👨⚕️ 主页: gis分享者
👨⚕️ 感谢各位大佬 点赞👍 收藏⭐ 留言📝 加关注✅!
文章目录
- 一、🍀前言
-
- [1.1 ☘️GLSL着色器](#1.1 ☘️GLSL着色器)
-
- [1.1.1 ☘️着色器类型](#1.1.1 ☘️着色器类型)
- [1.1.2 ☘️工作原理](#1.1.2 ☘️工作原理)
- [1.1.3 ☘️核心特点](#1.1.3 ☘️核心特点)
- [1.1.4 ☘️应用场景](#1.1.4 ☘️应用场景)
- [1.1.5 ☘️实战示例](#1.1.5 ☘️实战示例)
- 二、🍀基于噪声函数的顶点着色器动态插桩技术实现模型形变
-
- [1. ☘️实现思路](#1. ☘️实现思路)
- [2. ☘️代码样例](#2. ☘️代码样例)
一、🍀前言
本文详细介绍如何基于threejs在三维场景,基于噪声函数的顶点着色器动态插桩技术实现模型形变。亲测可用。希望能帮助到您。一起学习,加油!加油!
1.1 ☘️GLSL着色器
GLSL(OpenGL Shading Language)是OpenGL的核心编程语言,用于编写图形渲染管线中可定制的计算逻辑。其核心设计目标是通过GPU并行计算实现高效的图形处理,支持从基础几何变换到复杂物理模拟的多样化需求。
1.1.1 ☘️着色器类型
顶点着色器(Vertex Shader)
- 功能:处理每个顶点的坐标变换(如模型视图投影矩阵变换)、法线计算及顶点颜色传递。
- 输出:裁剪空间坐标gl_Position,供后续光栅化阶段使用。
片段着色器(Fragment Shader)
- 功能:计算每个像素的最终颜色,支持纹理采样、光照模型(如Phong、PBR)及后处理效果(如模糊、景深)。
- 输出:像素颜色gl_FragColor或gl_FragColor(RGBA格式)。
计算着色器(Compute Shader,高级)
- 功能:执行通用并行计算任务(如物理模拟、图像处理),不直接绑定渲染管线。
- 特点:通过工作组(Work Group)实现高效数据并行处理。
1.1.2 ☘️工作原理
渲染管线流程
- 顶点处理:CPU提交顶点数据(位置、颜色、纹理坐标),GPU并行执行顶点着色器处理每个顶点。
- 光栅化:将顶点数据转换为像素片段,生成片段着色器输入。
- 片段处理:GPU并行执行片段着色器计算每个像素颜色。
- 输出合并:将片段颜色与帧缓冲区混合,生成最终图像。
数据流动
- 顶点属性:通过glVertexAttribPointer传递位置、颜色等数据,索引由layout(location=N)指定。
- Uniform变量:CPU通过glGetUniformLocation传递常量数据(如变换矩阵、时间),在渲染循环中更新。
- 内置变量: gl_Position(顶点着色器输出):裁剪空间坐标。 gl_FragCoord(片段着色器输入):当前像素的窗口坐标。
gl_FrontFacing(片段着色器输入):判断像素是否属于正面三角形。
1.1.3 ☘️核心特点
语法特性
- C语言变体:支持条件语句、循环、函数等结构,天然适配图形算法。
- 向量/矩阵运算:内置vec2/vec3/vec4及mat2/mat3/mat4类型,支持点乘、叉乘等操作。
- 精度限定符:如precision mediump float,控制计算精度与性能平衡。
硬件加速
- 并行计算:GPU数千个核心并行执行着色器代码,适合处理大规模数据(如粒子系统、体素渲染)。
- 内存模型:支持常量内存(Uniform)、纹理内存(Sampler)及共享内存(计算着色器),优化数据访问效率。
灵活性
- 可编程管线:完全替代固定渲染管线,支持自定义光照、阴影、后处理效果。
- 跨平台兼容性:OpenGL ES(移动端)与WebGL(Web)均支持GLSL,代码可移植性强。
1.1.4 ☘️应用场景
游戏开发
- 实时渲染:实现PBR材质、动态阴影、屏幕空间反射。
- 特效系统:粒子火焰、流体模拟、布料物理。
- 性能优化:通过计算着色器加速AI计算、碰撞检测。
数据可视化
- 科学计算:将多维数据映射为颜色/高度图(如气象数据、流场可视化)。
- 信息图表:动态生成3D柱状图、热力图,增强数据表现力。
艺术创作
- 程序化生成:使用噪声函数(如Perlin、Simplex)生成地形、纹理。
- 交互式装置:结合传感器数据实时修改着色器参数,创造动态艺术作品。
教育与研究
- 算法实验:实时调试光线追踪、路径追踪算法。
- 教学工具:可视化线性代数运算(如矩阵变换、向量投影)。
1.1.5 ☘️实战示例
顶点着色器(传递法线与世界坐标):
javascript
#version 330 core
layout(location=0) in vec3 aPos;
layout(location=1) in vec3 aNormal;
out vec3 FragPos;
out vec3 Normal;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main() {
FragPos = vec3(model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal; // 模型空间到世界空间的法线变换
gl_Position = projection * view * vec4(FragPos, 1.0);
}片段着色器(实现Blinn-Phong光照):
javascript
#version 330 core
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec3 lightPos;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform vec3 lightColor;
uniform vec3 objectColor;
void main() {
// 环境光
vec3 ambient = 0.1 * lightColor;
// 漫反射
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = diff * lightColor;
// 镜面反射
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), 32);
vec3 specular = 0.5 * spec * lightColor;
// 最终颜色
vec3 result = (ambient + diffuse + specular) * objectColor;
FragColor = vec4(result, 1.0);
}二、🍀基于噪声函数的顶点着色器动态插桩技术实现模型形变
1. ☘️实现思路
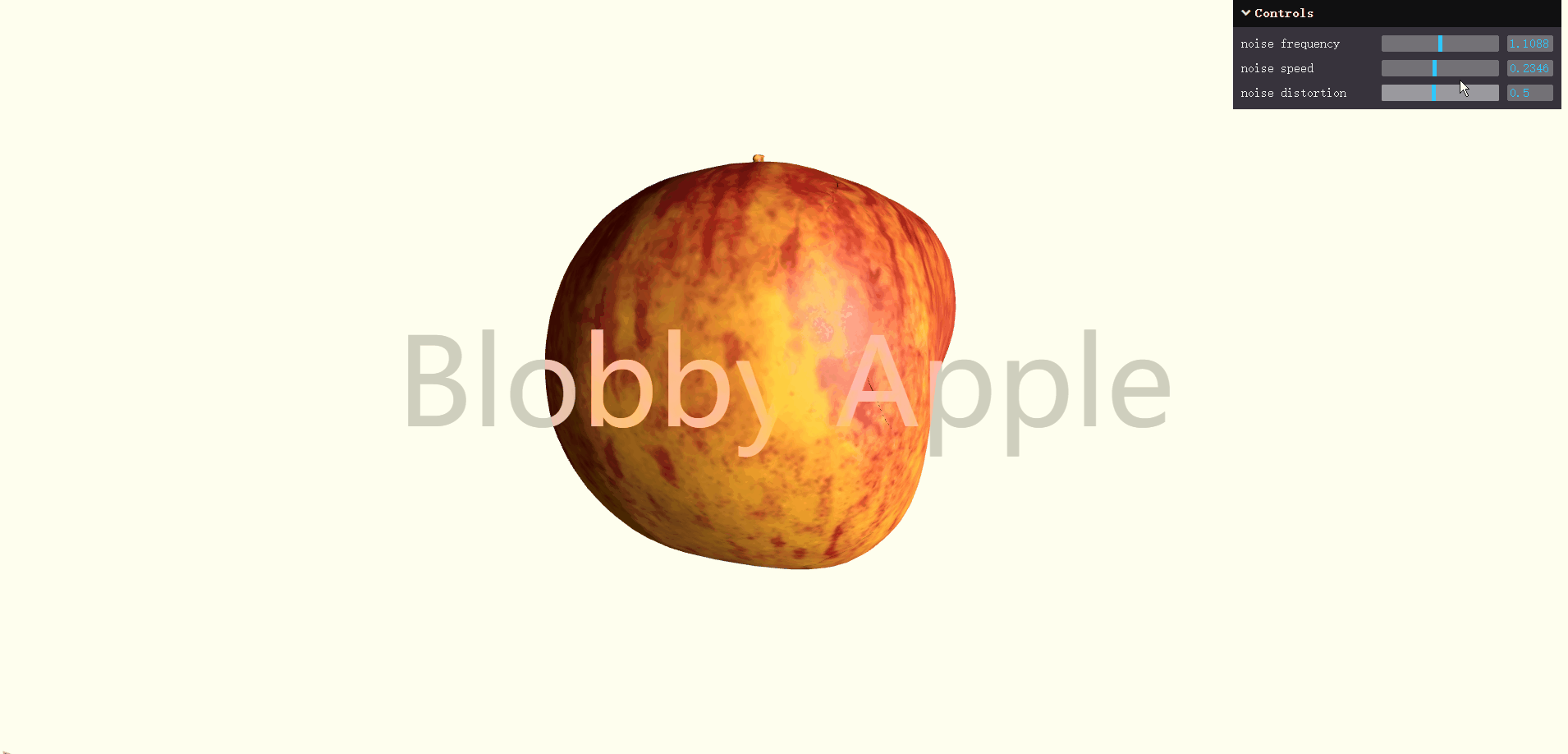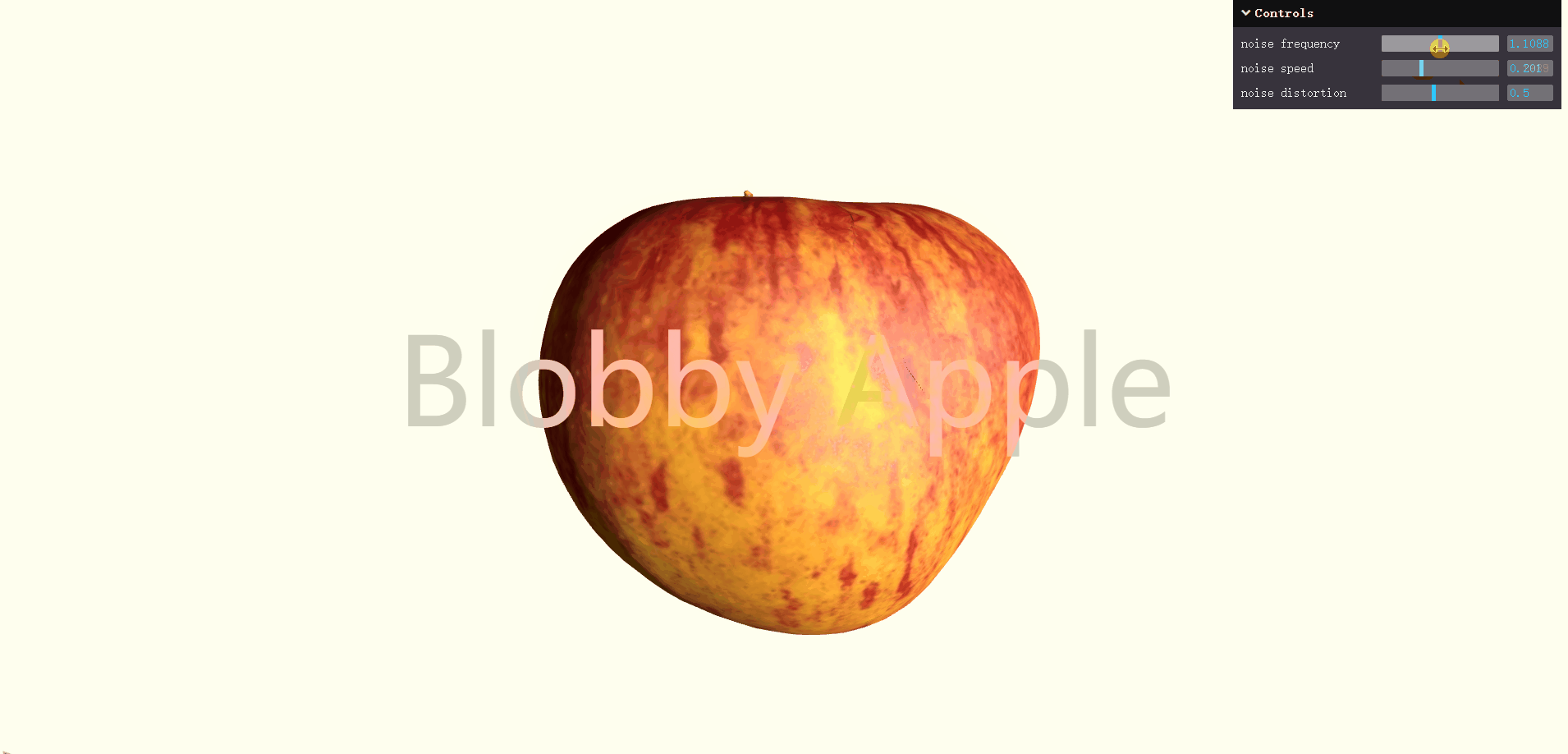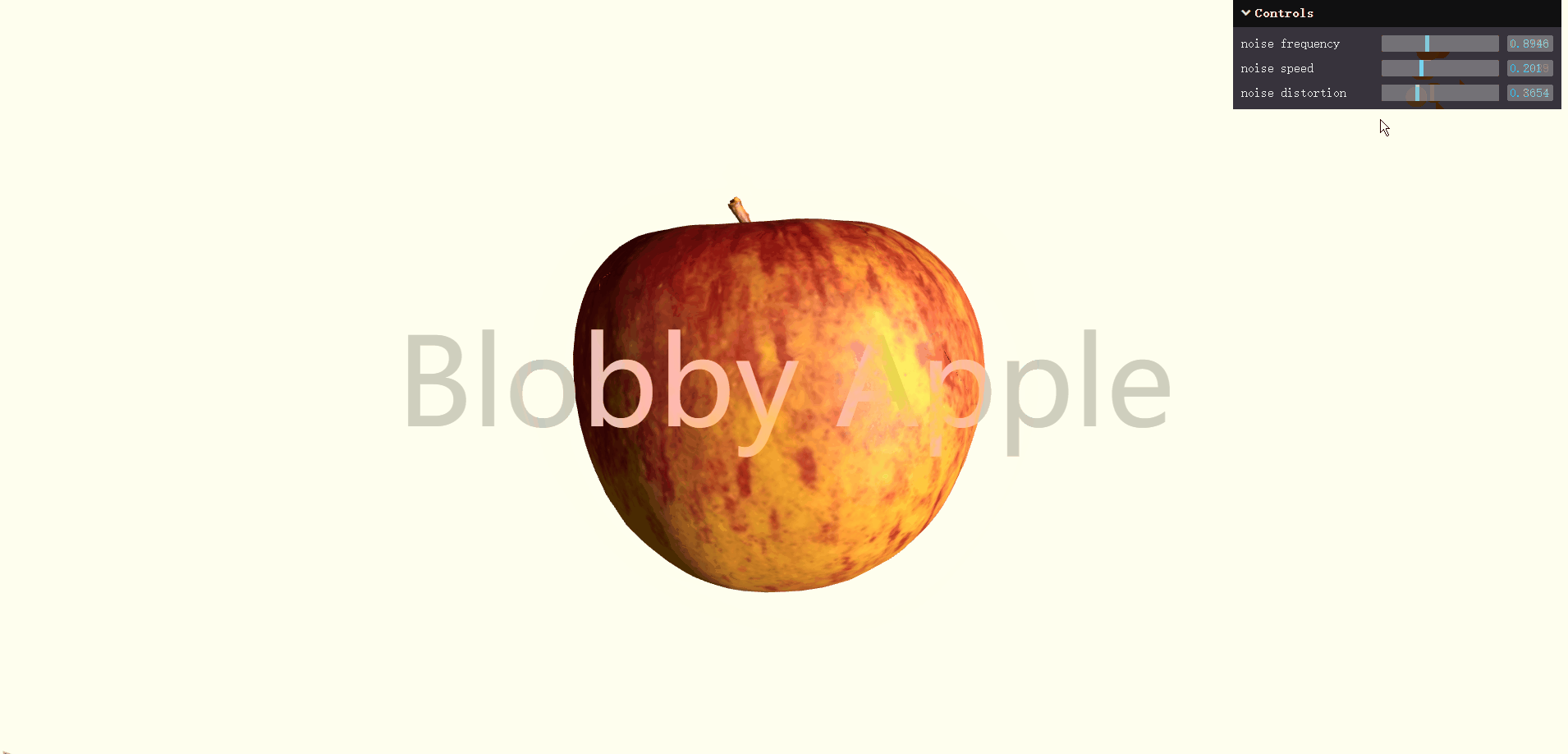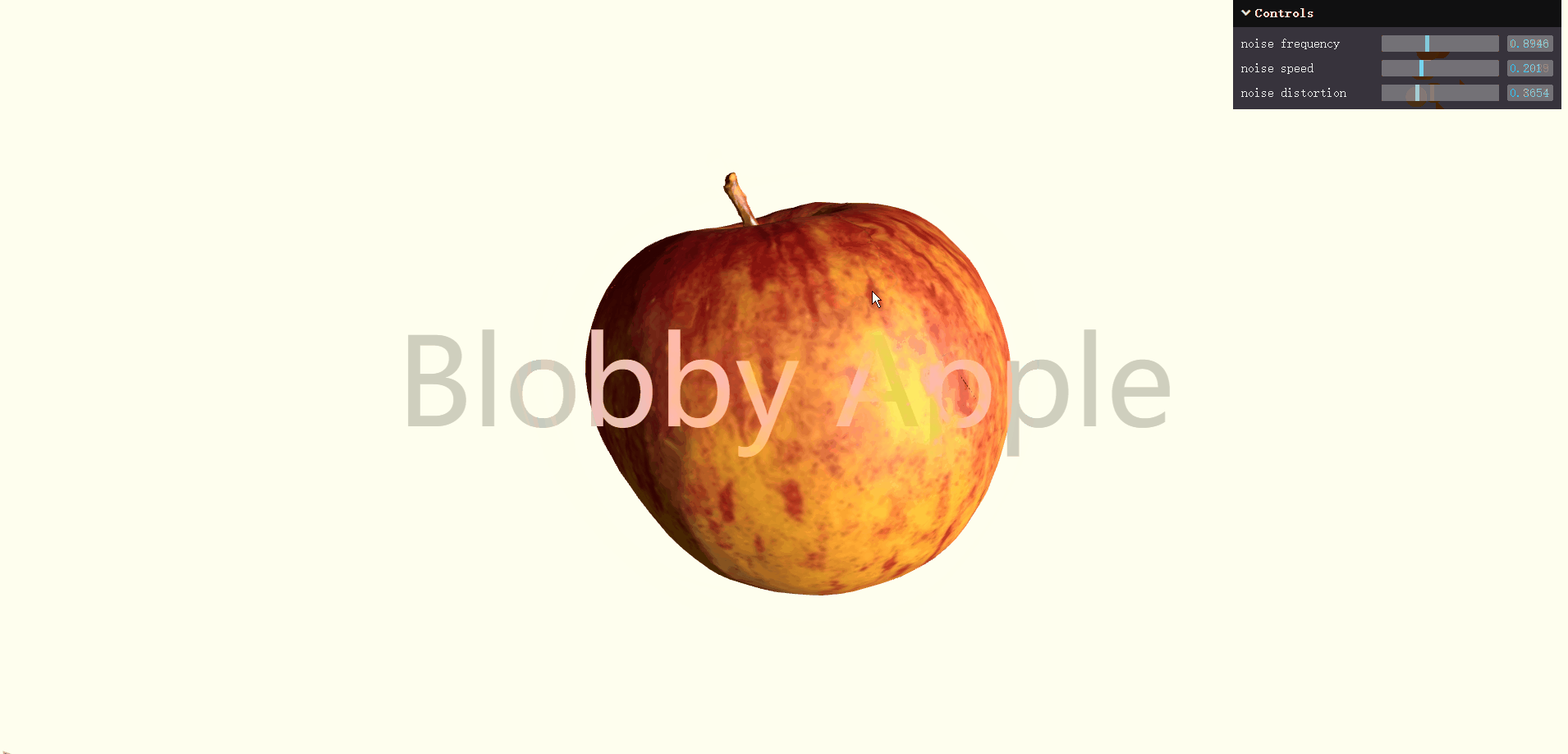
基于Three.js 加载 GLTF 模型,并通过自定义顶点着色器注入噪声函数,让苹果表面不断扭曲、律动,呈现出流体般的"blobby"质感;同时配合 OrbitControls 和 GUI 控件,用户可以交互调整形变频率、强度和速度。对前端工程师来说,它不仅是一个视觉上很酷的作品,更是学习 材质自定义、shader 插桩与实时形变 的优秀实践案例。具体代码参考代码样例。可以直接运行。
2. ☘️代码样例
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>基于噪声函数的顶点着色器动态插桩技术</title>
<script async src="https://unpkg.com/es-module-shims@1.6.3/dist/es-module-shims.js"></script>
<script type="importmap">
{
"imports": {
"three": "https://unpkg.com/three@0.164.0/build/three.module.min.js",
"three/addons/": "https://unpkg.com/three@0.164.0/examples/jsm/"
}
}
</script>
<style>
html,
body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.container {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background-color: #ffffee;
}
.page-title {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
font-size: 16vh;
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
user-select: none;
pointer-events: none;
mix-blend-mode: luminosity;
/* color: #DEB887; */
color: lightpink;
}
.lil-gui {
--width: 400px;
max-width: 90%;
--widget-height: 20px;
font-size: 15px;
--input-font-size: 15px;
--padding: 10px;
--spacing: 10px;
--slider-knob-width: 5px;
--background-color: rgba(5, 0, 15, 0.8);
--widget-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.3);
--focus-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.4);
--hover-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5);
--font-family: monospace;
z-index: 1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<canvas id="apple-canvas"></canvas>
<div class="page-title">
Blobby Apple
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script type="module">
import * as THREE from "three";
import { OrbitControls } from "three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js";
import { GUI } from "three/addons/libs/lil-gui.module.min.js";
import { GLTFLoader } from "three/addons/loaders/GLTFLoader.js";
const containerEl = document.querySelector(".container");
const canvasEl = document.querySelector("#apple-canvas");
let renderer, scene, camera, orbit, lightHolder, mesh;
initScene();
window.addEventListener("resize", updateSceneSize);
function initScene() {
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true,
canvas: canvasEl,
alpha: true
});
renderer.setPixelRatio(Math.min(window.devicePixelRatio, 2));
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
scene = new THREE.Scene();
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
45,
containerEl.clientWidth / containerEl.clientHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
camera.position.set(0, 1, 2);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
updateSceneSize();
const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff, 0.5);
scene.add(ambientLight);
const sideLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff, 10);
sideLight.position.set(15, 0, 15);
lightHolder = new THREE.Group();
lightHolder.add(sideLight);
scene.add(lightHolder);
orbit = new OrbitControls(camera, canvasEl);
orbit.enableZoom = false;
orbit.enablePan = false;
orbit.enableDamping = true;
orbit.autoRotate = true;
orbit.autoRotateSpeed = 2;
const gltfLoader = new GLTFLoader();
gltfLoader.load("https://ksenia-k.com/models/realistic-apple.glb", (gltf) => {
mesh = gltf.scene.children[0];
mesh.castShadow = true;
mesh.receiveShadow = true;
const material = mesh.material;
material.userData.time = { value: 0 };
material.userData.speed = { value: 0.2 };
material.userData.frequency = { value: 0.8 };
material.userData.distortion = { value: 0.5 };
const headers = `
uniform float u_time;
uniform float u_speed;
uniform float u_frequency;
uniform float u_distortion;
vec3 mod289(vec3 x) { return x - floor(x * (1.0 / 289.0)) * 289.0; }
vec4 permute(vec4 x) { return mod(((x*34.0)+1.0)*x, 289.0); }
vec4 taylorInvSqrt(vec4 r) { return 1.79284291400159 - 0.85373472095314 * r; }
vec3 fade(vec3 t) { return t*t*t*(t*(t*6.0-15.0)+10.0); }
float pnoise(vec3 P) {
vec3 Pi0 = mod(floor(P), vec3(4.));
vec3 Pi1 = mod(Pi0 + vec3(1.0), vec3(4.));
Pi0 = mod289(Pi0);
Pi1 = mod289(Pi1);
vec3 Pf0 = fract(P); // Fractional part for interpolation
vec3 Pf1 = Pf0 - vec3(1.0); // Fractional part - 1.0
vec4 ix = vec4(Pi0.x, Pi1.x, Pi0.x, Pi1.x);
vec4 iy = vec4(Pi0.yy, Pi1.yy);
vec4 iz0 = Pi0.zzzz;
vec4 iz1 = Pi1.zzzz;
vec4 ixy = permute(permute(ix) + iy);
vec4 ixy0 = permute(ixy + iz0);
vec4 ixy1 = permute(ixy + iz1);
vec4 gx0 = ixy0 * (1.0 / 7.0);
vec4 gy0 = fract(floor(gx0) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
gx0 = fract(gx0);
vec4 gz0 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx0) - abs(gy0);
vec4 sz0 = step(gz0, vec4(0.0));
gx0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gx0) - 0.5);
gy0 -= sz0 * (step(0.0, gy0) - 0.5);
vec4 gx1 = ixy1 * (1.0 / 7.0);
vec4 gy1 = fract(floor(gx1) * (1.0 / 7.0)) - 0.5;
gx1 = fract(gx1);
vec4 gz1 = vec4(0.5) - abs(gx1) - abs(gy1);
vec4 sz1 = step(gz1, vec4(0.0));
gx1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gx1) - 0.5);
gy1 -= sz1 * (step(0.0, gy1) - 0.5);
vec3 g000 = vec3(gx0.x, gy0.x, gz0.x);
vec3 g100 = vec3(gx0.y, gy0.y, gz0.y);
vec3 g010 = vec3(gx0.z, gy0.z, gz0.z);
vec3 g110 = vec3(gx0.w, gy0.w, gz0.w);
vec3 g001 = vec3(gx1.x, gy1.x, gz1.x);
vec3 g101 = vec3(gx1.y, gy1.y, gz1.y);
vec3 g011 = vec3(gx1.z, gy1.z, gz1.z);
vec3 g111 = vec3(gx1.w, gy1.w, gz1.w);
vec4 norm0 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g000, g000), dot(g010, g010), dot(g100, g100), dot(g110, g110)));
g000 *= norm0.x;
g010 *= norm0.y;
g100 *= norm0.z;
g110 *= norm0.w;
vec4 norm1 = taylorInvSqrt(vec4(dot(g001, g001), dot(g011, g011), dot(g101, g101), dot(g111, g111)));
g001 *= norm1.x;
g011 *= norm1.y;
g101 *= norm1.z;
g111 *= norm1.w;
float n000 = dot(g000, Pf0);
float n100 = dot(g100, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.yz));
float n010 = dot(g010, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.y, Pf0.z));
float n110 = dot(g110, vec3(Pf1.xy, Pf0.z));
float n001 = dot(g001, vec3(Pf0.xy, Pf1.z));
float n101 = dot(g101, vec3(Pf1.x, Pf0.y, Pf1.z));
float n011 = dot(g011, vec3(Pf0.x, Pf1.yz));
float n111 = dot(g111, Pf1);
vec3 fade_xyz = fade(Pf0);
vec4 n_z = mix(vec4(n000, n100, n010, n110), vec4(n001, n101, n011, n111), fade_xyz.z);
vec2 n_yz = mix(n_z.xy, n_z.zw, fade_xyz.y);
float n_xyz = mix(n_yz.x, n_yz.y, fade_xyz.x);
return 2.2 * n_xyz;
}
vec3 displacement(vec3 p) {
float t = 3. * u_speed * u_time;
float noise_shape = pnoise(p * u_frequency + mod(t, 4.));
vec3 pos = p - p * u_distortion * noise_shape;
return pos;
}
vec3 orthogonal(vec3 v) {
return normalize(abs(v.x) > abs(v.z) ? vec3(-v.y, v.x, 0.0) : vec3(0.0, -v.z, v.y));
}
`;
const displacementCalculation = `
vec3 displacedPosition = displacement(position);
vec3 displacedNormal = normalize(normal);
float offset = 1. / 128.;
vec3 tangent = orthogonal(normal);
vec3 bitangent = normalize(cross(normal, tangent));
vec3 neighbour1 = position + tangent * offset;
vec3 neighbour2 = position + bitangent * offset;
vec3 displacedNeighbour1 = displacement(neighbour1);
vec3 displacedNeighbour2 = displacement(neighbour2);
vec3 displacedTangent = displacedNeighbour1 - displacedPosition;
vec3 displacedBitangent = displacedNeighbour2 - displacedPosition;
displacedNormal = normalize(cross(displacedTangent, displacedBitangent));
`;
material.onBeforeCompile = (shader) => {
shader.uniforms.u_time = material.userData.time;
shader.uniforms.u_speed = material.userData.speed;
shader.uniforms.u_frequency = material.userData.frequency;
shader.uniforms.u_distortion = material.userData.distortion;
shader.vertexShader = headers + shader.vertexShader;
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
"void main() {",
"void main() {" + displacementCalculation
);
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
"#include <displacementmap_vertex>",
"transformed = displacedPosition;"
);
shader.vertexShader = shader.vertexShader.replace(
"#include <defaultnormal_vertex>",
THREE.ShaderChunk.defaultnormal_vertex.replace(
"vec3 transformedNormal = objectNormal;",
"vec3 transformedNormal = displacedNormal;"
)
);
};
scene.add(gltf.scene.children[0]);
render();
createControls();
});
}
function render(time) {
orbit.update();
lightHolder.quaternion.copy(camera.quaternion);
mesh.material.userData.time.value = 0.001 * time;
renderer.render(scene, camera);
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
function updateSceneSize() {
camera.aspect = containerEl.clientWidth / containerEl.clientHeight;
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(containerEl.clientWidth, containerEl.clientHeight);
}
function createControls() {
const gui = new GUI();
gui.close();
gui
.add(mesh.material.userData.frequency, "value", 0.2, 2)
.name("noise frequency");
gui.add(mesh.material.userData.speed, "value", 0.1, 0.4).name("noise speed");
gui
.add(mesh.material.userData.distortion, "value", 0.1, 1)
.name("noise distortion");
}
</script>
</html>效果如下
参考:源码