手写数字识别(MNIST 数据集)
最经典、最有代表性的项目之一。
项目目标:让机器学习模型识别手写数字图片(0-9),判断图片上写的是什么数字。
数据集:MNIST(Mixed National Institute of Standards and Technology)
- 共 70,000 张灰度图片(28×28 像素)
- 60,000 张训练图片
- 10,000 张测试图片
- 每张图片只包含一个手写数字
python
# 在环境里下载tensorflow,里面包含这个数据集
pip install numpy matplotlib tensorflow代码以及结果如下
导入库
py
# 导入库
import numpy as np # numpy库,提供多维数组对象
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #Matplotlib库,用于绘画
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist #TensorFlow 的 Keras 模块 --- MNIST 数据集
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential #Keras 模型类型
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten #Keras 神经网络层,Dense(全连接层),Flatten(展平层)
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical #Keras 工具函数解析
将整个库导入并起别名
import ... as ...
py
import numpy as np # numpy库,提供多维数组对象
py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #Matplotlib库,用于绘画从库中导入部分模块或函数
from ... import ...
py
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential #Keras 模型类型,只导入 Sequential 这个类
py
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten #Keras 神经网络层,Dense(全连接层),Flatten(展平层)从层模块中取出 Dense、Flatten 两个常用层
py
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical #Keras 工具函数,从工具模块中取出标签转化函数加载数据集
python
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_test) = mnist.load_data()
print("训练集形状:", features_train.shape)
print("测试集形状:", features_test.shape)分析
python
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
print("我拿到的数据:",mnist.load_data())|

|
可以看到获取到了两个元组数据,于是我们用
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_test)来获取数据,一个是训练数据,一个是测试数据
而每个元组里又有两个numpy.ndarrays数据array(feature)和arrary(label)
python
print(features_train)
print(label_train)
print("features_train 类型:", type(features_train))
print("label_train 类型:", type(label_train)) |
 |
|---|---|
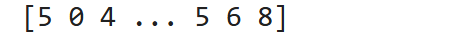 |
|
 |
|
python
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_test) = mnist.load_data()
print("训练集形状:", features_train.shape)
print("features_train 类型:", type(features_train))
print("features_train 元素类型:", features_train.dtype)
print(features_train[1])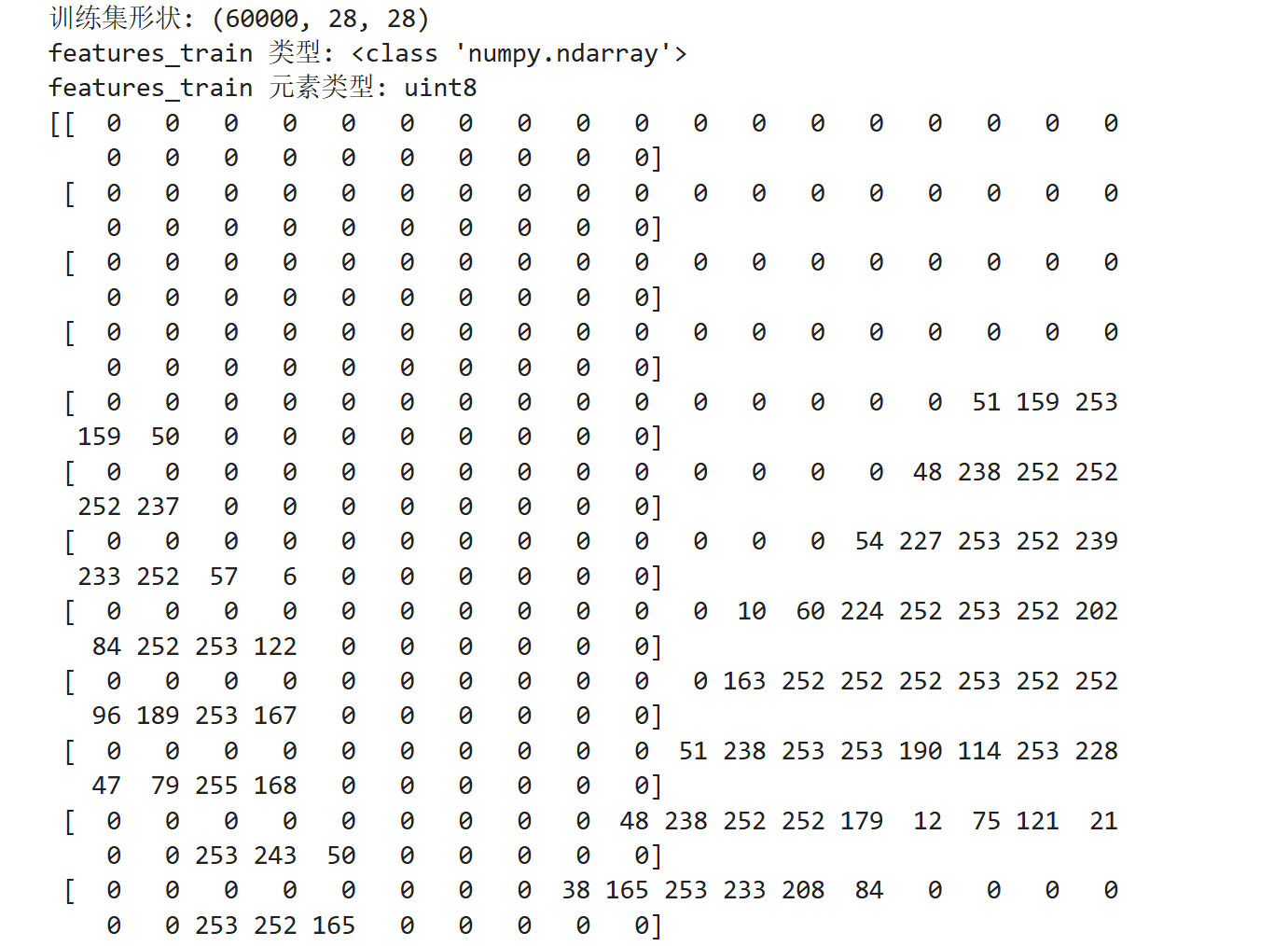
可以看到
features_train里是28*28的int8整型矩阵,一共有6000个
py
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_test) = mnist.load_data()
# print("训练集形状:", features_train.shape)
# print("features_train 类型:", type(features_train))
# print("features_train 元素类型:", features_train.dtype)
# print(features_train[1])
print("训练集形状:", label_train.shape)
print("label_train 类型:", type(label_train))
print("label_train 元素类型:", label_train.dtype)
print(label_train[:10])
可以看到
label_train里是6000个int8型的数字,也就是0-9的标签
数据可视化
看一看这里的灰度图片
python
plt.figure(figsize=(8,3))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(2,5,i+1)
plt.imshow(features_train[i], cmap='gray')
plt.title(f"Label: {label[i]}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
python
# 首先创建一个画布,大小为 8 英寸 × 3 英寸
plt.figure(figsize=(8,3))
python
# 放10张图片,编号从 0 到 9
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(2,5,i+1) #把画布划分成 2 行 5 列 的小格子(共 10 个小图)
plt.imshow(features_train[i], cmap='gray') #用灰度图颜色显示
plt.title(f "Label: {label[i]}") #动态显示标签:Label: 5、Label: 3
plt.axis('off') #去掉坐标轴
py
plt.show() #最后统一显示图像窗口数据预处理
归一化
python
features_train = features_train.astype("float32") / 255
features_test = features_test.astype("float32") / 255把图像的数据类型从 整数型(uint8) 转换为 浮点型(float32)
- MNIST 数据原始是 0~255 的整数(代表像素灰度值)
- 机器学习中的模型计算一般使用 浮点数,这样可以进行更精确的梯度计算。
归一化把像素值 归一化(Normalization) 到 0~1 之间。
因为每个像素的灰度值原本是0-255,归一化就变成0.0-0.1。这样能让训练更加稳定,不会因为数值太大导致梯度爆炸或收敛困难。

独热编码
标签是整数形式,但是神经网络在做分类时,最后一层会输出一个概率分布。
为了跟这个概率分布进行比较,我们需要把原本的标签(一个数字)也转成相同形状的概率向量 。
这就是 独热编码(One-hot encoding)。
to_categorical()的功能是把标签数字转成这种「向量表示」
| 原始标签 | One-hot 编码 |
|---|---|
| 0 | [1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] |
| 1 | [0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0] |
| 5 | [0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0] |
| 9 | [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1] |
python
label_train = to_categorical(label_train)
label_test = to_categorical(label_test)模型训练
构建顺序模型
python
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28)), # 把28x28二维图展平成784维向量
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层:128个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层:10类(数字0-9)
])| 层 | 作用 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28)) |
把图片摊平 | MNIST 图片是 28×28 像素的二维数组,需要摊平成一维向量(784个数)才能输入全连接层 |
Dense(128, activation='relu') |
全连接层(隐藏层) | 有 128 个神经元,每个神经元都连接前一层的所有输入。relu 是一种激活函数(能让模型学习非线性关系) |
Dense(10, activation='softmax') |
输出层 | 因为我们有 10 个类别(数字 0--9),所以输出 10 个概率;softmax 把它们归一化为「总和 = 1」的概率分布 |
编译模型
python
model.compile(
optimizer='adam', # 优化算法
loss='categorical_crossentropy', # 分类损失函数
metrics=['accuracy'] # 评估指标
)| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
optimizer='adam' |
优化算法,用来更新权重(Adam 是一种自适应学习率算法,非常常用) |
loss='categorical_crossentropy' |
损失函数:衡量模型预测与真实标签之间的差距。适合「多分类 + one-hot 标签」的任务 |
metrics=['accuracy'] |
训练时除了损失,还要计算准确率(accuracy)方便观察模型效果 |
训练模型
python
history = model.fit(
feature_train, label_train,
epochs=5,
batch_size=128,
validation_split=0.1
)| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
feature_train, label_train |
训练数据与标签 |
epochs=5 |
整个训练集会被重复学习 5 次 |
batch_size=128 |
每次送入网络的样本数量(越大训练越快,但显存占用高) |
validation_split=0.1 |
从训练集中拿出 10% 作为验证集,用来检测模型是否过拟合 |
history |
保存训练过程中的损失、准确率等指标,方便后面画图分析 |
输入:28x28灰度图
↓ Flatten
784维输入向量
↓ Dense(128, ReLU)
提取特征
↓ Dense(10, Softmax)
输出10个类别概率
↓
计算损失 → 优化器更新参数 → 重复多轮(epochs)模型评估
python
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(feature_test, label_test)
#让模型在测试集上跑一遍,不训练,只评估
print("测试集准确率:", test_acc)| 输出 | 含义 |
|---|---|
test_loss |
模型在测试集上的损失值(越小越好) |
test_acc |
模型在测试集上的准确率(accuracy) |
测试单张图片
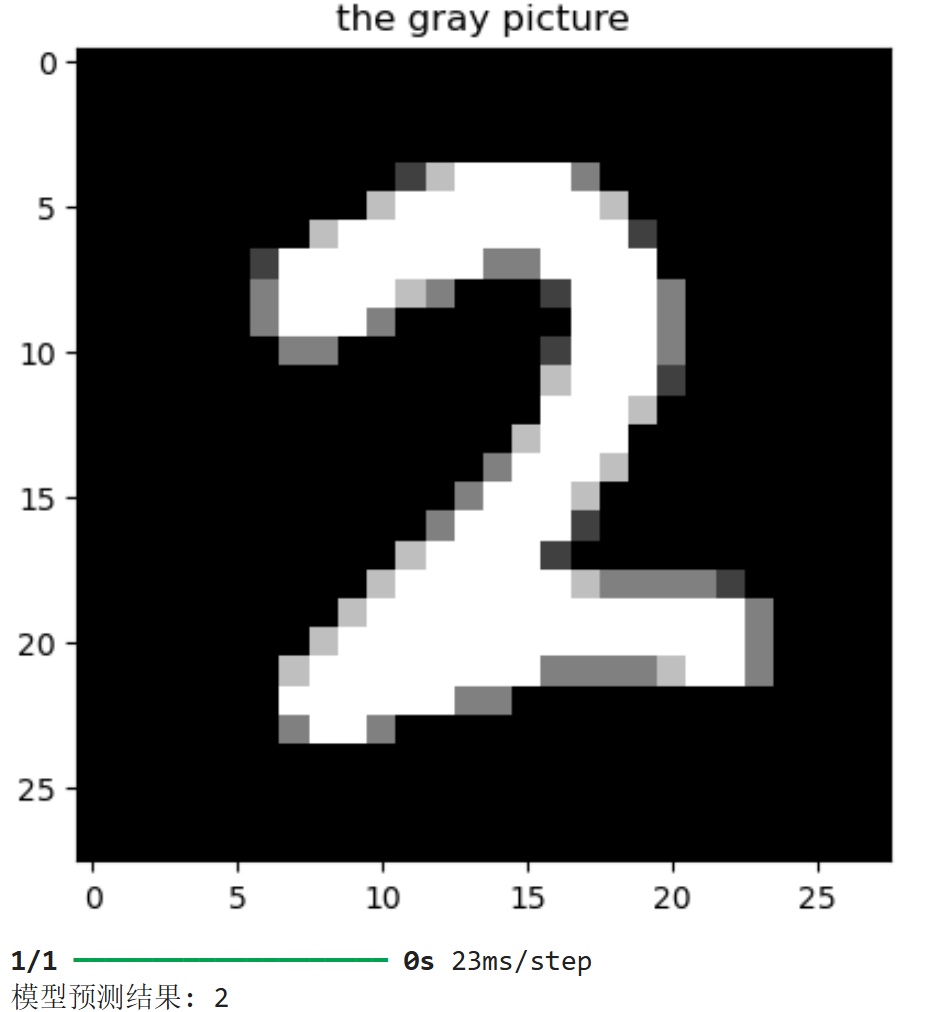
python
#展示一张图片
index = np.random.randint(0, 10000)#随机生成一个测试样本的索引(0 到 9999 之间)
plt.imshow(feature_test[index], cmap='gray')
plt.title("the gray picture")
plt.show()
python
# 模型预测部分
pred = model.predict(feature_test[index].reshape(1,28,28))
print("模型预测结果:", np.argmax(pred))| 操作 | 说明 |
|---|---|
feature_test[index] |
取出那张图片(形状是 (28,28)) |
.reshape(1,28,28) |
变形为模型能接受的输入 (1,28,28),表示"1张图片",因为模型要求输入是 批量(batch) 形式 |
model.predict(...) |
让模型输出预测结果(一个长度为 10 的数组,每个数代表对应数字的概率) |
代码:顺序模型
py
# 导入库
import numpy as np # numpy库,提供多维数组对象
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #Matplotlib库,用于绘画
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist #TensorFlow 的 Keras 模块 --- MNIST 数据集
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential #Keras 模型类型
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten #Keras 神经网络层,Dense(全连接层),Flatten(展平层)
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical #Keras 工具函数
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_test) = mnist.load_data()
print("训练集形状:", features_train.shape)
print("测试集形状:", features_test.shape)
#数据可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(8,3))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(2,5,i+1)
plt.imshow(features_train[i], cmap='gray')
plt.title(f"Label: {label[i]}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
#构建顺序模型
model = Sequential([
Flatten(input_shape=(28,28)), # 把28x28二维图展平成784维向量
Dense(128, activation='relu'), # 隐藏层:128个神经元
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层:10类(数字0-9)
])
#编译模型
model.compile(
optimizer='adam', # 优化算法
loss='categorical_crossentropy', # 分类损失函数
metrics=['accuracy'] # 评估指标
)
#训练模型
history = model.fit(
feature_train, label_train,
epochs=5,
batch_size=128,
validation_split=0.1
)
#模型评估
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(feature_test, label_test)
#让模型在测试集上跑一遍,不训练,只评估
print("测试集准确率:", test_acc)
#展示一张图片
index = np.random.randint(0, 10000)#随机生成一个测试样本的索引(0 到 9999 之间)
plt.imshow(feature_test[index], cmap='gray')
plt.title("the gray picture")
plt.show()
# 模型预测部分
pred = model.predict(feature_test[index].reshape(1,28,28))
print("模型预测结果:", np.argmax(pred))代码:CNN卷积神经网络
py
# 导入库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten, Dense, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
#加载数据
# 直接从 Keras 加载 MNIST 数据集
(features_train, label_train), (features_test, label_train) = mnist.load_data()
print("训练集形状:", features_train.shape)
print("测试集形状:", features_test.shape)
#数据预处理
# CNN 需要输入三维数据 (height, width, channels),而 MNIST 是灰度图(只有 1 个通道)
# 调整维度 (60000, 28, 28, 1)
features_train = features_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype("float32") / 255
features_test = features_test.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1).astype("float32") / 255
# One-hot 编码
label_train = to_categorical(label_train, 10)
label_train = to_categorical(label_train, 10)
#构建CNN模型
model = Sequential([
# 卷积层1:32个卷积核 3x3
Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3,3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28,28,1)),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2)),
# 卷积层2:64个卷积核 3x3
Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3,3), activation='relu'),
MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2)),
Flatten(), # 展平为一维
Dropout(0.5), # 防止过拟合
Dense(128, activation='relu'),
Dense(10, activation='softmax') # 输出层(10类)
])
#编译模型
model.compile(
optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy']
)
#训练模型
history = model.fit(
features_train, test_train,
epochs=5,
batch_size=128,
validation_split=0.1,
verbose=2
)
#评估模型
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(features_test, label_test)
print("测试集准确率:", round(test_acc * 100, 2), "%")
#随机预测展示
index = np.random.randint(0, len(x_test))
plt.imshow(x_test[index].reshape(28,28), cmap='gray')
plt.title("图片预览")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
pred = model.predict(x_test[index].reshape(1,28,28,1))
print("模型预测结果:", np.argmax(pred))