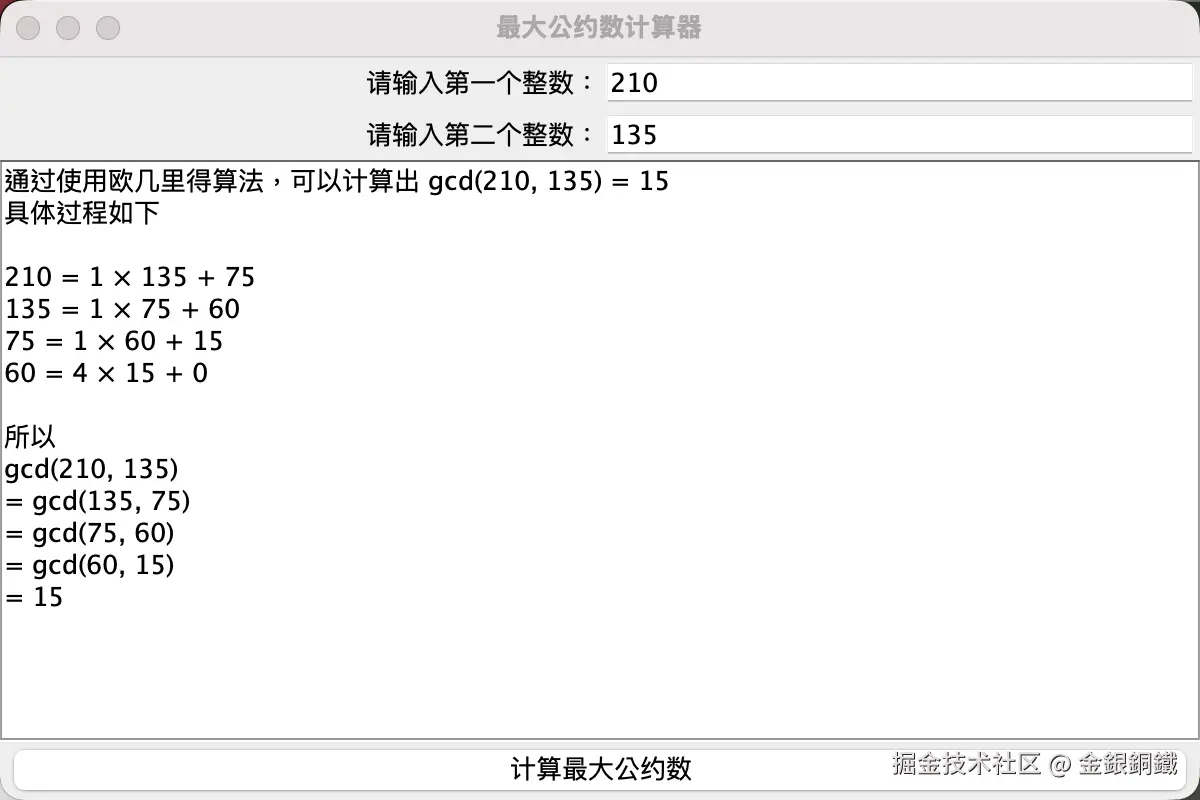
用 Swing 生成一个最大公约数计算器(展示计算过程)
背景
在 [Java] 用 Swing 生成一个最大公约数计算器 一文中,我们完成了一个简单的最大公约数计算器。示例效果如下图所示 ⬇️
它虽然可以计算出两个整数的最大公约数(两个整数不能同时为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 ),但是并没有展示计算过程。有的时候,我们也关心计算的过程,例如我们利用欧几里得算法计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 210 , 135 ) gcd(210, 135) </math>gcd(210,135) 时,计算过程可以这样表示
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> 210 = 1 × 135 + 75 135 = 1 × 75 + 60 75 = 1 × 60 + 15 60 = 4 × 15 + 0 210 = 1 \times 135 + 75\\ 135 = 1 \times 75 + 60\\ 75 = 1 \times 60 + 15\\ 60 = 4 \times 15 + 0\\ </math>210=1×135+75135=1×75+6075=1×60+1560=4×15+0
所以
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> g c d ( 210 , 135 ) = g c d ( 135 , 75 ) = g c d ( 75 , 60 ) = g c d ( 60 , 15 ) = 15 gcd(210, 135)\\ = gcd(135, 75)\\ = gcd(75, 60)\\ = gcd(60, 15)\\ = 15 </math>gcd(210,135)=gcd(135,75)=gcd(75,60)=gcd(60,15)=15
如果最大公约数计算器可以把上述过程展示出来,那就方便多了。所以我们的目标是做出下图这样的界面 ⬇️
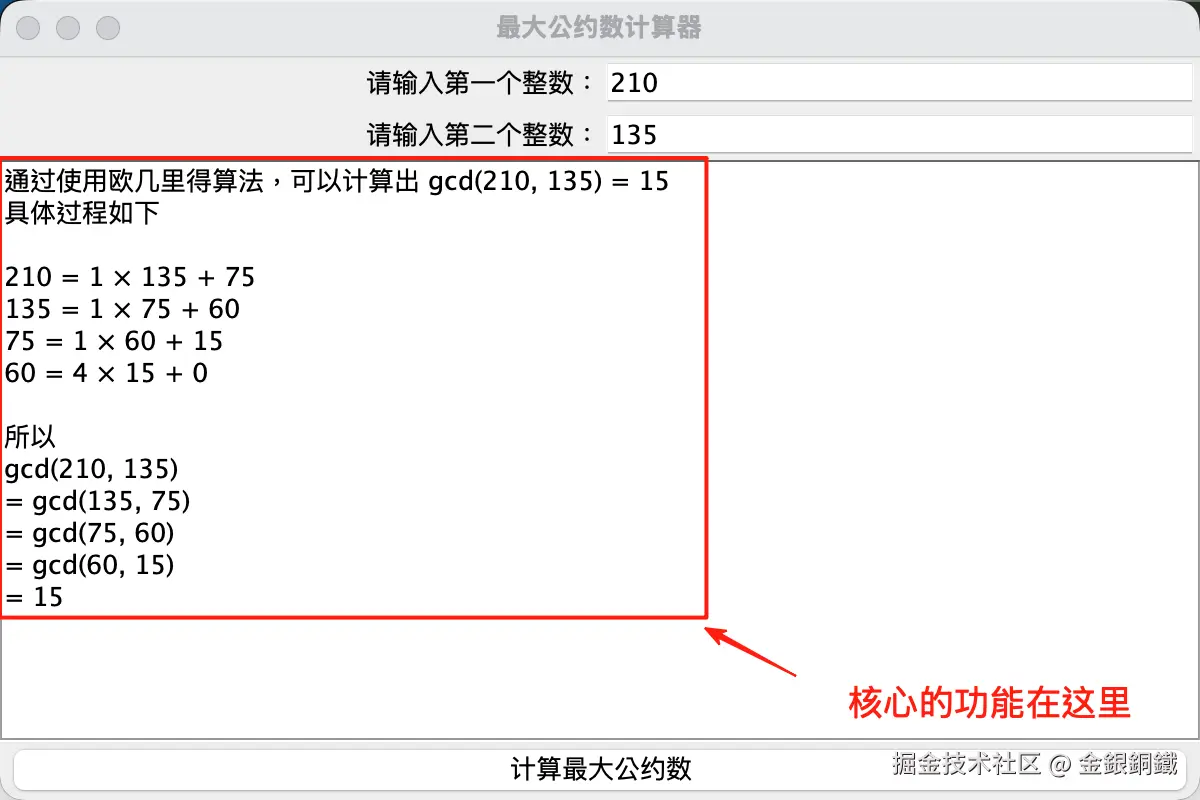
正文
需要保存哪些数据
我们先看看如果需要展示完整的计算过程,需要保存哪些数据。以计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 210 , 135 ) gcd(210, 135) </math>gcd(210,135) 为例,它的计算过程如下 ⬇️
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> 210 = 1 × 135 + 75 135 = 1 × 75 + 60 75 = 1 × 60 + 15 60 = 4 × 15 + 0 210 = 1 \times 135 + 75\\ 135 = 1 \times 75 + 60\\ 75 = 1 \times 60 + 15\\ 60 = 4 \times 15 + 0\\ </math>210=1×135+75135=1×75+6075=1×60+1560=4×15+0
每一行都可以看成是 ⬇️ ( <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> q i q_i </math>qi 表示第 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> i i </math>i 行的 商 , <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> r i r_i </math>ri 表示第 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> i i </math>i 行的 余数)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> a i = q i × b i + r i a_i = q_i \times b_i + r_i </math>ai=qi×bi+ri
看来我们只需要将所有的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a i , q i , b i , r i a_i, q_i, b_i, r_i </math>ai,qi,bi,ri 都保存下来(计算结束的条件是出现某个 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> r i = 0 r_i=0 </math>ri=0),就可以将完整的计算过程展示出来。
输入的标准化
只使用非负数
对非负整数 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a a </math>a 而言,不难验证 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( a , b ) = g c d ( − a , b ) gcd(a, b) = gcd(-a, b) </math>gcd(a,b)=gcd(−a,b),所以如果用户输入了 负整数 ,我们总是可以将其先转化为 非负整数 ,然后再进行计算。也就是说我们只要计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( ∣ a ∣ , ∣ b ∣ ) gcd(|a|, |b|) </math>gcd(∣a∣,∣b∣),就可以得到 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( a , b ) gcd(a, b) </math>gcd(a,b) 的值。
参数顺序的调整
由于 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( a , b ) = g c d ( b , a ) gcd(a, b) = gcd(b, a) </math>gcd(a,b)=gcd(b,a),所以可以调整参数 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a, b </math>a,b 的顺序。我们可以通过计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( max ( a , b ) , min ( a , b ) ) gcd(\max(a,b), \min(a, b)) </math>gcd(max(a,b),min(a,b)) 从而得到 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( a , b ) gcd(a, b) </math>gcd(a,b)。
代码
计算最大公约数的代码
基于上文的讨论,可以写出保存了计算过程中所有数据的 GCDCalculator 类 ⬇️
java
class GCDCalculator {
record CalculationDetails(
BigInteger a,
BigInteger b,
BigInteger gcd,
java.util.List<Equation> equationHolders
) {
/**
* A holder class for equation a = q * b + r
*/
record Equation(
BigInteger a,
BigInteger q,
BigInteger b,
BigInteger r
) {
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%s = %s × %s + %s", a, q, b, r);
}
}
}
private BigInteger toBigInteger(String num) {
return new BigInteger(num.trim());
}
public CalculationDetails calculateGCD(String a, String b) {
return calculateGCD(toBigInteger(a), toBigInteger(b));
}
public CalculationDetails calculateGCD(BigInteger a, BigInteger b) {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
BigInteger biggerOne;
BigInteger smallerOne;
if (a.compareTo(b) >= 0) {
biggerOne = a;
smallerOne = b;
} else {
biggerOne = b;
smallerOne = a;
}
if (biggerOne.equals(BigInteger.ZERO)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("两个整数不能都是0!");
}
var equations = doCalculateGCD(biggerOne, smallerOne);
BigInteger gcd = smallerOne.equals(BigInteger.ZERO) ? biggerOne : equations.getFirst().b;
return new CalculationDetails(biggerOne, smallerOne, gcd, equations);
}
private java.util.List<CalculationDetails.Equation> doCalculateGCD(BigInteger a, BigInteger b) {
if (b.equals(BigInteger.ZERO)) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
var result = doCalculateGCD(b, a.mod(b));
result.add(new CalculationDetails.Equation(a, a.divide(b), b, a.mod(b)));
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GCDCalculator gcdCalculator = new GCDCalculator();
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("0", "1").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("1", "0").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("100", "20").gcd); // should be 20
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("10", "12").gcd); // should be 2
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("233", "144").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("12345", "67890").gcd); // should be 15
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("54321", "9876").gcd); // should be 3
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("1160718174", "316258250").gcd); // should be 1078
}
}它的 main 函数里做了一些测试,最大公约数的计算结果结果符合预期。
完整的代码
既然我们的代码已经可以保存在计算最大公约数的过程中用到的所有数据,那么再添加一些和 Swing 相关的代码就可以将计算过程展示出来了。由于 Swing 的知识体系比较复杂,而它的知识点也比较零散,我自己也只是学了点皮毛,和 Swing 相关的代码就不展开说了。完整的代码如下 ⬇️
java
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class DetailedGCDCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> new CalcGreatestCommonDivisor().show());
}
}
class CalcGreatestCommonDivisor {
public void show() {
SimpleFrame frame = new SimpleFrame("最大公约数计算器");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
JPanel northPanel = new JPanel();
northPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 2));
JTextField textField1 = new JTextField();
northPanel.add(new JLabel("请输入第一个整数:", SwingConstants.RIGHT));
northPanel.add(textField1);
northPanel.add(new JLabel("请输入第二个整数:", SwingConstants.RIGHT));
JTextField textField2 = new JTextField();
northPanel.add(textField2);
JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea(8, 20);
textArea.setText("这里用于展示最大公约数的计算过程");
textArea.setEditable(false);
textArea.setLineWrap(true);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textArea);
frame.add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.add(northPanel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
JButton button = new JButton("计算最大公约数");
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
private final GCDCalculator calculator = new GCDCalculator();
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String rawA = textField1.getText();
String rawB = textField2.getText();
try {
var calculationDetails = calculator.calculateGCD(rawA, rawB);
String text = buildText(calculationDetails);
textArea.setText(text);
} catch (NumberFormatException exception) {
textArea.setText("Exception found " + exception.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException exception) {
textArea.setText(exception.getMessage());
}
}
});
frame.add(button, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
private String buildText(GCDCalculator.CalculationDetails calculationDetails) {
BigInteger a = calculationDetails.a();
BigInteger b = calculationDetails.b();
BigInteger gcd = calculationDetails.gcd();
List<GCDCalculator.CalculationDetails.Equation> equations = calculationDetails.equationHolders();
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(System.lineSeparator());
if (equations.isEmpty()) { // then b is 0 (so gcd(a, b) = a)
joiner.add(String.format("%s = 0 × %s", b, a));
joiner.add(String.format("%s = 1 × %s", a, a));
joiner.add(String.format("所以 gcd(%s, %s) = %s", a, b, gcd));
} else {
String firstLine = String.format("通过使用欧几里得算法,可以计算出 gcd(%s, %s) = %s", a, b, gcd.toString());
joiner.add(firstLine);
joiner.add("具体过程如下");
joiner.add("");
for (var equation : equations.reversed()) {
joiner.add(equation.toString());
}
joiner.add("");
joiner.add("所以");
boolean isFirstLine = true;
for (var equation : equations.reversed()) {
if (isFirstLine) {
joiner.add(String.format("gcd(%s, %s)", equation.a(), equation.b()));
isFirstLine = false;
} else {
joiner.add(String.format("= gcd(%s, %s)", equation.a(), equation.b()));
}
}
joiner.add("= " + gcd);
}
return joiner.toString();
}
}
class SimpleFrame extends JFrame {
public SimpleFrame(String title) {
setTitle(title);
setSize(600, 400);
}
}
class GCDCalculator {
record CalculationDetails(
BigInteger a,
BigInteger b,
BigInteger gcd,
java.util.List<Equation> equationHolders
) {
/**
* A holder class for equation a = q * b + r
*/
record Equation(
BigInteger a,
BigInteger q,
BigInteger b,
BigInteger r
) {
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%s = %s × %s + %s", a, q, b, r);
}
}
}
private BigInteger toBigInteger(String num) {
return new BigInteger(num.trim());
}
public CalculationDetails calculateGCD(String a, String b) {
return calculateGCD(toBigInteger(a), toBigInteger(b));
}
public CalculationDetails calculateGCD(BigInteger a, BigInteger b) {
a = a.abs();
b = b.abs();
BigInteger biggerOne;
BigInteger smallerOne;
if (a.compareTo(b) >= 0) {
biggerOne = a;
smallerOne = b;
} else {
biggerOne = b;
smallerOne = a;
}
if (biggerOne.equals(BigInteger.ZERO)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("两个整数不能都是0!");
}
var equations = doCalculateGCD(biggerOne, smallerOne);
BigInteger gcd = smallerOne.equals(BigInteger.ZERO) ? biggerOne : equations.getFirst().b;
return new CalculationDetails(biggerOne, smallerOne, gcd, equations);
}
private java.util.List<CalculationDetails.Equation> doCalculateGCD(BigInteger a, BigInteger b) {
if (b.equals(BigInteger.ZERO)) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
var result = doCalculateGCD(b, a.mod(b));
result.add(new CalculationDetails.Equation(a, a.divide(b), b, a.mod(b)));
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GCDCalculator gcdCalculator = new GCDCalculator();
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("0", "1").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("1", "0").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("100", "20").gcd); // should be 20
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("10", "12").gcd); // should be 2
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("233", "144").gcd); // should be 1
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("12345", "67890").gcd); // should be 15
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("54321", "9876").gcd); // should be 3
System.out.println(gcdCalculator.calculateGCD("1160718174", "316258250").gcd); // should be 1078
}
}请将以上代码保存为 DetailedGCDCalculator.java。 用下方的命令可以编译 DetailedGCDCalculator.java 并运行其中的 main 函数。
bash
javac DetailedGCDCalculator.java
java DetailedGCDCalculator运行示例
刚启动时
刚启动时,还没有任何输入 
测试用例 1: 计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 1 , 0 ) gcd(1, 0) </math>gcd(1,0)
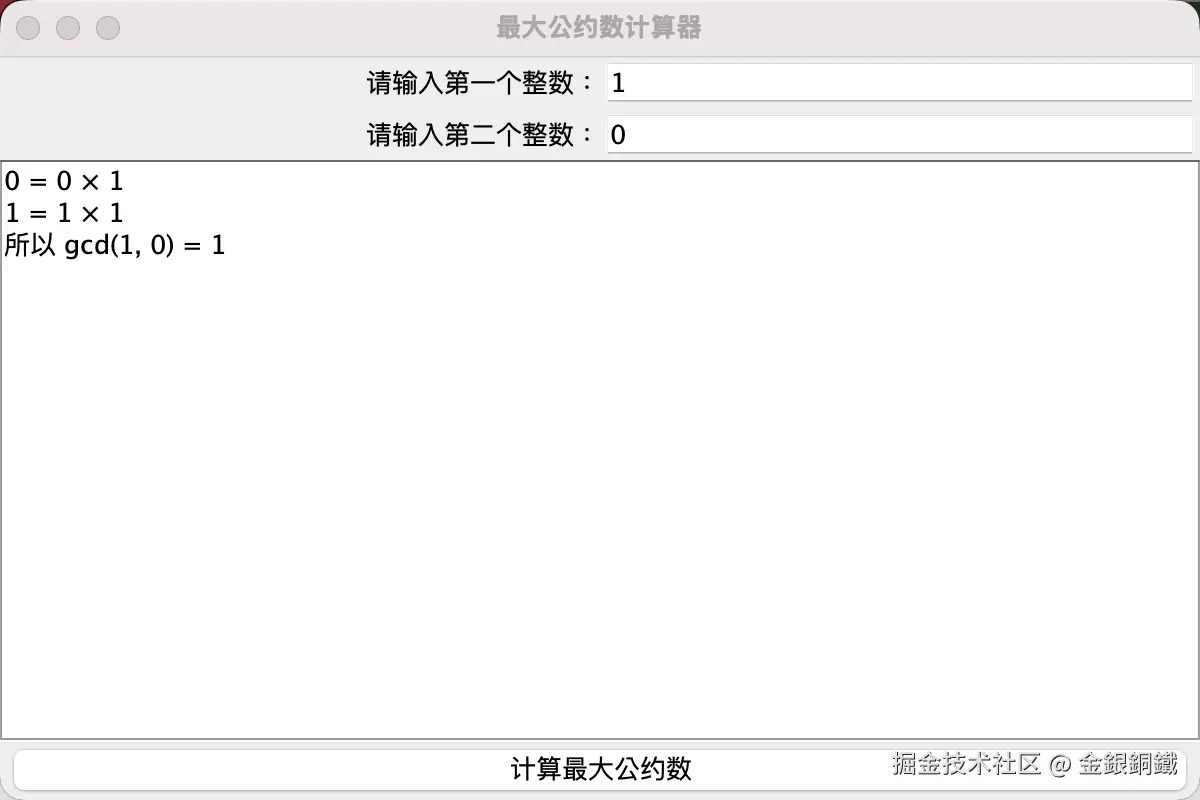
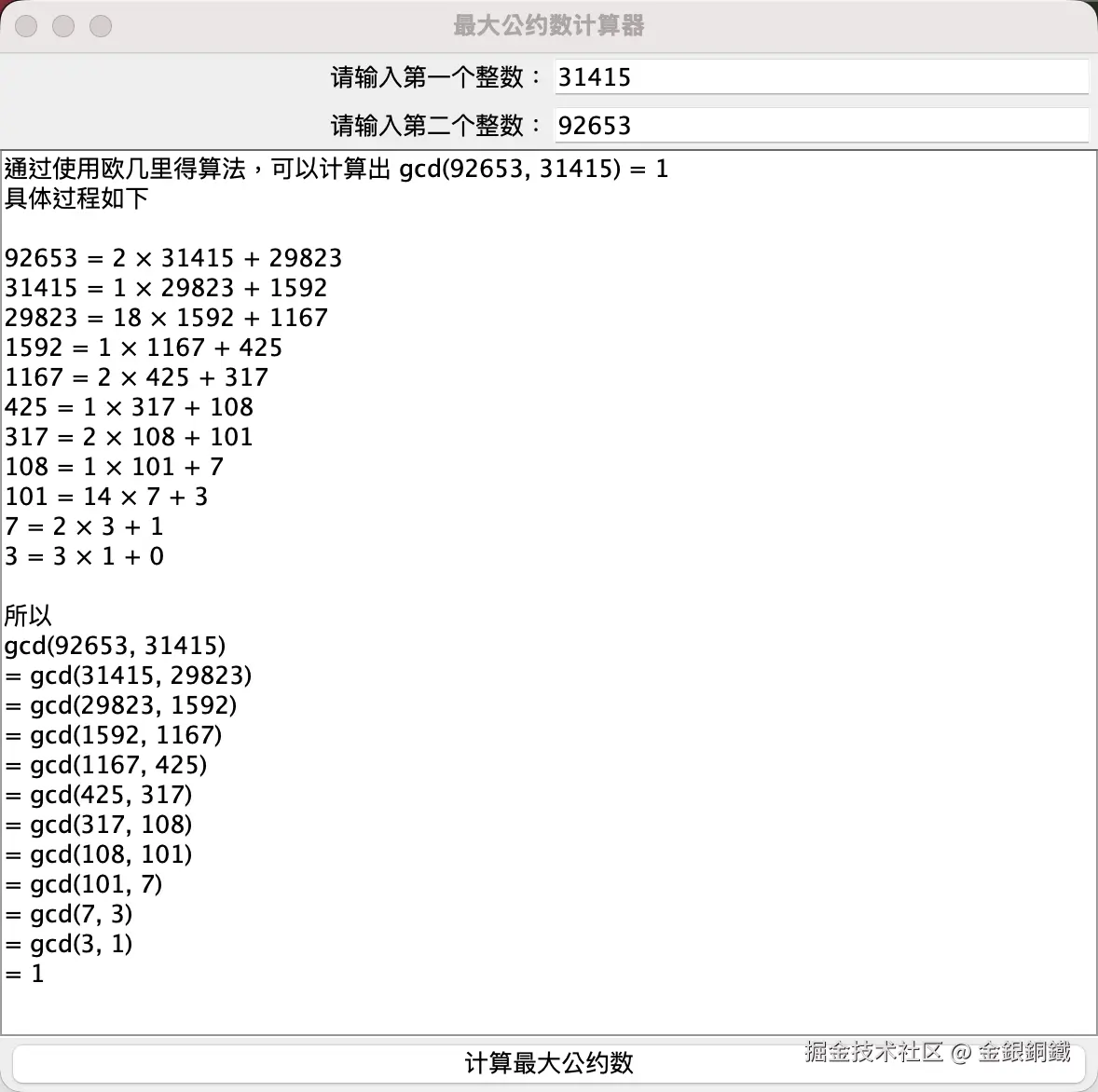
测试用例 2: 计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 31415 , 92653 ) gcd(31415, 92653) </math>gcd(31415,92653)
完整的计算步骤比较长,我将窗口放大后,截图如下 ⬇️
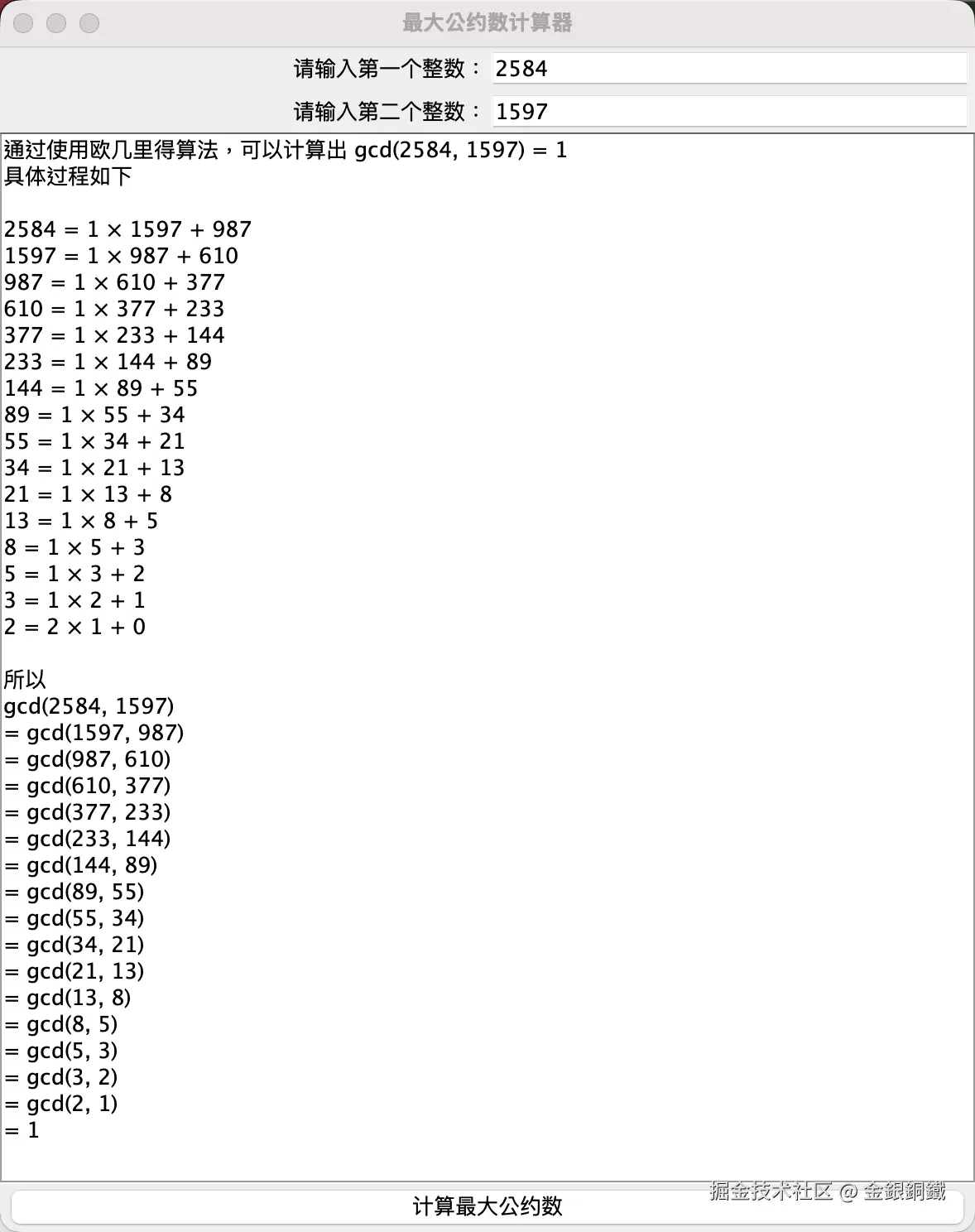
测试用例 3: 计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 2584 , 1597 ) gcd(2584, 1597) </math>gcd(2584,1597) ( <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1597 1597 </math>1597 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 2584 2584 </math>2584 是 Fibonacci 数列中相邻的两项,而 Fibonacci 数列中相邻两项的最大公约数总是 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1)
完整的计算步骤比较长,我将窗口放大后,截图如下 ⬇️
测试用例 4: 计算 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g c d ( 210 , 135 ) gcd(210, 135) </math>gcd(210,135)