损失函数系列之focal loss
Focal Loss在论文《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection 》中被提出,主要用于解决样本数据中的类别不平衡 问题。它是在标准交叉熵损失基础上的改进,通过动态调整易分类样本的权重,使模型在训练过程中更加关注难分类样本。
传统的做法:
重采样:采样少数类别样本,欠采样多数类别样本
调整类别权重:在损失函数中,给少数类别比较大的权重,给多样本较小的权重,让模型更加关注少数类别的样本。比如BCE
C E ( p i ) = − α t l o g ( p t ) CE(p_i)=-\alpha_tlog(p_t) CE(pi)=−αtlog(pt)
BCE解决了正负样本不平衡问题,但是没有区分易分还是难分样本,当容易区分的样本里有大量负样本,整个训练会围绕易区分的负样本进行,对正样本的效果很差。
Focal loss核心思想是:降低大量易分类样本的权重,使模型更加关注那些难以正确分类的样本。这在目标检测等任务中特别有效,在这些任务中,背景区域(负样本)通常远远多于前景目标(正样本),比例可能达到1000:1。
根据样本分类的难易程度赋予样本不同的权重
F L ( p i ) = − α ( 1 − p t ) γ log ( p t ) FL(p_i)=-\alpha(1-p_t)^\gamma\log(p_t) FL(pi)=−α(1−pt)γlog(pt)
代码
python
logits = preds
#---------------------------
preds = preds.view(-1, preds.size(-1)) #[B, C]
preds_logsoft = F.log_softmax(preds, dim=1) # log_softmax
preds_softmax = torch.exp(preds_logsoft) # softmax
#out[i][j] = input[i][index[i][j]] # if dim == 1
preds_softmax = preds_softmax.gather(1, labels.view(-1, 1))
preds_logsoft = preds_logsoft.gather(1, labels.view(-1, 1))
# 矩阵惩罚 a*b,
loss = -torch.mul(torch.pow((1 - preds_softmax), self.gamma),
preds_logsoft) # torch.pow((1-preds_softmax), self.gamma)
loss = self.alpha * loss
if self.size_average:
loss = loss.mean()
else:
loss = loss.sum()
return logits, loss
Dice loss
常用于图像语义分割任务,特别适用于前景和背景分割,其来源于dice系数,dice系数是用于衡量两个集合相似度的一个指标。
d i c e = 2 ∣ X ∩ Y ∣ ∣ X ∣ + ∣ Y ∣ dice=\frac{2|X \cap Y|}{|X|+|Y|} dice=∣X∣+∣Y∣2∣X∩Y∣
L d i c e = 1 − 2 ∣ X ∩ Y ∣ ∣ X ∣ + ∣ Y ∣ L_{dice}=1-\frac{2|X \cap Y|}{|X|+|Y|} Ldice=1−∣X∣+∣Y∣2∣X∩Y∣
Dice loss更加关注预测结果与真实结果的重合程度,而不是单纯的分类准确度,可以很好地解决样本不平衡问题。
python
import torch
def dice_coefficient(y_true, y_pred, smooth=1e-5):
"""
Dice = (2*|X & Y|)/( |X|+ |Y| )
= 2*sum(A*B)/(sum(A^2)+sum(B^2))
ref: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.04797v1.pdf
"""
y_true = y_true.view(-1)
y_pred = y_pred.view(-1)
intersection = (y_true * y_pred).sum()
return (2. * intersection + smooth) / (y_true.pow(2).sum() + y_pred.pow(2).sum() + smooth)
def dice_loss(y_true, y_pred):
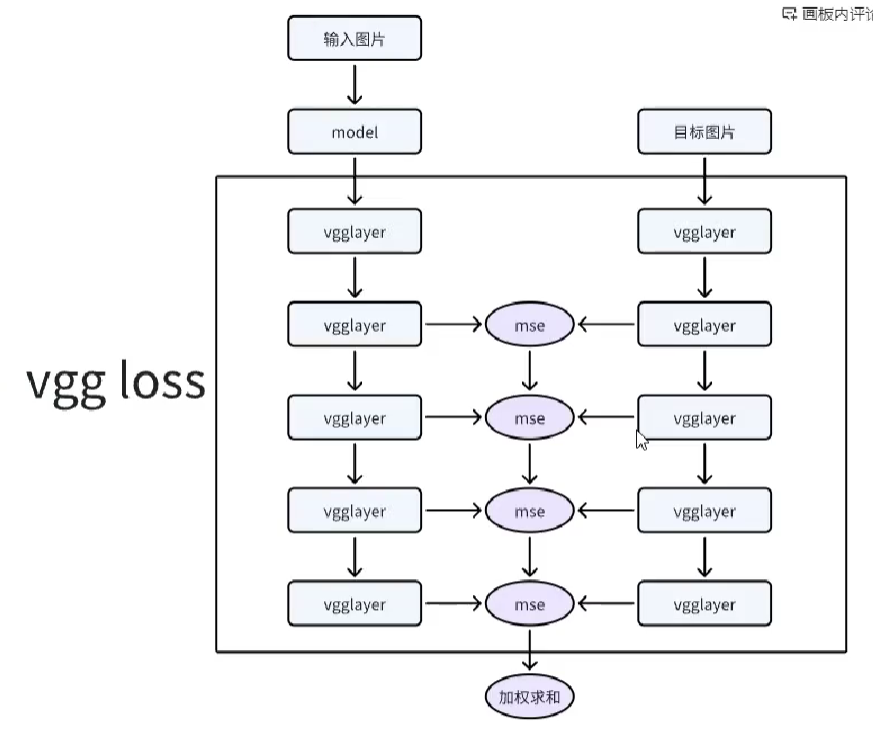
return 1 - dice_coefficient(y_true, y_pred)vgg loss
是内容损失的一种,衡量两个图像之间的感知相似性,更接近人类感知。vgg 是在特征方面计算的相似性而不是像素方面
可用于图像超分,风格转换等领域。
python
```python
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Vggloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, model) -> None:
super(Vggloss, self).__init__()
self.features = model.features
self.select_layers = ['3','8','13','22','31'] # 分别为五个大模块中的第二个relu层
self.weight = [1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0]
def output_features(self, x):
output = []
for name, module in self.features.named_children():
x = module(x)
if name in self.select_layers:
output.append(x)
return output
def forward(self, output, gt):
loss = []
output_features = self.output_features(output)
gt_features = self.output_features(gt)
for output_feature, gt_feature, weight in zip(output_features, gt_features, self.weight):
loss.append(F.mse_loss(output_feature, gt_feature)*weight)
return sum(loss)/len(loss)