写在前面
agent 这个话题其实是近年来最火的话题之一,这篇文章就来讲讲如何用go语言通过 mcp+llm+rag 做一个agent demo。
代码都在github上 https://github.com/CocaineCong/llm-mcp-rag ,过段时间B站会出coding视频,感兴趣的同学可以关注同名的B站账号~
整体架构
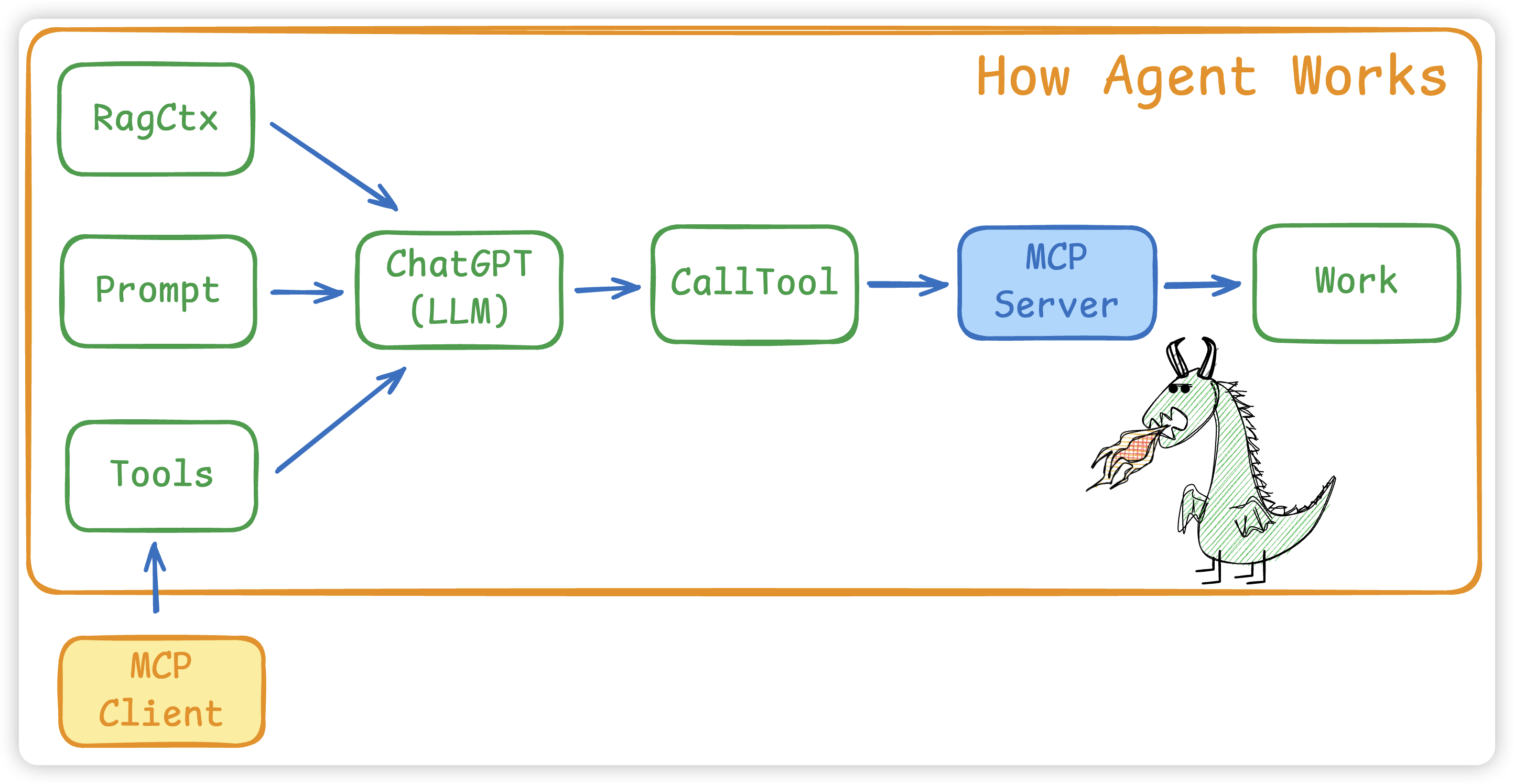
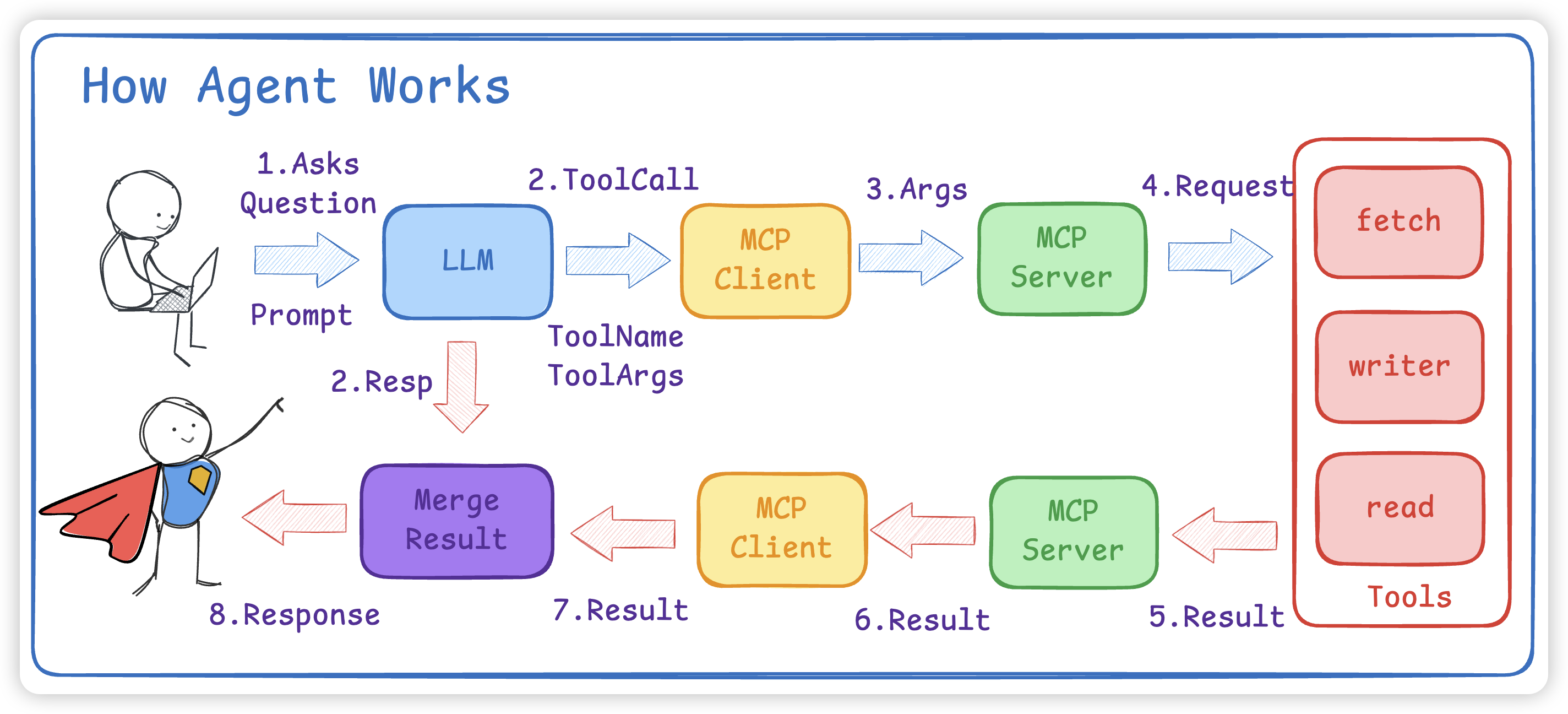
- 将
Prompt和MCP Client 的所有 Tools以及RAG内容给到 LLM - LLM会根据
Prompt + Tools给出使用步骤以及 tools 名字和对应的参数 - 如果有多个MCP Client,要先找到对应的 Tool 是哪个MCP Client
- 接着 MCP Client 会调用 Call Tool 使用工具
- 真正执行是在 MCP Server 中,大模型不会调用,而是需要我们写代码进行 ToolCall
举个例子:如果是想爬取一个网页的内容
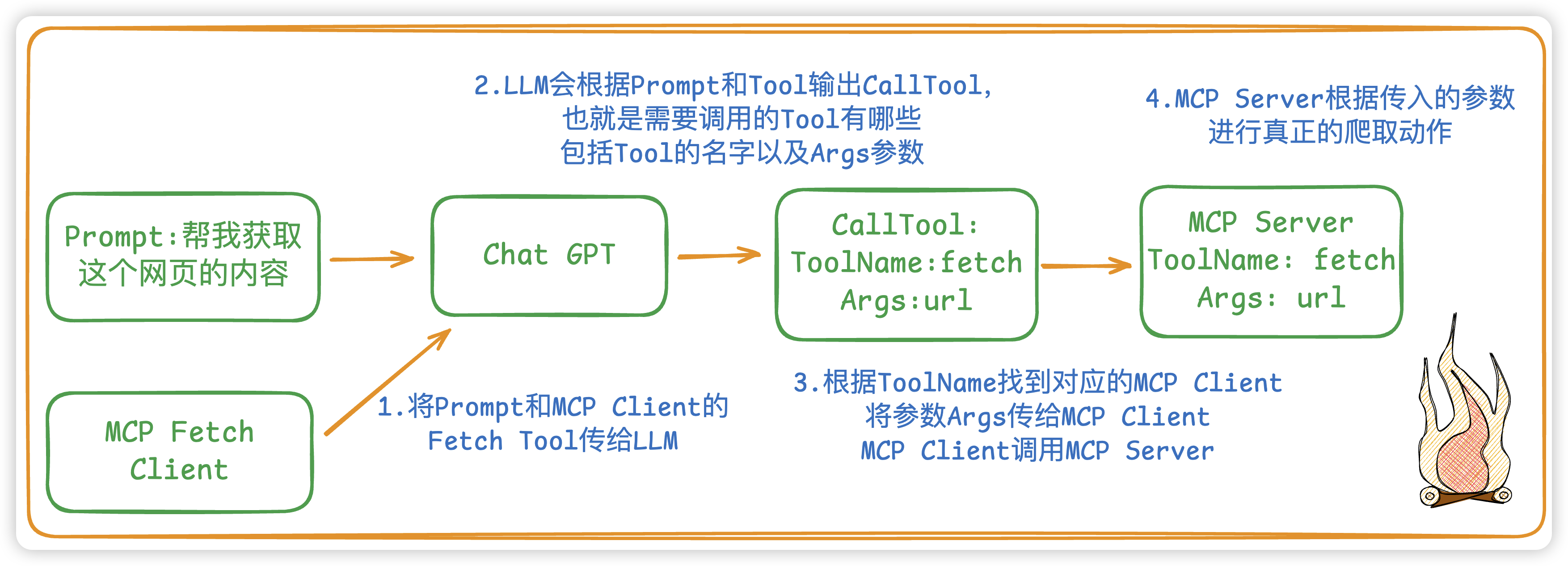
LLM
新建一个LLM,我们就选用 OpenAI 的 ChatGPT 了
- NewChatOpenAI:New一个LLM对象,必须要传一个model name
go
type ChatOpenAI struct {
Ctx context.Context
Model string // 模型名称
Tools []mcp.Tool // 所需要的工具
Message []openai.ChatCompletionMessageParamUnion // LLM的上下文信息(会话历史)
LLM openai.Client // 具体的客户端
}
func NewChatOpenAI(ctx context.Context, model string) *ChatOpenAI {
options := []option.RequestOption{
option.WithAPIKey(os.Getenv(ChatGPTOpenAPIKEY)),
option.WithBaseURL(os.Getenv(ChatGPTBaseURL)),
}
cli := openai.NewClient(options...)
llm := &ChatOpenAI{
Ctx: ctx,
Model: model,
LLM: cli,
Message: make([]openai.ChatCompletionMessageParamUnion, 0),
}
return llm
}- Chat:实现具体和LLM进行Chat,而
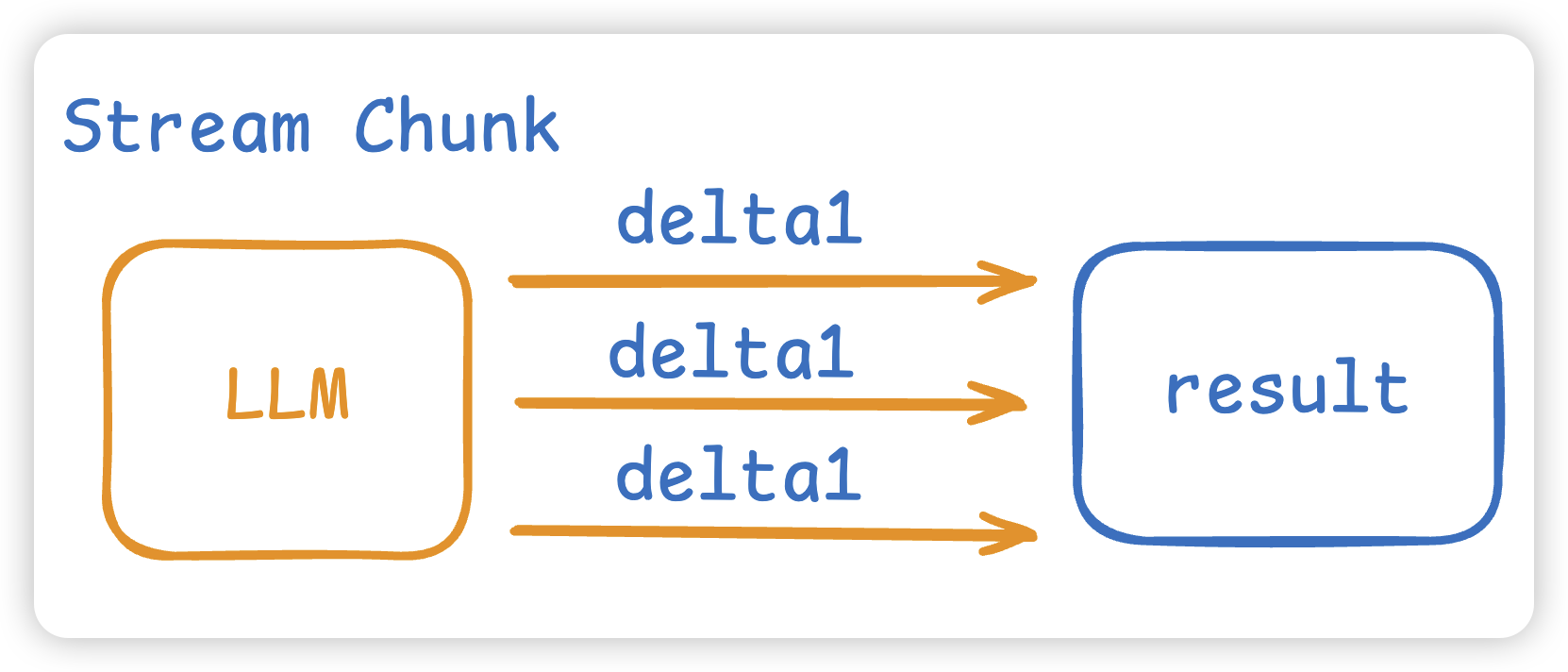
这里我们 Stream 流式进行模型的通信。而这个Chat函数的返回值有两个,一个是模型的结果,另一个是模型让我们调用的工具。
go
func (c *ChatOpenAI) Chat(prompt string) (result string, toolCall []openai.ToolCallUnion) {
// 将prompt保存到message中,作为模型的上下文通信的消息,相当于本次session的缓存动作
if prompt != "" {
c.Message = append(c.Message, openai.UserMessage(prompt))
}
// 将MCP Tool转为OpenAI所理解的Tool的格式
toolsParam := MCPTool2OpenAITool(c.Tools)
stream := c.LLM.Chat.Completions.NewStreaming(c.Ctx, openai.ChatCompletionNewParams{
Messages: c.Message,
Seed: openai.Int(0),
Model: c.Model,
Tools: toolsParam,
})
// 流式结果的累加器,用来将每个分片chunk拼接成完整的消息
acc := openai.ChatCompletionAccumulator{}
var toolCalls []openai.ToolCallUnion // LLM 返回的Tool的结果
for stream.Next() {
chunk := stream.Current() // 当前的stream流的chunk分片
acc.AddChunk(chunk) // 解析每一个chunk,将chunk进行结构化
// 模型完整生成的一个工具调用
if tool, ok := acc.JustFinishedToolCall(); ok {
toolCalls = append(toolCalls, openai.ToolCallUnion{
ID: tool.ID,
Function: openai.FunctionToolCallFunction{
Name: tool.Name,
Arguments: tool.Arguments,
},
})
}
// 模型所吐出的结果,一点一点进行拼接结果
if len(chunk.Choices) > 0 {
result += chunk.Choices[0].Delta.Content
}
}
if len(acc.Choices) > 0 { // 将本次模型的最终回复写入会话历史
c.Message = append(c.Message, acc.Choices[0].Message.ToParam())
}
return result, toolCalls
}MCP
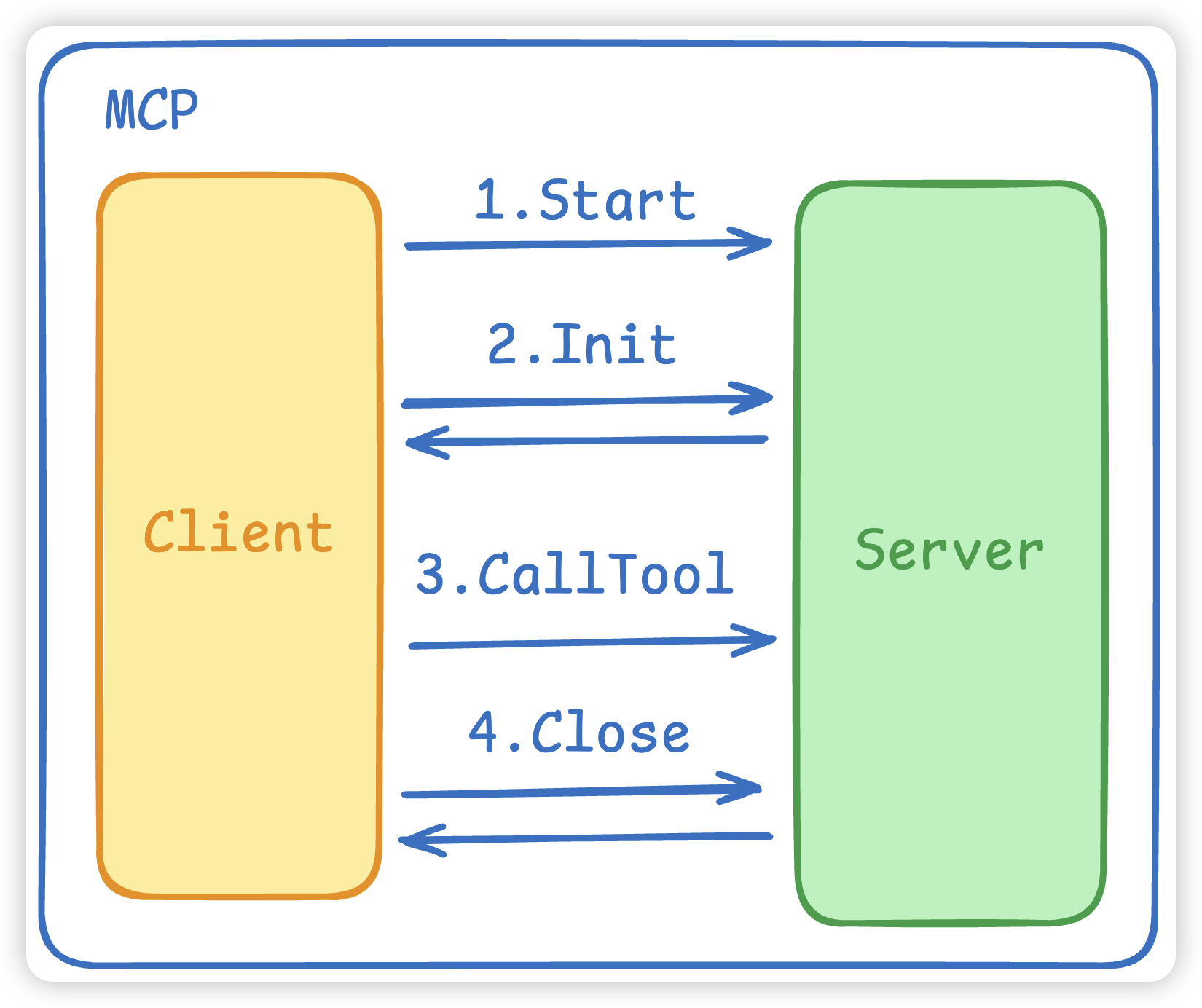
我们MCP用的是这个库 github.com/mark3labs/mcp-go,主要有三个组成部份。
- MCP 的Start启动连接,这会
拉起一个MCP Server进程并建立连接。 - MCP 的初始化 Initialize,这会进行
协议握手,双方进行确认。 - MCP 的 CallTool 将 ToolName 和 Args 发给MCP Server。
go
type MCPClient struct {
Ctx context.Context // 上下文
Client *client.Client // mcp的服务client
Tools []mcp.Tool // mcp 工具
Cmd string // 命令
Args []string // 参数
Env []string
}
func NewMCPClient(ctx context.Context, cmd string, env, args []string) *MCPClient {
stdioTransport := transport.NewStdio(cmd, env, args...) // 使用stdio进行连接通信
cli := client.NewClient(stdioTransport)
m := &MCPClient{Ctx: ctx, Client: cli, Cmd: cmd, Args: args, Env: env}
return m
}- Start:MCP Client的初始化
go
func (m *MCPClient) Start() error {
// 负责把 MCP 服务端真正跑起来并连上
err := m.Client.Start(m.Ctx)
if err != nil {
return err
}
mcpInitReq := mcp.InitializeRequest{}
mcpInitReq.Params.ProtocolVersion = mcp.LATEST_PROTOCOL_VERSION
mcpInitReq.Params.ClientInfo = mcp.Implementation{
Name: "example-client",
Version: "0.0.1",
}
// 让服务端认可我们的客户端与协议版本,再进入"可工作"的状态。
if _, err = m.Client.Initialize(m.Ctx, mcpInitReq); err != nil {
fmt.Println("mcp init error:", err)
return err
}
return err
}- CallTool: MCP进行工具调用,也就是调用MCP Server,具体的实现是在MCP Server中实行。
go
func (m *MCPClient) CallTool(name string, args any) (string, error) {
res, err := m.Client.CallTool(m.Ctx, mcp.CallToolRequest{
Params: mcp.CallToolParams{
Name: name,
Arguments: args,
},
})
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return mcp.GetTextFromContent(res.Content), nil
}Agent
接下来到我们的agent,agent主要是整合了上面的LLM和MCP。
- NewAgent:新建一个Agent
- 激活所有的mcp client 拿到所有的tools
- 激活并告诉llm有哪些tools
go
type Agent struct {
Ctx context.Context
MCPClient []*MCPClient
LLM *ChatOpenAI
Model string
}
func NewAgent(ctx context.Context, model string, mcpCli []*MCPClient) *Agent {
// 1. 激活所有的mcp client 拿到所有的tools
tools := make([]mcp.Tool, 0)
for _, item := range mcpCli {
// 启动 stdio 传输
err := item.Start()
if err != nil {
continue
}
err = item.SetTools()
if err != nil {
continue
}
tools = append(tools, item.GetTool()...)
}
// 2. 激活并告诉llm有哪些tools
llm := NewChatOpenAI(ctx, model, WithLLMTools(tools))
return &Agent{
Ctx: ctx,
MCPClient: mcpCli,
LLM: llm,
Model: model,
}
}- Invoke:具体和LLM通信
- 从上面我们知道 LLM 的 Chat 方法会返回响应和所需要用到的工具 ToolCalls,ToolCalls 里面有对应的ToolName 和所需要的 Args。
- 根据ToolName找到对应的MCP Client,并进行CallTool
- CallTool就是调用
MCP Server去真正的干活
⚠️注意:大模型是不会帮我们执行的,大模型只会给出一个步骤(也就是 tool name 和 tool args),而这个执行步骤是需要我们去写的,也就是真正的MCP Server
核心代码逻辑如下:
go
func (a *Agent) Invoke(prompt string) string {
if a.LLM == nil {
return ""
}
response, toolCalls := a.LLM.Chat(prompt)
for len(toolCalls) > 0 {
// 省略了一些代码... 找到是哪个MCP Client,并进行CallTool
if mcpTool.Name == toolCall.Function.Name {
toolText, err := mcpClient.CallTool(toolCall.Function.Name, toolCall.Function.Arguments)
if err != nil {
continue
}
a.LLM.Message = append(a.LLM.Message, openai.ToolMessage(toolText, toolCall.ID))
}
}
return response
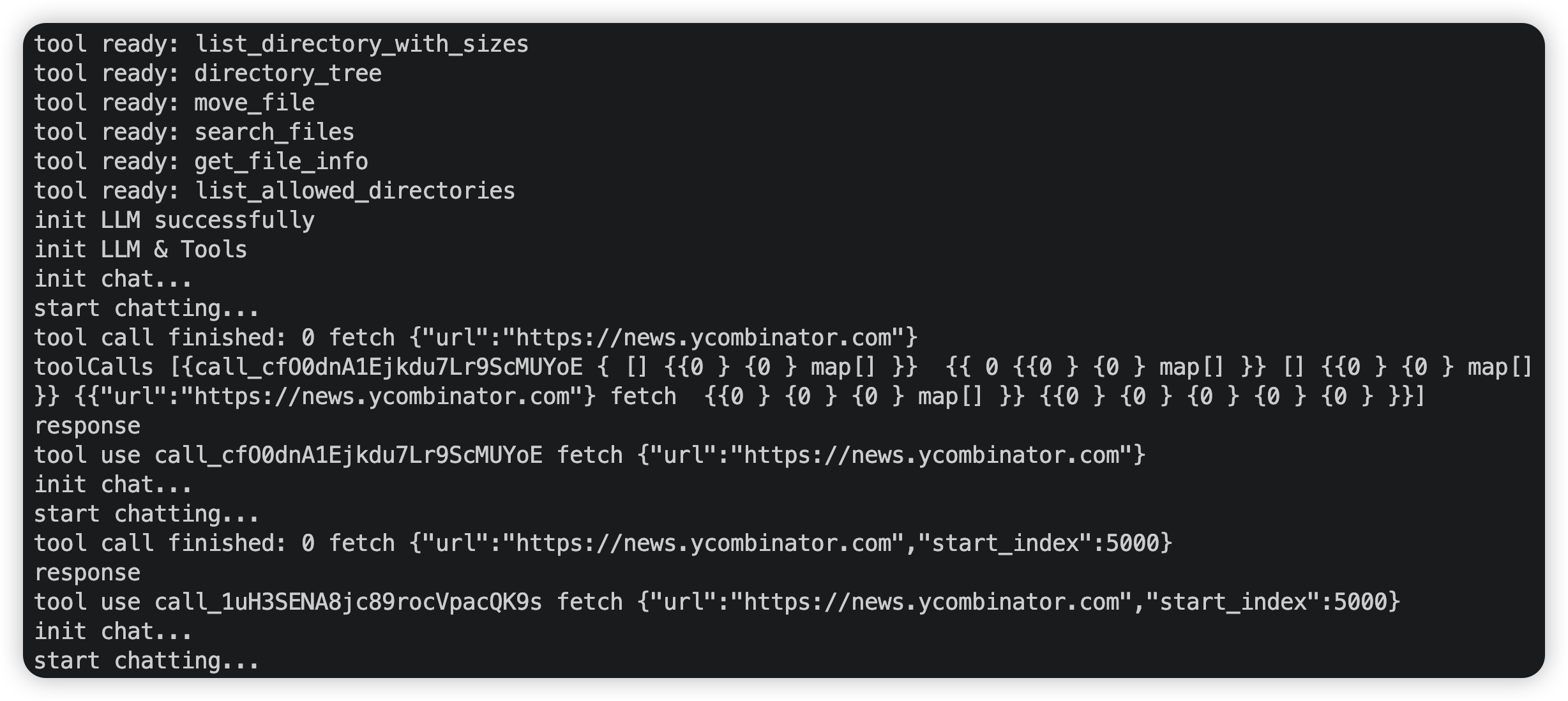
}运行结果: