1:前置说明
在学习二叉树的基本操作前,需先要创建一棵二叉树,然后才能学习其相关的基本操作。由于现在大家对二叉树结构掌握还不够深入,为了降低uu们的学习成本,此处手动快速创建一棵简单的二叉树,快速入二叉树操作学习,等二叉树结构了解的差不多时,我们反过头再来研究二叉树真正的创建方式。
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char BtDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
BtDataType value;
//左结点
struct BinaryTree* left;
//右结点
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BinaryTree;
////创建树节点(死编码方式)
BinaryTree* CreateTree(int value)
{
BinaryTree* Node = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
Node->value = value;
return Node;
}
int main()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Node3->left = Node6;
return 0;
}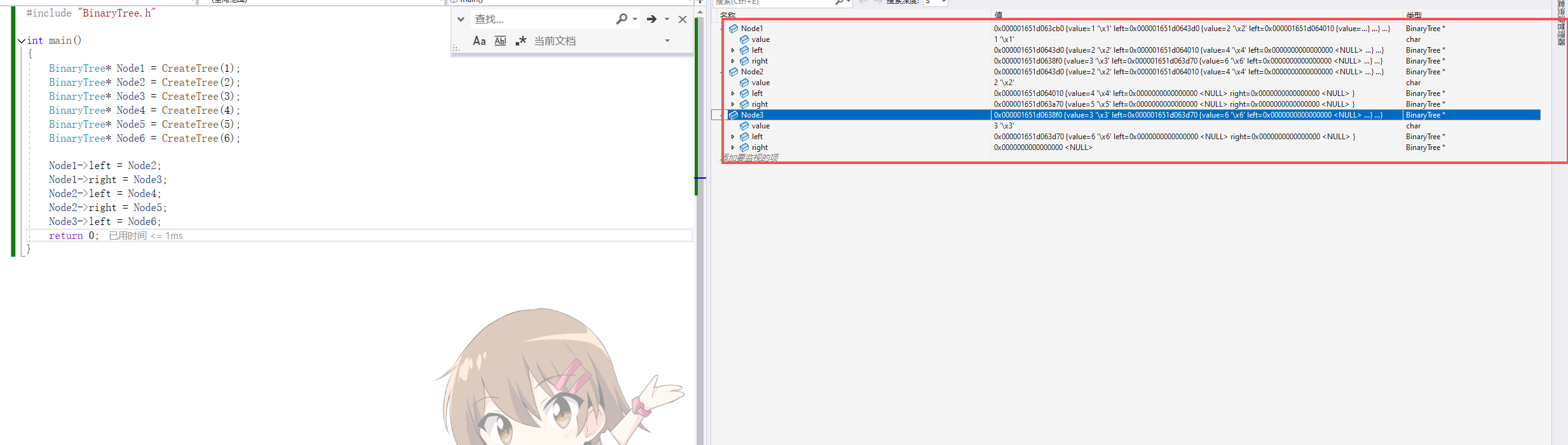
PS:上述代码并不是创建二叉树的方式,真正创建二叉树方式后面博主再详细讲解~
在看二叉树的基本操作前,我们再回顾一下二叉树的基本概念
- 空树.
- 非空:根节点,根节点的左子树、根节点的右子树组成的.
2:二叉树的链式结构实现
2.1:BinaryTree.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char BtDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
BtDataType value;
//左结点
struct BinaryTree* left;
//右结点
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BinaryTree;
////创建树节点(死编码方式)
BinaryTree* CreateTree(int value);
//
//通过前序遍历的数组"ABD##E#H##CF##G##"构建二叉树
//BinaryTree* CreateBinaryTree(BtDataType* str, int* pi);
//前序遍历
void Preorder(BinaryTree* root);
//中序遍历
void Inorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//后序遍历
void postorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//层序遍历
void Level_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//求树的结点个数
int Tree_Size(BinaryTree* root);
//求叶子节点的个数
int TreeLeafSize(BinaryTree* root);
//求树的高度
int TreeHeight(BinaryTree* root);
//求第K层的节点个数
int SizeLevelK(BinaryTree* root, int k);
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BinaryTree* TreeFind(BinaryTree* root, BtDataType value);
//判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BinaryTree* root);
//销毁树
void DestoryTree(BinaryTree* root);2.2:BinaryTree.c
2.2.1:前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历
学习二叉树结构,最简单的方式就是遍历。所谓 二叉树遍历 (Traversal) 是按照某种特定的规则,依次对二叉 树中的节点进行相应的操作,并且每个节点只操作一次 。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题,遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础.
按照规则,二叉树的遍历有: 前序 / 中序 / 后序的递归结构遍历 :
- 前序遍历(又称先序遍历)-------访问根节点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前即根 左子树 右子树.
- 中序遍历---------访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。(左子树 根 右子树)
- 后序遍历---------访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。(左子树 右子树 根)
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
BinaryTree* CreateTree(int value)
{
BinaryTree* Node = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
Node->value = value;
return Node;
}
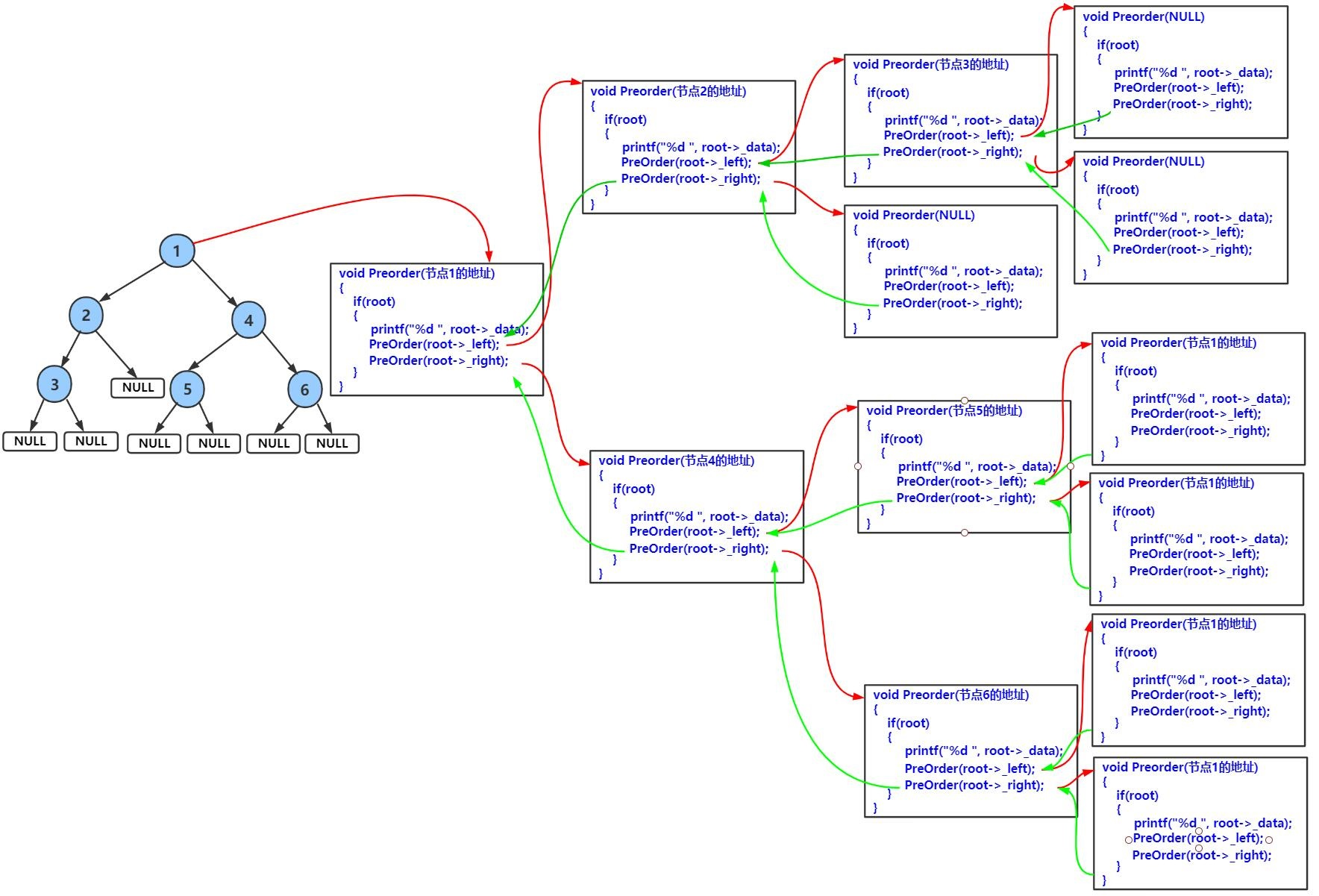
//前序遍历(根,左子树,右子树)
void Preorder(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
printf("%d ", root->value);
Preorder(root->left);
Preorder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历(左子树 根 右子树)
void Inorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
Inorder_Traversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->value);
Inorder_Traversal(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void Postorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
Postorder_Traversal(root->left);
Postorder_Traversal(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->value);
}前序遍历图解.
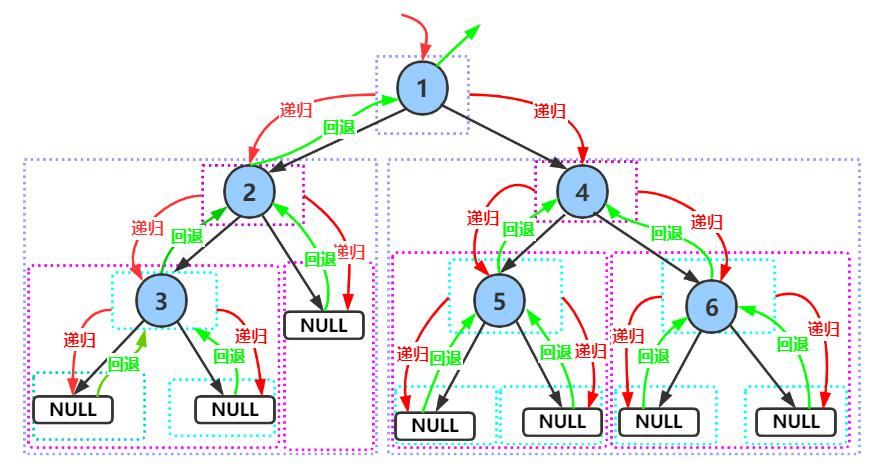
2.2.2:层序遍历
除了先序遍历、中序遍历、 后序遍历外,还可以对二叉树进行层序遍历。设二叉树的根节点所在 层数为1,层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根节点出发,首先访问第一层的树根节点,然后从左到右访问第2层上的节点,接着是第三层的节点,以此类推,自上而下,自左至右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历。
- 利用变量LevelSize记录每一层的节点个数
- 先获取队列的头.
- 然后将其pop.
- pop之后判断是否有孩子节点,若存在孩子节点则入队列.
- 遍历完一层后更新LevelSize.
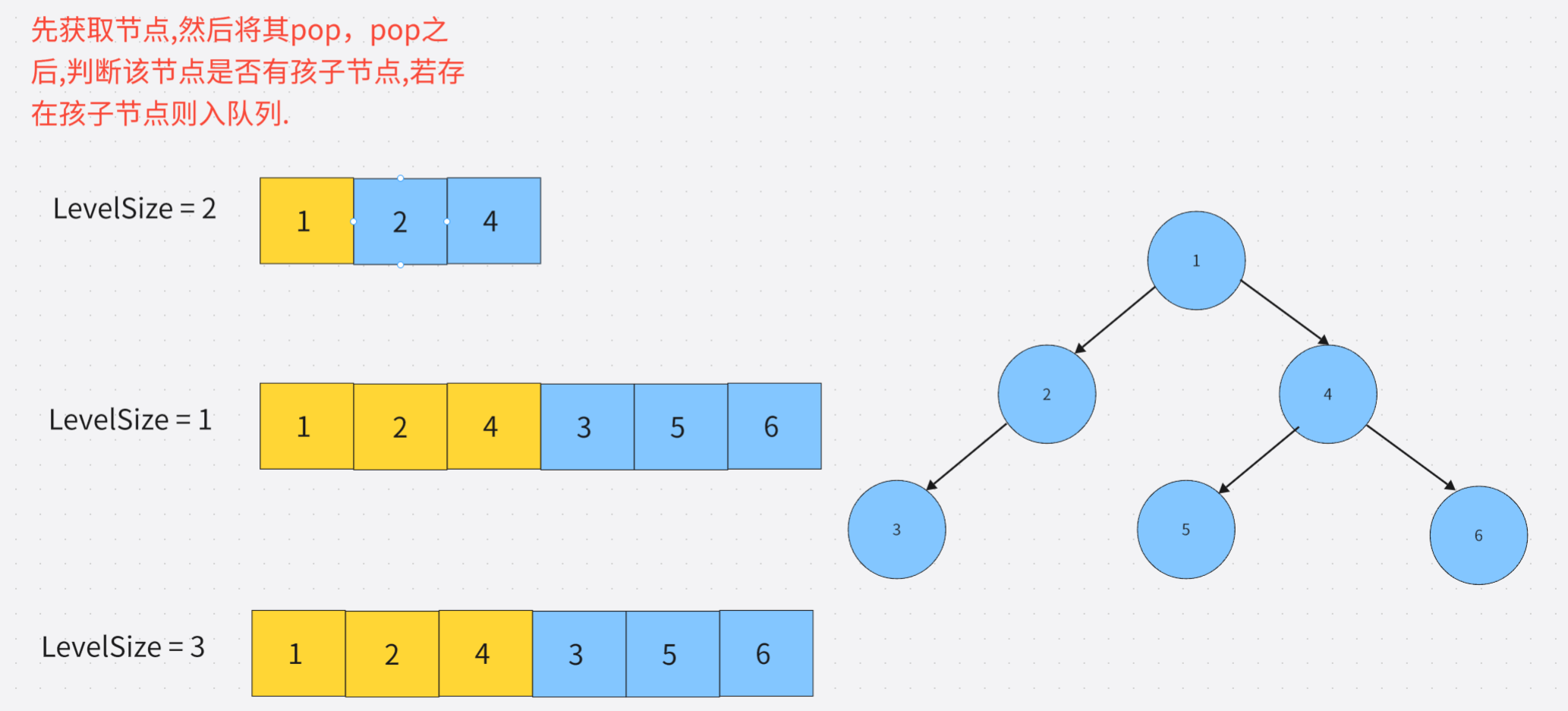
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
//层序遍历(利用队列先进先出的特点进行层序遍历
void Level_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
Queue Q;
QueueInit(&Q);
if (root != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, root);
}
//获取每一层的节点
int LevelSize = 1;
while(!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
while (LevelSize--)
{
//获取队头
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
printf("%d ", Front->value);
if(Front->left != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, Front->left);
}
if (Front->right != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, Front->right);
}
LevelSize = Queuesize(&Q);
}
}
QueueDestory(&Q);
}2.2.2.1:Queue.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct BinaryTree* QUDatatype;
//队头出队:头删,队尾入队->尾插
//链式栈
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QUDatatype value;
//存储下一个节点的地址
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
//代表队头,删除数据;头删
QueueNode* Qhead;
//代表队尾,入数据,以空间来换时间;尾插
QueueNode* Qtail;
//统计有效元素个数
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QUDatatype value);
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//获取队头元素
QUDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队尾元素
QUDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//获取队列中的有效元素个数
int Queuesize(Queue* pq);
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);2.2.2.2:Queue.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Queue.h"
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->Qhead = NULL;
pq->Qtail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QUDatatype value)
{
assert(pq);
//创建节点
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->value = value;
newnode->next = NULL;
//为空时
if (pq->Qhead == NULL)
{
pq->Qhead = newnode;
pq->Qtail = newnode;
}
//非空时
else
{
//尾节点链接新节点
pq->Qtail->next = newnode;
pq->Qtail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//确保不为空队列
assert(pq->size > 0);
//保存头结点的下一个节点
if (pq->Qhead == pq->Qtail)
{
pq->Qtail = NULL;
}
QueueNode* tmp = pq->Qhead->next;
free(pq->Qhead);
pq->Qhead = tmp;
pq->size--;
}
//获取队头元素
QUDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->Qhead);
return pq->Qhead->value;
}
//获取队尾元素
QUDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->Qtail);
return pq->Qhead->value;
}
//获取队列中的有效元素个数
int Queuesize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->Qtail == NULL ? true : false;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* current = pq->Qhead;
while (current != NULL)
{
//保存下一个节点
QueueNode* tmp = current->next;
free(current);
current = tmp;
}
pq->Qhead = NULL;
pq->Qtail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}2.2.3:求节点个数与叶子节点个数
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
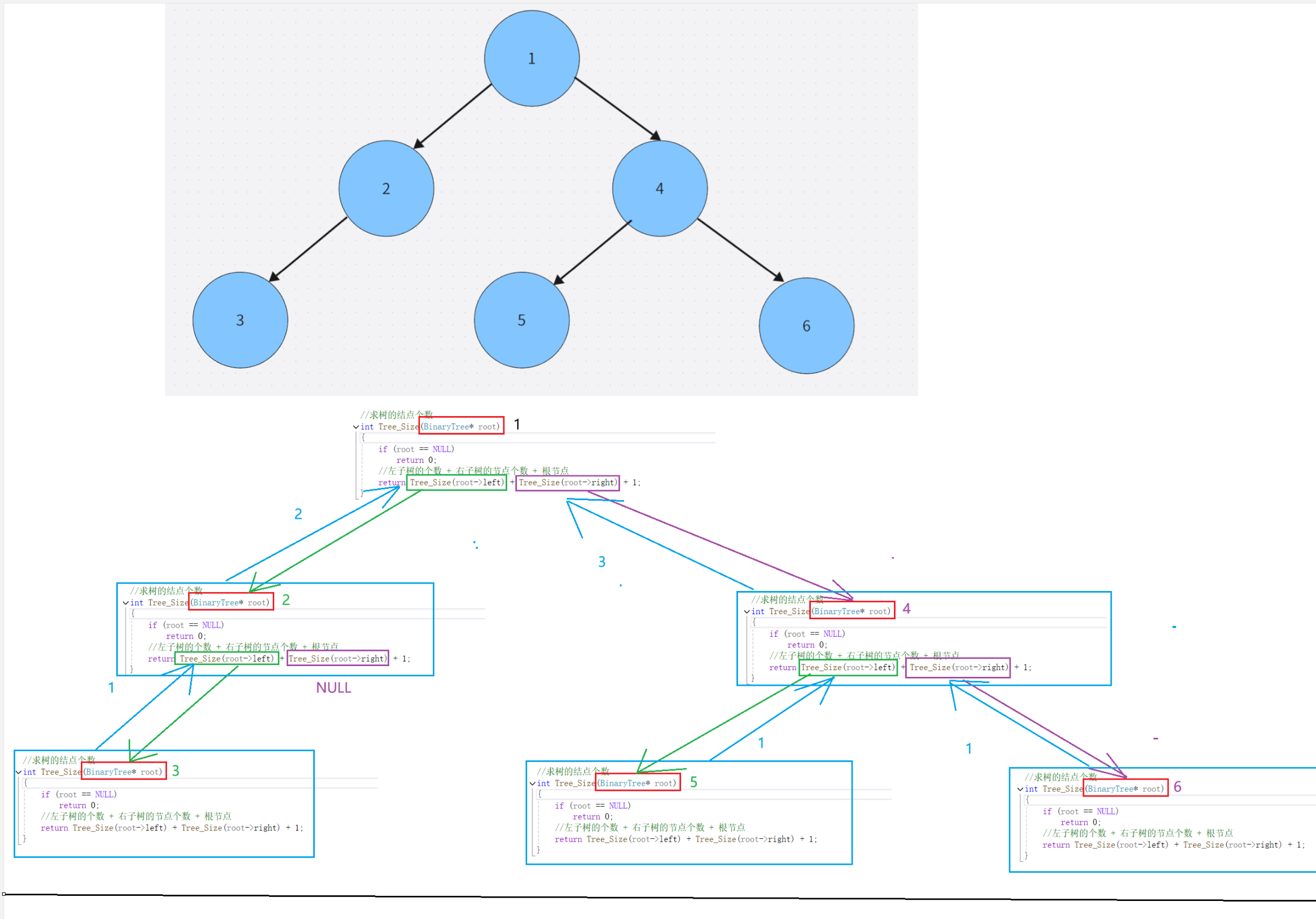
//求树的结点个数
int Tree_Size(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//左子树的个数 + 右子树的节点个数 + 根节点
return Tree_Size(root->left) + Tree_Size(root->right) + 1;
}
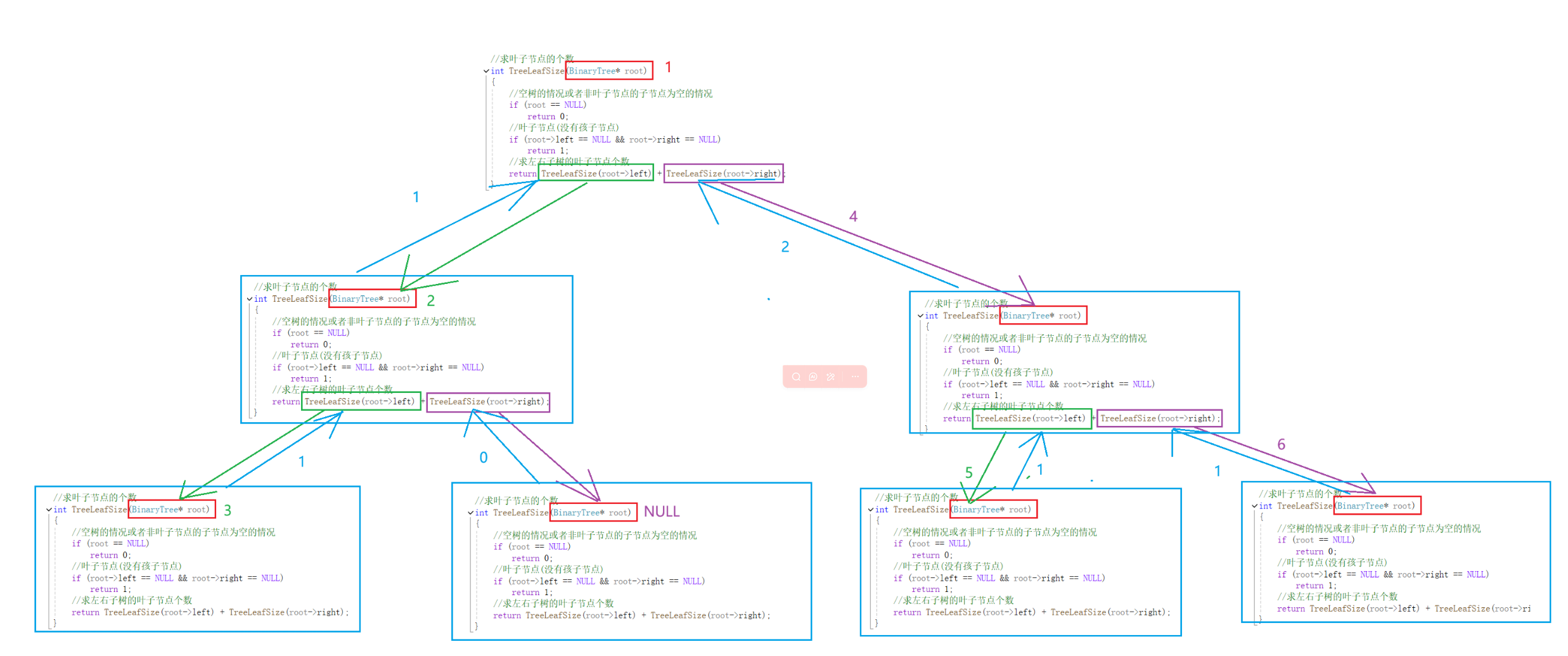
//求叶子节点的个数
int TreeLeafSize(BinaryTree* root)
{
//空树的情况或者非叶子节点的子节点为空的情况
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//叶子节点(没有孩子节点)
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
//求左右子树的叶子节点个数
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
2.2.4:求树的高度与第K层的节点个数
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
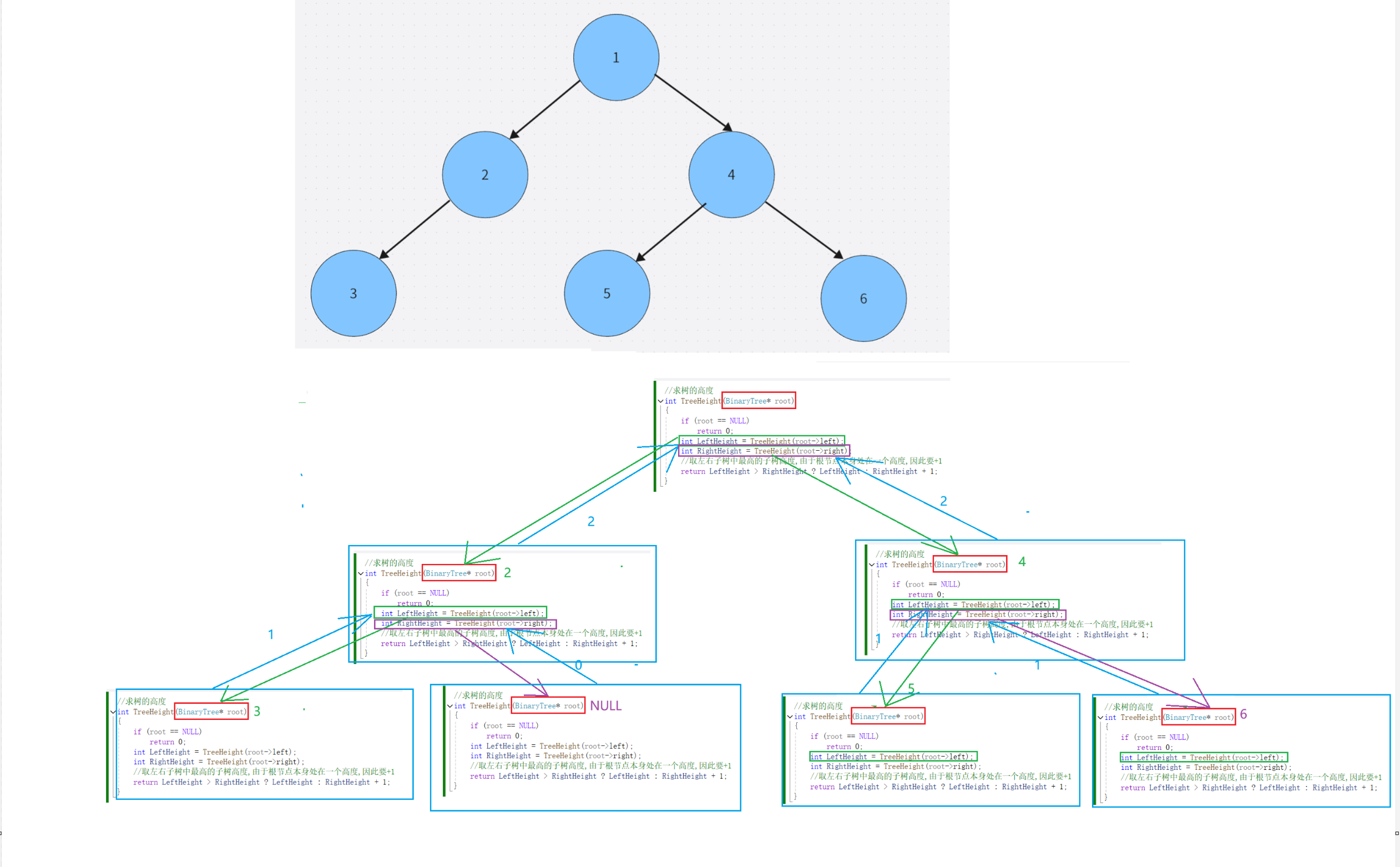
//求树的高度
int TreeHeight(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int LeftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int RightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
//取左右子树中最高的子树高度,由于根节点本身处在一个高度,因此要+1
return LeftHeight > RightHeight ? LeftHeight : RightHeight + 1;
}
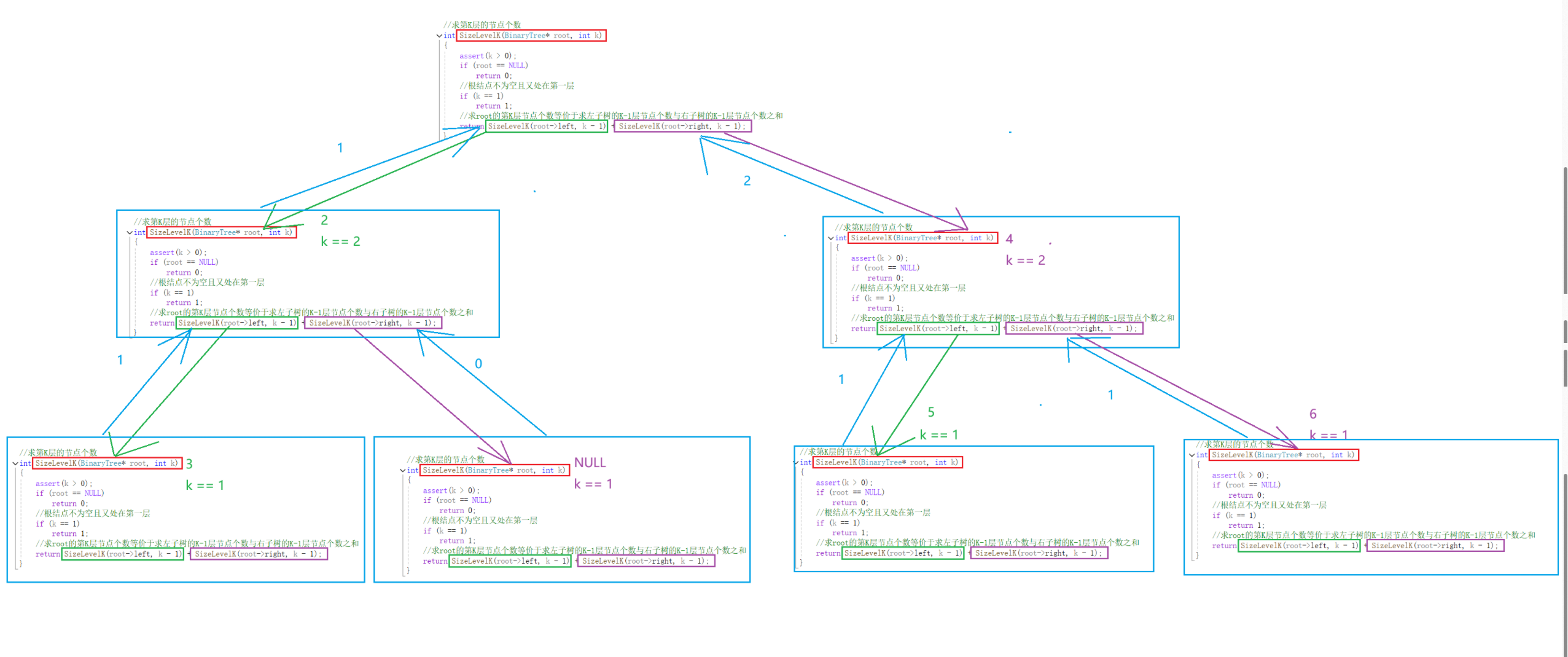
//求第K层的节点个数
int SizeLevelK(BinaryTree* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//根结点不为空且又处在第一层
if (k == 1)
return 1;
//求root的第K层节点个数等价于求左子树的K-1层节点个数与右子树的K-1层节点个数之和
return SizeLevelK(root->left, k - 1) + SizeLevelK(root->right, k - 1);
}
2.2.5:查找值为x的节点
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
//二叉树查找值为x的结点,利用前序遍历查找
BinaryTree* TreeFind(BinaryTree* root, BtDataType value)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->value == value)
return root;
BinaryTree* LeftNode = TreeFind(root->left, value);
if (LeftNode != NULL)
return LeftNode;
BinaryTree* RightNode = TreeFind(root->right, value);
if (RightNode != NULL)
return RightNode;
//当既没有在根找到,又没有在左树找到,也没有在右树找到,则返回NULL
return NULL;
}2.2.6:判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树与销毁二叉树
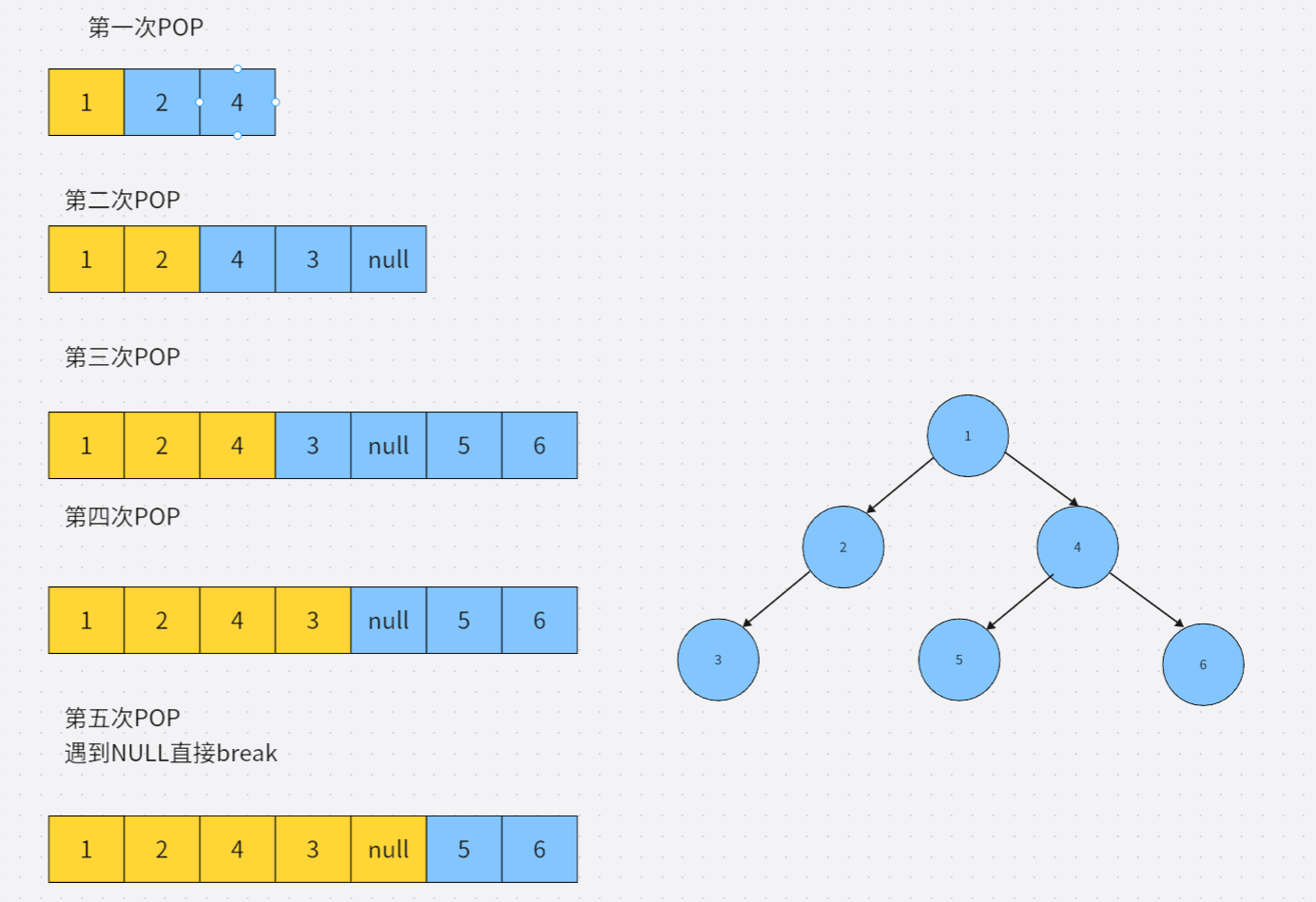
- **完全二叉树的定义:**在一棵二叉树(从上到下,从左到右)中,若除了最后一层外,其余所有层的节点都完全填满(即每一层的节点数达到该层所能容纳的最大值),且最后一层的节点从左至右连续排列(不允许存在右节点无左节点的情况),则称其为完全二叉树.
- 一旦出现空节点(null),后续所有节点必须都是空节点 (即不允许空节点后还有非空节点)。除最后一层外,所有层必须被节点完全填满(通过层序遍历中 "空节点出现的时机" 判断)
- 若树为空,直接判定为完全二叉树。
- 使用队列进行层序遍历,依次入队所有节点(包括空节点)。
- 遍历过程中,一旦遇到第一个空节点,标记 "已出现空节点"。
- 若标记后再遇到非空节点,说明违反完全二叉树规则(空节点后有非空节点),返回 false。
- 遍历结束后未出现违规情况,返回 true。
cpp
//判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
Queue Q;
QueueInit(&Q);
QueuePush(&Q, root);
//利用层序遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
//遇到空,直接跳出循环
if (Front == NULL)
break;
QueuePush(&Q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&Q, Front->right);
}
//检测是否连续为NULL
while (!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
//先获取队头元素
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
//由于完全二叉树的特性为只要出现NULL节点,后续所有节点必须都是空节点,若队列的队头依旧不为空,那说明不连续
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueueDestory(&Q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestory(&Q);
return true;
}
//销毁树
void DestoryTree(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
//使用后序遍历销毁树
DestoryTree(root->left);
DestoryTree(root->right);
free(root);
}2.3:Test.c
2.3.1:测试前序,中序,后序遍历
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
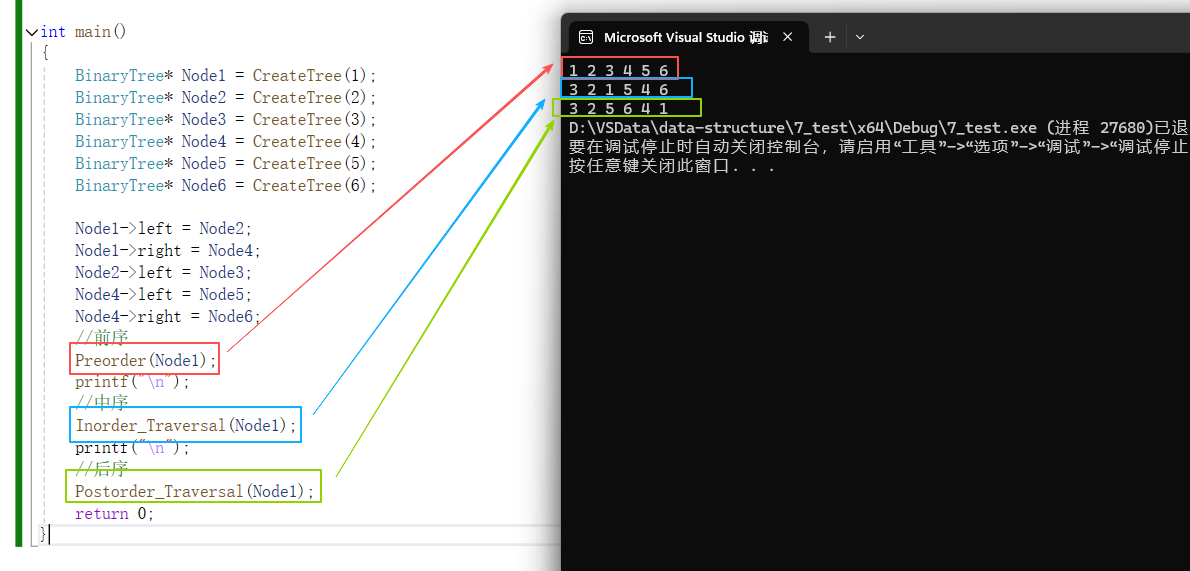
int main()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
//前序
Preorder(Node1);
printf("\n");
//中序
Inorder_Traversal(Node1);
printf("\n");
//后序
Postorder_Traversal(Node1);
return 0;
}
2.3.2:测试层序遍历
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
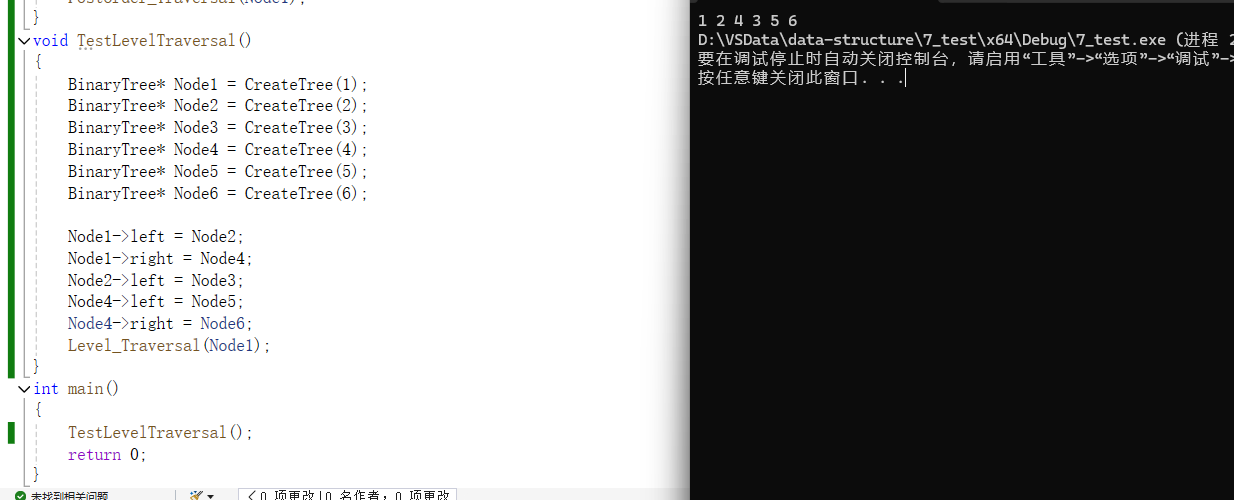
void TestLevelTraversal()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
Level_Traversal(Node1);
}
int main()
{
TestLevelTraversal();
return 0;
}
2.3.3:测试求节点个数与叶子节点个数
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
void TestSizeAndLeafSize()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("节点个数为:>%d\n",Tree_Size(Node1));
printf("叶子节点个数为:>%d\n",TreeLeafSize(Node1));
}
int main()
{
TestSizeAndLeafSize();
return 0;
}2.3.4:测试树的高度与第K层的节点个数
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
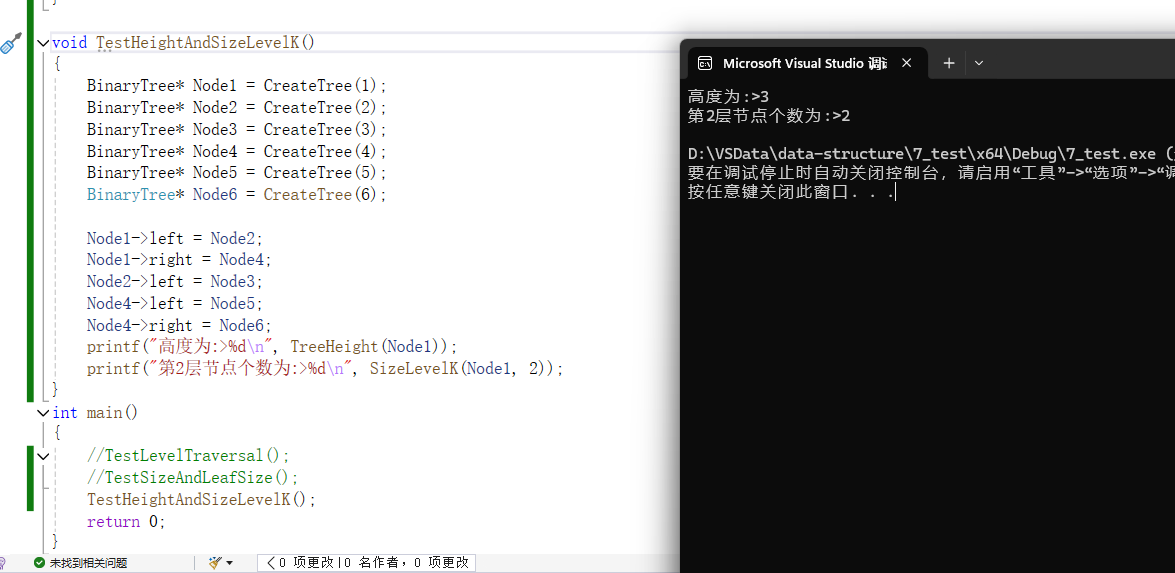
void TestHeightAndSizeLevelK()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("高度为:>%d\n", TreeHeight(Node1));
printf("第2层节点个数为:>%d\n", SizeLevelK(Node1, 2));
}
int main()
{
TestHeightAndSizeLevelK();
return 0;
}
2.3.5:测试查找值为x的节点
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
void TestFind()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("%p\n", TreeFind(Node1,6));
printf("%p\n", TreeFind(Node1,7));
}
int main()
{
TestFind();
return 0;
}
2.3.6:测试判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树与销毁树
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
void TestBinaryTreeCompleteAndDestory()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeComplete(Node1));
}
int main()
{
TestBinaryTreeCompleteAndDestory();
return 0;
}
3:二叉树的链式结构实现总代码
3.1:BinaryTree.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char BtDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTree
{
BtDataType value;
//左结点
struct BinaryTree* left;
//右结点
struct BinaryTree* right;
}BinaryTree;
////创建树节点(死编码方式)
BinaryTree* CreateTree(int value);
//前序遍历
void Preorder(BinaryTree* root);
//中序遍历
void Inorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//后序遍历
void Postorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//层序遍历
void Level_Traversal(BinaryTree* root);
//求树的结点个数
int Tree_Size(BinaryTree* root);
//求叶子节点的个数
int TreeLeafSize(BinaryTree* root);
//求树的高度
int TreeHeight(BinaryTree* root);
//求第K层的节点个数
int SizeLevelK(BinaryTree* root, int k);
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BinaryTree* TreeFind(BinaryTree* root, BtDataType value);
//判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BinaryTree* root);
//销毁树
void DestoryTree(BinaryTree* root);3.2:BinaryTree.c
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
#include "Queue.h"
BinaryTree* CreateTree(int value)
{
BinaryTree* Node = (BinaryTree*)malloc(sizeof(BinaryTree));
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
Node->value = value;
return Node;
}
//前序遍历(根,左子树,右子树)
void Preorder(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
printf("%d ", root->value);
Preorder(root->left);
Preorder(root->right);
}
//中序遍历(左子树 根 右子树)
void Inorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
Inorder_Traversal(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->value);
Inorder_Traversal(root->right);
}
//后序遍历
void Postorder_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
return;
Postorder_Traversal(root->left);
Postorder_Traversal(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->value);
}
//层序遍历(利用队列先进先出的特点进行层序遍历
void Level_Traversal(BinaryTree* root)
{
Queue Q;
QueueInit(&Q);
if (root != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, root);
}
//获取每一层的节点
int LevelSize = 1;
while(!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
while (LevelSize--)
{
//获取队头
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
printf("%d ", Front->value);
if(Front->left != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, Front->left);
}
if (Front->right != NULL)
{
QueuePush(&Q, Front->right);
}
LevelSize = Queuesize(&Q);
}
}
QueueDestory(&Q);
}
//求树的结点个数
int Tree_Size(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//左子树的个数 + 右子树的节点个数 + 根节点
return Tree_Size(root->left) + Tree_Size(root->right) + 1;
}
//求叶子节点的个数
int TreeLeafSize(BinaryTree* root)
{
//空树的情况或者非叶子节点的子节点为空的情况
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//叶子节点(没有孩子节点)
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
//求左右子树的叶子节点个数
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
//求树的高度
int TreeHeight(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int LeftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int RightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
//取左右子树中最高的子树高度,由于根节点本身处在一个高度,因此要+1
return LeftHeight > RightHeight ? LeftHeight : RightHeight + 1;
}
//求第K层的节点个数
int SizeLevelK(BinaryTree* root, int k)
{
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
//根结点不为空且又处在第一层
if (k == 1)
return 1;
//求root的第K层节点个数等价于求左子树的K-1层节点个数与右子树的K-1层节点个数之和
return SizeLevelK(root->left, k - 1) + SizeLevelK(root->right, k - 1);
}
//二叉树查找值为x的结点,利用前序遍历查找
BinaryTree* TreeFind(BinaryTree* root, BtDataType value)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->value == value)
return root;
BinaryTree* LeftNode = TreeFind(root->left, value);
if (LeftNode != NULL)
return LeftNode;
BinaryTree* RightNode = TreeFind(root->right, value);
if (RightNode != NULL)
return RightNode;
//当既没有在根找到,又没有在左树找到,也没有在右树找到,则返回NULL
return NULL;
}
//判断一棵树是否为完全二叉树
bool BinaryTreeComplete(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
Queue Q;
QueueInit(&Q);
QueuePush(&Q, root);
//利用层序遍历
while (!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
//遇到空,直接跳出循环
if (Front == NULL)
break;
QueuePush(&Q, Front->left);
QueuePush(&Q, Front->right);
}
//检测是否连续为NULL
while (!QueueEmpty(&Q))
{
//先获取队头元素
BinaryTree* Front = QueueFront(&Q);
QueuePop(&Q);
//由于完全二叉树的特性为只要出现NULL节点,后续所有节点必须都是空节点,若队列的队头依旧不为空,那说明不连续
if (Front != NULL)
{
QueueDestory(&Q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestory(&Q);
return true;
}
//销毁树
void DestoryTree(BinaryTree* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return;
}
//使用后序遍历销毁树
DestoryTree(root->left);
DestoryTree(root->right);
free(root);
}3.3:Queue.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct BinaryTree* QUDatatype;
//队头出队:头删,队尾入队->尾插
//链式栈
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QUDatatype value;
//存储下一个节点的地址
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
//代表队头,删除数据;头删
QueueNode* Qhead;
//代表队尾,入数据,以空间来换时间;尾插
QueueNode* Qtail;
//统计有效元素个数
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QUDatatype value);
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//获取队头元素
QUDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//获取队尾元素
QUDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//获取队列中的有效元素个数
int Queuesize(Queue* pq);
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);3.4:Queue.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Queue.h"
//初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->Qhead = NULL;
pq->Qtail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QUDatatype value)
{
assert(pq);
//创建节点
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->value = value;
newnode->next = NULL;
//为空时
if (pq->Qhead == NULL)
{
pq->Qhead = newnode;
pq->Qtail = newnode;
}
//非空时
else
{
//尾节点链接新节点
pq->Qtail->next = newnode;
pq->Qtail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//确保不为空队列
assert(pq->size > 0);
//保存头结点的下一个节点
if (pq->Qhead == pq->Qtail)
{
pq->Qtail = NULL;
}
QueueNode* tmp = pq->Qhead->next;
free(pq->Qhead);
pq->Qhead = tmp;
pq->size--;
}
//获取队头元素
QUDatatype QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->Qhead);
return pq->Qhead->value;
}
//获取队尾元素
QUDatatype QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->Qtail);
return pq->Qhead->value;
}
//获取队列中的有效元素个数
int Queuesize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->Qtail == NULL ? true : false;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* current = pq->Qhead;
while (current != NULL)
{
//保存下一个节点
QueueNode* tmp = current->next;
free(current);
current = tmp;
}
pq->Qhead = NULL;
pq->Qtail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}3.5:Test.c
cpp
#include "BinaryTree.h"
void TestTraversal()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
//前序
Preorder(Node1);
printf("\n");
//中序
Inorder_Traversal(Node1);
printf("\n");
//后序
Postorder_Traversal(Node1);
}
void TestLevelTraversal()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
Level_Traversal(Node1);
}
void TestSizeAndLeafSize()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("节点个数为:>%d\n",Tree_Size(Node1));
printf("叶子节点个数为:>%d\n",TreeLeafSize(Node1));
}
void TestHeightAndSizeLevelK()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("高度为:>%d\n", TreeHeight(Node1));
printf("第2层节点个数为:>%d\n", SizeLevelK(Node1, 2));
}
void TestFind()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("%p\n", TreeFind(Node1,6));
printf("%p\n", TreeFind(Node1,7));
}
void TestBinaryTreeCompleteAndDestory()
{
BinaryTree* Node1 = CreateTree(1);
BinaryTree* Node2 = CreateTree(2);
BinaryTree* Node3 = CreateTree(3);
BinaryTree* Node4 = CreateTree(4);
BinaryTree* Node5 = CreateTree(5);
BinaryTree* Node6 = CreateTree(6);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node4;
Node2->left = Node3;
Node4->left = Node5;
Node4->right = Node6;
printf("%d\n", BinaryTreeComplete(Node1));
}
int main()
{
//TestLevelTraversal();
//TestSizeAndLeafSize();
//TestHeightAndSizeLevelK();
//TestFind();
TestBinaryTreeCompleteAndDestory();
return 0;
}