一.队列的定义
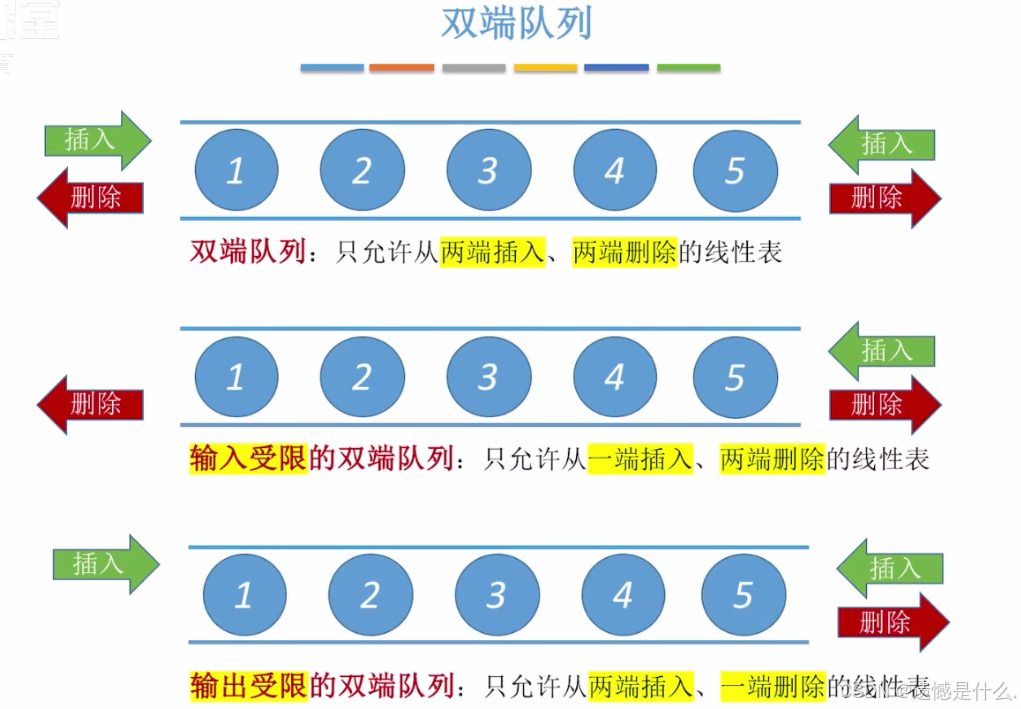
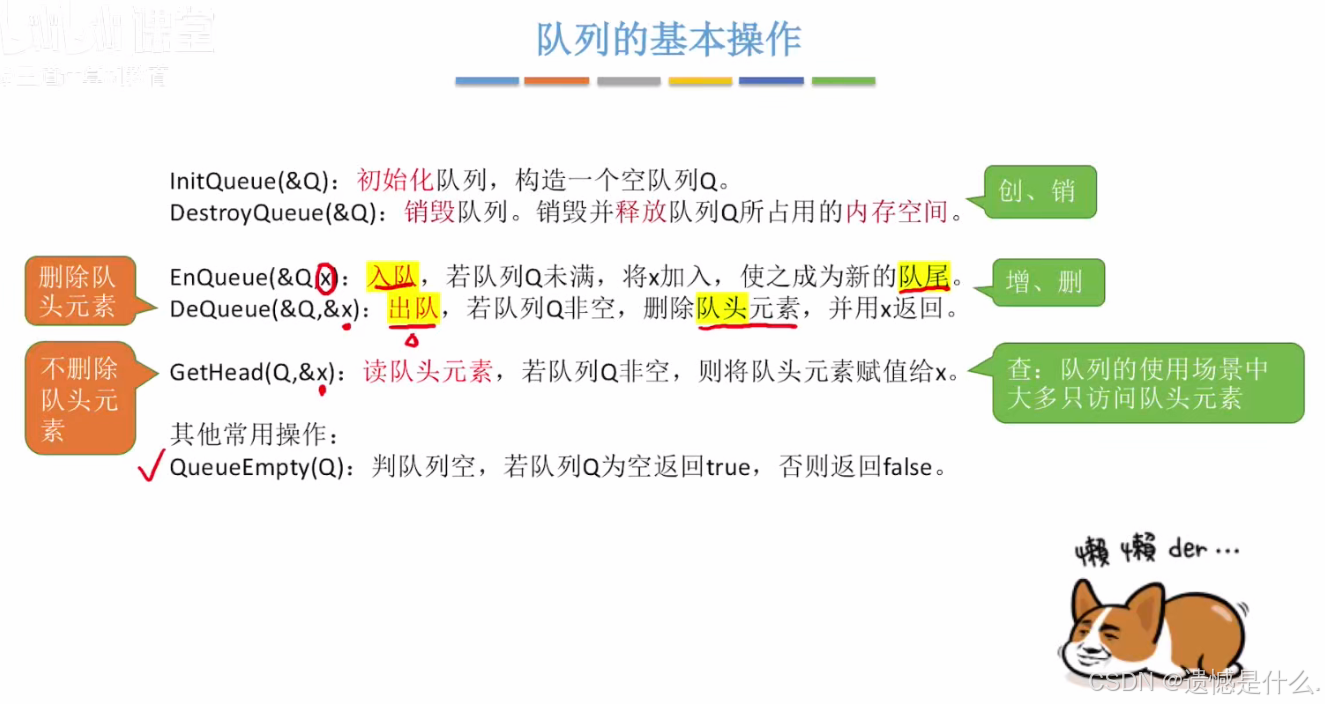
队列 (Queue) 是只允许在一端进行插入,在另一端删除的线性表
**重要术语:**队头,队尾,空队列
队列的特点: 先进先出(First In First Out), 栈则是后进先出
二.顺序存储入队操作
1.入队操作问题
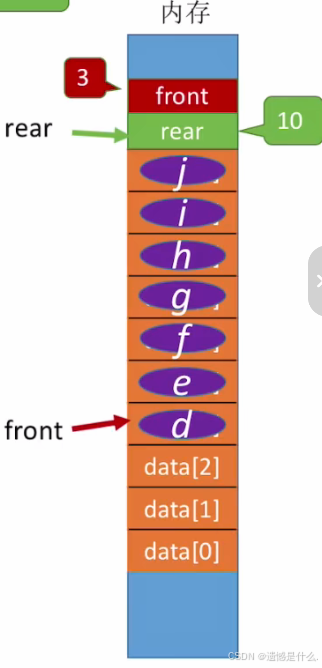
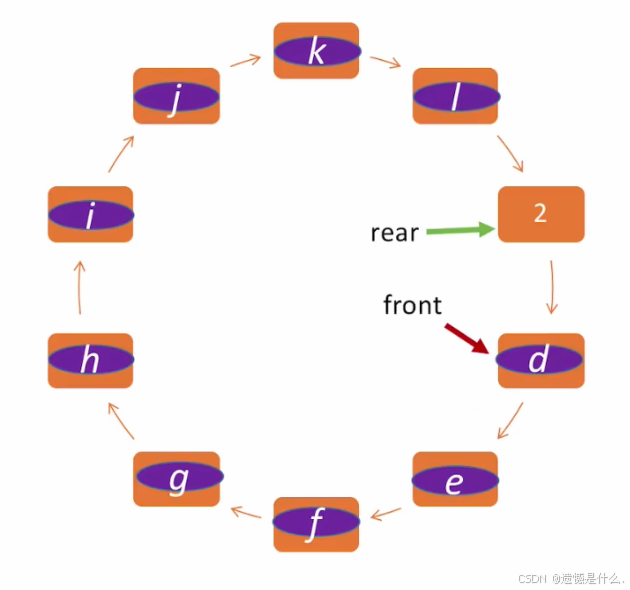
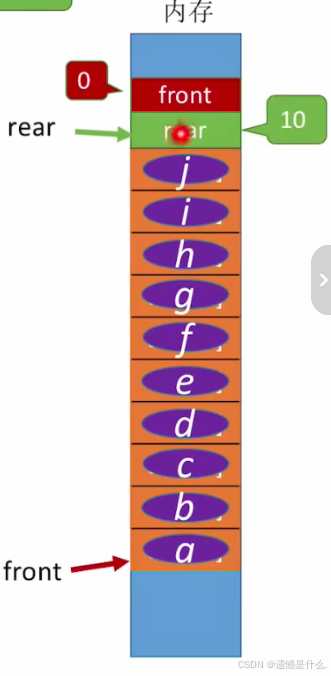 现在队列处于满队状态:
现在队列处于满队状态:
即front指向data[0]位置, front = 0;
队尾指针 rear 指向MaxSize = 10;
此时队列元素以及存满.
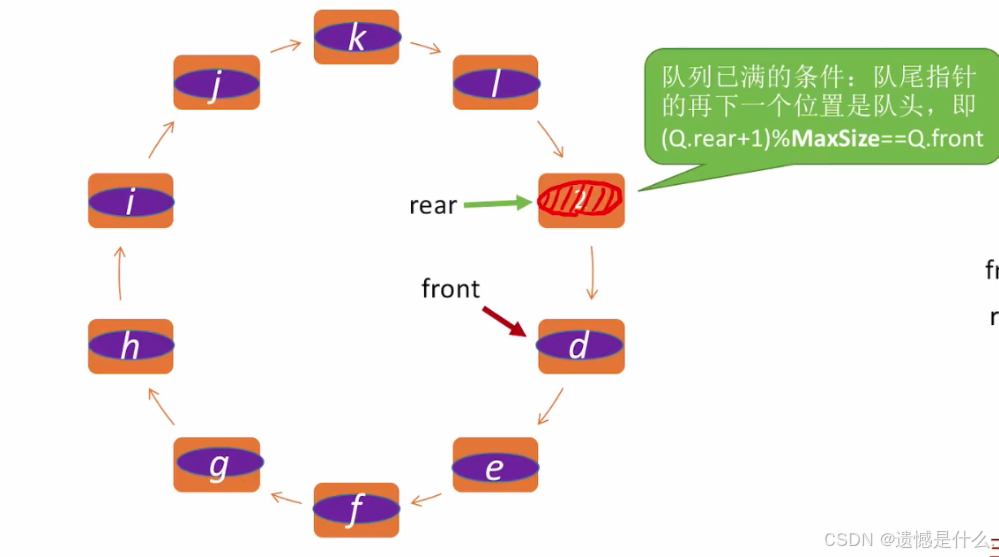
队列已满条件:
rear == MaxSize ? ? ?
并不严谨, 看下一张图
cpp
// 入队(循环队列)
bool EnQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType x) {
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize == Q.front) // 队列已满
return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x; // 将 x 插入队尾
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize; // 队尾指针后移(循环)
return true;
}
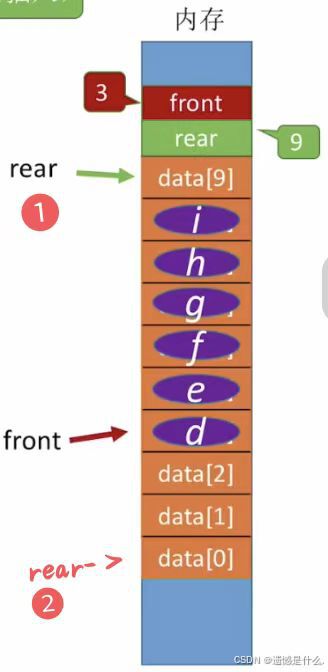 如左图所示:
如左图所示:
此时,当 rear == MaxSize 时,队列并没有满队,
解决这个问题只需进行一个取余的操作:
如右图所示:
此时 rear 指向队尾元素 data[9],
现在在 data[9] 的位置插入元素 j ,
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize;
即, (9 + 1) % 10 = 0,
此时 rear 指向 data[0];
即可继续插入元素.
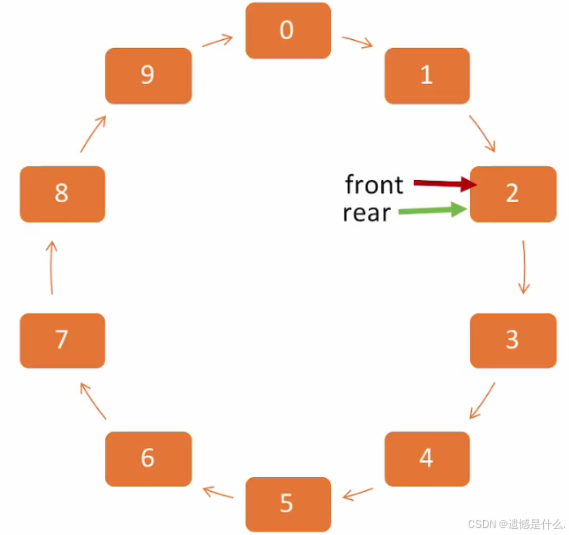
经过此番操作,该队列似乎循环了起来,又称为:
"循环队列"
cpp
Q.data[Q.rear] = x; //将新元素x插入队尾
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize; //队尾指针 +1 再取模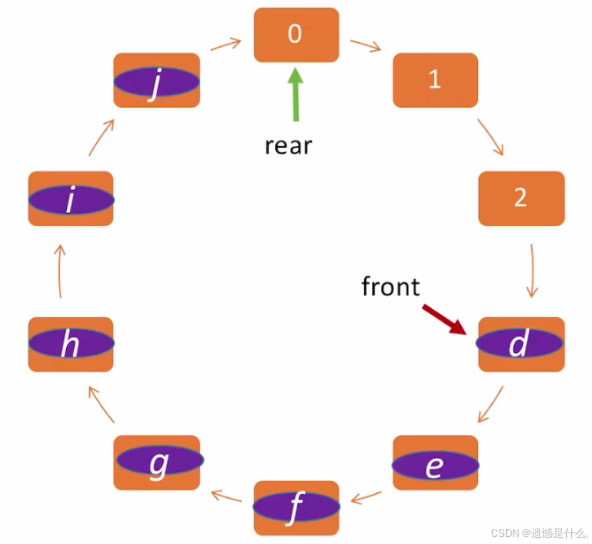
2.入队操作完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front, rear;
}SqQueue;
//初始化队列
void InitQueue(SqQueue& Q) {
//初始时 队头,队尾指针指向0
Q.rear = Q.front = 0;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front)
return true; //队空
else
return false;
}
//入队
bool EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType x) {
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize == Q.front) // 队满
return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x; //将x插入队尾
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize; //队尾指针后移
return true;
}
int main(){
SqQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q, 10);
EnQueue(Q, 20);
EnQueue(Q, 30);
//输出队头元素(不出队)
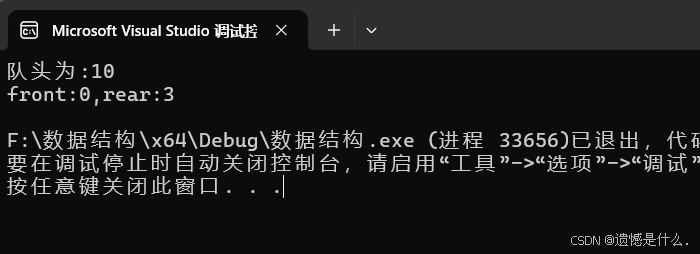
cout << "队头为:" << Q.data[Q.front] << endl;
//输出 rear 和 front 指针位置
cout << "front:" << Q.front << ",rear:" << Q.rear << endl;
}运行结果:
三.顺序存储出队操作
1.出队操作图解
 First
First 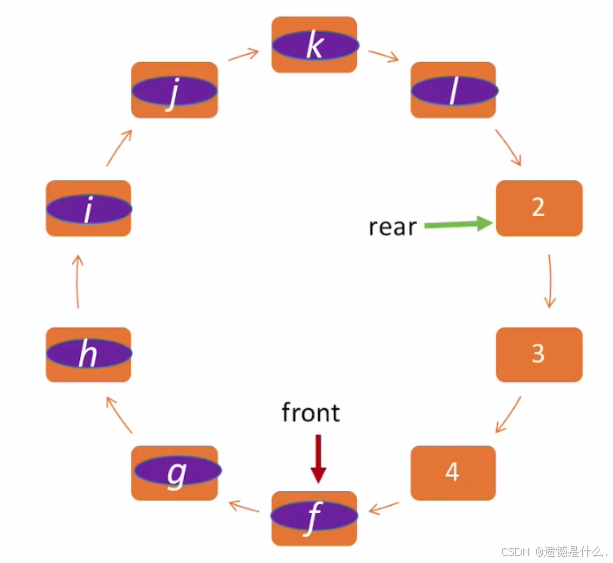 Second
Second
 Forth
Forth 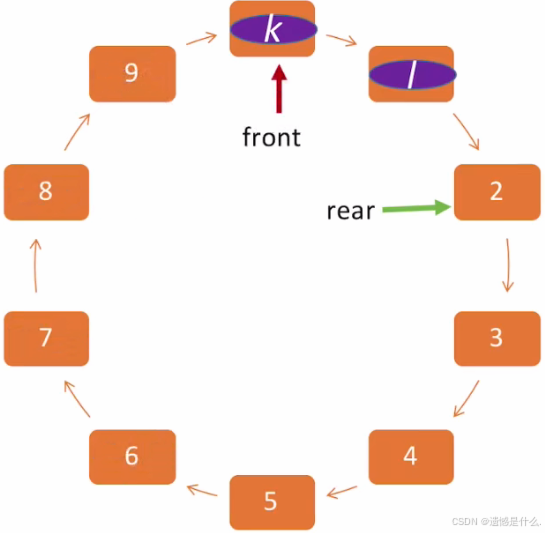 Third
Third
cpp
/* 出队(删除队头元素,并用 x 返回) */
bool DeQueue(SqQueue &Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front) // 队空
return false; // 队空则报错
x = Q.data[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MaxSize; // 队头指针后移(循环)
return true;
}
/* 获得队头元素的值,用 x 返回(不出队) */
bool GetHead(SqQueue Q, ElemType &x) {
if (Q.rear == Q.front) // 队空
return false; // 队空则报错
x = Q.data[Q.front];
return true;
}2.出队操作完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front, rear;
} SqQueue;
// 初始化、判空、入队函数略(与之前相同)
void InitQueue(SqQueue& Q) {
Q.rear = Q.front = 0;
}
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue Q) {
return Q.rear == Q.front;
}
bool EnQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType x) {
if ((Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize == Q.front) // 队满
return false;
Q.data[Q.rear] = x;
Q.rear = (Q.rear + 1) % MaxSize;
return true;
}
/* ---------- 新增:出队操作 ---------- */
bool DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, ElemType& x) {
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) // 队空不能出队
return false;
x = Q.data[Q.front]; // 取出队头元素
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MaxSize; // 头指针循环后移
return true;
}
int main() {
SqQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
EnQueue(Q, 10);
EnQueue(Q, 20);
EnQueue(Q, 30);
ElemType e;
DeQueue(Q, e); // 第一次出队
cout << "出队元素: " << e << endl;
DeQueue(Q, e); // 第二次出队
cout << "出队元素: " << e << endl;
// 此时队列还剩一个元素 30
cout << "当前队头: " << Q.data[Q.front] << endl;
cout << "front: " << Q.front << ", rear: " << Q.rear << endl;
return 0;
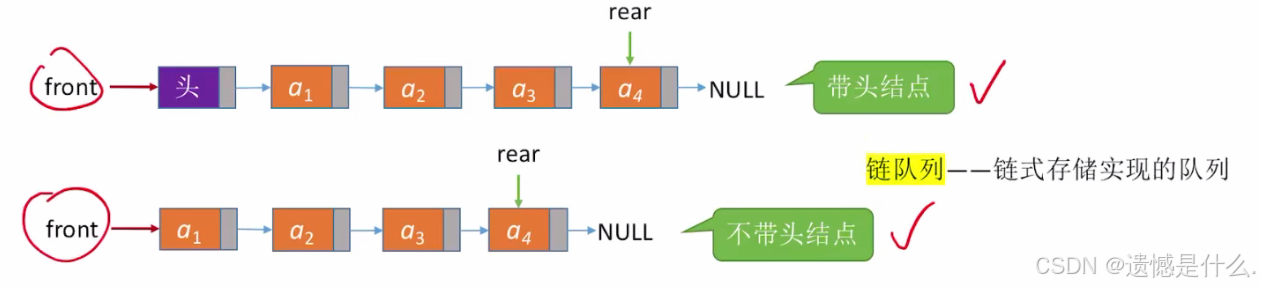
}四.队列的链式实现(带头结点)
1.带头结点与不带头结点
2.带头结点的入队操作
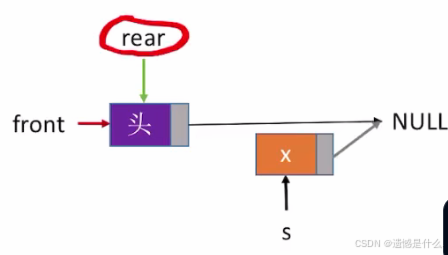
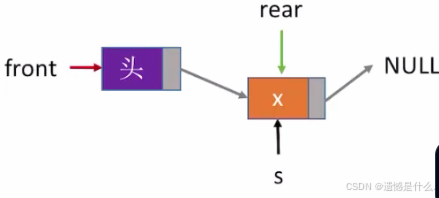
一个新的元素想要入队,那么肯定包含在函数中,
首先用malloc函数申请一个新的结点:
LinkNode * s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
然后把数据元素 x 放在这个新的结点当中:
s->data = x;
因为入队是在表尾进行的, 所以新插入的结点肯定是最后一个结点,
所有把新结点的next指针域设为NULL:
s->next = NULL;
现在要将头结点与新元素 x 连接, 所以将 rear 的 next 指针指向 s :
Q.rear->next = s;
最后将表尾指针指向新的表尾:
Q.rear = s;
cpp
//入队(带头结点)
void EnQueue(LinkNode& Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode* s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
Q.rear->next = s; //新结点插入到 rear 之后
Q.rear = s; //修改表尾指针
}3.带头结点的出队操作
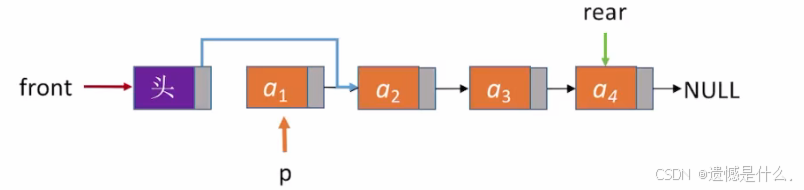
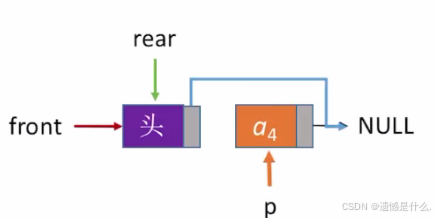
出队操作,首先判断队列是否为空:
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return false;
}
然后修改头结点的后向指针:
Q.front->next = p->next;
如果删除的是表尾最后一个结点,则需要特殊处理(如图2) :
if (Q.rear == p) {
Q.rear = Q.front;
}
如果不是则释放p(如图1):
free(p);
注意,出队时使用了x的地址:
ElemType& x
cpp
//出队(带头结点)
void DeQueue(LinkNode& Q, ElemType& x) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return false;
}
LinkNode* p = Q.front->next;
x = p->data; //用变量 x 返回队头元素
Q.front->next =p ->next; //修改头结点的 next 指针
if (Q.rear == p){ //此次是最后一个结点出队
Q.rear = Q.front; //修改 rear 指针
}
free(p); //释放结点空间
return true;
}4.带头结点的完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct LinkNode {
ElemType data;
struct LinkNode* next;
}LinkNode;
typedef struct {
LinkNode* front, * rear;
}LinkQueue;
//初始化队列(带头结点)
void InitQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
//初始时 front rear 都指向头结点
Q.front = Q.rear = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
Q.front->next = NULL;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(LinkQueue Q) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//入队(带头结点)
void EnQueue(LinkQueue& Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode* s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
Q.rear->next = s;
Q.rear = s;
}
//出队(带头结点)
bool DeQueue(LinkQueue& Q, ElemType& x) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear) {
return false;
}
LinkNode* p = Q.front->next;
x = p->data; //用变量 x 返回队头元素
Q.front->next =p ->next; //修改头结点的 next 指针
if (Q.rear == p){ //此次是最后一个结点出队
Q.rear = Q.front; //修改 rear 指针
}
free(p); //释放结点空间
return true;
}
/* ---------- 测试 ---------- */
int main() {
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
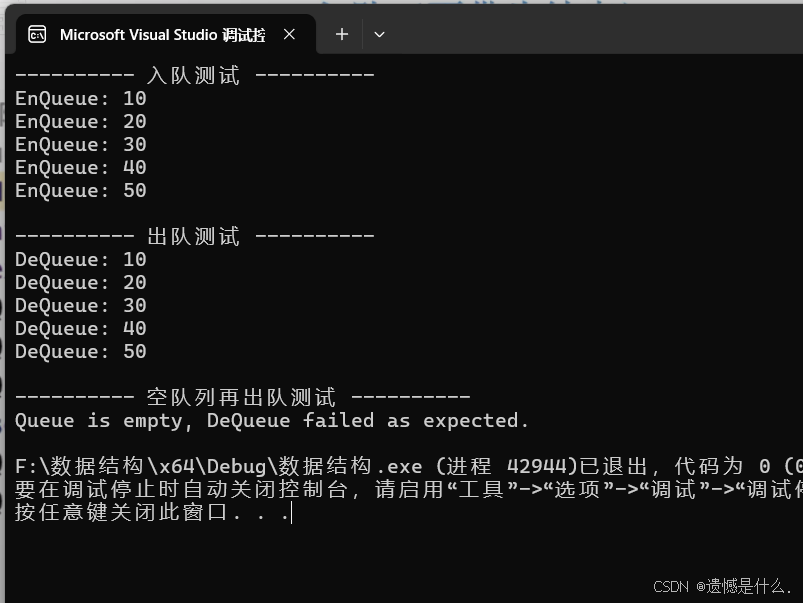
cout << "---------- 入队测试 ----------" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
EnQueue(Q, i * 10);
cout << "EnQueue: " << i * 10 << endl;
}
cout << "\n---------- 出队测试 ----------" << endl;
ElemType x;
while (!IsEmpty(Q)) {
if (DeQueue(Q, x))
cout << "DeQueue: " << x << endl;
}
cout << "\n---------- 空队列再出队测试 ----------" << endl;
if (!DeQueue(Q, x))
cout << "Queue is empty, DeQueue failed as expected." << endl;
// 释放头结点,防止内存泄漏
free(Q.front);
return 0;
}
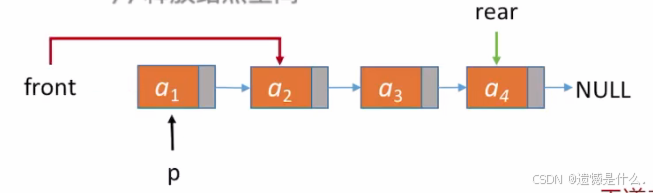
五.队列的链式实现(不带头结点)
1.入队操作
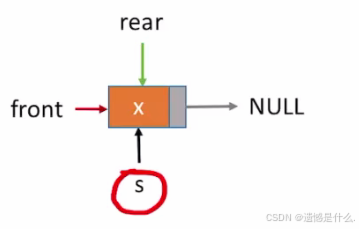 不带头结点时,在插入第一个入队元素时就需要特殊处理
不带头结点时,在插入第一个入队元素时就需要特殊处理
刚开始 rear 和 front 都是指向 NULL
所以插入第一个元素时需要对这两个指针进行修改
首先使用malloc获取存储空间:
LinkNode * s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
然后插入的 s 是队尾元素:
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
接下来进行判断:如果队列为空, 即Q.front == NULL;
那我们就将 front 和 rear 都指向 s;
最后不要忘记修改表尾指针指向:
Q.rear->next = s;
Q.rear = s;
cpp
//入队(不带头结点)
void EnQueue(LinkNode& Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode* s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
if (Q.front == NULL) { //在空队列中插入第一个元素
Q.front = s; //修改队头,队尾指针
Q.rear = s;
}
else {
Q.rear->next = s; //新结点插入到 rear 结点之后
Q.rear = s; //修改 rear 指针
}
}2.出队操作
cpp
//出队(不带头结点)
bool DeQueue(LinkNode& Q, ElemType& x) {
if (Q.front == NULL)
return false; //空队
LinkNode* p = Q.front; //p指向此次出队的结点
x = p->data; //用变量 x 返回队头元素
Q.front = p->next; //修改 front 指针
if (Q.rear == p) { //此次是最后一个结点出队
Q.front = NULL; //front 指向 null
Q.rear = NULL; //rear 指向 null
}
free(p);
return true;
}3.不带头结点的完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct LinkNode {
ElemType data;
struct LinkNode* next;
}LinkNode;
typedef struct {
LinkNode* front, * rear;
}LinkQueue;
//初始化队列(不带头结点)
void InitQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
//初始时 front rear 都指向NULL
Q.front = NULL;
Q.rear = NULL;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool IsEmpty(LinkQueue Q) {
if (Q.front == NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//入队(不带头结点)
void EnQueue(LinkQueue& Q, ElemType x) {
LinkNode* s = (LinkNode*)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = NULL;
if (Q.front == NULL) { //在空队列中插入第一个元素
Q.front = s; //修改队头,队尾指针
Q.rear = s;
}
else {
Q.rear->next = s; //新结点插入到 rear 结点之后
Q.rear = s; //修改 rear 指针
}
}
//出队(不带头结点)
bool DeQueue(LinkQueue& Q, ElemType& x) {
if (Q.front == NULL)
return false; //空队
LinkNode* p = Q.front; //p指向此次出队的结点
x = p->data; //用变量 x 返回队头元素
Q.front = p->next; //修改 front 指针
if (Q.rear == p) { //此次是最后一个结点出队
Q.front = NULL; //front 指向 null
Q.rear = NULL; //rear 指向 null
}
free(p);
return true;
}
int main() {
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
cout << "---------- 入队测试 ----------" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) {
EnQueue(Q, i * 10);
cout << "EnQueue: " << i * 10 << endl;
}
cout << "\n---------- 出队测试 ----------" << endl;
ElemType x;
while (!IsEmpty(Q)) {
if (DeQueue(Q, x))
cout << "DeQueue: " << x << endl;
}
cout << "\n---------- 空队列再出队测试 ----------" << endl;
if (!DeQueue(Q, x))
cout << "Queue is empty, DeQueue failed as expected." << endl;
return 0;
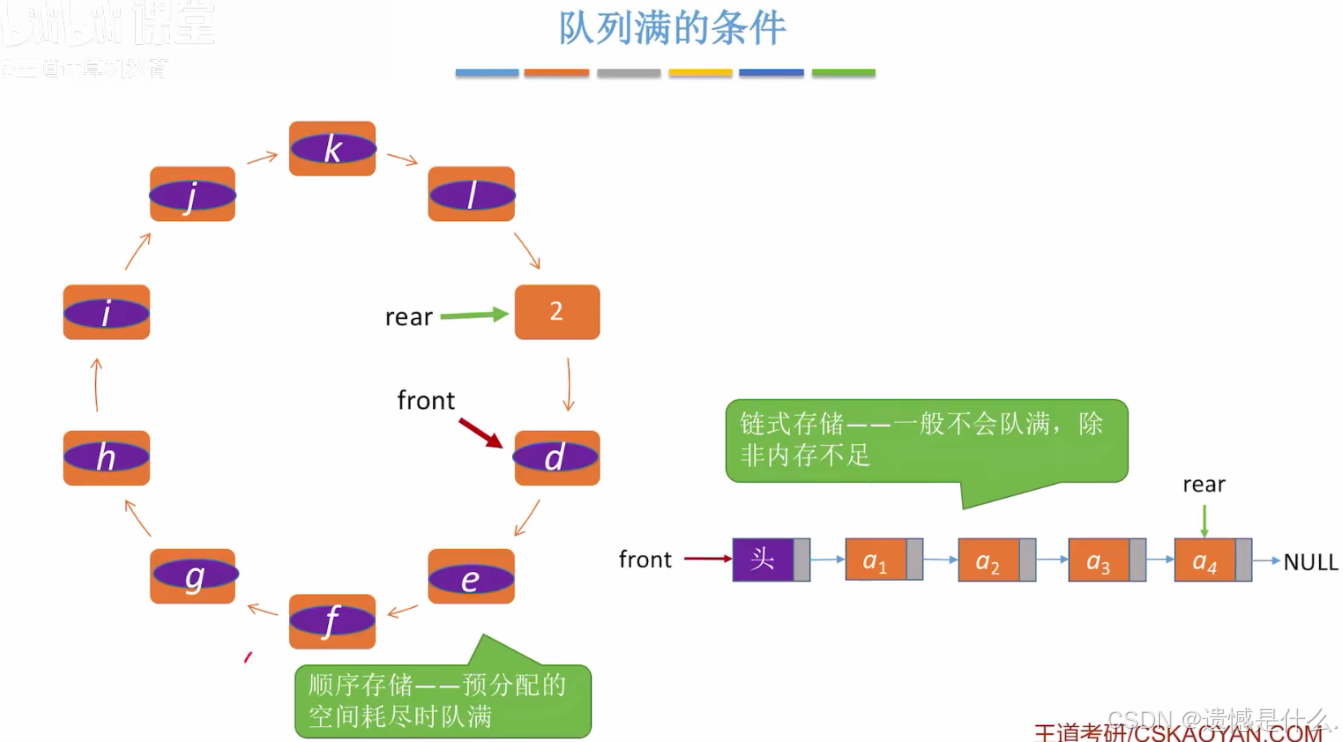
}六.队列满的条件(顺序与链式)
七.双端队列