


专栏:算法的魔法世界
个人主页:手握风云
目录
[1.1. 组合总和](#1.1. 组合总和)
[1.2. 字母大小写全排列](#1.2. 字母大小写全排列)
[1.3. 优美的排列](#1.3. 优美的排列)
[1.4. N 皇后](#1.4. N 皇后)
一、例题讲解
1.1. 组合总和

给定无重复元素的整数数组candidates和目标整数target,找出数组中所有能使数字和等于target的不同组合,以列表形式返回(组合顺序可任意)。candidates中的同一个数字可无限制重复选取,并且两种组合若至少一个数字的选取数量不同,则视为不同组合。
解法一:根据决策树,我们可以看出,如果我们选了某个位置的数字,那么不用考虑前面位置的数字,或者如果在搜索过程中,如果组合总和大于 target,就要实行剪枝。递归方法只需要关心上一个位置选了什么,接下来就从这一个位置开始枚举。我们依然需要用到全局变量 path 来记录路径和, ret 作为最后的返回值。当路径和 >= 目标值时,记录结果并返回。
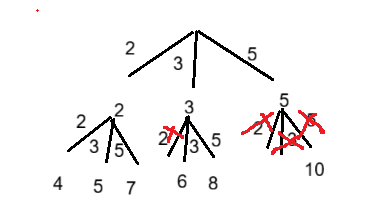
完整代码实现:
java
class Solution {
int aim = 0;
List<Integer> path;
List<List<Integer>> ret;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
aim = target;
path = new ArrayList<>();
ret = new ArrayList<>();
// 深搜,从索引0开始,当前和为0
dfs(candidates, 0, 0);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int pos, int sum) {
// 如果当前和等于目标和,将当前路径添加到结果列表中
if (sum == aim) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
// 如果当前和大于目标和或者已经遍历完所有候选数字,则返回
if (sum > aim || pos >= candidates.length) {
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
path.add(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates, i, sum + candidates[i]);
// 回溯,移除最后添加的数字
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}解法二:这次的思路是从给定的候选数字数组中找出所有和为目标值的组合,其中每个数字可以被重复使用。对于每个数字,考虑使用它0次、1次、2次...直到总和超过目标值;当总和等于目标值时,将当前组合加入结果集。回溯时,需要移除当前添加的所有当前数字,以便尝试其他组合。
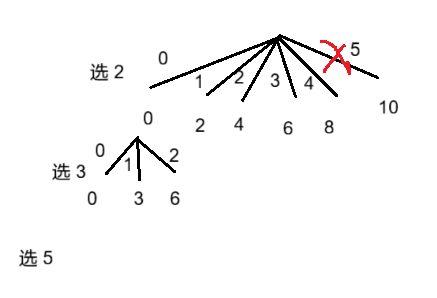
完整代码实现:
java
class Solution {
int aim = 0;
List<Integer> path;
List<List<Integer>> ret;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
aim = target;
path = new ArrayList<>();
ret = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(candidates, 0, 0);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int[] candidates, int pos, int sum) {
if (sum == aim) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if (sum > aim || pos == candidates.length) {
return;
}
// 遍历当前数字的可能使用次数
for (int k = 0; k * candidates[pos] + sum <= aim; k++) {
// 如果不是第一次使用当前数字,则将其加入路径
if (k != 0) {
path.add(candidates[pos]);
}
dfs(candidates, pos + 1, sum + k * candidates[pos]);
}
for (int k = 1; k * candidates[pos] + sum <= aim; k++) {
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}1.2. 字母大小写全排列

给定字符串 s,对字符串中的每个字母(数字不处理)进行「大小写转换」操作(可转也可保留原大小写),生成所有可能得到的不同字符串,最终返回这些字符串的集合(集合内字符串顺序无要求)。
对字符串 s 进行遍历,当遇到的是字母字符时,需要进行大小写转化,并添加到全局变量 StringBuffer letter 中,如果是数字,直接添加。当遍历到字符串的最后一个字符时,递归结束,此时删除最后一个字符进行回溯。
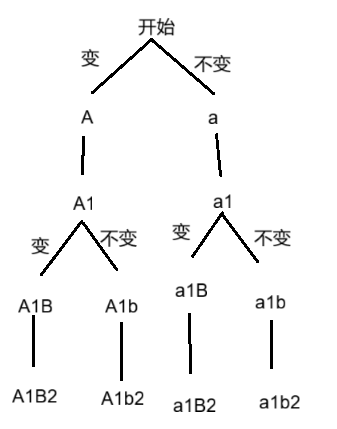
完整代码实现:
java
class Solution {
StringBuffer letter;
List<String> ret;
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
letter = new StringBuffer();
ret = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(s, 0);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(String s, int pos) {
// 到达字符串末尾,将当前组合添加到结果列表中
if (pos == s.length()) {
ret.add(letter.toString());
return;
}
char ch = s.charAt(pos);
letter.append(ch);
// 递归处理下一个位置
dfs(s, pos + 1);
// 回溯,删除最后一个字符
letter.deleteCharAt(letter.length() - 1);
// 如果当前字符是字母,则尝试转换大小写
if (Character.isLetter(ch)) {
char tmp = change(ch);
letter.append(tmp);
dfs(s, pos + 1);
// 回溯,删除最后一个字符
letter.deleteCharAt(letter.length() - 1);
}
}
private char change(char ch) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(ch)) {
// 大写转小写
ch = Character.toLowerCase(ch);
} else {
// 小写转大写
ch = Character.toUpperCase(ch);
}
return ch;
}
}1.3. 优美的排列

给定整数 n,计算并返回可以构造出的优美排列的总数量 。数组 perm 需满足下述 两个条件之一,即可称为 "优美的排列":
- 条件 1:数组第 i 位的元素
perm[i]能被下标i整除(perm[i] % i == 0); - 条件 2:下标
i能被数组第 i 位的元素perm[i]整除(i % perm[i] == 0)。
根据决策树,依次从1------n选取数字作为第一个位置,每个元素只能选一次,如果该数字在某个索引位置能满足上面两个条件时,则继续向下递归,当尝试完所有数字后,说明已经找到一个优美的排列。
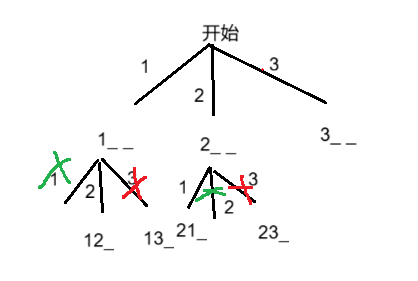
完整代码实现:
java
class Solution {
boolean[] check; // 标记数组,用于标记某个数是否被使用过
int ret;
public int countArrangement(int n) {
check = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(1, n);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int pos, int n) {
// 递归终止条件,当pos等于n+1时,说明已经找到了一种排列方式
if (pos == n + 1) {
ret++;
return;
}
// 遍历1到n的所有数,尝试将每个数放在pos位置
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!check[i] && (i % pos == 0 || pos % i == 0)) {
// 如果i没有被使用过,并且i和pos互为因子,则将i放在pos位置
check[i] = true;
dfs(pos + 1, n);
// 回溯,将i从pos位置移除,并标记为未使用过
check[i] = false;
}
}
}
}1.4. N 皇后
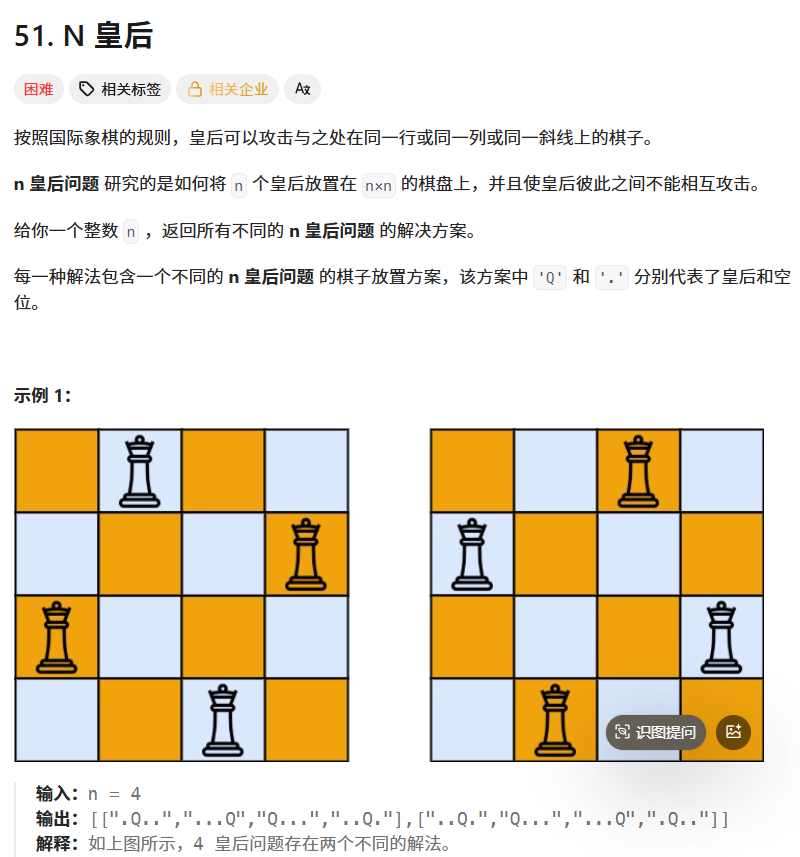
在 n×n 的棋盘上放置 n 个皇后,确保皇后之间无法相互攻击(遵循国际象棋皇后规则:不能处于同一行、同一列,或同一 45°/135° 斜线上)。返回所有不同的合法解决方案,每个方案以列表形式呈现 ------ 列表中的每个元素是字符串,代表棋盘的一行,其中 'Q' 表示皇后,'.' 表示空位。
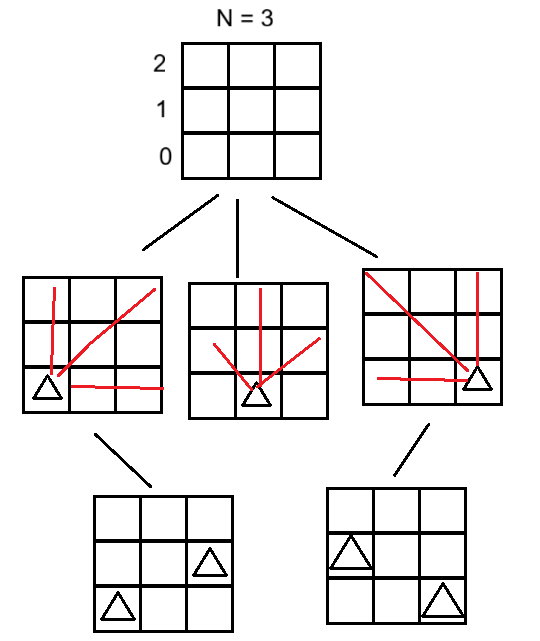
本题的决策树,我们需要一个格子一个格子去考虑剪枝的策略。当我们在某一行的一个格子上放上皇后之后,其他的格子能不能放皇后,我们可以使用布尔类型的数组数组 col[n] 标记某一列是否已有皇后。若 col[j] = true,说明第 j 列已有皇后,当前位置 (i,j) 不能放。对于对角线上的判断:主对角线的数学特征是 "行 - 列的差值固定"(如 y−x=b)。为了避免负数,用 i - j + n(n 是棋盘规模)作为数组索引。若 digi1[i - j + n] = true,说明同一主对角线已有皇后。副对角线的判断:副对角线的数学特征是 "行 + 列的和固定"(如 x+y=b)。用 i + j 作为数组索引。若 digi2[i + j] = true,说明同一副对角线已有皇后。
图中决策树的每个节点,代表 "在某一行放置皇后的位置",如果每个分支因某一列或者对角线冲突直接剪枝;最终能走到叶子节点时,就是一个合法的 "N 皇后布局"。
完整代码实现:
java
class Solution {
boolean[] checkCol, checkDg1, checkDg2;
List<List<String>> ret;
char[][] path;
int m;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
m = n;
checkCol = new boolean[n];
checkDg1 = new boolean[n * 2];
checkDg2 = new boolean[n * 2];
ret = new ArrayList<>();
path = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(path[i], '.');
}
dfs(0);
return ret;
}
private void dfs(int row) {
// 递归终止条件:如果已经处理完所有行,将当前解添加到结果列表中
if (row == m) {
List<String> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
// 将当前路径中的棋盘状态转换为为字符串列表
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
tmp.add(new String(path[i]));
}
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
}
// 遍历当前行的所有列
for (int col = 0; col < m; col++) {
// 两个对角线是否有皇后
if (!checkCol[col] && !checkDg1[row - col + m] && !checkDg2[row + col]) {
// 放置皇后
path[row][col] = 'Q';
// 标记该列和对角线已被占用
checkCol[col] = checkDg1[row - col + m] = checkDg2[row + col] = true;
dfs(row + 1);
// 回溯,移除皇后
path[row][col] = '.';
checkCol[col] = checkDg1[row - col + m] = checkDg2[row + col] = false;
}
}
}
}