InfluxDB配合Grafana:打造专业监控可视化平台
1 可视化监控的重要性
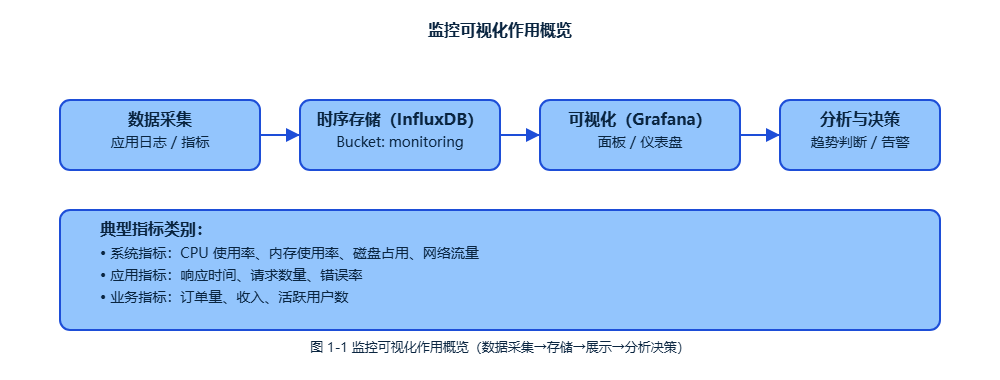
数据收集了一大堆,如果不能直观地展示出来,那就像有了金矿却不知道怎么挖。Grafana就是那把挖金子的铲子,能把InfluxDB里的时序数据变成漂亮的图表和仪表盘。
监控数据可视化不只是为了好看,更重要的是能让我们快速发现问题、分析趋势、做出决策。一张图胜过千行日志,这话一点不假。
1.1 Grafana的核心优势
丰富的图表类型
从简单的折线图到复杂的热力图,Grafana支持几十种可视化方式。不管是展示CPU使用率的时间趋势,还是显示服务器状态的仪表盘,都能找到合适的图表类型。
强大的查询编辑器
Grafana内置了InfluxQL和Flux查询编辑器,支持语法高亮、自动补全、查询历史等功能。即使不熟悉查询语言,也能通过可视化界面构建复杂查询。
灵活的告警机制
可以基于查询结果设置告警规则,支持邮件、钉钉、Slack等多种通知方式。当CPU使用率超过阈值时,立即发送告警通知。
1.2 架构设计思路
我们的监控可视化架构包含三个核心组件:
应用程序 → InfluxDB → Grafana → 用户界面
↓ ↓ ↓
数据采集 数据存储 数据展示这种架构的好处是职责分离,每个组件专注做好自己的事情。应用程序负责收集指标,InfluxDB负责高效存储,Grafana负责美观展示。
2 环境搭建与配置
图 2-1 Docker Compose 部署拓扑(容器、端口与依赖关系)
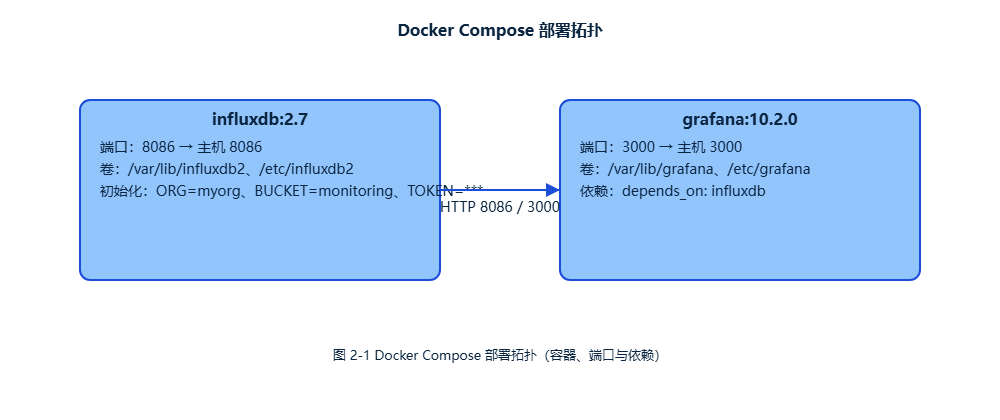
2.1 Docker快速部署
最简单的方式是用Docker Compose一键部署整套环境。
yaml
version: '3.8'
services:
influxdb:
image: influxdb:2.7
container_name: influxdb
ports:
- "8086:8086"
environment:
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_MODE=setup
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_USERNAME=admin
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_PASSWORD=password123
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ORG=myorg
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_BUCKET=monitoring
- DOCKER_INFLUXDB_INIT_ADMIN_TOKEN=my-super-secret-auth-token
volumes:
- influxdb-data:/var/lib/influxdb2
- influxdb-config:/etc/influxdb2
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:10.2.0
container_name: grafana
ports:
- "3000:3000"
environment:
- GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=admin123
- GF_INSTALL_PLUGINS=grafana-clock-panel,grafana-simple-json-datasource
volumes:
- grafana-data:/var/lib/grafana
- grafana-config:/etc/grafana
depends_on:
- influxdb
volumes:
influxdb-data:
influxdb-config:
grafana-data:
grafana-config:启动命令很简单:
bash
docker-compose up -d等容器启动完成后,访问 http://localhost:3000 就能看到Grafana登录界面,用户名admin,密码admin123。
2.2 数据源配置
在Grafana中添加InfluxDB数据源是第一步。进入Configuration → Data Sources → Add data source,选择InfluxDB。
InfluxDB 2.x配置参数:
- URL: http://influxdb:8086
- Organization: myorg
- Token: my-super-secret-auth-token
- Default Bucket: monitoring
配置完成后点击"Save & Test",看到绿色的"Data source is working"就说明连接成功了。
3 Java应用集成Grafana
3.1 监控数据生产者
首先我们需要一个Java应用来产生监控数据。这里创建一个完整的监控数据生产者。
java
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClient;
import com.influxdb.client.InfluxDBClientFactory;
import com.influxdb.client.WriteApiBlocking;
import com.influxdb.client.domain.WritePrecision;
import com.influxdb.client.write.Point;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import java.lang.management.ManagementFactory;
import java.lang.management.MemoryMXBean;
import java.lang.management.OperatingSystemMXBean;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
public class MonitoringApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MonitoringApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Component
public class MetricsProducer {
private InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
private WriteApiBlocking writeApi;
private final Random random = new Random();
private final String hostname = "demo-server";
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
this.influxDBClient = InfluxDBClientFactory.create(
"http://localhost:8086",
"my-super-secret-auth-token".toCharArray(),
"myorg",
"monitoring"
);
this.writeApi = influxDBClient.getWriteApiBlocking();
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 5000) // 每5秒执行一次
public void collectSystemMetrics() {
try {
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
// 收集真实的系统指标
OperatingSystemMXBean osBean = ManagementFactory.getOperatingSystemMXBean();
MemoryMXBean memoryBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
// CPU使用率(模拟数据,因为Java获取CPU使用率比较复杂)
double cpuUsage = 20 + random.nextGaussian() * 10;
cpuUsage = Math.max(0, Math.min(100, cpuUsage));
Point cpuPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "cpu")
.addField("usage_percent", cpuUsage)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 内存使用率
long usedMemory = memoryBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getUsed();
long maxMemory = memoryBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getMax();
double memoryUsage = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory * 100;
Point memoryPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "memory")
.addField("used_bytes", usedMemory)
.addField("max_bytes", maxMemory)
.addField("usage_percent", memoryUsage)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 磁盘使用率(模拟数据)
double diskUsage = 45 + random.nextGaussian() * 5;
diskUsage = Math.max(0, Math.min(100, diskUsage));
Point diskPoint = Point.measurement("system_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("metric_type", "disk")
.addTag("mount_point", "/")
.addField("usage_percent", diskUsage)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 网络流量(模拟数据)
long networkIn = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(1000000, 10000000);
long networkOut = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong(500000, 5000000);
Point networkPoint = Point.measurement("network_metrics")
.addTag("host", hostname)
.addTag("interface", "eth0")
.addField("bytes_in", networkIn)
.addField("bytes_out", networkOut)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 批量写入
writeApi.writePoints(Arrays.asList(cpuPoint, memoryPoint, diskPoint, networkPoint));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("收集系统指标失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 10000) // 每10秒执行一次
public void collectApplicationMetrics() {
try {
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
// 模拟应用性能指标
double responseTime = 100 + random.nextGaussian() * 50;
responseTime = Math.max(10, responseTime);
int requestCount = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(50, 200);
int errorCount = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(0, 5);
double errorRate = (double) errorCount / requestCount * 100;
Point appPoint = Point.measurement("application_metrics")
.addTag("service", "user-service")
.addTag("endpoint", "/api/users")
.addField("response_time_ms", responseTime)
.addField("request_count", requestCount)
.addField("error_count", errorCount)
.addField("error_rate_percent", errorRate)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
// 数据库连接池指标
int activeConnections = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(5, 20);
int idleConnections = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10, 30);
int totalConnections = activeConnections + idleConnections;
Point dbPoint = Point.measurement("database_metrics")
.addTag("pool_name", "hikari-pool")
.addField("active_connections", activeConnections)
.addField("idle_connections", idleConnections)
.addField("total_connections", totalConnections)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoints(Arrays.asList(appPoint, dbPoint));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("收集应用指标失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000) // 每30秒执行一次
public void collectBusinessMetrics() {
try {
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
// 模拟业务指标
int userRegistrations = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(0, 10);
int orderCount = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(20, 100);
double revenue = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble(1000, 5000);
int activeUsers = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(500, 2000);
Point businessPoint = Point.measurement("business_metrics")
.addTag("region", "beijing")
.addTag("product", "mobile_app")
.addField("user_registrations", userRegistrations)
.addField("order_count", orderCount)
.addField("revenue", revenue)
.addField("active_users", activeUsers)
.time(timestamp, WritePrecision.NS);
writeApi.writePoint(businessPoint);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("收集业务指标失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void cleanup() {
if (influxDBClient != null) {
influxDBClient.close();
}
}
}3.2 Grafana API集成
有时候我们需要通过程序来管理Grafana的仪表盘、数据源等。Grafana提供了完整的REST API。
java
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.http.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class GrafanaApiService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final String grafanaUrl = "http://localhost:3000";
private final String apiKey = "your-grafana-api-key"; // 需要在Grafana中生成
public GrafanaApiService() {
this.restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
private HttpHeaders createHeaders() {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
headers.setBearerAuth(apiKey);
return headers;
}
// 创建数据源
public String createDataSource(String name, String url, String token, String org, String bucket) {
try {
Map<String, Object> dataSource = new HashMap<>();
dataSource.put("name", name);
dataSource.put("type", "influxdb");
dataSource.put("url", url);
dataSource.put("access", "proxy");
dataSource.put("isDefault", false);
Map<String, Object> jsonData = new HashMap<>();
jsonData.put("version", "Flux");
jsonData.put("organization", org);
jsonData.put("defaultBucket", bucket);
jsonData.put("httpMode", "POST");
dataSource.put("jsonData", jsonData);
Map<String, Object> secureJsonData = new HashMap<>();
secureJsonData.put("token", token);
dataSource.put("secureJsonData", secureJsonData);
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> request = new HttpEntity<>(dataSource, createHeaders());
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(
grafanaUrl + "/api/datasources", request, String.class);
return response.getBody();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("创建数据源失败", e);
}
}
// 创建仪表盘
public String createDashboard(String title, String description) {
try {
Map<String, Object> dashboard = createSystemMonitoringDashboard(title, description);
Map<String, Object> request = new HashMap<>();
request.put("dashboard", dashboard);
request.put("overwrite", true);
request.put("message", "Created by Java API");
HttpEntity<Map<String, Object>> httpRequest = new HttpEntity<>(request, createHeaders());
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity(
grafanaUrl + "/api/dashboards/db", httpRequest, String.class);
return response.getBody();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("创建仪表盘失败", e);
}
}
private Map<String, Object> createSystemMonitoringDashboard(String title, String description) {
Map<String, Object> dashboard = new HashMap<>();
dashboard.put("title", title);
dashboard.put("description", description);
dashboard.put("tags", new String[]{"monitoring", "system"});
dashboard.put("timezone", "browser");
dashboard.put("refresh", "30s");
// 时间范围设置
Map<String, Object> time = new HashMap<>();
time.put("from", "now-1h");
time.put("to", "now");
dashboard.put("time", time);
// 创建面板
dashboard.put("panels", createPanels());
return dashboard;
}
private Object[] createPanels() {
return new Object[] {
createCpuPanel(),
createMemoryPanel(),
createDiskPanel(),
createNetworkPanel(),
createApplicationPanel()
};
}
private Map<String, Object> createCpuPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 1);
panel.put("title", "CPU使用率");
panel.put("type", "timeseries");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 12, "x", 0, "y", 0));
// 查询配置
Map<String, Object> target = new HashMap<>();
target.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.metric_type == \"cpu\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"usage_percent\")");
target.put("refId", "A");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{target});
// 图表选项
Map<String, Object> fieldConfig = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("unit", "percent");
defaults.put("min", 0);
defaults.put("max", 100);
fieldConfig.put("defaults", defaults);
panel.put("fieldConfig", fieldConfig);
return panel;
}
private Map<String, Object> createMemoryPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 2);
panel.put("title", "内存使用率");
panel.put("type", "timeseries");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 12, "x", 12, "y", 0));
Map<String, Object> target = new HashMap<>();
target.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.metric_type == \"memory\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"usage_percent\")");
target.put("refId", "A");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{target});
Map<String, Object> fieldConfig = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("unit", "percent");
defaults.put("min", 0);
defaults.put("max", 100);
fieldConfig.put("defaults", defaults);
panel.put("fieldConfig", fieldConfig);
return panel;
}
private Map<String, Object> createDiskPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 3);
panel.put("title", "磁盘使用率");
panel.put("type", "gauge");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 8, "x", 0, "y", 8));
Map<String, Object> target = new HashMap<>();
target.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.metric_type == \"disk\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"usage_percent\") " +
"|> last()");
target.put("refId", "A");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{target});
Map<String, Object> fieldConfig = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("unit", "percent");
defaults.put("min", 0);
defaults.put("max", 100);
// 阈值设置
Map<String, Object> thresholds = new HashMap<>();
thresholds.put("mode", "absolute");
thresholds.put("steps", new Object[]{
Map.of("color", "green", "value", 0),
Map.of("color", "yellow", "value", 70),
Map.of("color", "red", "value", 90)
});
defaults.put("thresholds", thresholds);
fieldConfig.put("defaults", defaults);
panel.put("fieldConfig", fieldConfig);
return panel;
}
private Map<String, Object> createNetworkPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 4);
panel.put("title", "网络流量");
panel.put("type", "timeseries");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 8, "x", 8, "y", 8));
// 入站流量查询
Map<String, Object> targetIn = new HashMap<>();
targetIn.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"network_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"bytes_in\") " +
"|> derivative(unit: 1s, nonNegative: true)");
targetIn.put("refId", "A");
targetIn.put("alias", "入站流量");
// 出站流量查询
Map<String, Object> targetOut = new HashMap<>();
targetOut.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"network_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"bytes_out\") " +
"|> derivative(unit: 1s, nonNegative: true)");
targetOut.put("refId", "B");
targetOut.put("alias", "出站流量");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{targetIn, targetOut});
Map<String, Object> fieldConfig = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("unit", "Bps");
fieldConfig.put("defaults", defaults);
panel.put("fieldConfig", fieldConfig);
return panel;
}
private Map<String, Object> createApplicationPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 5);
panel.put("title", "应用响应时间");
panel.put("type", "stat");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 8, "x", 16, "y", 8));
Map<String, Object> target = new HashMap<>();
target.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"application_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"response_time_ms\") " +
"|> mean()");
target.put("refId", "A");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{target});
Map<String, Object> fieldConfig = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> defaults = new HashMap<>();
defaults.put("unit", "ms");
defaults.put("displayName", "平均响应时间");
fieldConfig.put("defaults", defaults);
panel.put("fieldConfig", fieldConfig);
return panel;
}
// 获取仪表盘列表
public String getDashboards() {
try {
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<>(createHeaders());
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.exchange(
grafanaUrl + "/api/search?type=dash-db",
HttpMethod.GET,
request,
String.class);
return response.getBody();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("获取仪表盘列表失败", e);
}
}
// 删除仪表盘
public String deleteDashboard(String uid) {
try {
HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<>(createHeaders());
ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.exchange(
grafanaUrl + "/api/dashboards/uid/" + uid,
HttpMethod.DELETE,
request,
String.class);
return response.getBody();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("删除仪表盘失败", e);
}
}
}3.3 自动化仪表盘管理
我们可以创建一个管理服务,自动化地创建和更新Grafana仪表盘。
java
@Service
public class DashboardManagementService {
private final GrafanaApiService grafanaApiService;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
public DashboardManagementService(GrafanaApiService grafanaApiService) {
this.grafanaApiService = grafanaApiService;
this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
@PostConstruct
public void initializeDashboards() {
try {
// 创建系统监控仪表盘
createSystemMonitoringDashboard();
// 创建应用性能仪表盘
createApplicationPerformanceDashboard();
// 创建业务指标仪表盘
createBusinessMetricsDashboard();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("初始化仪表盘失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void createSystemMonitoringDashboard() {
try {
String result = grafanaApiService.createDashboard(
"系统监控总览",
"服务器系统资源监控,包括CPU、内存、磁盘、网络等指标"
);
JsonNode response = objectMapper.readTree(result);
if (response.has("uid")) {
System.out.println("系统监控仪表盘创建成功,UID: " + response.get("uid").asText());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("创建系统监控仪表盘失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void createApplicationPerformanceDashboard() {
// 这里可以创建专门的应用性能监控仪表盘
// 包含响应时间、吞吐量、错误率等指标
}
private void createBusinessMetricsDashboard() {
// 这里可以创建业务指标监控仪表盘
// 包含用户注册、订单量、收入等业务相关指标
}
// 定期更新仪表盘配置
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 2 * * ?") // 每天凌晨2点执行
public void updateDashboards() {
try {
// 获取现有仪表盘列表
String dashboardsJson = grafanaApiService.getDashboards();
JsonNode dashboards = objectMapper.readTree(dashboardsJson);
for (JsonNode dashboard : dashboards) {
String title = dashboard.get("title").asText();
String uid = dashboard.get("uid").asText();
// 根据标题判断是否需要更新
if (title.contains("系统监控")) {
updateSystemMonitoringDashboard(uid);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("更新仪表盘失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void updateSystemMonitoringDashboard(String uid) {
// 这里可以实现仪表盘的更新逻辑
// 比如添加新的面板、修改查询语句等
}
}4 高级可视化技巧
4.1 动态仪表盘变量
Grafana支持变量功能,可以让用户动态选择要查看的服务器、时间范围等。这样一个仪表盘就能适应不同的查看需求。
java
@Service
public class DynamicDashboardService {
public Map<String, Object> createDashboardWithVariables() {
Map<String, Object> dashboard = new HashMap<>();
dashboard.put("title", "动态系统监控");
// 创建变量
Object[] templating = createTemplatingVariables();
dashboard.put("templating", Map.of("list", templating));
// 创建使用变量的面板
dashboard.put("panels", createDynamicPanels());
return dashboard;
}
private Object[] createTemplatingVariables() {
return new Object[] {
createHostVariable(),
createMetricTypeVariable(),
createTimeRangeVariable()
};
}
private Map<String, Object> createHostVariable() {
Map<String, Object> variable = new HashMap<>();
variable.put("name", "host");
variable.put("type", "query");
variable.put("label", "服务器");
variable.put("multi", true);
variable.put("includeAll", true);
// 查询所有主机名
Map<String, Object> query = new HashMap<>();
query.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: -24h) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> keep(columns: [\"host\"]) " +
"|> distinct(column: \"host\")");
query.put("refId", "hosts");
variable.put("query", query);
variable.put("refresh", 1); // 每次打开仪表盘时刷新
return variable;
}
private Map<String, Object> createMetricTypeVariable() {
Map<String, Object> variable = new HashMap<>();
variable.put("name", "metric_type");
variable.put("type", "custom");
variable.put("label", "指标类型");
variable.put("multi", false);
// 自定义选项
variable.put("options", new Object[] {
Map.of("text", "CPU", "value", "cpu"),
Map.of("text", "内存", "value", "memory"),
Map.of("text", "磁盘", "value", "disk")
});
variable.put("current", Map.of("text", "CPU", "value", "cpu"));
return variable;
}
private Map<String, Object> createTimeRangeVariable() {
Map<String, Object> variable = new HashMap<>();
variable.put("name", "time_range");
variable.put("type", "interval");
variable.put("label", "时间间隔");
variable.put("options", new Object[] {
Map.of("text", "1分钟", "value", "1m"),
Map.of("text", "5分钟", "value", "5m"),
Map.of("text", "15分钟", "value", "15m"),
Map.of("text", "1小时", "value", "1h")
});
variable.put("current", Map.of("text", "5分钟", "value", "5m"));
return variable;
}
private Object[] createDynamicPanels() {
return new Object[] {
createDynamicMetricPanel()
};
}
private Map<String, Object> createDynamicMetricPanel() {
Map<String, Object> panel = new HashMap<>();
panel.put("id", 1);
panel.put("title", "动态指标监控 - $metric_type");
panel.put("type", "timeseries");
panel.put("gridPos", Map.of("h", 8, "w", 24, "x", 0, "y", 0));
// 使用变量的查询
Map<String, Object> target = new HashMap<>();
target.put("query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.metric_type == \"$metric_type\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.host =~ /^$host$/) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"usage_percent\") " +
"|> aggregateWindow(every: $time_range, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)");
target.put("refId", "A");
panel.put("targets", new Object[]{target});
return panel;
}
}4.2 告警规则配置
Grafana的告警功能可以基于查询结果触发通知。我们可以通过API来配置告警规则。
java
@Service
public class AlertRuleService {
private final GrafanaApiService grafanaApiService;
public AlertRuleService(GrafanaApiService grafanaApiService) {
this.grafanaApiService = grafanaApiService;
}
public void createCpuAlertRule() {
Map<String, Object> alertRule = new HashMap<>();
alertRule.put("uid", "cpu-high-alert");
alertRule.put("title", "CPU使用率过高告警");
alertRule.put("condition", "A");
alertRule.put("data", createCpuAlertData());
alertRule.put("noDataState", "NoData");
alertRule.put("execErrState", "Alerting");
alertRule.put("for", "5m"); // 持续5分钟才触发告警
// 告警注解
Map<String, String> annotations = new HashMap<>();
annotations.put("summary", "服务器CPU使用率超过阈值");
annotations.put("description", "服务器 {{ $labels.host }} CPU使用率为 {{ $value }}%,超过80%阈值");
alertRule.put("annotations", annotations);
// 告警标签
Map<String, String> labels = new HashMap<>();
labels.put("severity", "warning");
labels.put("team", "infrastructure");
alertRule.put("labels", labels);
// 这里需要调用Grafana的告警API
// 实际实现需要根据Grafana版本调整
}
private Object[] createCpuAlertData() {
Map<String, Object> query = new HashMap<>();
query.put("refId", "A");
query.put("queryType", "");
query.put("model", Map.of(
"query",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: -5m) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r.metric_type == \"cpu\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"usage_percent\") " +
"|> mean()",
"refId", "A"
));
Map<String, Object> condition = new HashMap<>();
condition.put("refId", "B");
condition.put("queryType", "");
condition.put("model", Map.of(
"conditions", new Object[] {
Map.of(
"evaluator", Map.of("params", new double[]{80}, "type", "gt"),
"operator", Map.of("type", "and"),
"query", Map.of("params", new String[]{"A"}),
"reducer", Map.of("params", new Object[]{}, "type", "last"),
"type", "query"
)
},
"refId", "B"
));
return new Object[]{query, condition};
}
public void createMemoryAlertRule() {
// 类似CPU告警的内存告警规则
}
public void createResponseTimeAlertRule() {
// 应用响应时间告警规则
}
}5 性能优化与最佳实践
5.1 查询优化
Grafana的性能很大程度上取决于底层查询的效率。优化查询是提升仪表盘性能的关键。
java
@Service
public class QueryOptimizationService {
// 使用聚合窗口减少数据点
public String createOptimizedTimeSeriesQuery(String measurement, String field, String timeRange) {
return String.format(
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: %s) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"%s\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"%s\") " +
"|> aggregateWindow(every: %s, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)",
timeRange, measurement, field, calculateAggregationInterval(timeRange)
);
}
private String calculateAggregationInterval(String timeRange) {
// 根据时间范围自动计算合适的聚合间隔
if (timeRange.contains("1h")) return "30s";
if (timeRange.contains("6h")) return "2m";
if (timeRange.contains("24h")) return "5m";
if (timeRange.contains("7d")) return "30m";
return "1m";
}
// 使用下采样减少数据传输
public String createDownsampledQuery(String measurement, String field, String timeRange) {
return String.format(
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") " +
"|> range(start: %s) " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"%s\") " +
"|> filter(fn: (r) => r._field == \"%s\") " +
"|> aggregateWindow(every: 1m, fn: mean) " +
"|> limit(n: 1000)", // 限制返回的数据点数量
timeRange, measurement, field
);
}
// 并行查询多个指标
public Map<String, String> createParallelQueries(String[] metrics, String timeRange) {
Map<String, String> queries = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < metrics.length; i++) {
String refId = String.valueOf((char)('A' + i));
queries.put(refId, createOptimizedTimeSeriesQuery("system_metrics", metrics[i], timeRange));
}
return queries;
}
}5.2 缓存策略
对于更新频率不高的数据,可以使用缓存来提升查询性能。
java
@Service
public class DashboardCacheService {
private final RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private final InfluxDBClient influxDBClient;
public DashboardCacheService(RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate,
InfluxDBClient influxDBClient) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
this.influxDBClient = influxDBClient;
}
@Cacheable(value = "dashboard-data", key = "#query + '-' + #timeRange")
public String getCachedQueryResult(String query, String timeRange) {
try {
QueryApi queryApi = influxDBClient.getQueryApi();
List<FluxTable> tables = queryApi.query(query);
// 将查询结果转换为JSON格式
return convertTablesToJson(tables);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("查询失败", e);
}
}
private String convertTablesToJson(List<FluxTable> tables) {
// 实现FluxTable到JSON的转换
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
List<Map<String, Object>> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (FluxTable table : tables) {
for (FluxRecord record : table.getRecords()) {
Map<String, Object> point = new HashMap<>();
point.put("time", record.getTime());
point.put("value", record.getValue());
point.put("measurement", record.getMeasurement());
point.put("field", record.getField());
// 添加所有标签
record.getValues().forEach((key, value) -> {
if (key.startsWith("_") || key.equals("result") || key.equals("table")) {
return;
}
point.put(key, value);
});
result.add(point);
}
}
try {
return mapper.writeValueAsString(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("JSON转换失败", e);
}
}
// 预热缓存
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 300000) // 每5分钟执行一次
public void warmupCache() {
String[] commonQueries = {
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") |> range(start: -1h) |> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"system_metrics\")",
"from(bucket: \"monitoring\") |> range(start: -24h) |> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == \"application_metrics\")"
};
for (String query : commonQueries) {
try {
getCachedQueryResult(query, "-1h");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("预热缓存失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// 清理过期缓存
@CacheEvict(value = "dashboard-data", allEntries = true)
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0 */6 * * ?") // 每6小时清理一次
public void clearExpiredCache() {
System.out.println("清理仪表盘缓存");
}
}这套InfluxDB配合Grafana的可视化方案提供了完整的监控数据展示能力。从数据收集到可视化展示,再到告警通知,形成了一个闭环的监控体系。
关键是要根据实际业务需求来设计仪表盘,不要为了炫酷而炫酷。好的监控仪表盘应该能让人一眼就看出系统的健康状况,快速定位问题所在。记住,简洁明了比花里胡哨更重要。