插入新结点。(要注意的是要保持逻辑一致性,插入相等的值不要一会往右走,一会往左走)
来模拟一下吧:
cpp
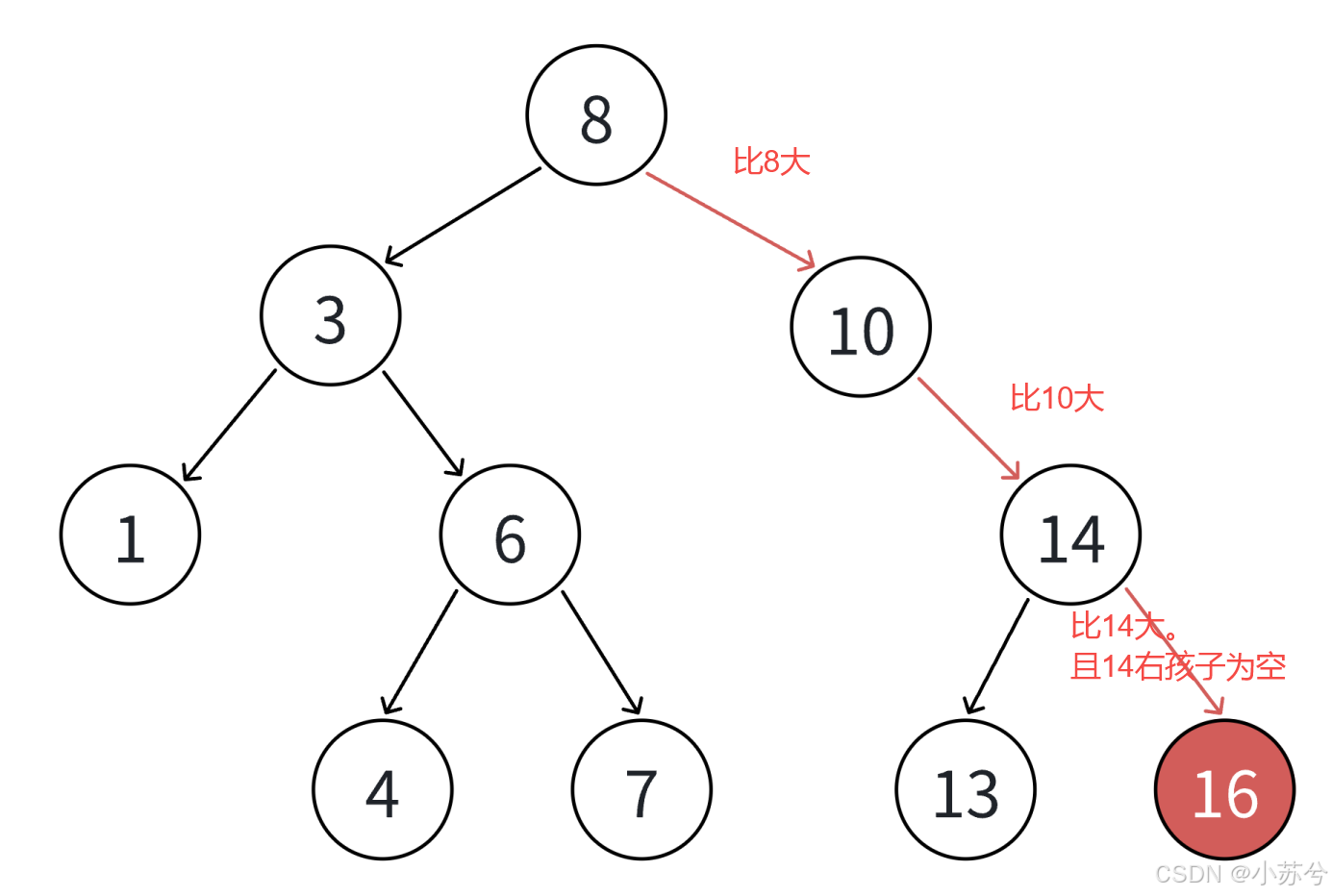
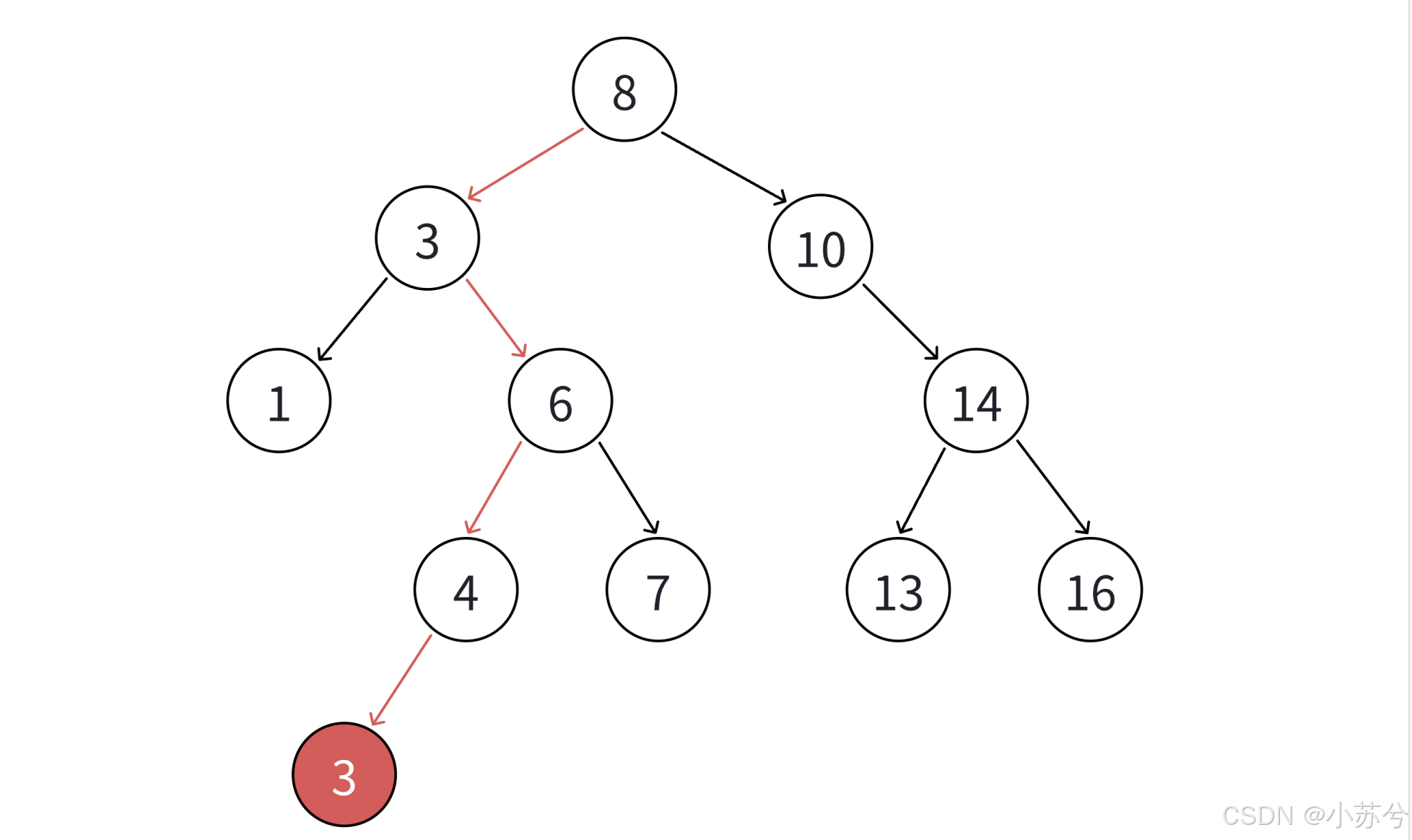
int a[] = {8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13};
- 插入16
- 插入3
插入就是与根节点比较,然后再与子树的根节点比较......依次比较,最后"没得比了"就确定位置呗。
ok,下面我们基于上面的代码框架完成插入的代码,为了方便一点,我们就不再写二叉树的主框架,直接完成我们现在说的函数就行,后面同理。
cpp
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
_root = new Node(key);
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else//我们这里等于的话,默认不插入,也可以插入,可自行实现
return false;
}
//找到位置了,但不知是左右哪个
if (key < parent->_key)
parent->_leftchild = new Node(key);
else
parent->_rightchild = new Node(key);
return true;
}四、二叉搜索树的查找
查找与插入的思想是一样的,我们来看步骤:
- 从根开始比较,查找x,x比根的值大则往右边走查找,x比根值小则往左边走查找;
- 最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在;
- 如果不支持插入相等的值,找到x即可返回;
- 如果支持插入相等的值,意味着有多个x存在,一般要求查找中序的第一个x。如下图,查找3,要找到1的右孩子的那个3返回。
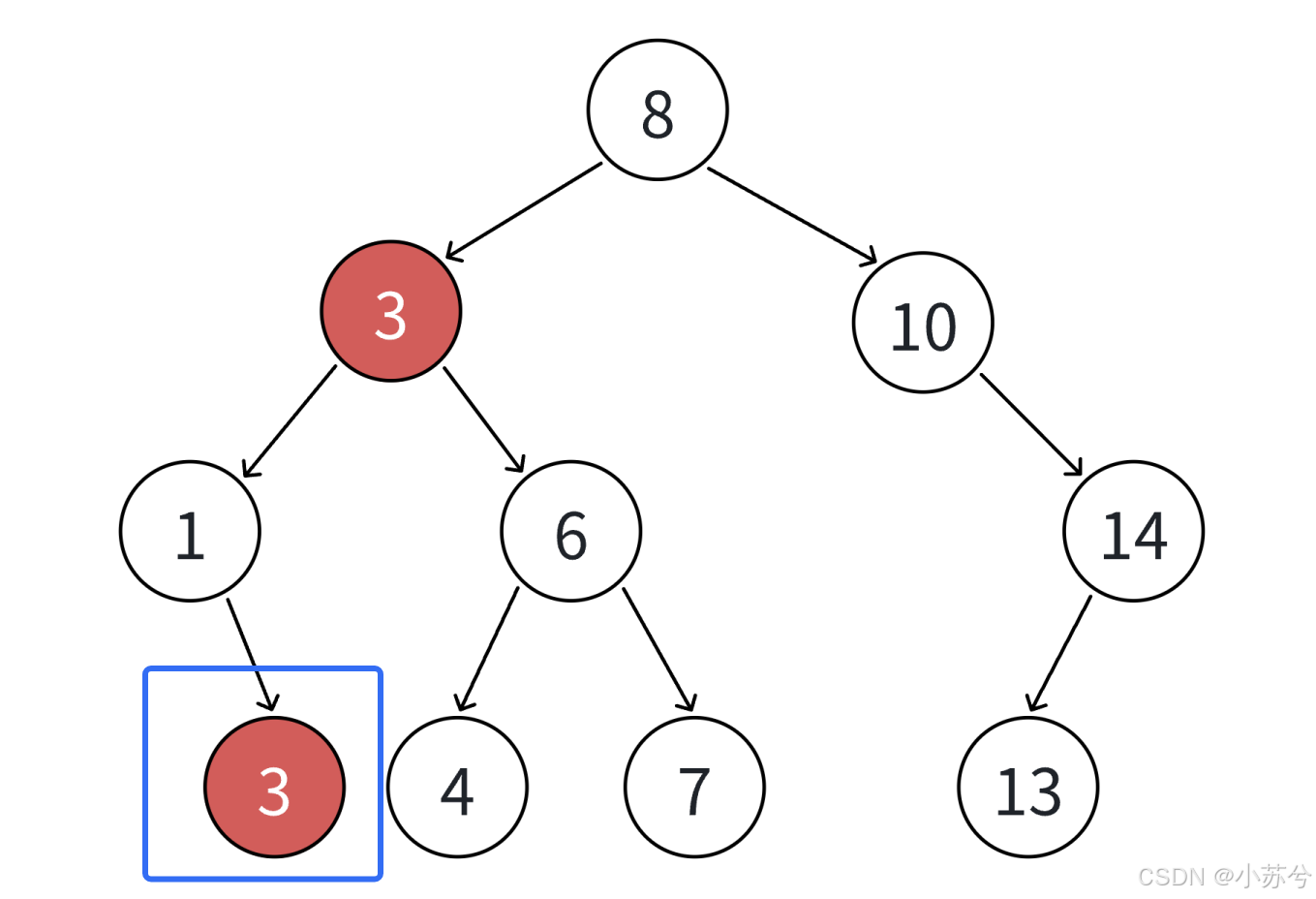
可以,查找是较为简单的,直接看代码:
cpp
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_rightchild;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_leftchild;
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}五、二叉搜索树的删除
其实,二叉搜索树的重头戏就是删除,那么下面我们就慢慢分析吧。
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回false。
如果查找元素存在则分以下四种情况分别处理:(假设要删除的结点为N)
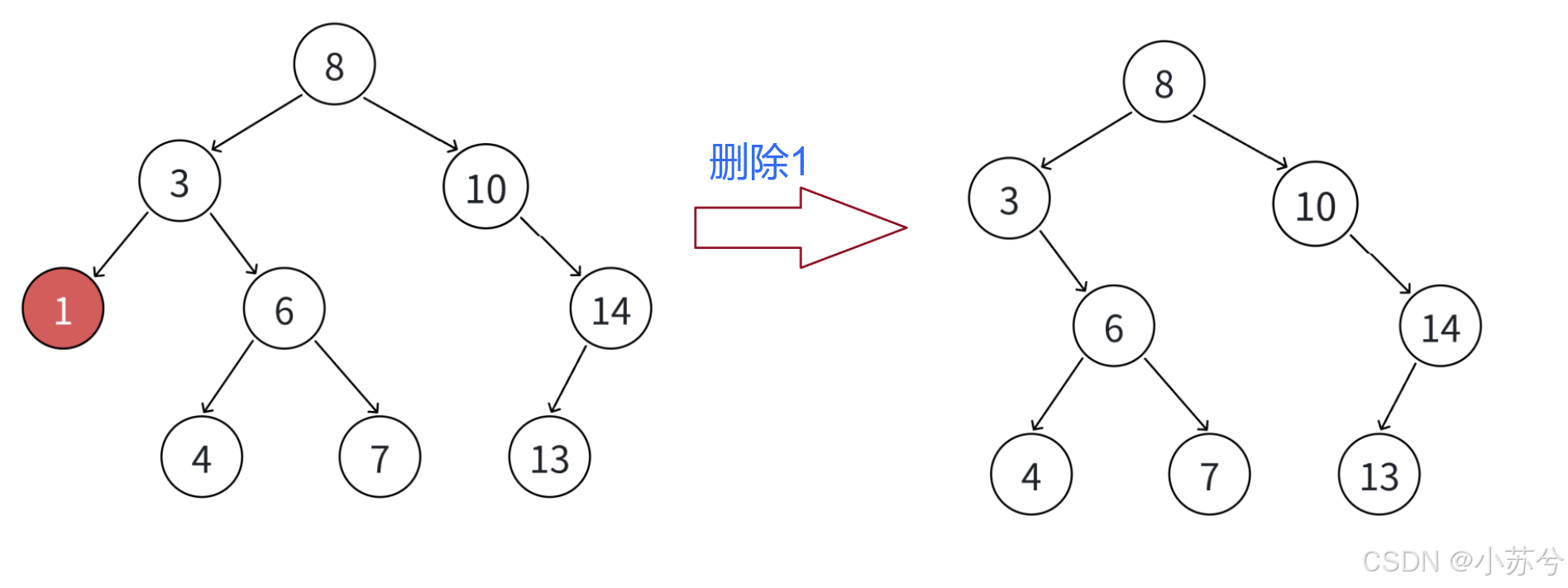
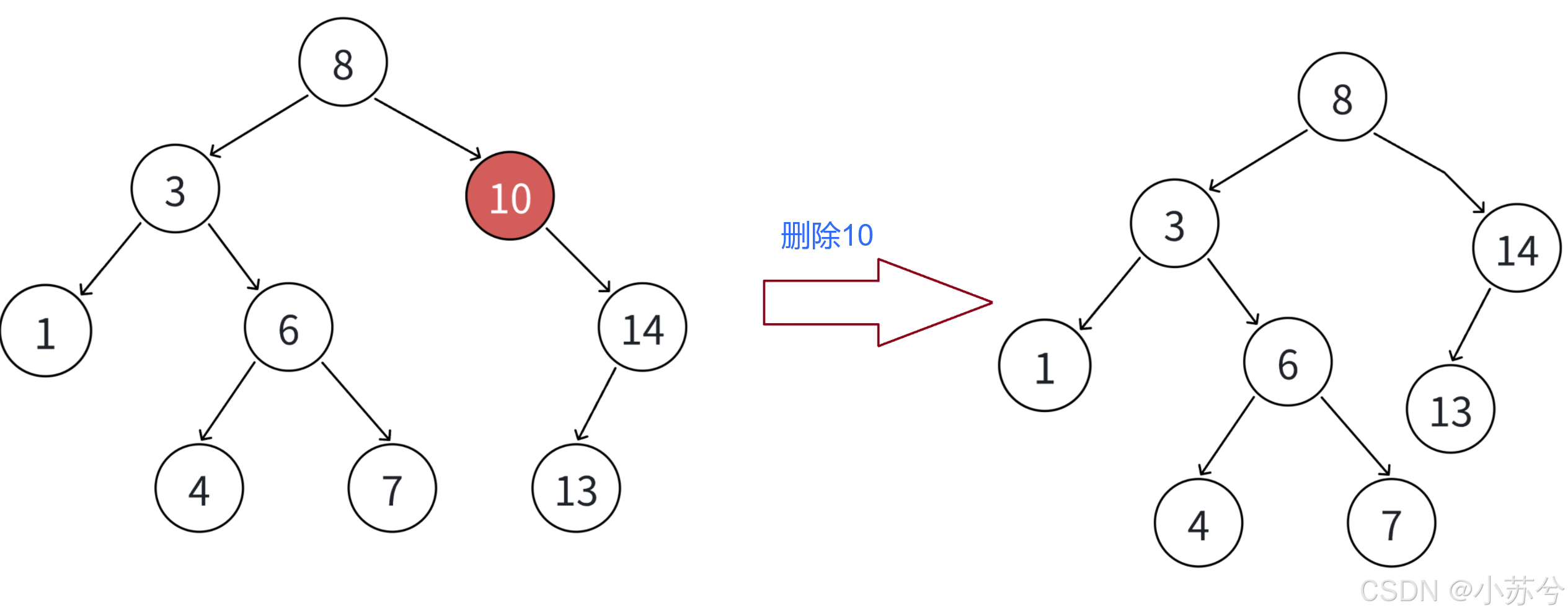
- 要删除结点N左右孩子均为空
把N结点的父亲对应孩指针指向空,直接删除N结点即可。
- 要删除的结点N左孩子为空,右孩子结点不为空
把N结点的父亲对应孩子指针指向N的右孩子,直接删除N结点
- 要删除的结点N右孩子为空,左孩子结点不为空
把N结点的父亲对应孩子指针指向N的左孩子,直接删除N结点
当然,情况1可以当成2或者3处理,效果是⼀样的。
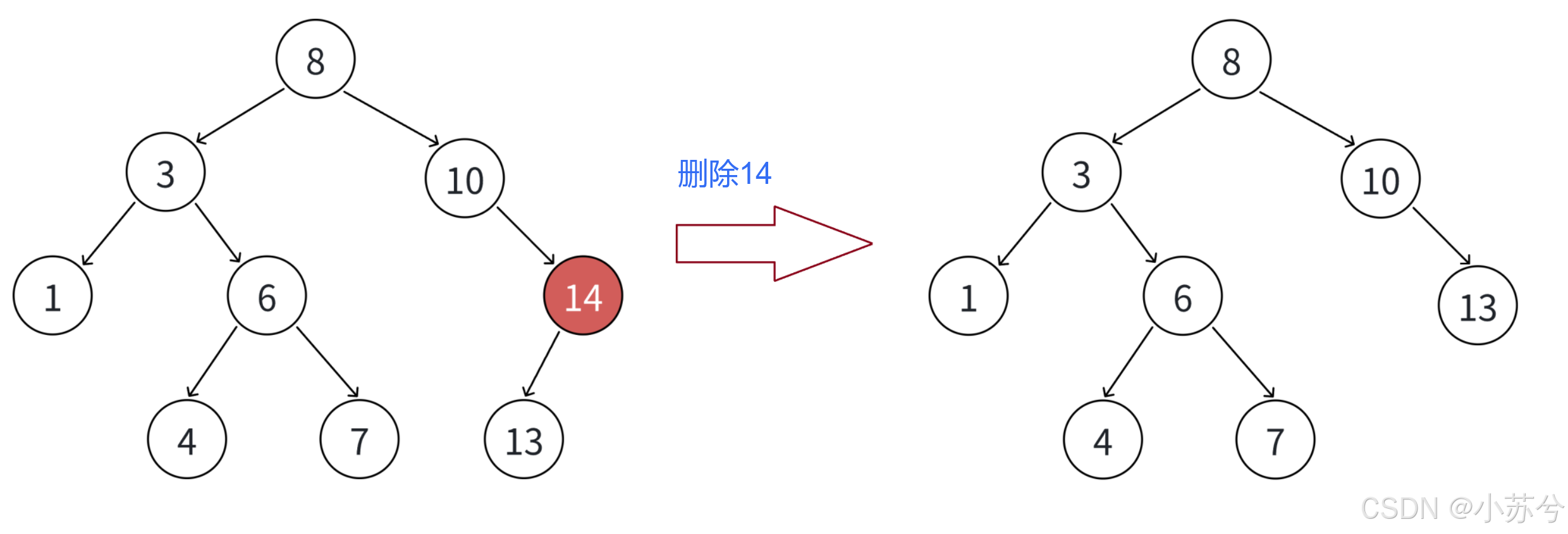
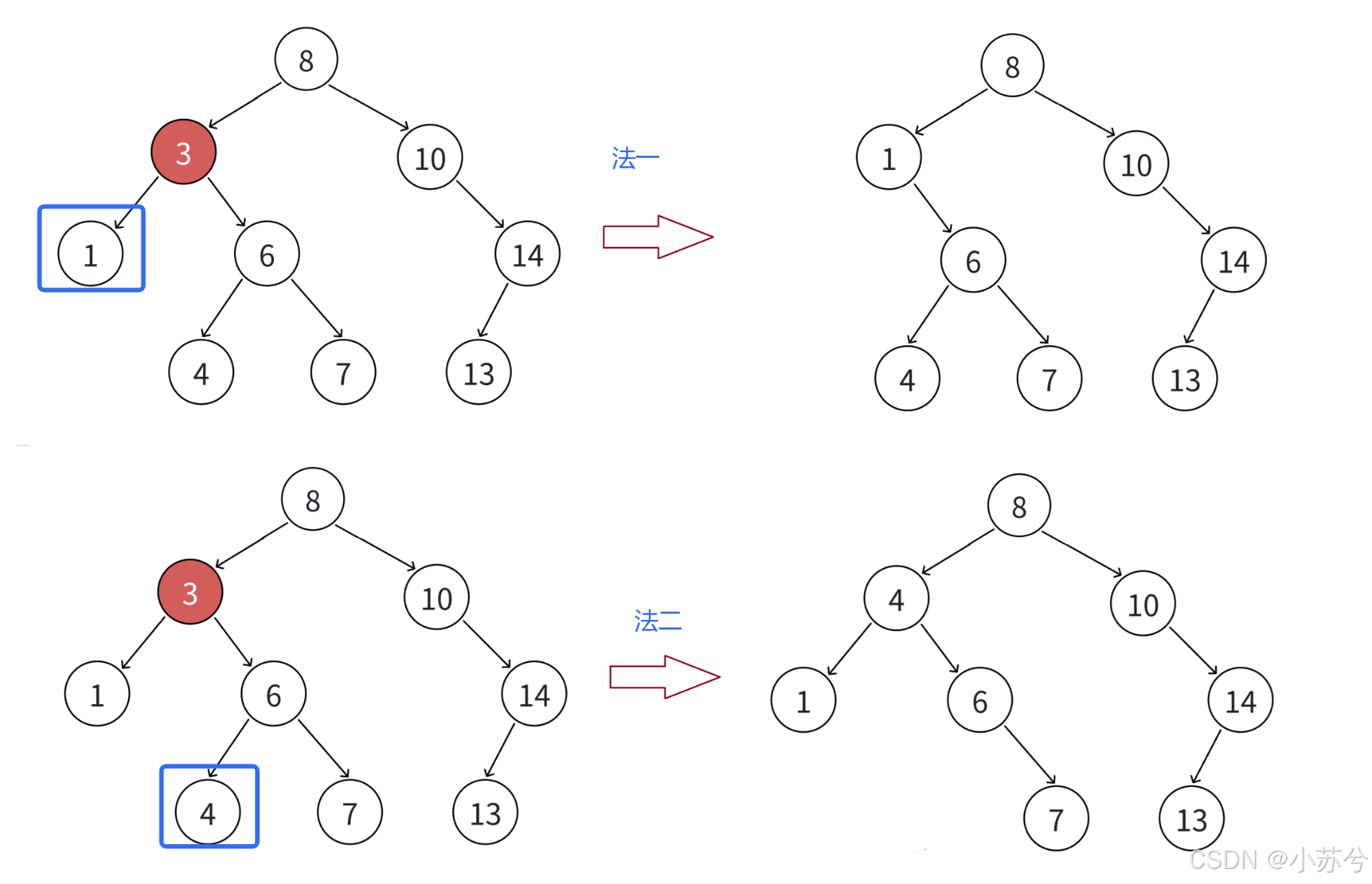
- 要删除的结点N左右孩子结点均不为空
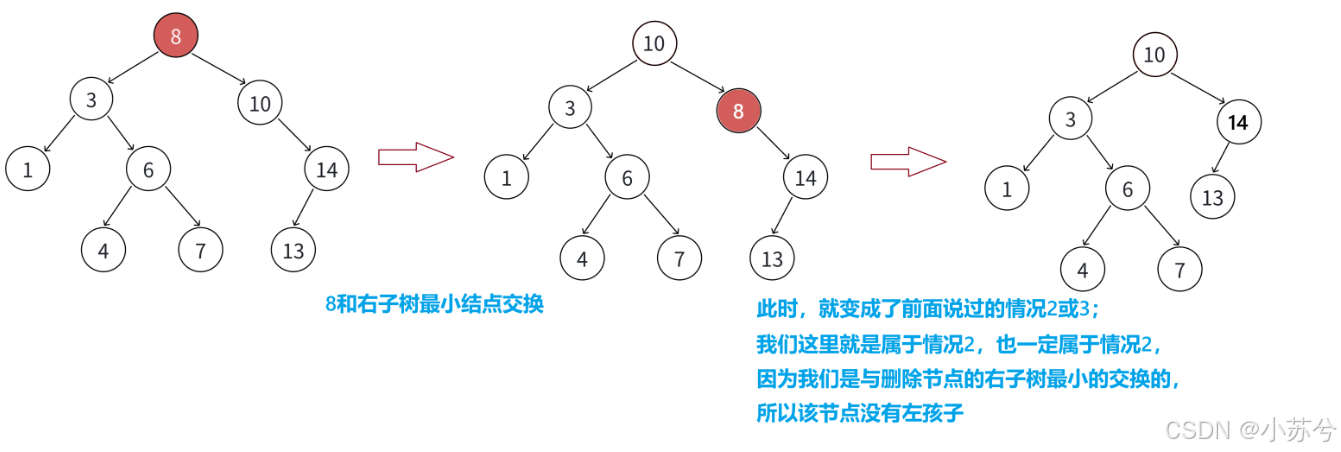
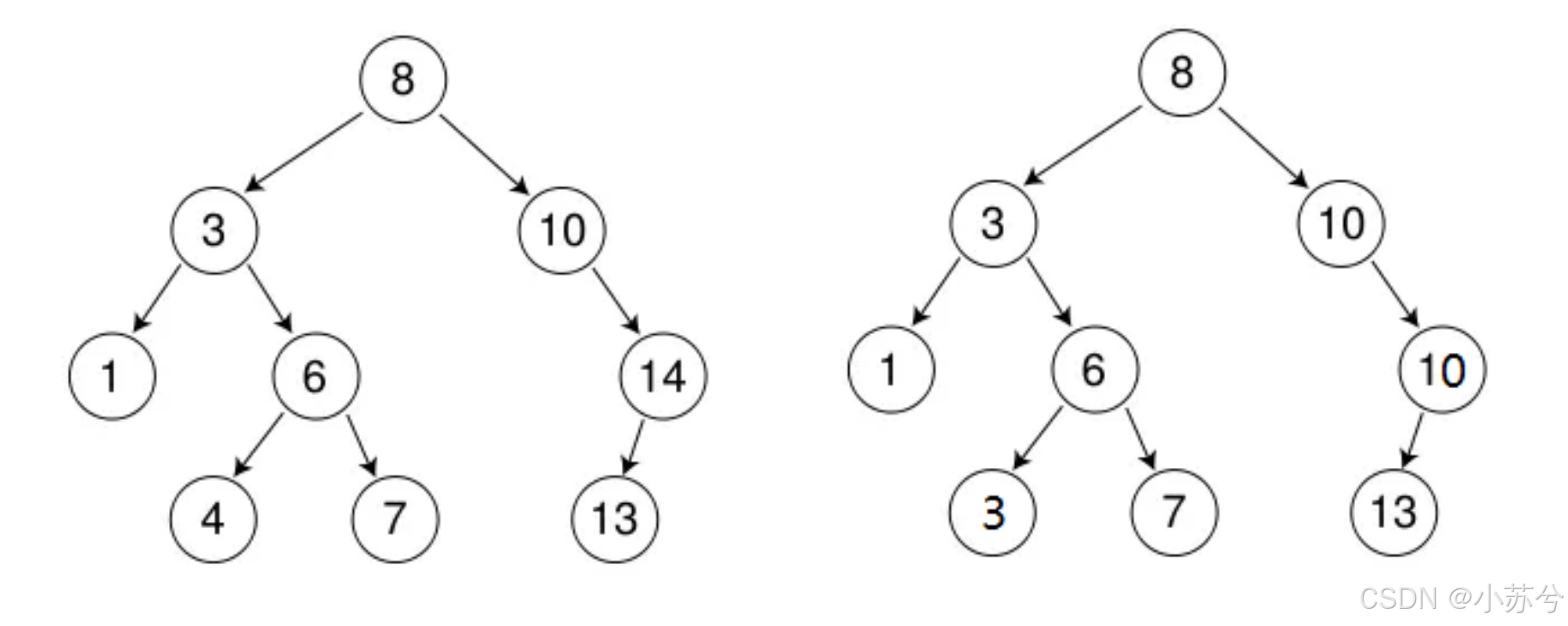
还是以上面为例,假设我要删除3,有两种方法:
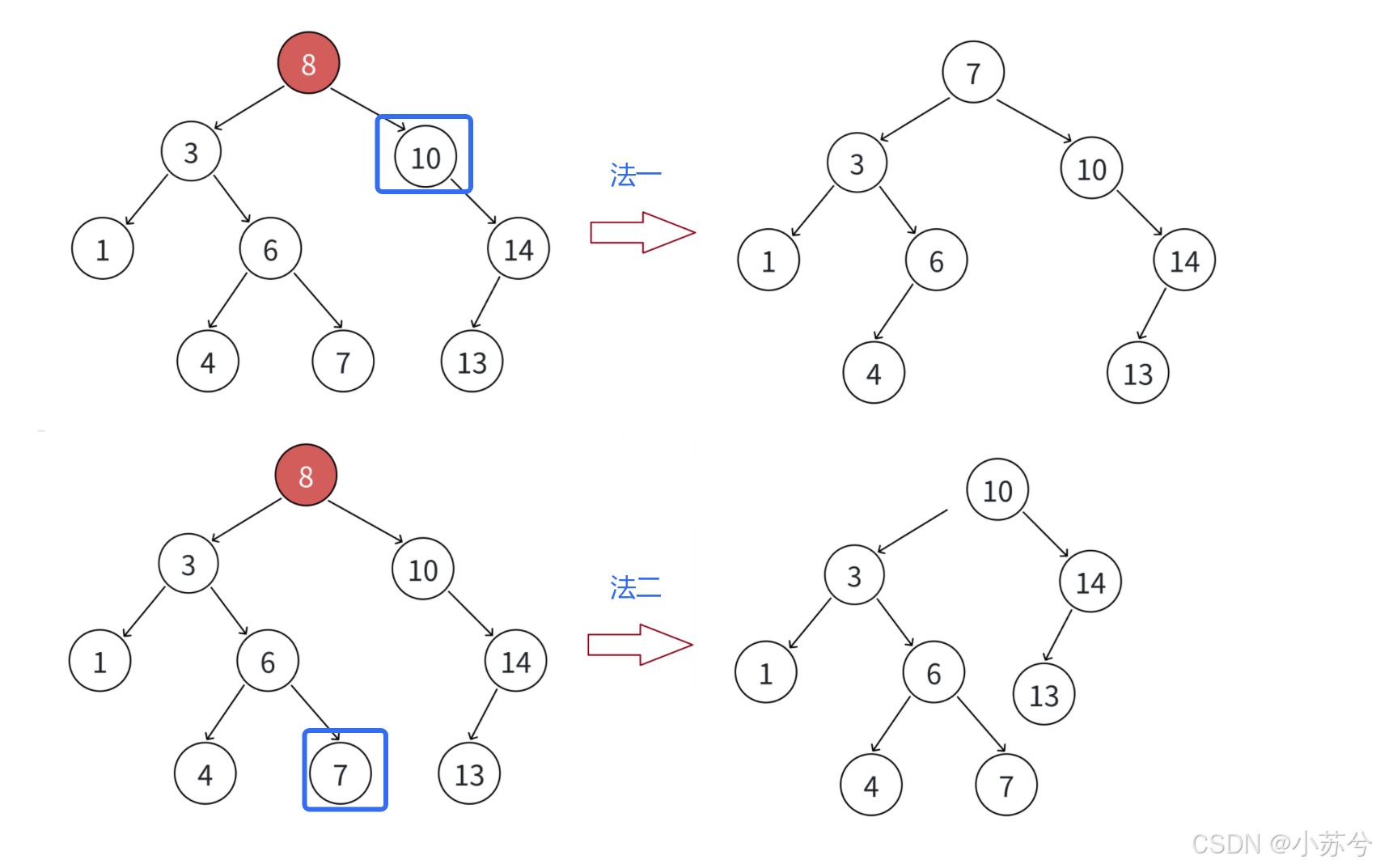
可以看出,我们只要使得删除结点之后树的重新为二叉搜索树即可,要使其重新满足二叉搜索树的性质,我们只能在子树中找合适的节点。我们再来看一下删除8的情况:
ok,可见,最后一种删除是最复杂的,那我们对于这种情况再详细展开:
总结:无法直接删除N结点,因为N的两个孩子无处安放,只能用替换法删除。找N左子树的值最大结点R(最右结点)或者N右子树的值最小结点R(最左结点)替代N,因为这两个结点中任意一个,放到N的位置,都满足二叉搜索树的规则。替代N的意思就是N和R的两个结点的值交换,转而变成删除R结点,R结点符合情况2或情况3,可以直接删除。
有了上面的理解,现在我们就可以完成二叉搜索树的删除代码了:
cpp
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//找key节点和双亲节点
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
break;
}
if (cur == nullptr)
return false;
//删除(分情况)
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr && cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//没孩子结点
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = nullptr;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
parent->_leftchild = nullptr;
else
parent->_rightchild = nullptr;
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr || cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//有一个孩子结点
{
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
}
else
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//有两个孩子结点
{
//用左孩子中最大结点或者右孩子最小的节点来补
//左孩子中最大结点
Node* prev = cur;
Node* curi = cur->_leftchild;
while (curi->_rightchild != nullptr)
{
prev = curi;
curi = curi->_rightchild;
}
cur->_key = curi->_key;
if (curi == prev->_rightchild)
prev->_rightchild = curi->_leftchild;
else
prev->_leftchild = curi->_leftchild;
delete curi;
}
return true;
}六、二叉搜索树的实现代码
接下来,我们主要的代码都有了,现在就把代码较为完整的写在一起,顺便再加上拷贝构造、赋值重载、析构、中序遍历(输出的节点值将按照从小到大的顺序排列,对于二叉搜索树)......
cpp
//结点
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{
K _key;
BSTreeNode<K>* _leftchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode<K>* _rightchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_key(key)
{
}
};
//主框架
template<class K>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:
//已经声明了其他构造函数,导致编译器不再隐式生成默认构造函数,用 = default 使得编译器自动生成默认构造函数。
BSTree() = default;
//拷贝构造
BSTree(BSTree& t)
{
_root = BST_Copy(t._root);
}
Node* BST_Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = new Node(root->_key);
cur->_leftchild = BST_Copy(root->_leftchild);
cur->_rightchild = BST_Copy(root->_rightchild);
return cur;
}
//赋值重载
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
std::swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
//析构
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
}
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_leftchild);
Destroy(root->_rightchild);
delete root;
}
//插入
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
_root = new Node(key);
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else//等于默认不插入
return false;
}
//找到位置了,但不知是左右哪个
if (key < parent->_key)
parent->_leftchild = new Node(key);
else
parent->_rightchild = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//查找
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_rightchild;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_leftchild;
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
//删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//找key节点和双亲节点
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
break;
}
if (cur == nullptr)
return false;
//删除(分情况)
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr && cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//没孩子结点
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = nullptr;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
parent->_leftchild = nullptr;
else
parent->_rightchild = nullptr;
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr || cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//有一个孩子结点
{
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
}
else
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//有两个孩子结点
{
//用左孩子中最大结点或者右孩子最小的节点来补
//左孩子中最大结点
Node* prev = cur;
Node* curi = cur->_leftchild;
while (curi->_rightchild != nullptr)
{
prev = curi;
curi = curi->_rightchild;
}
cur->_key = curi->_key;
if (curi == prev->_rightchild)
prev->_rightchild = curi->_leftchild;
else
prev->_leftchild = curi->_leftchild;
delete curi;
}
return true;
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_leftchild);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_rightchild);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};七、二叉搜索树key和key/value使用场景
为了更好的学习STL中的map和set,我们这里再对二叉搜索树key和key/value再来详细说明一下。
7.1 key说明与使用
只有 key 作为关键码,结构中只需要存储 key 即可 ,关键码即为需要搜索到的值,搜索场景只需要判断 key 在不在。
key 的搜索场景实现的二叉树搜索树支持增删查,但是不支持修改,修改 key 破坏搜索树结构了。
场景 1:
小区无人值守车库,小区车库买了车位的业主车才能进入小区,那么物业会把买了车位的业主的车牌号录入后台系统,车辆进入时扫描车牌在不在系统中,在则抬杆,不在则提示非本小区车辆,无法进入。
场景 2:
检查一篇英文文章单词拼写是否正确,将词库中所有单词放入二叉搜索树,读取文章中的单词,查找是否存在于二叉搜索树中,不在则波浪线标红提示。
7.2 key/value说明与使用
每一个关键码 key,都有与之对应的值 value ,value 可以任意类型对象。树的结构中(结点)除了需要存储 key 还要存储对应的 value。增 / 删 / 查还是以 key 为关键字走二叉搜索树的规则进行比较,可以快速查找到 key 对应的 value。
key/value 的搜索场景实现的二叉树搜索树支持修改,但是不支持修改 key,修改 key 破坏搜索树性质了,可以修改 value。
场景 1:
简单中英互译字典,树的结构中(结点)存储 key(英文)和 value(中文),搜索时输入英文,则同时查找到对应的中文。
场景 2:
商场无人值守车库,入口进场时扫描车牌,记录车牌和入场时间,出口离场时,扫描车牌,查找入场时间,用当前时间 - 入场时间计算出停车时长,计算出停车费用,缴费后抬杆,车辆离场。
场景 3:
统计一篇文章中单词出现的次数,读取一个单词,查找单词是否存在,不存在这个说明第一次出现,(单词,1);单词存在,则 + 单词对应的次数。
它们分别对应STL中的map和set,下篇文章我会对于map和set进行深入讲解。我们前面写的代码是key模型,只存储了key,有兴趣的也可以实现key/value模型的二叉搜索树的代码,其实就是把结构中存储的 key 改为 key/value,然后再刚刚别的就行,参考代码如下:
cpp
template<class K,class V>
struct BSTreeNode
{
K _key;
V _val;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _leftchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode<K,V>* _rightchild = nullptr;
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& val)
:_key(key)
,_val(val)
{
}
};
template<class K,class V>
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:
BSTree() = default;
BSTree(BSTree& t)
{
BST_Copy(t._root);
}
void BST_Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Insert(root->_key, root->_val);
BST_Copy(root->_leftchild);
BST_Copy(root->_rightchild);
}
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
std::swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
}
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_leftchild);
Destroy(root->_rightchild);
delete root;
}
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& val)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
_root = new Node(key,val);
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (key > cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else//存在
return false;
}
//找到位置了,但不知是左右哪个
if (key < parent->_key)
parent->_leftchild = new Node(key, val);
else
parent->_rightchild = new Node(key, val);
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
cur = cur->_rightchild;
else if (cur->_key > key)
cur = cur->_leftchild;
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//找key节点和双亲节点
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur != nullptr)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
break;
}
if (cur == nullptr)
return false;
//删除(分情况)
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr && cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//没孩子结点
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = nullptr;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
parent->_leftchild = nullptr;
else
parent->_rightchild = nullptr;
delete cur;
}
else if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr || cur->_rightchild == nullptr)//有一个孩子结点
{
if (cur->_leftchild == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_rightchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_rightchild;
}
}
else
{
if (cur == _root)
{
_root = cur->_leftchild;
}
else if (parent->_leftchild == cur)
{
parent->_leftchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
else
{
parent->_rightchild = cur->_leftchild;
}
}
delete cur;
}
else//有两个孩子结点
{
//用左孩子中最大结点或者右孩子最小的节点来补
//左孩子中最大结点
Node* prev = cur;
Node* curi = cur->_leftchild;
while (curi->_rightchild != nullptr)
{
prev = curi;
curi = curi->_rightchild;
}
cur->_key = curi->_key;
if (curi == prev->_rightchild)
prev->_rightchild = curi->_leftchild;
else
prev->_leftchild = curi->_leftchild;
delete curi;
}
return true;
}
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_InOrder(root->_leftchild);
cout << root->_key << ":" << " " << root->_val << ";";
_InOrder(root->_rightchild);
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};总结
二叉搜索树结构简单、效率高,是学习平衡树和 STL 容器(如 map、set)的基础。掌握它,有助于更好地理解后续的数据结构与算法。
如果本文对您有启发:
✅ 点赞 - 让更多人看到这篇硬核技术解析 !
✅ 收藏 - 实战代码随时复现
✅ 关注 - 获取数据结构系列深度更新
您的每一个[三连]都是我们持续创作的动力!✨