1、回文链表 hot
分析:
法一:先放到数组,再双指针对比。时间复杂度 O(n+1/2n)=O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)。
法二,递归:先递归判断两边是不是回文,递归出来再判断中间是不是回文。先记录 head,再从 head 开始递归到 tail,tail 与 head 层层从边缘到中间比较。时间复杂度:递归遍历 O(n),再双向遍历 O(2n),共 O(n)。空间复杂度:栈深度 O(n)。
法三:先快慢指针获取中间节点,再翻转后半部分节点,对比完了再翻转回去。时间复杂度 O(获取中点1/2n+翻转1/2n+对比1/2n+翻转1/2n) = O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。缺点:因为对原链表进行了修改,所以多线程时对链表的操作要加锁。
代码:
法二,递归:
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private ListNode front; // 记录左节点
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
front = head;
return isCycle(head);
}
public boolean isCycle(ListNode cur) {
if (cur == null) return true; // 递归结束条件
if (!isCycle(cur.next)) return false; // 靠两边的节点不满足回文,返回 false
if (front.val != cur.val) return false; // 靠中间的不满足回文,返回 false
front = front.next; // 更新左节点,比较下一对
return true;
}
}法三:
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
// 1. 快慢指针获取中间节点
ListNode middle = getMiddle(head);
// 2. 把中间结点后的链表翻转
reserve(middle);
// 3. 对比
ListNode t1 = head, t2 = middle.next;
boolean flag = true;
while (t2 != null) {
if (t1.val != t2.val) {
flag = false;
break;
}
t1 = t1.next;
t2 = t2.next;
}
// 4. 把链表翻转回去,恢复原样
reserve(middle);
return flag;
}
public ListNode getMiddle (ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
public void reserve (ListNode head) {
ListNode t = head.next;
head.next = null;
while (t != null) {
ListNode next = t.next;
t.next = head.next;
head.next = t;
t = next;
}
}
}2、随机链表的复制 hot
题目 :138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)

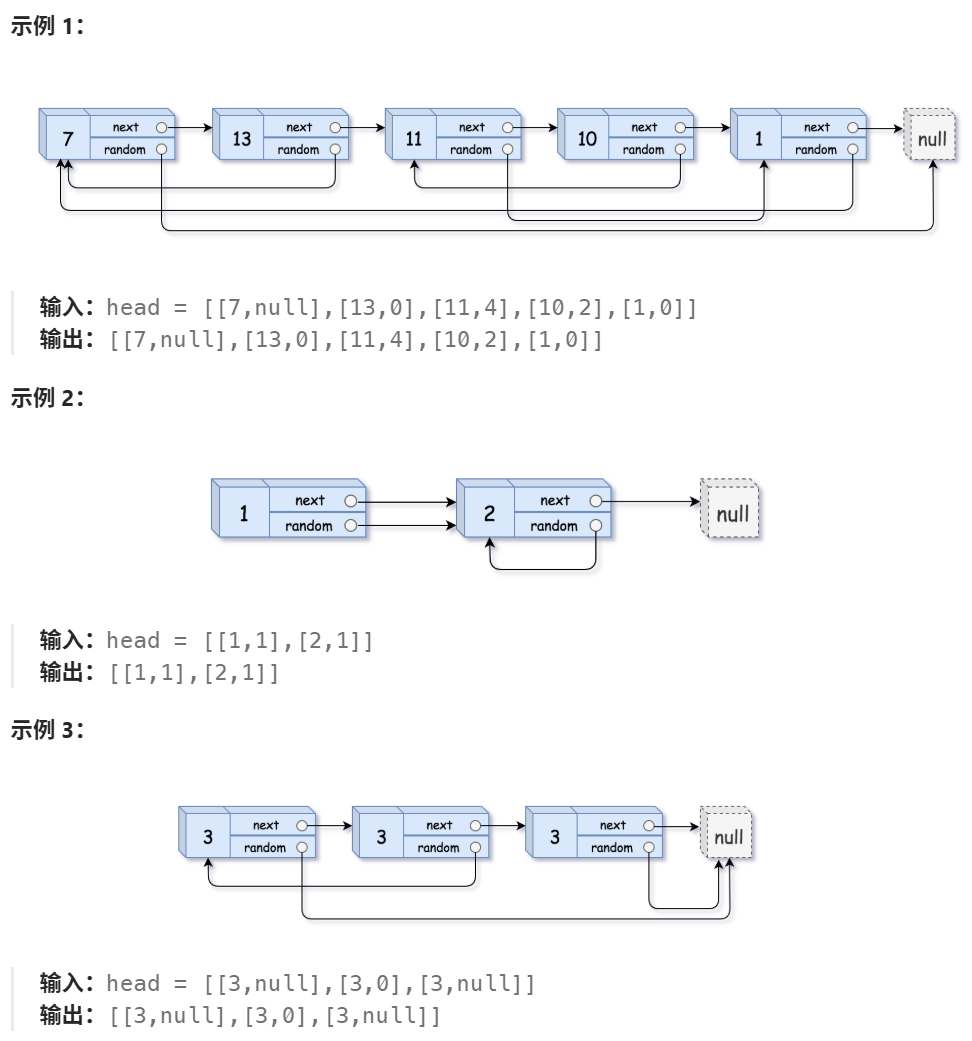
分析:对于每个节点,我们需要访问并创建其下一个节点和随机节点,并插入新链表中。但是因为是随机节点,所以我们并不知道下一个节点/随机节点是否已经在之前被创建,如果不进行判断就会创建并连接多余的节点。当然也可以不判断,先遍历一遍创建完整链表,把旧-新节点对放到 map;再遍历一遍每个节点的随机节点,从 map 中取出对应的新节点进行连接。
时间复杂度 O(2n) = O(n),空间复杂度 哈希表 O(n)。
代码:
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 1. 创建正常链表
Node t = head;
Node newHead = new Node(0), tail = newHead;
while (t != null) {
Node node = new Node(t.val);
map.put(t, node);
tail.next = node;
tail = tail.next;
t = t.next;
}
// 2. 连接随机节点
t = head;
tail = newHead.next;
while (t != null) {
Node node = map.get(t.random);
tail.random = node;
tail = tail.next;
t = t.next;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}3、LRU 缓存 hot
题目 :146. LRU 缓存 - 力扣(LeetCode)

分析:哈希表(频繁查找 key 对应的节点 O(1))+双向链表(频繁删除尾节点,单链表无法获取尾节点前驱)删插都是 O(1)。
- LRUCache(int capacity):初始化容量、双向链表。
- int get(int key):哈希表里查 key 对应的 node,没有则返回 -1;有则将其移动到链头(最近使用),并返回 value。
- void put(int key, int value):哈希表查 key 对应的 node,有则将其移动到链头,并更新 value;没有则插入到链头,如果size超过了容量,就删除链尾最久没有使用的 node。
- 使用空值的头结点、尾节点,方便删除、插入。
代码:
java
class LRUCache {
class DoubleListNode {
int key;
int val;
DoubleListNode pre;
DoubleListNode next;
public DoubleListNode () {
}
public DoubleListNode (int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
private DoubleListNode head, tail;
private int size, capacity;
private Map<Integer, DoubleListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
head = new DoubleListNode();
tail = new DoubleListNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DoubleListNode node = map.get(key);
// 存在则移到链头,返回 val
if (node != null) {
int val = node.val;
removeToHead(node);
return val;
}
// 不存在,返回 -1
return -1;
}
public void put(int key, int val) {
DoubleListNode node = map.get(key);
// 如果存在,则更新值,并移到链头
if (node != null) {
node.val = val;
removeToHead(node);
return;
}
// 不存在,则创建新节点插到链头
DoubleListNode newNode = new DoubleListNode(key, val);
map.put(key, newNode);
insertToHead(newNode);
size++;
// 如果链表大小超过容量,删除尾部最久没使用的
if (size > capacity) {
deleteTail();
size--;
}
}
public void removeToHead(DoubleListNode node) {
delete(node);
insertToHead(node);
}
public void delete(DoubleListNode node) {
DoubleListNode pre = node.pre;
DoubleListNode next = node.next;
pre.next = next;
next.pre = pre;
}
public void insertToHead(DoubleListNode node) {
node.next = head.next;
node.next.pre = node;
head.next = node;
node.pre = head;
}
public void deleteTail() {
DoubleListNode deleteNode = tail.pre;
DoubleListNode pre = deleteNode.pre;
map.remove(deleteNode.key);
pre.next = tail;
tail.pre = pre;
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/