Linux系统编程------进程通信之有名管道
有名管道
有名管道可以使互不相关的两个进程互相通信。有名管道可以通过路径名,并且在文件系统中可见。进程通过为文件IO操作有名管道。不支持lseek()操作,遵循先进先出原则。
mkfifo
c
int mkfifo(const char* filename, mode_t mode);功能:创建管道文件。
filename:要创建的管道。
mode:管道的访问权限,一般用八进制数表示。
返回值:成功返回0,出错返回-1
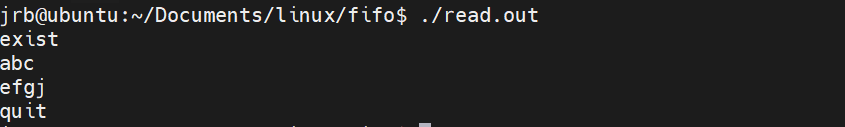
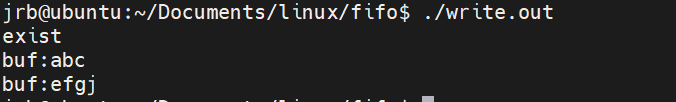
实例:通过管道进行多进程输入输出
代码:
read.c
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int fd;
char buf[32];
if (mkfifo("./fifo", 0666) < 0) {
if (errno == EEXIST) {
printf("exist\n");
} else {
perror("mkfifo err");
return -1;
}
}
fd = open("./fifo", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0 ) {
perror("open failed:");
return -1;
}
while(1) {
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin);
write(fd, buf,strlen(buf));
if (strncmp(buf, "quit", 4) == 0)
break;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}write.c
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int fd;
int dest_fd;
char buf[32];
if (mkfifo("./fifo", 0666) < 0) {
if (errno == EEXIST) {
printf("exist\n");
} else {
perror("mkfifo err");
return -1;
}
}
fd = open("./fifo", O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0 ) {
perror("open failed:");
return -1;
}
while(1) {
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if(strncmp(buf, "quit",4) == 0)
break;
printf("buf:%s", buf);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}执行结果: