卡码网题目链接
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1173
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1174
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1175
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1176
题解
101.孤岛的总面积
怎么不计算有边缘面积的岛屿呢?

最后只要重新遍历一遍地图就可以,因为是求面积。
在dfs遍历中,遇到海洋要跳过,这是一个错误点。
bfs很多语法不太熟悉,要照着写。
102.沉没孤岛
能不能把上一题用到的graph留下,对照着原始的graph将其孤岛变为0,再输出,这样的话代码几乎和上题一样。看看题解有没有什么更好的方法。
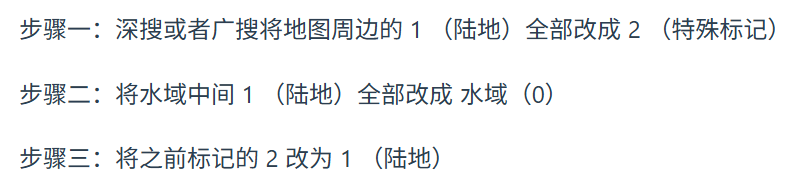
果然有更好的方法,就是标记2。
103.水流问题
遍历每一个点,看是否能到达第一组边界和第二组边界,同时每次遍历它周边的点时要看是否是坡度相等或更低的地形。还要一个visited数组,每次遍历时重新初始化为全False,避免重复遍历同一个点。
看了下题解,直接用visited的true痕迹记录到达第一边界和第二边界与否。


104.建造最大岛屿
暴力法,对每个点变成1,然后从该点开始bfs遍历计算当前的岛屿面积是多少,总的取最大值就行,但会不会和上一题一样是超时?看题解知道的,记住这样的算法时间复杂度是n^4。
优化方法看着有些难,c++和python的实现都是。题解的代码看不懂,建议多看。
代码
python
#101.孤岛的总面积
#dfs法
point = [[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
def dfs(graph, x, y):
graph[x][y] = 0
for i in range(4):
nextx = x + point[i][0]
nexty = y + point[i][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] == 0:
continue;
dfs(graph, nextx, nexty)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
for i in range(n):
if graph[i][0] == 1:
dfs(graph, i, 0)
if graph[i][m - 1] == 1:
dfs(graph, i, m - 1)
for j in range(m):
if graph[0][j] == 1:
dfs(graph, 0, j)
if graph[n - 1][j] == 1:
dfs(graph, n - 1, j)
result = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
result += 1
print(result)
#bfs法
from collections import deque
point = [[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
def bfs(graph, x, y):
queue = deque()
queue.append(x)
queue.append(y)
while queue:
i = queue.popleft()
j = queue.popleft()
graph[i][j] = 0
for t in range(4):
nextx = i + point[t][0]
nexty = j + point[t][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] == 0:
continue;
queue.append(nextx)
queue.append(nexty)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
for i in range(n):
if graph[i][0] == 1:
bfs(graph, i, 0)
if graph[i][m - 1] == 1:
bfs(graph, i, m - 1)
for j in range(m):
if graph[0][j] == 1:
bfs(graph, 0, j)
if graph[n - 1][j] == 1:
bfs(graph, n - 1, j)
result = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
result += 1
print(result)
python
#102.沉没孤岛
#dfs法
point = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
def dfs(graph, x, y):
graph[x][y] = 2
for i in range(4):
nextx = x + point[i][0]
nexty = y + point[i][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] == 1:
dfs(graph, nextx, nexty)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
for i in range(n):
if graph[i][0] == 1:
dfs(graph, i, 0)
if graph[i][m - 1] == 1:
dfs(graph, i, m - 1)
for j in range(m):
if graph[0][j] == 1:
dfs(graph, 0, j)
if graph[n - 1][j] == 1:
dfs(graph, n - 1, j)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
graph[i][j] = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 2:
graph[i][j] = 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m - 1):
print(f"{graph[i][j]} ", end = '')
print(graph[i][m - 1])
#bfs法
from collections import deque
point = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]]
def bfs(graph, x, y):
queue = deque()
queue.append(x)
queue.append(y)
while queue:
i = queue.popleft()
j = queue.popleft()
graph[i][j] = 2
for t in range(4):
nextx = i + point[t][0]
nexty = j + point[t][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] == 1:
queue.append(nextx)
queue.append(nexty)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
for i in range(n):
if graph[i][0] == 1:
bfs(graph, i, 0)
if graph[i][m - 1] == 1:
bfs(graph, i, m - 1)
for j in range(m):
if graph[0][j] == 1:
bfs(graph, 0, j)
if graph[n - 1][j] == 1:
bfs(graph, n - 1, j)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 1:
graph[i][j] = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if graph[i][j] == 2:
graph[i][j] = 1
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m - 1):
print(f"{graph[i][j]} ", end = '')
print(graph[i][m - 1])
python
#103.水流问题
#我写的不对的代码
point = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
def dfs(graph, visited, x, y, local_contact):
visited[x][y] = True
for i in range(4):
nextx = x + point[i][0]
nexty = y + point[i][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] <= graph[x][y] and visited[nextx][nexty] == False:
if nextx == 0 or nexty == 0:
local_contact[x][y][0] = True
if nextx == n - 1 or nexty == m - 1:
local_contact[x][y][1] = True
visited[nextx][nexty] = True
dfs(graph, visited, nextx, nexty, local_contact)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
result = []
local_contact = [[[False] * 2 for _ in range(m)] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
dfs(graph, visited, i, j, local_contact)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if local_contact[i][j][0] == True and local_contact[i][j][1] == True:
result.append([i, j])
for i in range(len(result)):
print(f"{result[i][0]} {result[i][1]}")
#题解的暴力法,跟我的思路一样,实现不同,具体去看题解的代码,因为是c++不好放上来,而且这个思路超时了,时间复杂度是O(M^2*N*2)
#代码略
#优化代码
point = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
def dfs(graph, visited, x, y):
visited[x][y] = True
for i in range(4):
nextx = x + point[i][0]
nexty = y + point[i][1]
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(graph) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(graph[0]):
continue
if graph[nextx][nexty] >= graph[x][y] and visited[nextx][nexty] == False:
#visited[nextx][nexty] = True
dfs(graph, visited, nextx, nexty)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for i in range(n):
graph.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
result = []
firstBorder = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
secondBorder = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
dfs(graph, firstBorder, i, 0)
dfs(graph, secondBorder, i, m - 1)
for j in range(m):
dfs(graph, firstBorder, 0, j)
dfs(graph, secondBorder, n - 1, j)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if firstBorder[i][j] == True and secondBorder[i][j] == True:
result.append([i, j])
for i in range(len(result)):
print(f"{result[i][0]} {result[i][1]}")
python
#104.建造最大岛屿


