如果能让Claude直接读取你的GitHub仓库、操作Notion文档、查询数据库,那该有多爽?但现实是,每次接入一个新服务,你都要写一堆工具定义、测试API、处理异常...简直是体力活。
MCP(Model Context Protocol)就是来解决这个痛点的。 它把集成外部服务的脏活累活全部打包到标准化的服务端,你只需要连上去就能用。就像你不需要自己实现HTTP协议一样,你也不需要从零开始写GitHub的100个API工具。
这篇文章会带你从零开始理解MCP的工作原理,并亲手搭建一个完整的文档管理系统。看完你就知道怎么让Claude成为你的得力助手。
一、MCP到底解决了什么问题?
传统方式的痛点
假设你要做一个聊天界面,用户可以问Claude:"我的GitHub上有哪些开着的PR?"
++没有MCP时你需要做什么:++
- 研究GitHub API文档,找到获取PR的接口
- 为每个API端点写工具定义(JSON Schema)
- 实现工具函数,处理认证、请求、错误
- 测试每个工具,确保Claude能正确调用
- 维护这一大堆代码
GitHub的功能极其庞大------仓库、PR、Issue、Projects...你得写几十上百个工具定义。更要命的是,GitHub API一更新,你的代码就得跟着改。
MCP的解决方案
MCP把工具定义和执行逻辑都搬到了专门的MCP Server上。 你的应用只需要连接这个Server,就能获得所有工具,不用自己写一行集成代码。
arduino
传统方式:你的应用 → 写100个工具 → 调用GitHub API
MCP方式:你的应用 → MCP Client → MCP Server(已经实现好的100个工具) → GitHub API关键优势:
- 工具定义已经写好 --- 别人帮你测试过的高质量工具
- 维护成本转移 --- API变更由MCP Server作者处理
- 标准化接口 --- 所有MCP Server用统一的协议通信
二、MCP的核心架构:三个角色,一套流程
架构概览
arduino
用户提问
↓
你的应用(MCP Client)
↓
MCP Server(工具集合)
↓
外部服务(GitHub/Notion/数据库...)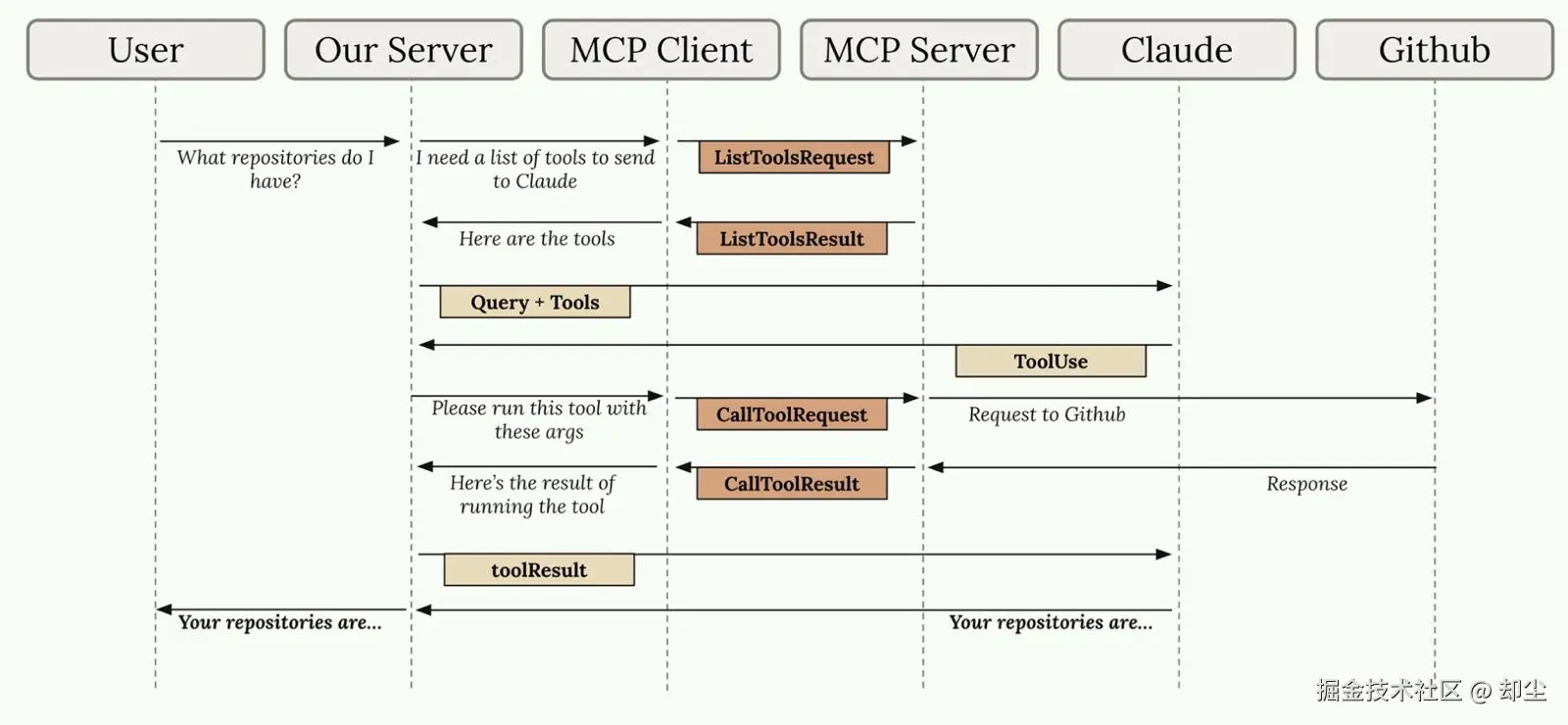
MCP Client 是你的应用代码,负责和MCP Server通信。
MCP Server 是独立的服务进程,封装了某个领域的工具(比如GitHub专属Server、AWS专属Server)。
通信协议 支持多种传输方式:标准输入输出(stdio)、HTTP、WebSocket等。最常见的是本地运行时用stdio。
一次完整的对话流程
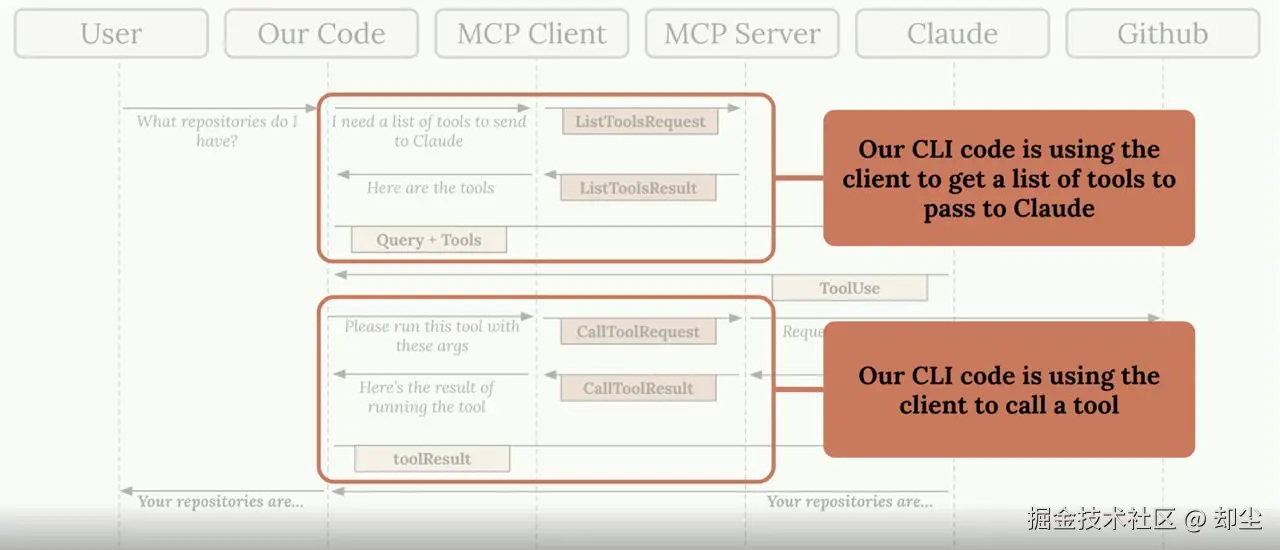
以"我有哪些仓库?"这个问题为例:
- 用户发起提问 → 你的应用收到请求
- 获取可用工具 → 应用通过Client向Server发送
ListToolsRequest - Server返回工具列表 → 比如
get_repos、list_issues等 - 发送给Claude → 应用把问题+工具列表一起发给Claude API
- Claude决策 → "我需要调用
get_repos工具" - 执行工具 → 应用通过Client发送
CallToolRequest给Server - Server调用GitHub API → 获取真实数据
- 结果回流 → Server返回
CallToolResult,应用再发给Claude - Claude生成回答 → "你有3个仓库:repo1、repo2、repo3"
- 返回用户 → 应用展示最终答案
这个流程看起来步骤很多,但每个组件职责清晰 。MCP Client帮你抽象掉了和Server通信的复杂性,你只需要调用简单的list_tools()和call_tool()方法。
三、动手实战:搭建一个文档管理Server
理论讲完,现在写代码。我们要实现一个内存文档管理系统,支持读取和编辑文档。
3.1 初始化MCP Server
使用官方Python SDK,创建Server只需一行:
python
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP("DocumentMCP", log_level="ERROR")准备一些测试文档:
python
docs = {
"deposition.md": "This deposition covers the testimony of Angela Smith, P.E.",
"report.pdf": "The report details the state of a 20m condenser tower.",
"financials.docx": "These financials outline the project's budget",
"outlook.pdf": "This document presents the projected future performance",
"plan.md": "The plan outlines the steps for implementation.",
"spec.txt": "Technical requirements for the equipment"
}3.2 定义第一个工具:读取文档
用装饰器定义工具,SDK会自动生成Claude能理解的JSON Schema:
python
from pydantic import Field
@mcp.tool(
name="read_doc_contents",
description="Read the contents of a document and return it as a string."
)
def read_document(
doc_id: str = Field(description="Id of the document to read")
):
if doc_id not in docs:
raise ValueError(f"Doc with id {doc_id} not found")
return docs[doc_id]关键点:
@mcp.tool装饰器自动注册工具Field提供参数描述,帮助Claude理解每个参数的用途- 类型提示(
str)提供自动校验 - 返回值直接返回字符串,SDK处理序列化
3.3 定义第二个工具:编辑文档
实现简单的查找替换功能:
python
@mcp.tool(
name="edit_document",
description="Edit a document by replacing a string with a new string."
)
def edit_document(
doc_id: str = Field(description="Id of the document to edit"),
old_str: str = Field(description="Text to replace. Must match exactly."),
new_str: str = Field(description="New text to insert.")
):
if doc_id not in docs:
raise ValueError(f"Doc with id {doc_id} not found")
docs[doc_id] = docs[doc_id].replace(old_str, new_str)
return f"Successfully replaced '{old_str}' with '{new_str}' in {doc_id}"对比传统方式: 如果不用MCP,你需要手写这样的JSON Schema:
python
{
"name": "edit_document",
"description": "Edit a document...",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"doc_id": {"type": "string", "description": "..."},
"old_str": {"type": "string", "description": "..."},
"new_str": {"type": "string", "description": "..."}
},
"required": ["doc_id", "old_str", "new_str"]
}
}用SDK后,这些全部自动生成。
四、调试神器:MCP Inspector
写完代码后怎么测试?MCP SDK内置了一个浏览器调试工具。
启动Inspector
bash
mcp dev mcp_server.py访问http://127.0.0.1:6274,你会看到一个Web界面。
测试工具
- 点击Connect按钮启动Server
- 进入Tools 标签,点击List Tools
- 选择
read_doc_contents工具 - 输入
doc_id为report.pdf - 点击Run Tool
- 查看返回结果:
"The report details the state of a 20m condenser tower."
测试工具链
可以连续测试多个工具:
- 先用
edit_document修改文档 - 再用
read_doc_contents验证修改是否生效
Inspector会保持Server状态,所以修改会持久化(在内存中)。
开发建议: 在写复杂工具时,先在Inspector里测试边界条件(比如传入不存在的doc_id),确保错误处理正确。
五、实现MCP Client:连接Server的桥梁
Server写完了,现在需要一个Client来使用这些工具。
5.1 Client架构
Client包含两部分:
- ClientSession --- SDK提供的底层连接对象
- 自定义Client类 --- 封装Session,简化使用
为什么要封装?因为Session需要手动管理资源(连接的打开和关闭),封装后可以用Python的async with自动处理。
5.2 实现核心方法
列出所有工具
python
async def list_tools(self) -> list[types.Tool]:
result = await self.session().list_tools()
return result.tools这个方法返回Server提供的所有工具定义,你会把这些工具发给Claude。
执行工具
python
async def call_tool(
self, tool_name: str, tool_input: dict
) -> types.CallToolResult | None:
return await self.session().call_tool(tool_name, tool_input)当Claude决定调用某个工具时,你用这个方法转发请求给Server。
5.3 测试Client
Client文件通常包含一个测试入口:
python
if __name__ == "__main__":
import asyncio
async def test():
async with MCPClient() as client:
tools = await client.list_tools()
print(f"Found {len(tools)} tools:")
for tool in tools:
print(f" - {tool.name}: {tool.description}")
asyncio.run(test())运行:
bash
uv run mcp_client.py你应该看到:
bash
Found 2 tools:
- read_doc_contents: Read the contents of a document...
- edit_document: Edit a document by replacing a string...六、Resources:给应用提供数据
Tools是给Claude用的,Resources是给你的应用代码用的。典型场景是UI自动补全或注入上下文。
使用场景
假设你要实现一个@文档名的提及功能:
- 输入
@时,自动补全显示所有可用文档 - 选择文档后,自动把文档内容注入到发给Claude的Prompt里
这需要两个操作:
- 获取文档列表 --- 用于自动补全
- 获取单个文档内容 --- 用于注入上下文
定义Resources
静态Resource:列出所有文档
python
@mcp.resource(
"docs://documents",
mime_type="application/json"
)
def list_docs() -> list[str]:
return list(docs.keys())URI是固定的docs://documents,返回文档ID列表。
模板Resource:获取单个文档
python
@mcp.resource(
"docs://documents/{doc_id}",
mime_type="text/plain"
)
def fetch_doc(doc_id: str) -> str:
if doc_id not in docs:
raise ValueError(f"Doc with id {doc_id} not found")
return docs[doc_id]URI包含参数{doc_id},SDK会自动解析并传给函数。
Client端读取Resource
python
import json
from pydantic import AnyUrl
async def read_resource(self, uri: str) -> Any:
result = await self.session().read_resource(AnyUrl(uri))
resource = result.contents[0]
if isinstance(resource, types.TextResourceContents):
if resource.mimeType == "application/json":
return json.loads(resource.text)
return resource.text工作流程:
- 应用代码调用
client.read_resource("docs://documents") - Client发送
ReadResourceRequest给Server - Server执行
list_docs()函数 - 返回
["deposition.md", "report.pdf", ...] - 应用用这个列表填充自动补全UI
七、Prompts:预定义的工作流
Prompts是给用户用的高质量模板。用户触发后,直接发送精心设计的指令给Claude。
为什么需要Prompts?
用户当然可以自己输入"把report.pdf转成markdown格式",但效果可能不理想。作为MCP Server作者,你可以提供一个经过反复测试的优化Prompt,处理各种边缘情况。
这样用户只需要点一个按钮或输入/format report.pdf,就能获得最佳结果。
实现Format命令
python
from mcp.server.fastmcp import base
@mcp.prompt(
name="format",
description="Rewrites the contents of a document in Markdown format."
)
def format_document(
doc_id: str = Field(description="Id of the document to format")
) -> list[base.Message]:
prompt = f"""Your goal is to reformat a document to be written with markdown syntax.
The id of the document you need to reformat is:
<document_id>
{doc_id}
</document_id>
Add headers, bullet points, tables, etc as necessary. Use the 'edit_document' tool to modify the document. After reformatting, return a summary of changes made.
"""
return [base.UserMessage(prompt)]关键设计:
- Prompt清晰说明任务目标
- 用XML标签包裹变量,避免混淆
- 指示Claude使用哪些工具完成任务
- 返回的是消息列表,支持多轮对话(可以包含UserMessage和AssistantMessage)
Client端调用Prompt
python
async def list_prompts(self) -> list[types.Prompt]:
result = await self.session().list_prompts()
return result.prompts
async def get_prompt(self, prompt_name: str, args: dict[str, str]):
result = await self.session().get_prompt(prompt_name, args)
return result.messages用户输入/format plan.md时:
- 应用识别
/format命令 - 调用
client.get_prompt("format", {"doc_id": "plan.md"}) - 获得填充好变量的完整Prompt
- 把Prompt发给Claude API
- Claude自动调用
read_doc_contents和edit_document完成任务
八、三大原语的使用决策
MCP提供了三种机制,分别服务于不同的控制主体:
Tools:模型控制
谁决定? Claude自主决定何时调用
适用场景:
- 给Claude提供计算能力(执行代码、数学运算)
- 让Claude访问实时数据(查询数据库、调用API)
- 赋予Claude操作能力(创建Issue、发送邮件)
示例: 用户问"3的平方根是多少?",Claude自动调用execute_javascript工具计算。
Resources:应用控制
谁决定? 你的应用代码决定何时获取
适用场景:
- UI自动补全(获取候选列表)
- 注入上下文(把文档内容加到Prompt里)
- 预加载数据(应用启动时获取配置)
示例: 用户输入@,应用调用Resource获取文档列表,显示在下拉菜单。
Prompts:用户控制
谁决定? 用户通过按钮、命令触发
适用场景:
- 预定义工作流(一键生成报告、批量处理)
- 优化过的指令(复杂任务的最佳Prompt)
- 快捷操作(斜杠命令、工具栏按钮)
示例: 用户点击"格式化文档"按钮,应用获取format Prompt并发送给Claude。
九、完整流程串联:从提问到响应
现在把所有部分组合起来,看一个完整的交互流程。
场景1:读取文档
用户输入: "report.pdf里写了什么?"
应用调用 client.list_tools() → 获取 [read_doc_contents, edit_document]
应用发送请求到Claude API:
json{ "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "report.pdf里写了什么?"}], "tools": [{...read_doc_contents定义...}, {...edit_document定义...}] }
- Claude返回:
json{ "stop_reason": "tool_use", "content": [{ "type": "tool_use", "name": "read_doc_contents", "input": {"doc_id": "report.pdf"} }] }
应用调用 client.call_tool("read_doc_contents", {"doc_id": "report.pdf"}) → Server返回 "The report details the state of a 20m condenser tower."
应用把工具结果发回Claude:
json{ "messages": [...之前的消息..., { "role": "user", "content": [{ "type": "tool_result", "tool_use_id": "...", "content": "The report details..." }] }] }
- Claude返回最终答案: "报告详细说明了一个20米冷凝塔的状态。"
场景2:使用Resource注入上下文
用户输入: @report.pdf "总结这个文档"
用户输入@后,应用调用 client.read_resource("docs://documents") → 获取 ["deposition.md", "report.pdf", "financials.docx", ...]
显示自动补全,用户选择 report.pdf
应用调用 client.read_resource("docs://documents/report.pdf") → 获取文档内容
应用构造Prompt并发送给Claude: { "messages": [{ "role": "user", "content": "这是report.pdf的内容:\n\nThe report details...\n\n请总结这个文档。" }] }
Claude直接根据提供的内容生成总结,无需调用工具
场景3:触发Prompt工作流
用户输入: /format plan.md
应用识别/命令,调用 client.list_prompts() → 获取 [{name: "format", description: "Rewrites..."}]
用户选择format命令,输入doc_id为plan.md
应用调用 client.get_prompt("format", {"doc_id": "plan.md"}) → 获取填充好的Prompt消息
应用把Prompt作为初始消息发送给Claude:
json{ "messages": [{ "role": "user", "content": "Your goal is to reformat...<document_id>plan.md</document_id>..." }], "tools": [...所有可用工具...] }
- Claude自动执行:
- 调用 read_doc_contents 获取plan.md内容
- 分析内容,决定如何格式化
- 调用 edit_document 多次,添加markdown语法
- 返回格式化完成的总结
十、关键技术细节
1. 错误处理
Tools和Resources中抛出的异常会被自动捕获并返回给Client:
json
@mcp.tool(name="read_doc")
def read_document(doc_id: str):
if doc_id not in docs:
raise ValueError(f"Doc with id {doc_id} not found")
return docs[doc_id]Claude会收到错误信息,并可能重试或换个策略。
2. 类型安全
使用Pydantic的Field可以提供运行时校验:
json
from pydantic import Field, validator
@mcp.tool(name="edit_doc")
def edit_document(
doc_id: str = Field(description="...", min_length=1),
old_str: str = Field(description="...", min_length=1),
new_str: str = Field(description="...")
):
# min_length会自动校验,不满足条件会拒绝请求
...3. 异步支持
所有Client方法都是异步的,需要在async函数中调用:
json
async def main():
async with MCPClient() as client:
tools = await client.list_tools()
result = await client.call_tool("read_doc", {"doc_id": "report.pdf"})4. 资源清理
使用async with确保Session正确关闭:
json
class MCPClient:
async def __aenter__(self):
# 创建并启动Session
return self
async def __aexit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
# 关闭Session,释放资源
pass十一、常见问题
Q1: MCP和直接调用API有什么区别?
直接调用API: 你需要自己写工具定义、处理认证、管理请求。
使用MCP: 工具定义已经写好,认证由Server处理,你只需要连接并使用。
类比: 就像你不会自己实现HTTP协议去访问网站,而是用浏览器或requests库。MCP就是外部服务集成的"标准库"。
Q2: MCP Server谁来写?
通常由服务提供商官方 或社区开发者编写。比如AWS可能会发布官方MCP Server,包含所有AWS服务的工具。也有很多开源MCP Server可以直接用。
Q3: 一个应用可以连接多个MCP Server吗?
可以。你的Client可以同时连接GitHub Server、Notion Server、AWS Server等,Claude可以跨Server调用工具。
Q4: MCP支持哪些编程语言?
官方SDK支持Python和TypeScript。其他语言可以实现MCP协议(基于JSON-RPC 2.0)。
Q5: 性能如何?
MCP基于本地进程通信(stdio)或网络协议,延迟很低。工具调用的耗时主要取决于实际API(比如GitHub API的响应时间)。
十二、总结:MCP的价值
MCP的核心价值在于标准化和复用:
- 降低集成成本 --- 不用为每个服务从零开始写工具
- 提高工具质量 --- 使用经过测试的成熟实现
- 简化维护负担 --- API变更由Server作者处理
- 加速开发速度 --- 专注业务逻辑,而非集成细节
如果你要构建AI应用,并且需要让Claude访问外部服务,MCP是目前最优雅的解决方案。它不会限制你的灵活性,反而通过标准化让你的应用更易扩展。
相关资源:
- 社区Server列表:github.com/anthropics/...