建议使用小熊猫C++
http://royqh.net/redpandacpp/download/
实验 一 类与对象(2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握类的定义和对象的声明;
2.掌握具有不同访问属性的成员的访问方式;
3.掌握构造函数和析构函数的编写方法;
4.掌握类的组合的使用方法。
二、实验内容
1.设计一个 Tree (树)类,有成员 ages (树龄),成员函数 grow(int years) ages 加上years,age( )显示 tree 对象的 ages 的值。
2.设计一个用于人事管理的People类。考虑到通用性,可以只抽象出所有人员都具有的属性:num(编号),name(姓名) ,birth(生日),id(身份证号)等等。其中"生日"定义为一个"日期"类内嵌子对象。用成员函数实现对人员的信息录入和显示。
三、实验指导
题目1
-
定义Tree类的框架
-
在Tree类中加入一个数据成员ages,类型为整型。【访问权限同学们自己思考设计】
-
在Tree类中加入成员函数:【访问权限同学们自己思考设计】
①Tree类的默认构造函数:实现为Tree类对象的ages成员初始化
②grow(int years) :为某个Tree类的对象的ages增加years年
③age( ):显示Tree类对象的ages
4.编写main( )函数,在其中建立两个Tree类的对象,分别测试该类中的所有成员函数。
题目2
- 编写Date(日期)类,Date类中包括3个数据成员(year,mon,day)以及如下成员函数:
①构造函数【同学们自己设计构造函数的个数和形式】
②复制构造函数
③修改日期的函数
④显示日期的函数
⑤析构函数
- 编写People类,People类中包括4个数据成员(num, name, id, birth),其中birth为Date类的对象;以及如下成员函数:
①构造函数【同学们自己设计构造函数的个数和形式】
②复制构造函数
③信息录入函数:实现对某个People类对象的信息录入
④信息显示函数:实现对某个People类对象的信息显示
⑤析构函数
- 编写main( )函数,在其中建立两个Date类的对象和两个People类的对象,分别测试这两类中的所有成员函数。
四 、考核标准
本实验总计15分。
1、题目1总计5分
-
类的设计与编写 (3分)
-
程序功能,运行结果的正确性(2分)
2、题目2总计10分
-
友好的用户界面 (2分)
-
Date类的编写 (2分)
-
People类的编写,要求实现类的组合机制 (4分)
-
程序功能,运行结果的正确性 (2分)
五、实验代码
题目1
Tree.cpp
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//------Tree------
class Tree {
private:
int ages;
public:
Tree();
Tree(int age);
int grow(int years);
void age();
};
//默认构造函数
Tree::Tree() {
ages = 0;
}
//有参构造函数
Tree::Tree(int age) {
ages = age;
}
//生长
int Tree::grow(int years) {
ages = ages + years;
return ages;
}
//显示
void Tree::age() {
cout << "树龄:" << ages << endl;
}
int main() {
int ages, years;
cout << "输入树龄和生长年限:" << endl;
cin >> ages >> years;
Tree tree(ages);
tree.age();
cout << "生长后的";
tree.grow(years);
tree.age();
return 0;
}题目2
People.cpp
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
// ------Date------
class Date {
private:
int year;
int month;
int day;
public:
Date();
Date(int year, int month, int day);
Date(Date& date1);
void changeDate(Date d);
string showDate();
~Date();
};
//空参
Date::Date() {
year = 2022;
month = 2;
day = 22;
// cout<<"----默认构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//构造函数
Date::Date(int years, int months, int days) {
year = years;
month = months;
day = days;
// cout<<"----有参构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//复制构造函数 -->用已有的对象初始化新生成的对象
Date::Date(Date& d) {
year = d.year;
month = d.month;
day = d.day;
// cout << "----复制构造函数被调用" << endl;
}
//改变日期
void Date::changeDate(Date date) {
year = date.year;
month = date.month;
day = date.day;
}
//显示日期
string Date::showDate() {
return to_string(year) + "年" + to_string(month) + "月" + to_string(day) + "日";
}
//析构函数
Date ::~Date() {
// cout<<"----析构函数被调用"<<endl;
}
// ------People类------
class People {
private:
int num;
string name;
int id;
Date birth;
public:
People();
People(int nums, string names, int ids, Date births);
People(People& p1);
void writePeople(People p);
void showPeople();
~People();
};
//空参
People::People() {
// cout<<"****默认构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//构造函数
People::People(int nums, string names, int ids, Date births) {
num = nums;
name = names;
id = ids;
birth = births;
// cout<<"****有参构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//复制构造函数
People::People(People& p) {
num = p.num;
name = p.name;
id = p.id;
birth = p.birth;
// cout<<"****复制构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//录入信息
void People::writePeople(People p) {
num = p.num;
name = p.name;
id = p.id;
birth = p.birth;
}
//显示信息
void People::showPeople() {
cout << "序号:" << num << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << name << endl;
cout << "身份证号:" << id << endl;
cout << "生日:" << birth.showDate() << endl;
}
//析构函数
People::~People() {
// cout << "****析构函数被调用" << endl;
}
int main() {
Date date;
string str = date.showDate();
cout << str << endl;
//---------------------------------
Date date0(2011, 1, 1);
date0.changeDate(date0);
string str1 = date0.showDate();
cout << str1 << endl;
cout << " " << endl;
Date date1(2001, 1, 2);
People people1(1, "张三", 20215131, date1);
People p1;
p1.writePeople(people1);
p1.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
Date date2(2001, 1, 2);
People people2(2, "李四", 20215837, date2);
People p2;
p2.writePeople(people2);
p2.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
Date date3(2001, 1, 2);
People people3(3, "王五", 20215639, date3);
People p3;
p3.writePeople(people3);
p3.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
return 0;
}实验 二 C++程序的结构 (2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握程序运行中变量的作用域、生存期和可见性;
2.掌握类的静态成员和友元函数的使用;
3.掌握使用工程和多文件结构编写程序的方法。
二、实验内容
1.设计并编写Songer(歌手)类,使用静态数据成员和静态成员函数实现统计当前歌手的数量,使用友元函数实现任意两个歌手之间的Pk。
2.将实验一中第2题的内容使用工程和多文件结构实现。
三、实验指导
题目1
- Songer类包含如下数据成员:
①name (姓名)
②fans_count (粉丝数)
③count (当前歌手人数) 【静态数据成员】
- 在Songer类中加入成员函数:
①构造函数:初始化name和fans_count,并对count做适当操作
②复制构造函数:【同学们自己设计并编写】
③Set函数:输入fans_count的值(即修改粉丝数)
④析构函数 【同学们自己设计并编写】
⑤ShowCount函数:显示当前歌手的数量。【静态成员函数】
- 编写Songer类的友元函数:Pk(Songer &s1,Songer &s2),实现比较两个Songer类对象的fans_count并输出结果。
【例如:如果s1的姓名是张三,有100个粉丝;s2的姓名是李四,有120个粉丝,输出李四战胜张三】
- 设计编写main( )函数,在其中建立三个Songer类的对象,测试该类中所有成员函数和友元函数。
注:学有余力的同学可以广开脑洞,在完成题目要求基础上设计并编写合理功能。
题目2:【根据课堂学习,熟练掌握建立工程以及使用多文件编写程序的方法】
四 、考核标准
本实验总计10分。
1、题目1总计5分
-
类的设计与编写 (2分)
-
静态成员以及友元函数的编写(2分)
3.程序功能,运行结果的正确性(1分)
2、题目2总计5分
-
程序结构框架的合理性以及操作熟练性 (3分)
-
程序功能,运行结果的正确性 (2分)
五、实验代码
题目1
Songer.cpp
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Songer {
friend void PK(Songer& s1, Songer& s2);
private:
string name; //姓名
int fans_count; //粉丝数
static int count; //当前歌手数
public:
Songer();
Songer(string names, int fans_counts);
Songer(Songer& r);
void setfans_cout(int fans_counts);
~Songer();
static void ShowCount();
void show();
};
int Songer::count = 0;
Songer::Songer() {
name = "无";
fans_count = 0;
count++;
}
Songer::Songer(string names, int fans_counts) {
name = names;
fans_count = fans_counts;
count++;
}
Songer::~Songer() {
count--;
}
Songer::Songer(Songer& r) {
name = r.name;
fans_count = r.fans_count;
count++;
}
void Songer::setfans_cout(int fans_counts) {
fans_count = fans_counts;
}
void Songer::ShowCount() {
cout << "当前歌手的数量:" << Songer::count << endl;
}
void Songer::show() {
cout << "歌手姓名:" << name << ","
<< "\t粉丝数量:" << fans_count << "\t" << endl;
}
//友元
void PK(Songer& s1, Songer& s2) {
if (s1.fans_count != s2.fans_count) {
if (s1.fans_count > s2.fans_count) {
cout << s1.name << "战胜" << s2.name << endl;
} else {
cout << s2.name << "战胜" << s1.name << endl;
}
} else {
cout << s1.name << "与" << s2.name << "打成平手" << endl;
}
}
int main() {
Songer s1;
s1.show();
s1.ShowCount();
Songer s2("张三", 100);
s2.setfans_cout(90);
s2.show();
s2.ShowCount();
Songer s3("李四", 120);
PK(s2, s3);
return 0;
}题目2
Date.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
private:
int year;
int month;
int day;
public:
Date();
Date(int year, int month, int day);
Date(Date& date1);
void changeDate(Date d);
string showDate();
~Date();
};Date.cpp
cpp
#include "Date.h"
Date::Date() {
year = 2022;
month = 2;
day = 22;
// cout<<"----默认构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//构造函数
Date::Date(int years, int months, int days) {
year = years;
month = months;
day = days;
// cout<<"----有参构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//复制构造函数 -->用已有的对象初始化新生成的对象
Date::Date(Date& d) {
year = d.year;
month = d.month;
day = d.day;
// cout << "----复制构造函数被调用" << endl;
}
//改变日期
void Date::changeDate(Date date) {
year = date.year;
month = date.month;
day = date.day;
}
//显示日期
string Date::showDate() {
return to_string(year) + "年" + to_string(month) + "月" + to_string(day) + "日";
}
//析构函数
Date ::~Date() {
// cout<<"----析构函数被调用"<<endl;
}People.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include"Date.h"
using namespace std;
class People
{
private:
int num;
string name;
int id;
Date birth;
public:
People();
People(int nums, string names, int ids, Date births);
People(People& p1);
void writePeople(People p);
void showPeople();
~People();
};People.cpp
cpp
#include "People.h"
#include "Date.h"
//空参
People::People() {
// cout<<"****默认构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//构造函数
People::People(int nums, string names, int ids, Date births) {
num = nums;
name = names;
id = ids;
birth = births;
// cout<<"****有参构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//复制构造函数
People::People(People& p) {
num = p.num;
name = p.name;
id = p.id;
birth = p.birth;
// cout<<"****复制构造函数被调用"<<endl;
}
//录入信息
void People::writePeople(People p) {
num = p.num;
name = p.name;
id = p.id;
birth = p.birth;
}
//显示信息
void People::showPeople() {
cout << "序号:" << num << endl;
cout << "姓名:" << name << endl;
cout << "身份证号:" << id << endl;
cout << "生日:" << birth.showDate() << endl;
}
//析构函数
People::~People() {
// cout << "****析构函数被调用" << endl;
}main.cpp
cpp
#include"Date.h"
#include"People.h"
int main() {
Date date;
string str = date.showDate();
cout << str << endl;
//---------------------------------
Date date0(2011, 1, 1);
date0.changeDate(date0);
string str1 = date0.showDate();
cout << str1 << endl;
cout << " " << endl;
Date date1(2001, 1, 2);
People people1(1, "张三", 20215131, date1);
People p1;
p1.writePeople(people1);
p1.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
Date date2(2001, 1, 2);
People people2(2, "李四", 20215837, date2);
People p2;
p2.writePeople(people2);
p2.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
Date date3(2001, 1, 2);
People people3(3, "王五", 20215639, date3);
People p3;
p3.writePeople(people3);
p3.showPeople();
cout << " " << endl;
return 0;
}实验 三 C++中的 动态内存分配 (2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握使用new运算符创建对象的方法;
2.掌握使用delete运算符释放对象内存的方法;
3.掌握使用面向对象思想实现链表类并对链表进行操作的方法。
二、实验内容
1.设计并编写链表类,能够实现链表的初始化(建立)、输出释放等功能。
三、实验指导
- 链表由若干个结点【Node类对象】构成(每个结点有data域和next域,假设每个结点的data域是一个整数,并且没有重复元素),那么某个链表的逻辑示意图如下:
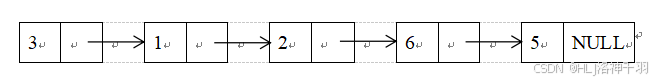
图3-1 链表逻辑结构示意图
下面给出链表中结点类的定义:
class Node //结点类
{ public:
Node( ); //构造函数
void SetNext(Node *p); //设置后继结点
int Getd(); //得到当前结点的数据值
Node *GetNext( ); //得到后继结点的地址
~Node( ); //析构函数
private:
int data;
Node *next;
};
Node::Node( )
{ cin>>data; next=NULL;}
void Node::SetNext(Node *p)
{ next=p;}
int Node::Getd( )
{ return data;}
Node* Node::GetNext( )
{ return next;}
Node::~Node( )
{ cout<<data<<" 被析构!"<<endl;}
上面的Node类代码同学们可以直接使用,下面(2)、(3)为必做内容
- 利用Node类,设计并编写Link(链表)类,类中包含:
数据成员
Head //头指针
Num //链表中结点个数 【即链表的长度】
函数成员:
Link( ) //初始化(建立)空链表
Link(int n) //初始化(建立)一个具有n个结点的链表
【在建立链表的过程中按值从小到大排序】
LinkPrint( ) //输出链表中所有结点data域的值
GetHead( ) //返回链表的头指针
~Link( ) //释放链表中所有结点的内存空间
- 编写main( )函数,测试Link类中所有函数
【选作内容:编写Link类的如下成员函数,根据实际完成情况有加分】
Link_Insert(int x) //在链表中插入值为x的结点
Link_Delete( int x) //删除链表中值为x的结点
Link_Connect(Link &p) //两个链表的连接
【即将p链表连接在当前链表的尾部】
Link( Link &p) //使用深复制编写复制构造函数
自己设计Node类中data的类型,使本题实现一个具体的应用
四 、考核标准
本实验总计10分。
-
Link类的框架 (2分)
-
Link类成员函数的实现(5分)
-
main()函数编写的合理性及功能演示(3分)
五、实验代码
Node.h
cpp
#pragma once
class Node
{
private:
int data;
Node* next;
public:
Node();//构造函数
Node(int data);
void setNext(Node* p);//设置后继节点
int getd();//得到当前节点的的数据值
Node* getNext();//得到后继结点的地址
void setd(int x);
~Node();//析构函数
};Node.cpp
cpp
#include "Node.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
Node::Node() : next(NULL) {
cin >> data;
}
Node::Node(int data) : data(data), next(NULL) {}
void Node::setNext(Node* p) {
next = p;
}
int Node::getd() {
return data;
}
Node*Node::getNext() {
return next;
}
void Node::setd(int x) {
data = x;
}
Node::~Node() {
}Link.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"Node.h"
using namespace std;
class Link
{
private:
Node *head;
int num;
public:
Link(); //初始化(建立)空链表
Link(int n); //初始化(建立)一个具有n个结点的链表,在建立链表的过程中按值从小到大排序
void LinkPrint(); //输出链表中所有结点data域的值
Node *GetHead(); //返回链表的头指针
~Link(); //释放链表中所有结点的内存空间
void Link_Insert(int x); //在链表中插入值为x的结点
void Link_Delete(int x); //删除链表中值为x的结点
void Link_Connect(Link& p); //两个链表的连接,即将p链表连接在当前链表的尾部
Link(Link &p); //使用深复制编写复制构造函数
};Link.cpp
cpp
#include "Link.h"
#include"Node.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//初始化(建立)空链表
Link::Link() {
head = NULL;
num = 0;
}
//初始化(建立)一个具有n个结点的链表
Link::Link(int n) {
head = NULL;
num = 0;
if (n <= 0) return;
int x;
cin >> x;
head = new Node(x);
num = 1;
Node* p = head;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cin >> x;
p->setNext(new Node(x));
p = p->getNext();
num++;
}
}
//输出链表中所有结点data域的值
void Link::LinkPrint() {
Node* p = head;
if (head != NULL) {
while (p->getNext() != NULL) {
cout << p->getd() << " ";
p = p->getNext();
}
cout << p->getd() << " " << endl;
} else {
cout << "链表中没有数据" << endl;
}
}
//返回链表的头指针
Node *Link::GetHead() {
return head;
}
//释放链表中所有结点的内存空间
Link::~Link() {
Node* current = head;
while (current != NULL) {
Node* next = current->getNext();
delete current;
current = next;
}
head = NULL;
num = 0;
}
//在链表中插入值为x的结点
void Link::Link_Insert(int x) {
Node* temp = new Node(x);
num++;
if (head == NULL) {
head = temp;
} else {
if (x < head->getd()) {
temp->setNext(head);
head = temp;
} else {
Node* p = head;
while (p->getNext() != NULL && p->getNext()->getd() < x) {
p = p->getNext();
}
temp->setNext(p->getNext());
p->setNext(temp);
}
}
}
//删除链表中值为x的结点
void Link::Link_Delete(int x) {
if (head->getd() == x) {
Node* temp = head;
head = head->getNext();
delete temp;
} else {
Node* p = head;
while (p->getNext() != NULL && p->getNext()->getd() != x) {
p = p->getNext();
}
if (p->getNext() != NULL) {
Node* temp = p->getNext();
p->setNext(p->getNext()->getNext());
delete temp;
} else {
cout << "没有数据" << endl;
}
}
}
//两个链表的连接,即将p链表连接在当前链表的尾部
void Link::Link_Connect(Link& p) {
if (p.head == NULL) return;
if (head == NULL) {
head = new Node(p.head->getd());
Node* p1 = head;
Node* p2 = p.head->getNext();
while (p2 != NULL) {
p1->setNext(new Node(p2->getd()));
p1 = p1->getNext();
p2 = p2->getNext();
}
} else {
Node* p1 = head;
while (p1->getNext() != NULL) {
p1 = p1->getNext();
}
Node* p2 = p.head;
while (p2 != NULL) {
p1->setNext(new Node(p2->getd()));
p1 = p1->getNext();
p2 = p2->getNext();
}
}
num += p.num;
}
//使用深复制编写复制构造函数
Link::Link(Link& p) {
head = NULL;
num = 0;
Node* p1 = p.head;
while (p1 != NULL) {
Link_Insert(p1->getd());
p1 = p1->getNext();
}
}main.cpp
cpp
#include"Node.h"
#include"Link.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n1,n2,n3;
cout << "请输入链表1的初始长度:" << endl;
cin >> n1;
cout << "请往链表中输入数据:" << endl;
Link link1(n1);
cout << "显示链表1:" << endl;
link1.LinkPrint();
cout << "请输入插入的数据:";
cin >> n2;
link1.Link_Insert(n2);
cout << " 插入后链表为:";
link1.LinkPrint();
link1.Link_Delete(n2);
cout << "删除后:" << endl;
link1.LinkPrint();
cout << "请输入链表2的初始长度:" << endl;
cin >> n3;
cout << "请往链表中输入数据:" << endl;
Link link2(n3);
cout << "显示链表2:" << endl;
link2.LinkPrint();
link1.Link_Connect(link2);
cout << "连接后链表为:" << endl;
link1.LinkPrint();
return 0;
}实验四 继承和派生(2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握利用继承和派生机制定义并实现派生类的方法;
2.掌握派生类构造函数的编写方法;
3、掌握测试具有继承结构的类家族中各类对象的方法。
二、实验内容
1.设计并编写Person(人员)类、Student(学生)类和Graduate(研究生)类,并测试这些类。
三、实验指导
1、类之间的和关系:
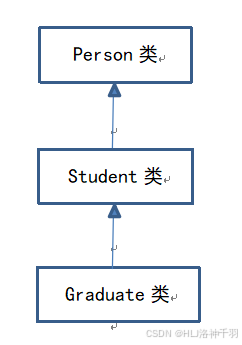
图4-1 各个类继承结构示意图
2、具体内容
- 设计并编写Person类,包括:
数据成员
① name //姓名
② sex //性别
③ age //年龄
函数成员
①默认(无参)构造函数
②有参构造函数
③复制构造函数
④设置信息函数
⑤显示信息函数
- Person类派生出Student类,Student类中添加:
数据成员
① Num //学号
② School //学校
③ Major //专业
函数成员
①默认(无参)构造函数
②有参构造函数
③复制构造函数 【③为选做】
④设置信息函数
⑤显示信息函数
- Student类派生出Graduate类,Graduate类中添加:
数据成员
① Research_Direction //研究方向
函数成员
①默认(无参)构造函数
②有参构造函数
③复制构造函数 【③为选做】
④设置信息函数
⑤显示信息函数
- 设计并编写main函数,测试编写的类。
四 、考核标准
本实验总计10分。
-
Person类的设计与实现 (2分)
-
Student类的设计与实现 (3分)
-
Graduate类的设计与实现 (3分)
-
main()函数编写的合理性及功能演示(2分)
五、实验代码
Person.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Person {
private:
string name;//姓名
string sex;//性别
int age;//年龄
public:
Person();
Person(string name, string sex, int age);
Person(Person& p);
string getName();
void setName(string name);
string getSex();
void setSex(string sex);
int getAge();
void setAge(int age);
void setPerson();
void showMessage();
};Person.cpp
cpp
#include "Person.h"
Person::Person() {
name = " ";
sex = " ";
age = 0;
}
Person::Person(string name, string sex, int age) {
this->name = name;
this->sex = sex;
this->age = age;
}
Person::Person(Person& p) {
name = p.name;
sex = p.sex;
age = p.age;
}
void Person::setName(string name) {
this->name = name;
}
void Person::setSex(string sex) {
this->sex = sex;
}
void Person::setAge(int age) {
this->age = age;
}
string Person::getName() {
return name;
}
string Person::getSex() {
return sex;
}
int Person::getAge() {
return age;
}
void Person::setPerson() {
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "设置姓名:" << endl;
cin >> name;
cout << "设置性别:" << endl;
cin >> sex;
cout << "设置年龄:" << endl;
cin >> age;
}
void Person::showMessage() {
cout << "姓名:" << getName() << endl;
cout << "性别:" << getSex() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << getAge() << endl;
}Student.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include"Person.h"
class Student: public Person {
private:
int Num;//学号
string School;//学校
string Major;//专业
public:
Student();
Student(string name, string sex, int age, int num, string school, string major);
Student(Student& r);
void setStudent();
void showMessage();
int getNum();
string getSchool();
string getMajor();
};Student.cpp
cpp
#include "Student.h"
#include"Person.h"
Student::Student() {
Num = 0;
School = "无";
Major = "无";
}
Student::Student(string names, string sexs, int ages, int num, string school, string major): Person(names, sexs, ages) {
Num = num;
School = school;
Major = major;
}
Student::Student(Student& r) : Person(r) {
Num = r.Num;
School = r.School;
Major = r.Major;
}
void Student::setStudent() {
setPerson();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "设置学生学号为:" << endl;
cin >> Num;
cout << "设置学生学校为:" << endl;
cin >> School;
cout << "设置学生专业为:" << endl;
cin >> Major;
}
void Student::showMessage() {
cout << "姓名为:" << getName() << endl;
cout << "性别为:" << getSex() << endl;
cout << "年龄为:" << getAge() << endl;
cout << "该学生的学号为:" << Num << endl;
cout << "该学生的学校为:" << School << endl;
cout << "该学生的专业为:" << Major << endl;
}
int Student::getNum() {
return Num;
}
string Student::getSchool() {
return School;
}
string Student::getMajor() {
return Major;
}Graduate.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include"Person.h"
#include"Student.h"
class Graduate: public Student {
private:
string Research_Direction;
public:
Graduate();
Graduate(string names, string sexs, int ages, int num, string school, string major, string Research_Direction);
Graduate(Graduate& r);
void setGraduate();
void showMessage();
};Gradute.cpp
cpp
#include "Graduate.h"
#include"Person.h"
#include"Student.h"
Graduate::Graduate() {
Research_Direction = "无";
}
Graduate::Graduate(string names, string sexs, int ages, int num, string school, string major, string Research_Direction) : Student(names, sexs, ages, num, school, major) {
Research_Direction = Research_Direction;
}
Graduate::Graduate(Graduate& r) : Student(r) {
Research_Direction = r.Research_Direction;
}
void Graduate::setGraduate() {
setStudent();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "设置研究方向:" << endl;
cin >> Research_Direction;
}
void Graduate::showMessage() {
cout << "姓名为:" << getName() << endl;
cout << "性别为:" << getSex() << endl;
cout << "年龄为:" << getAge() << endl;
cout << "该学生的学号为:" << getNum() << endl;
cout << "该学生的学校为:" << getSchool() << endl;
cout << "该学生的专业为:" << getMajor() << endl;
cout << "研究方向:" << Research_Direction << endl;
}main.cpp
cpp
#include"Person.h"
#include"Student.h"
#include"Graduate.h"
int main() {
//----------------------------------------
cout << "Person类测试-->" << endl;
cout << "" << endl;
Person p1;
cout << "调用Person无参构造:" << endl;
p1.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
Person p2("钟离", "男", 20);
cout << "调用Person有参构造:" << endl;
p2.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "修改Person类信息:" << endl;
p2.setPerson();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "显示Person类数据:" << endl;
p2.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
//-------------------------------------------
cout << "Student类测试-->" << endl;
cout << "" << endl;
Student s1;
cout << "调用Student类无参构造:" << endl;
s1.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
Student s2("钟离", "男", 20, 20215031, "黑龙江大学", "软件工程");
cout << "调用Student类有参构造" << endl;
s2.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "修改Student类信息:" << endl;
s2.setStudent();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "显示Student类数据:" << endl;
s2.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
//--------------------------------------------
cout << "Graduate类测试-->" << endl;
cout << "" << endl;
Graduate g1;
cout << "调用Graduate类无参的构造方法:" << endl;
g1.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
Graduate g2("钟离", "男", 20, 20215031, "黑龙江大学", "软件工程", "JAVA工程师");
cout << "调用Graduate类有参构造:" << endl;
g2.showMessage();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "修改Graduate类信息:" << endl;
g2.setGraduate();
cout << "" << endl;
cout << "显示Graduate类数据" << endl;
g2.showMessage();
return 0;
}实验 五 运算符重载 (2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握运算符重载的作用;
2.掌握运算符重载为成员函数的方法;
- 掌握运算符重载为非成员函数的方法
二、实验内容
1.为实验二中编写的Songer(歌手)类重载"+"、">"、"=="、前置"++"、后置"++"等运算符,使Song类的功能更丰富。
三、实验指导(其中1-5为必做,6为选做**)**
- 重载"+"运算符,实现如下功能
**例:**s1是Songer类的对象,则 s1+100 能够实现将s1的粉丝数加100
- 将">"运算符重载为成员函数,实现如下功能
**例:**s1、s2是Songer类的对象,则 s1>s2 能够实现比较s1的粉丝数是否多于s2的粉丝数
- 将"=="运算符重载为友元函数,实现如下功能
**例:**如s1、s2是Songer类的对象,则 s1==s2 能够实现比较s1的粉丝数是否等于s2的粉丝数
- 将前置"++"运算符重载为成员函数,实现如下功能
**例:**s1是Songer类的对象,则 ++s1 能够实现将s1的粉丝数加10
- 将后置"++"运算符重载为友元函数,实现如下功能
**例:**s1是Songer类的对象,则 s1++ 能够实现将s1的粉丝数加10
6.【选做】:重载"<<"运算符,实现如下功能
**例:**s1是Songer类的对象,则 cout<<s1 能够实现输出s1的信息(姓名、粉丝数)
四 、考核标准
本实验总计10分。
-
各个重载运算符的编写 (6分)
-
main函数测试这些运算符的合理性及正确性 (4分)
五、实验代码
Songer.cpp
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Songer {
friend void PK(Songer& s1, Songer& s2);
private:
string name; //姓名
int fans_count; //粉丝数
static int count; //当前歌手数
public:
Songer();
Songer(string names, int fans_counts);
Songer(Songer& r1);
void setfans_cout(int fans_counts);
~Songer();
static void ShowCount();
void show();
Songer operator+(int x);
bool operator>(Songer& r);
friend bool operator==(Songer& c1, Songer& c2);
Songer& operator++();
friend Songer operator++(Songer& c1, int);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& co, Songer s1);
};
int Songer::count = 0;
Songer::Songer() {
name = "无";
fans_count = 0;
count++;
}
Songer::Songer(string names, int fans_counts) {
name = names;
fans_count = fans_counts;
count++;
}
Songer::~Songer() {
count--;
}
Songer::Songer(Songer& r) {
name = r.name;
fans_count = r.fans_count;
count++;
}
void Songer::setfans_cout(int fans_counts) {
fans_count = fans_counts;
}
void Songer::ShowCount() {
cout << "当前歌手的数量:" << Songer::count << endl;
}
void Songer::show() {
cout << "歌手姓名:" << name << ","
<< "\t粉丝数量:" << fans_count << "\t" << endl;
}
//友元
void PK(Songer& s1, Songer& s2) {
if (s1.fans_count != s2.fans_count) {
if (s1.fans_count > s2.fans_count) {
cout << s1.name << "战胜" << s2.name << endl;
} else {
cout << s2.name << "战胜" << s1.name << endl;
}
} else {
cout << s1.name << "与" << s2.name << "打成平手" << endl;
}
}
//重载"+"运算符
Songer Songer::operator+(int x) {
Songer s = *this;
s.fans_count = s.fans_count + x;
return s;
}
//将">"运算符重载为成员函数
bool Songer::operator>(Songer& r) {
return (fans_count > r.fans_count);
}
//将"=="运算符重载为友元函数
bool operator==(Songer& c1, Songer& c2) {
return (c1.fans_count == c2.fans_count);
}
//将前置"++"运算符重载为成员函数
Songer &Songer:: operator++() {
fans_count = fans_count + 10;
return *this;
}
//将后置"++"运算符重载为友元函数
Songer operator++(Songer& s1, int) {
Songer s = s1;
s1.fans_count = s1.fans_count + 10;
return s;
}
//重载"<<"运算符
ostream& operator<<(ostream& co, Songer s1) {
cout << "姓名:" << s1.name << " 粉丝数:" << s1.fans_count;
return co;
}
int main() {
Songer s1("张三", 90);
Songer s2("李四", 90);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << "s1+100:" << endl;
s1 = s1 + 100;
cout << s1 << endl;
++s1;
cout << "++s1:" << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
Songer s;
s = s1++;
cout << "s1++:" << endl;
cout << s << endl;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
return 0;
}实验六 虚函数(2学时)
一、实验目的
1.掌握作用的作用;
2.掌握纯虚函数的使用;
- 掌握使用虚函数实现动态多态性。
二、实验内容
1.树结构是一类重要的非线性数据结构。树结构在客观世界中广泛存在,如人类社会的族谱和各种社会组织机构都可以用树形象表示,树在计算机领域中也得到广泛应用,尤以二叉树最为常用。
- 有以下Tree(树)、Binary_Tree(二叉树)和Binary_Sort_Tree(二叉排序树)类的定义,其中Binary_Tree继承了Tree,Binary_Sort_Tree继承了Binary_Tree。
class Tree//树
{
public:
virtual void show();
virtual ~Tree();
};
Tree::~Tree()
{
cout<<"析构一个树对象!"<<endl;
}
void Tree::show()
{
cout<<"树是非常重要的一种数据结构!"<<endl;
}
class Binary_Tree:public Tree//二叉树
{
public:
virtual void show();
virtual ~Binary_Tree();
};
Binary_Tree::~Binary_Tree()
{
cout<<"析构一个二叉树对象!"<<endl;
}
void Binary_Tree::show()
{
cout<<"二叉树每个结点至多有两棵子树,且有左右之分!"<<endl;
}
class Binary_Sort_Tree:public Binary_Tree//二叉排序树
{
public:
virtual void show();
virtual ~Binary_Sort_Tree();
};
Binary_Sort_Tree::~Binary_Sort_Tree()
{
cout<<"析构一个二叉排序树对象!"<<endl;
}
void Binary_Sort_Tree::show()
{
cout<<"二叉排序树首先是一颗二叉树!"<<endl;
cout<<"如果左子树不空,左子树小于根节点!"<<endl;
cout<<"如果右子树不空,右子树大于根节点!"<<endl;
}
三、实验指导
-
定义一个Tree的引用做参数的函数,在函数中访问show()函数,通过三种不同的对象来调用该函数以实现多态性。
-
定义一个Tree的指针做参数的函数,在函数中访问show()函数,通过三种不同对象的地址来调用该函数以实现多态性。
-
定义一个Tree类的指针,通过new操作产生不同的对象,然后delete该指针,观察虚析构实现的多态性。
-
(选做)如果将Tree类中show函数改为纯虚函数,在(3)中会出现什么情况?
四、考核标准
本实验总计10分。
-
(3分)
-
(3分)
-
(4分)
五、实验代码
Tree.cpp
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Tree {
public:
virtual void show();
//virtual void show()=0;
virtual ~Tree();
};
Tree::~Tree() {
cout << "析构一个树对象!" << endl;
}
void Tree::show() {
cout << "树是一个非常重要的数据结构" << endl;
}
class Binary_Tree : public Tree {
public:
virtual void show();
virtual ~Binary_Tree();
};
Binary_Tree::~Binary_Tree() {
cout << "析构一个二叉树对象!" << endl;
}
void Binary_Tree::show() {
cout << "二叉树每个节点至多有两颗子树,且有左右之分!" << endl;
}
class Binary_Sort_Tree : public Binary_Tree { //二叉排序树
public:
virtual void show();
virtual ~Binary_Sort_Tree();
};
Binary_Sort_Tree::~Binary_Sort_Tree() {
cout << "析构一个二叉排序树对象!" << endl;
}
void Binary_Sort_Tree::show() {
cout << "二叉排序树首先是一颗二叉树!" << endl;
cout << "如果左子树不空,左子树小于根节点!" << endl;
cout << "如果右子树不空,右子树大于根节点!" << endl;
}
//定义一个Tree的引用做参数的函数,在函数中访问show()函数,通过三种不同的对象来调用该函数以实现多态性。
void show(Tree& tree) {
tree.show();
cout << "*************" << endl;
}
//定义一个Tree的指针做参数的函数,在函数中访问show()函数,通过三种不同对象的地址来调用该函数以实现多态性。
void show1(Tree* tree) {
tree->show();
cout << "*************" << endl;
}
void test0() {
Tree t1;
Binary_Tree b1;
Binary_Sort_Tree s1;
show(t1);
show(b1);
show(s1);
cout << endl << "------------------" << endl;
Tree t2;
Binary_Tree b2;
Binary_Sort_Tree s2;
show1(&t2);
show1(&b2);
show1(&s2);
cout << endl << "------------------" << endl;
}
//定义一个Tree类的指针,通过new操作产生不同的对象,然后delete该指针,观察虚析构实现的多态性
void test1() {
Tree* t3 = new Tree();
delete (t3);
Tree* t4 = new Binary_Tree();
delete (t4);
Tree* t5 = new Binary_Sort_Tree();
delete (t5);
}
int main() {
test0();
cout << "+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+" << endl;
test1();
}作业Set集合
set.cpp
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
private:
int data;
Node* next;
public:
Node(int x);
Node();
int getData();
void setData(int x);
Node* getNext();
void setNext(Node* t);
};
Node::Node() {
data = 0;
next = NULL;
}
Node::Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
int Node::getData() {
return data;
}
void Node::setData(int x) {
data = x;
}
Node* Node::getNext() {
return next;
}
void Node::setNext(Node* t) {
next = t;
}
class Set {
private:
Node* head;
public:
Set();
Set(int* array, int length);
Set(Set& p);
Set(Set* p);
~Set();
void add(Node* p);
void add(int x);
void delet(int x);
void outPut();
friend Set* intersect(Set& s1, Set& s2);
friend Set* merge(Set& s1, Set& s2);
friend Set* subtraction(Set& s1, Set& s2);
friend bool judge_equal(Set& s1, Set& s2);
friend bool judge_contain(Set& s1, Set& s2);
bool judge_empty();
int size();
void clear();
Node* getHead();
void setHead(Node* p);
};
Set::Set() {
head = NULL;
}
Set::Set(int* array, int length) {
head = new Node(array[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
add(array[i]);
}
}
Node* Set::getHead() {
return head;
}
void Set::setHead(Node* p) {
head = p;
}
void Set::add(Node* p) {
add(p->getData());
}
void Set::add(int x) {
Node* p = new Node();
p->setData(x);
if (head == NULL) {
head = p;
return;
}
Node* temp = head->getNext();
Node* atm = head;
if (p->getData() < head->getData()) {
p->setNext(head);
head = p;
} else {
while (true) {
if (p->getData() == atm->getData())
return;
if (temp == NULL && p->getData()) {
atm->setNext(p);
return;
}
if (p->getData() < temp->getData()) {
break;
}
atm = atm->getNext();
temp = temp->getNext();
}
p->setNext(atm->getNext());
atm->setNext(p);
}
}
Set::Set(Set& p) {
head = new Node(p.getHead()->getData());
Node* temp = p.getHead()->getNext();
while (temp != NULL) {
Node* p = new Node(temp->getData());
add(p);
temp = temp->getNext();
}
}
Set::Set(Set* p) {
head = new Node(p->getHead()->getData());
Node* temp = p->getHead()->getNext();
while (temp != NULL) {
Node* q = new Node(temp->getData());
add(q);
temp = temp->getNext();
}
}
Set::~Set() {
Node* p = head;
Node* q;
while (p != NULL) {
q = p->getNext();
delete p;
p = q;
}
}
void Set::outPut() {
Node* temp = head;
if (temp == NULL)
return;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->getData() << " ";
temp = temp->getNext();
}
cout << endl;
}
void Set::delet(int x) {
Node* s = head;
if (head->getData() == x) {
head = head->getNext();
return;
}
while (s->getNext()->getData() != x) {
if (s->getNext() == NULL) {
cout << "无此值" << endl;
}
s = s->getNext();
}
s->setNext(s->getNext()->getNext());
}
Set* intersect(Set& s1, Set& s2) {
Node* head1 = s1.getHead();
Node* head2 = s2.getHead();
Set* s3 = new Set();
while (head1 != NULL && head2 != NULL) {
if (head1->getData() == head2->getData()) {
s3->add(head1->getData());
head1 = head1->getNext();
head2 = head2->getNext();
} else if (head1->getData() < head2->getData()) {
head1 = head1->getNext();
} else {
head2 = head2->getNext();
}
}
return s3;
}
Set* merge(Set& s1, Set& s2) {
Set* s3 = new Set(s1);
Node* temp = s2.getHead();
while (temp != NULL) {
s3->add(temp->getData());
temp = temp->getNext();
}
return s3;
}
Set* subtraction(Set& s1, Set& s2) {
Set* c3 = intersect(s1, s2);
Node* temp = c3->getHead();
while (temp != NULL) {
s1.delet(temp->getData());
temp = temp->getNext();
}
c3->setHead(s1.getHead());
return c3;
}
bool judge_equal(Set& s1, Set& s2) {
Node* head1 = s1.getHead();
Node* head2 = s2.getHead();
while (head1 != NULL || head2 != NULL) {
if (head1 == NULL || head2 == NULL)
return false;
else if (head1->getData() == head2->getData()) {
head1 = head1->getNext();
head2 = head2->getNext();
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool judge_contain(Set& s1, Set& s2) {
//算出交集
Set* s3 = intersect(s1, s2);
//构造交集的set对象
Set s4(s3);
//如果这个交集s4和其中一个s1/s2相同,就是包含
if (judge_equal(s4, s1) || judge_equal(s4, s2)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
bool Set::judge_empty() {
if (head == NULL)
return true;
return false;
}
int Set::size() {
int count = 0;
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
count++;
temp = temp->getNext();
}
return count;
}
void Set::clear() {
head = NULL;
}
int main() {
int a[] = { 0, 4, 1, 2, 3, 1 };
int b[] = { 3, 4 };
int length_a = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
int length_b = sizeof(b) / sizeof(b[0]);
Set c1(a, length_a);
Set c2(b, length_b);
Set c3(a, length_a);
c1.add(5);
c1.outPut();
c3.delet(3);
c3.outPut();
intersect(c1, c2)->outPut();
merge(c1, c2)->outPut();
//判断是否包含
cout << judge_contain(c1, c2) << endl;
subtraction(c1, c2)->outPut();
cout << judge_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
c1.clear();
cout << c1.judge_empty() << endl;
exit(0);
return 0;
}
若觉得有帮助,欢迎点赞关注,一起成长进步~
声明:本文仅供学习交流,禁作商用;禁篡改、歪曲及有偿传播,引用需标明来源。侵权必究。