全排列Ⅰ

java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
boolean[] check;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
check=new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums){
if(nums.length==path.size()){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(check[i]==false){
path.add(nums[i]);
check[i]=true;
dfs(nums);
check[i]=false;
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
}子集

法1:
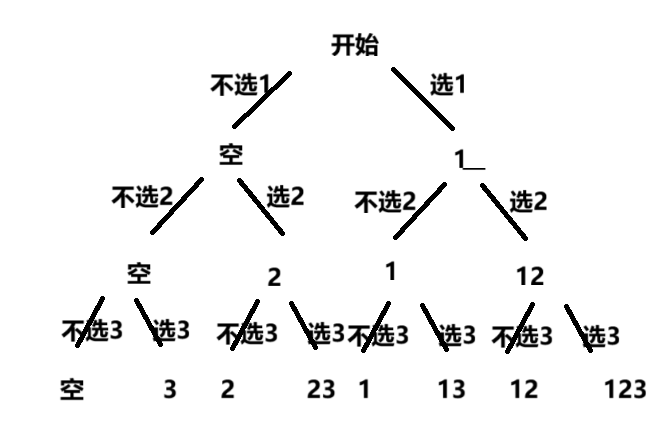
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nums,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int index){
if(index==nums.length){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return ;
}
// 选
path.add(nums[index]);
dfs(nums,index+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
// 不选
dfs(nums,index+1);
}
}法2:
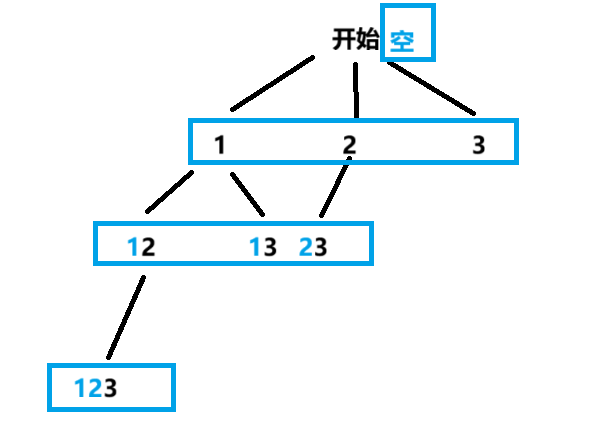
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
dfs(nums,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int index){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
for(int i=index;i<nums.length;i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}找出所有子集的异或总和再求和
1863. 找出所有子集的异或总和再求和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
异或有一个非常特殊的性质a ^ b ^ b = a,这样正好可以完成代码的回溯
java
class Solution {
int sum;
int path;
public int subsetXORSum(int[] nums) {
dfs(nums,0);
return sum;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int pos){
sum+=path;
for(int i=pos;i<nums.length;i++){
path^=nums[i];
dfs(nums,i+1);
path^=nums[i];
}
}
}全排列Ⅱ

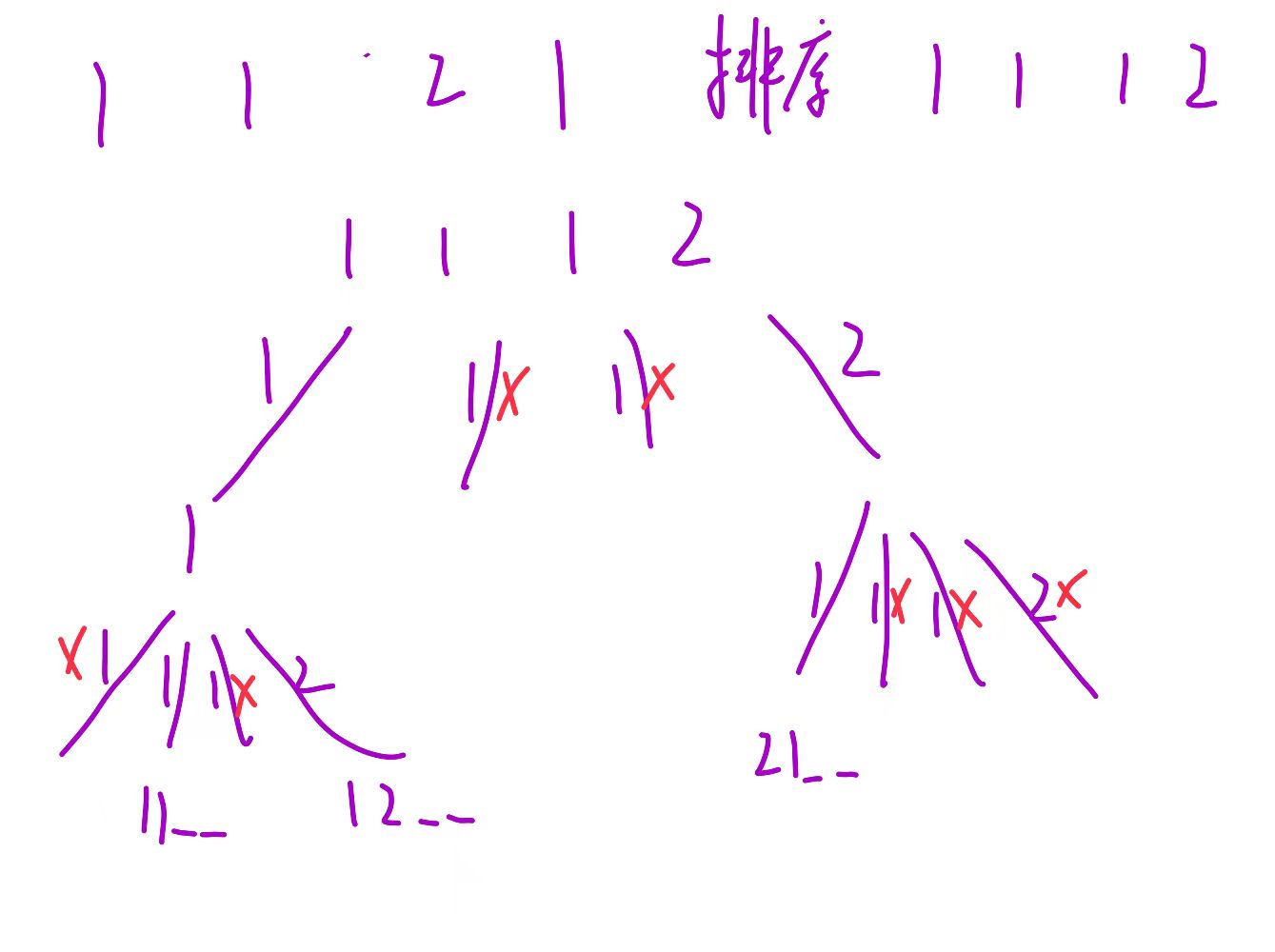
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
boolean[] check;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
check=new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(nums,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int pos){
if(pos==nums.length){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return ;
}
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(check[i]==true || (i!=0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && check[i-1]==false)){
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
check[i]=true;
dfs(nums,pos+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
check[i]=false;
}
}
}电话号码的字母组合

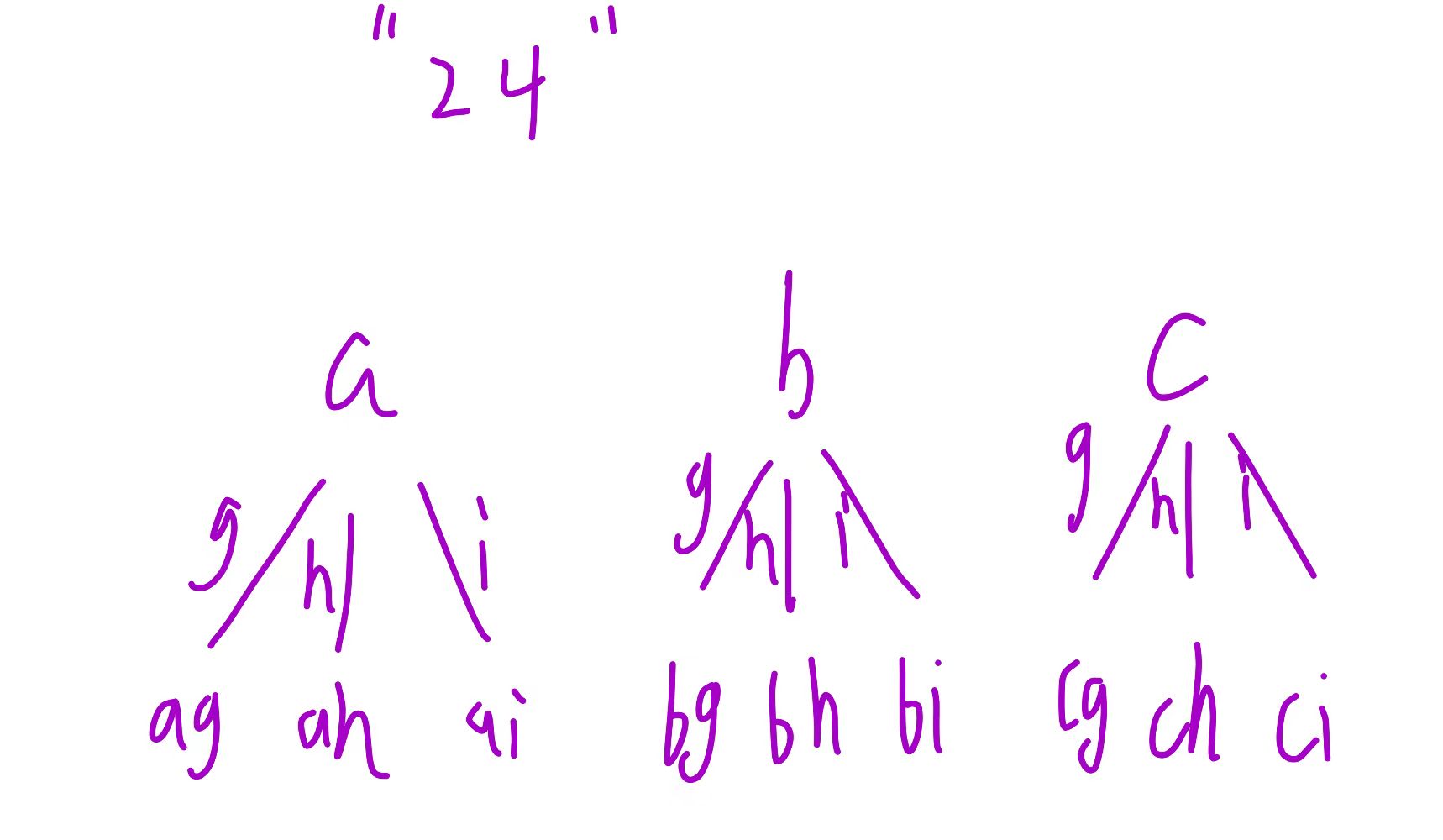
java
class Solution {
String[] hash={"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
List<String> ret;
StringBuffer path;
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new StringBuffer();
if(digits.length()==0){
return ret;
}
dfs(digits,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(String digits,int pos){
if(pos==digits.length()){
ret.add(path.toString());
return ;
}
String s=hash[digits.charAt(pos)-'0'];
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
path.append(s.charAt(i));
dfs(digits,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
}
}
}括号生成
java
class Solution {
int count;
List<String> ret;
StringBuffer path;
int left;
int right;
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
count=n;
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new StringBuffer();
dfs();
return ret;
}
public void dfs(){
// 递归出口
if(right==count){
ret.add(path.toString());
return;
}
// 左递归
if(left<count){
path.append('(');
left++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
left--;
}
// 右递归
if(right<left){
path.append(')');
right++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
right--;
}
}
}组合

java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
int n,k;
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n1, int k1) {
n=n1;
k=k1;
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
int start=1;
dfs(start);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int start){
if(path.size()==k){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i=start;i<=n;i++){
path.add(i);
dfs(i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}目标和

java
class Solution {
int ret;
int t;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
t=target;
ret=0;
dfs(nums,0,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int pos,int path){
if(pos==nums.length){
if(path==t){
ret++;
}
return;
}
dfs(nums,pos+1,path+nums[pos]);
dfs(nums,pos+1,path-nums[pos]);
}
}组合总和

java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
int t;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] nums, int target) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new ArrayList<>();
t=target;
dfs(nums,0,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums,int pos,int sum){
if(sum==t){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
if(sum>t || pos==nums.length){
return ;
}
for(int i=pos;i<nums.length;i++){
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,i,sum+nums[i]);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}字母大小的全排列

java
class Solution {
List<String> ret;
StringBuffer path;
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new StringBuffer();
dfs(s,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(String s,int pos){
if(pos==s.length()){
ret.add(path.toString());
return;
}
char ch=s.charAt(pos);
// 不改变
path.append(ch);
dfs(s,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
// 改变
if(ch<'0' ||ch>'9'){
char c=change(ch);
path.append(c);
dfs(s,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
}
}
public char change(char ch){
if(ch>='a' && ch<='z'){
return ch-=32;
}
return ch+=32;
}
}优美的队列

java
class Solution {
boolean[] check;
Integer ret;
int n;
public int countArrangement(int n1) {
check=new boolean[n1+1];
ret=0;
n=n1;
dfs(1);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int pos){
if(pos==n+1){
ret++;
return ;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(check[i]==false && (pos % i==0 || i % pos==0)){
check[i]=true;
dfs(pos+1);
check[i]=false;
}
}
}
}N皇后

java
class Solution {
boolean[] checkCol,checkDig1,checkDig2;
List<List<String>> ret;
int n;
char[][] path;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n1) {
n=n1;
checkCol=new boolean[n];
checkDig1=new boolean[2*n];
checkDig2=new boolean[2*n];
ret=new ArrayList<>();
path=new char[n][n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
Arrays.fill(path[i],'.');
}
dfs(0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int row){
if(row==n){
List<String> tmp=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
tmp.add(new String(path[i]));
}
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for(int col=0;col<n;col++){
if(checkCol[col]==false && checkDig1[col+row]==false && checkDig2[row-col+n]==false){
path[row][col]='Q';
checkCol[col]=checkDig1[col+row]=checkDig2[row-col+n]=true;
dfs(row+1);
path[row][col]='.';
checkCol[col]=checkDig1[col+row]=checkDig2[row-col+n]=false;
}
}
}
}有效的数独
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] row,col;
boolean[][][] grid;
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
row=new boolean[9][10];
col=new boolean[9][10];
grid=new boolean[3][3][10];
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
if(board[i][j]!='.'){
int num=board[i][j]-'0';
if(row[i][num]==true || col[j][num]==true || grid[i/3][j/3][num]==true){
return false;
}
row[i][num]=col[j][num]=grid[i/3][j/3][num]=true;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}解数独


java
class Solution {
boolean[][] row;
boolean[][] col;
boolean[][][] grid;
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
row=new boolean[9][10];
col=new boolean[9][10];
grid=new boolean[3][3][10];
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
if(board[i][j]!='.'){
int num=board[i][j]-'0';
row[i][num]=true;
col[j][num]=true;
grid[i/3][j/3][num]=true;
}
}
}
dfs(board);
}
public boolean dfs(char[][] board){
for(int i=0;i<9;i++){
for(int j=0;j<9;j++){
if(board[i][j]=='.'){
for(int n=1;n<=9;n++){
if(row[i][n]==false && col[j][n]==false && grid[i/3][j/3][n]==false){
board[i][j]=(char)('0'+n);
row[i][n]=col[j][n]=grid[i/3][j/3][n]=true;
if(dfs(board)==true){
return true;
}
board[i][j]='.';
row[i][n]=col[j][n]=grid[i/3][j/3][n]=false;
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}单词搜索
java
class Solution {
int m,n;
char[] word;
boolean[][] check;
int[] dx={0,0,-1,1};
int[] dy={-1,1,0,0};
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word1) {
word=word1.toCharArray();
m=board.length;
n=board[0].length;
check=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(board[i][j]==word[0]){
check[i][j]=true;
if(dfs(board,i,j,1)){
return true;
}
check[i][j]=false;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char[][] board,int i,int j,int pos){
if(pos==word.length){
return true;
}
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && check[x][y]==false && board[x][y]==word[pos]){
check[x][y]=true;
if(dfs(board,x,y,pos+1)){
return true;
}
check[x][y]=false;
}
}
return false;
}
}黄金矿工

解法一
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] check;
int m,n;
int[] dx={1,-1,0,0};
int[] dy={0,0,1,-1};
int ret;
int count;
public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {
m=grid.length;
n=grid[0].length;
count=0;
check=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]!=0){
check[i][j]=true;
ret=Math.max(ret,dfs(grid,i,j,0));
check[i][j]=false;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
public int dfs(int[][] grid,int i,int j,int sum){
sum+=grid[i][j];
int max=sum;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if( x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n &&grid[x][y]!=0 && check[x][y]==false){
check[i][j]=true;
max=Math.max(max,dfs(grid,x,y,sum));
check[i][j]=false;
}
}
return max;
}
}解法二
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] check;
int m,n;
int[] dx={1,-1,0,0};
int[] dy={0,0,1,-1};
int ret;
public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {
m=grid.length;
n=grid[0].length;
check=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]!=0){
check[i][j]=true;
dfs(grid,i,j,grid[i][j]);
check[i][j]=false;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[][] grid,int i,int j,int sum){
ret=Math.max(ret,sum);
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if( x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && grid[x][y]!=0 && check[x][y]==false){
check[x][y]=true;
dfs(grid,x,y,sum+grid[x][y]);
check[x][y]=false;
}
}
}
}不同路径Ⅲ

直接进行暴搜,先统计0的数量,然后当step走过的步数和0的数量相等的时候,则算一条路径
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] check;
int[] dx={0,0,-1,1};
int[] dy={1,-1,0,0};
int m,n;
int path;
int count0;
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
m=grid.length;
n=grid[0].length;
check=new boolean[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==0){
count0++;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
check[i][j]=true;
dfs(grid,i,j,0);
}
}
}
return path;
}
public void dfs(int[][] grid,int i,int j,int step){
if(grid[i][j]==2){
if(step==count0+1){
path++;
}
return;
}
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && grid[x][y]!=-1 && check[x][y]==false){
check[x][y]=true;
dfs(grid,x,y,step+1);
check[x][y]=false;
}
}
}
}