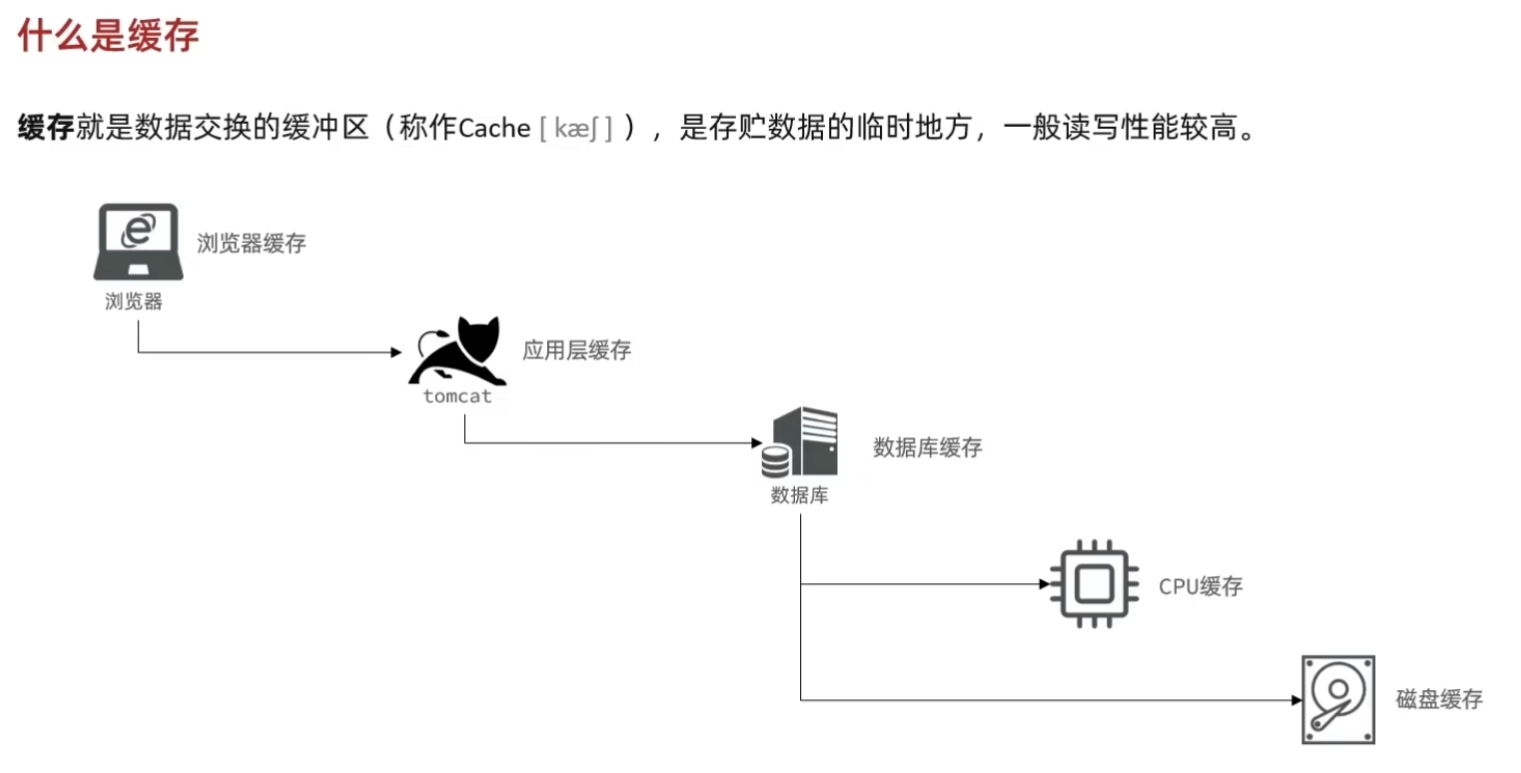
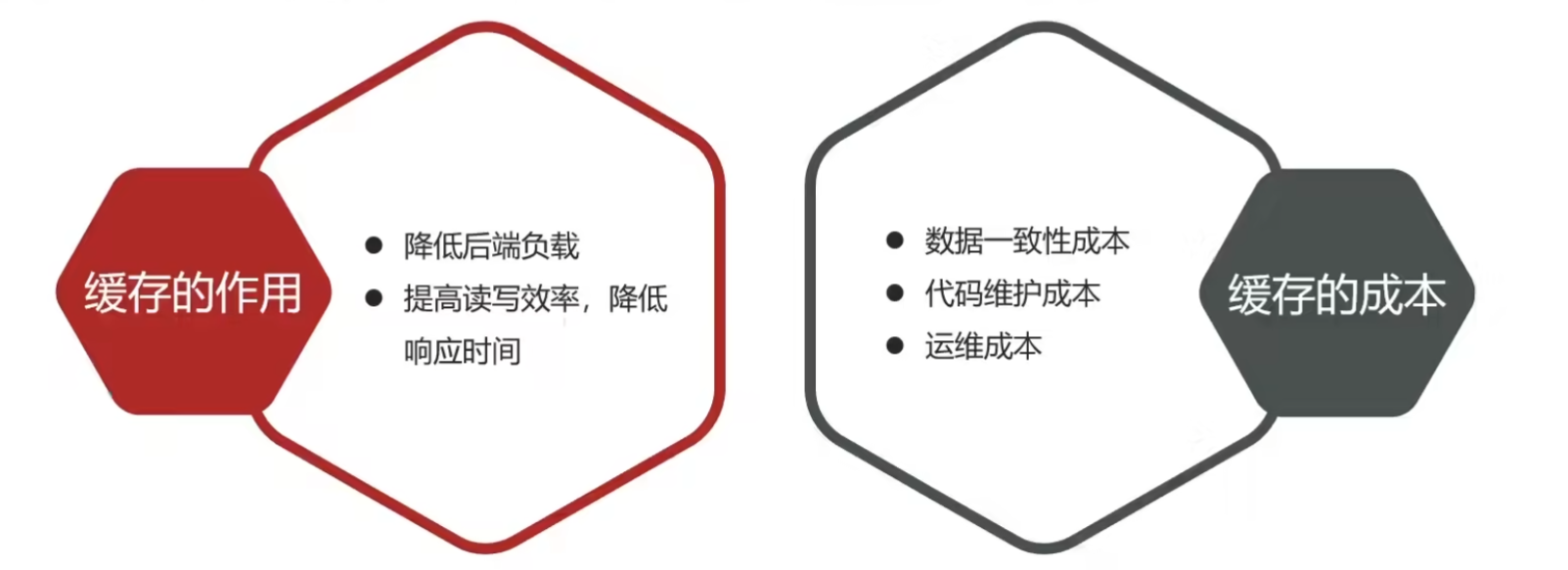
1.缓存介绍
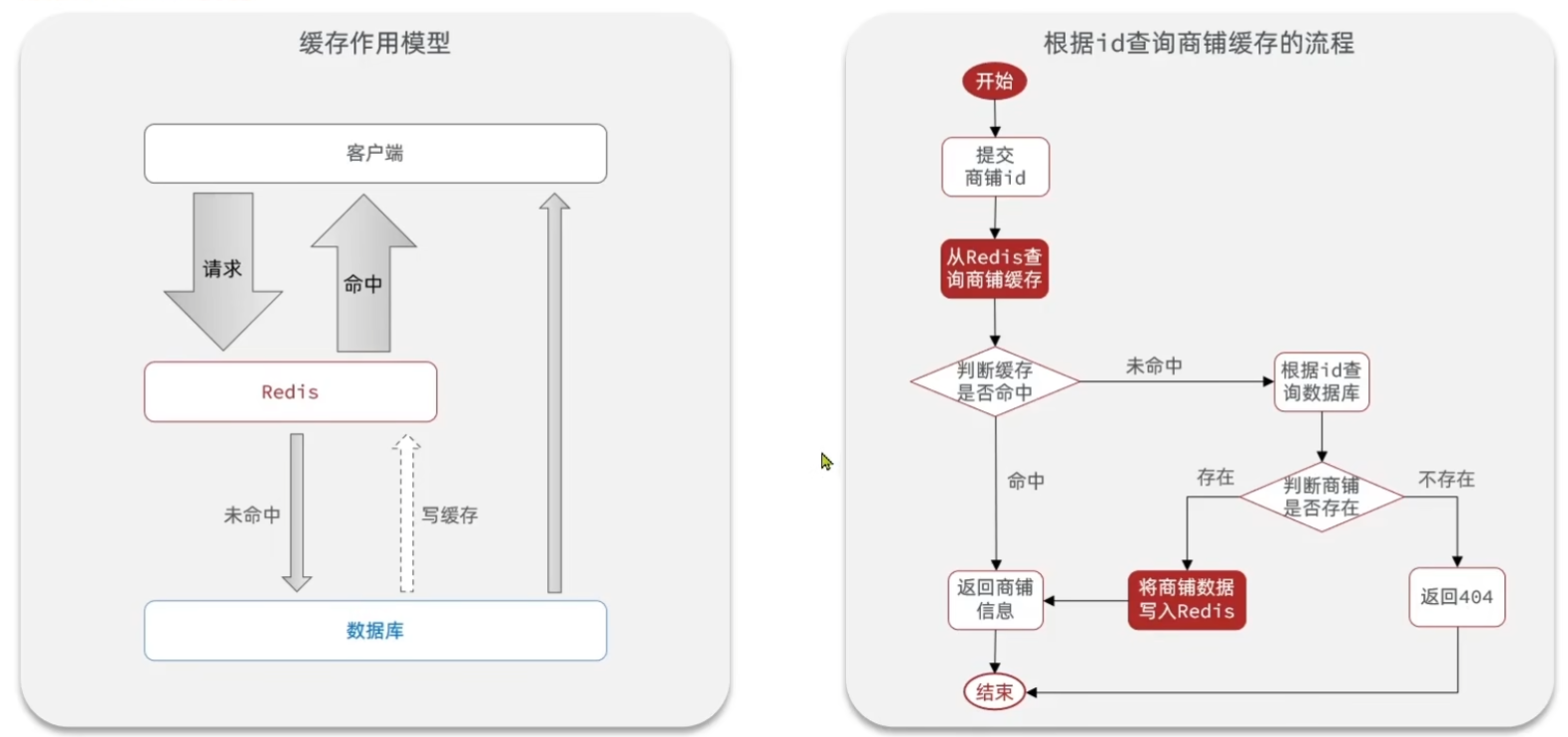
2.添加redis缓存
执行流程:
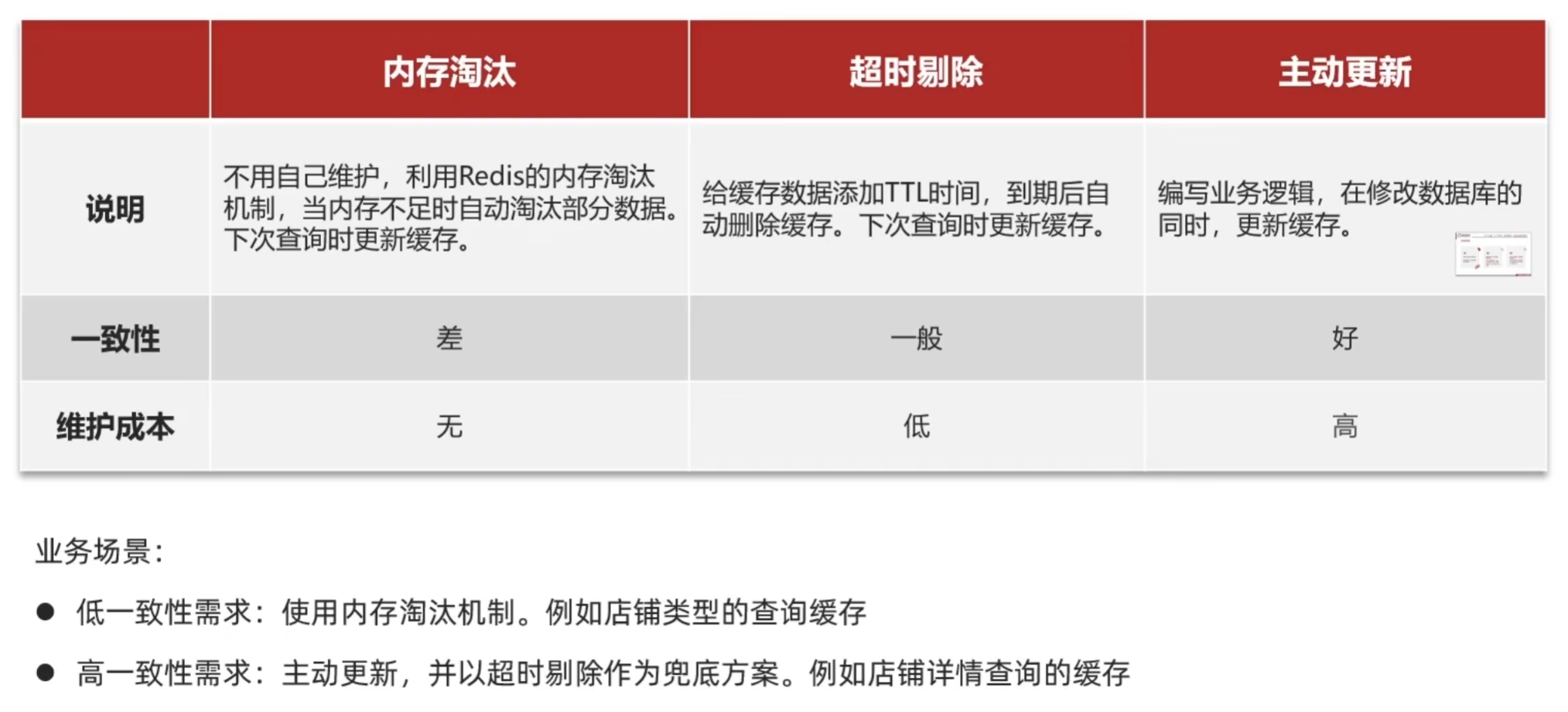
3. 缓存更新策略

对于先操作缓存还是先操作数据库:
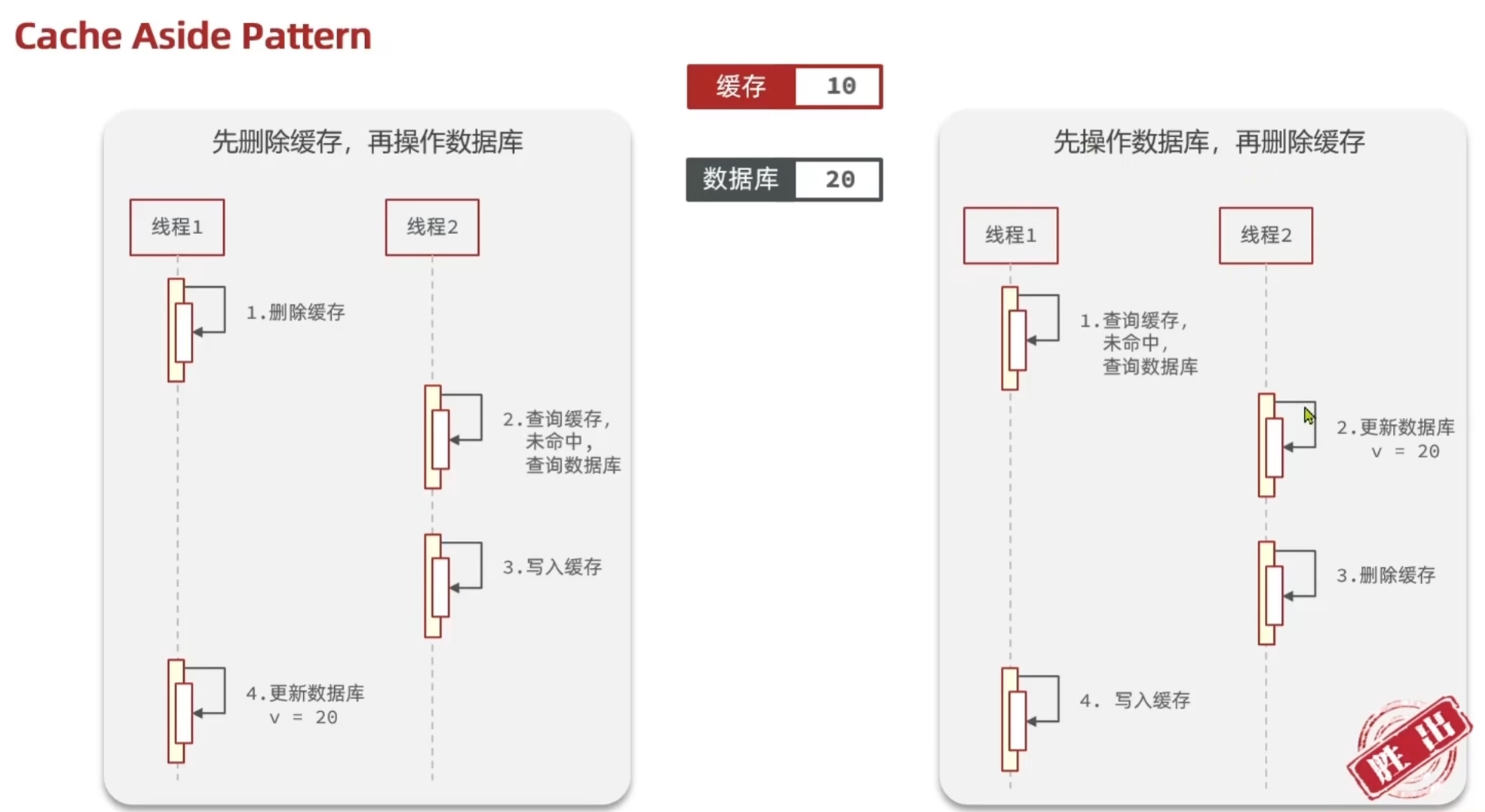
虽然两种方案都存在线程安全问题,但右边发生的概率比左边发生的概率小得多

4.缓存穿透
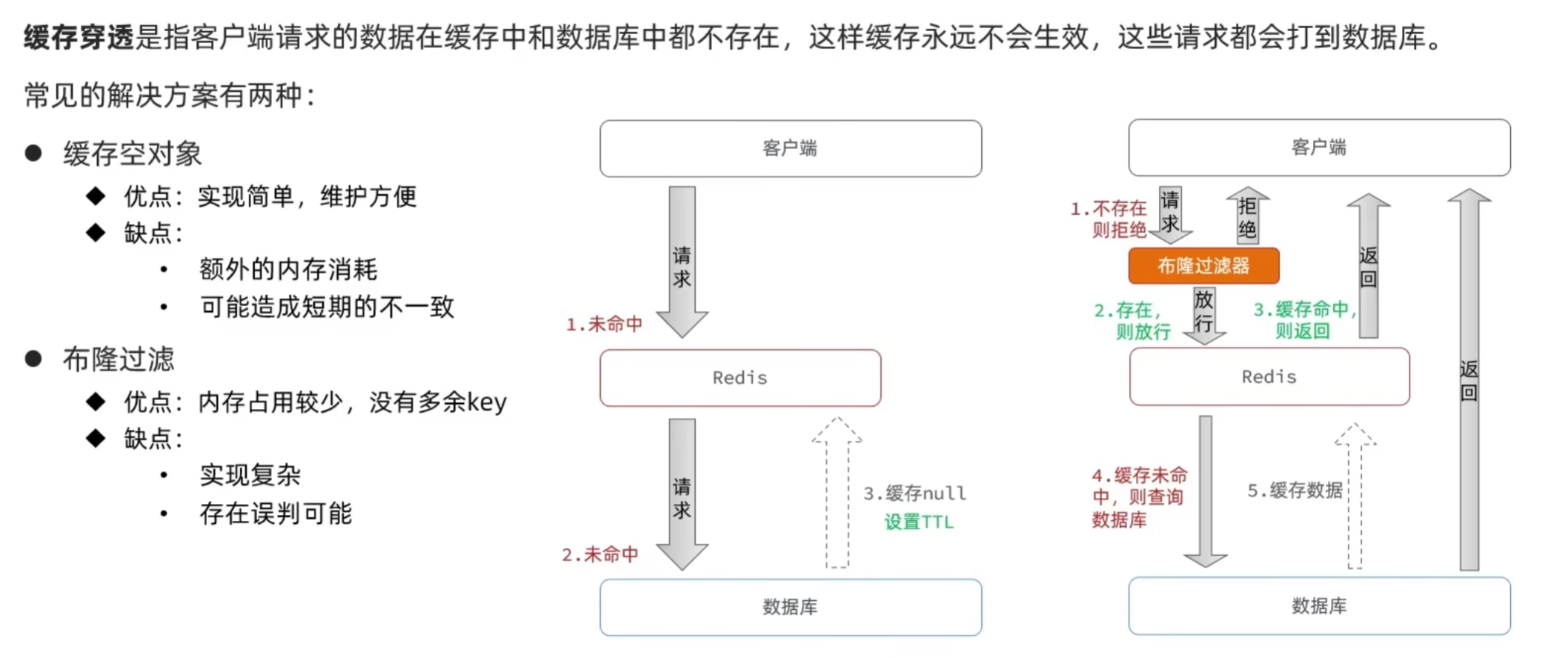
业务层防缓存穿透的查询方法:
java
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Override
public Result queryById(Long id) {
//缓存穿透
Shop shop = queryWithPassThrough(id);
// 7.返回
return Result.ok(shop);
}
public Shop queryWithPassThrough(Long id) {
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺缓存
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);
}
//判断命中的是否是空字符串 ""
if (shopJson != null) {//shopJson不为空就只能为""
return null;
}
// 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库 即shopJson == null,说明redis中的缓存过期
Shop shop = getById(id);
// 5.数据库不存在,返回错误
if (shop == null) {
//将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return null;
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 7.返回
return shop;
}
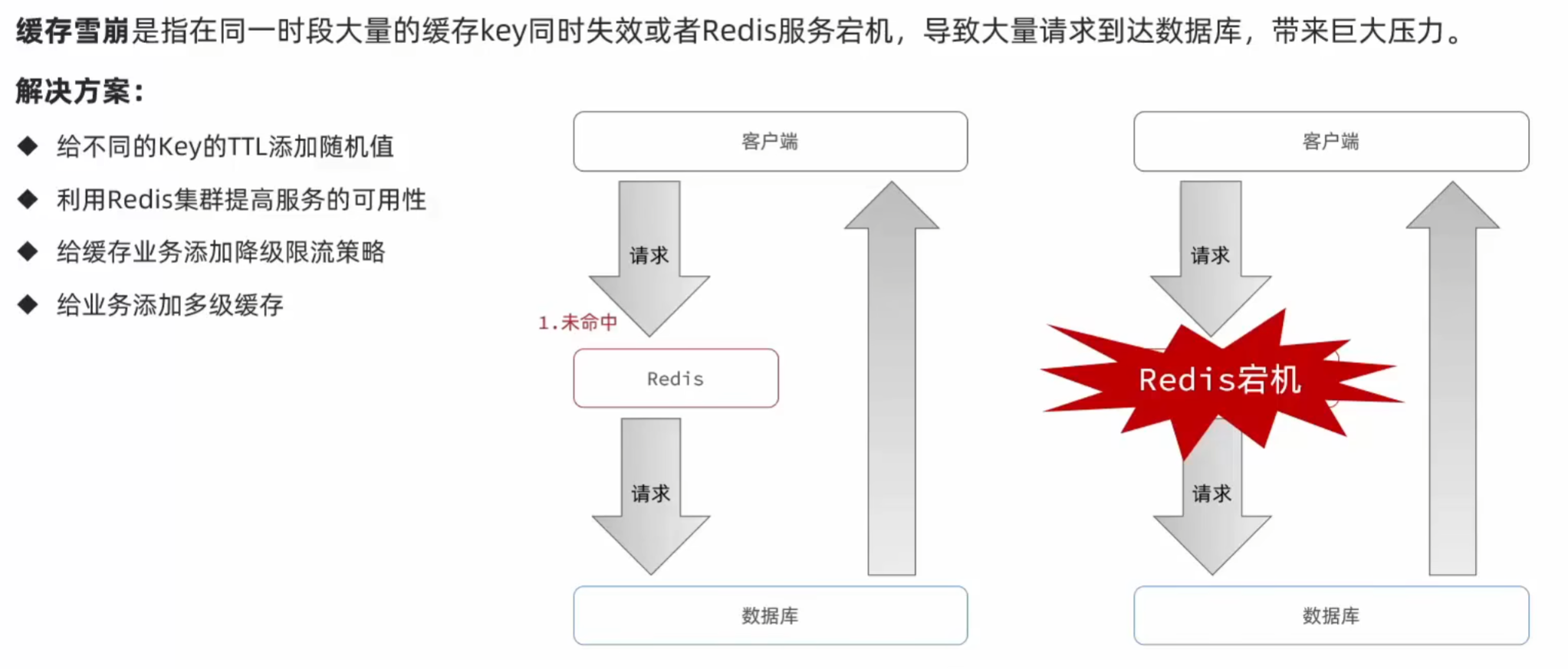
}5. 缓存雪崩
6.缓存击穿
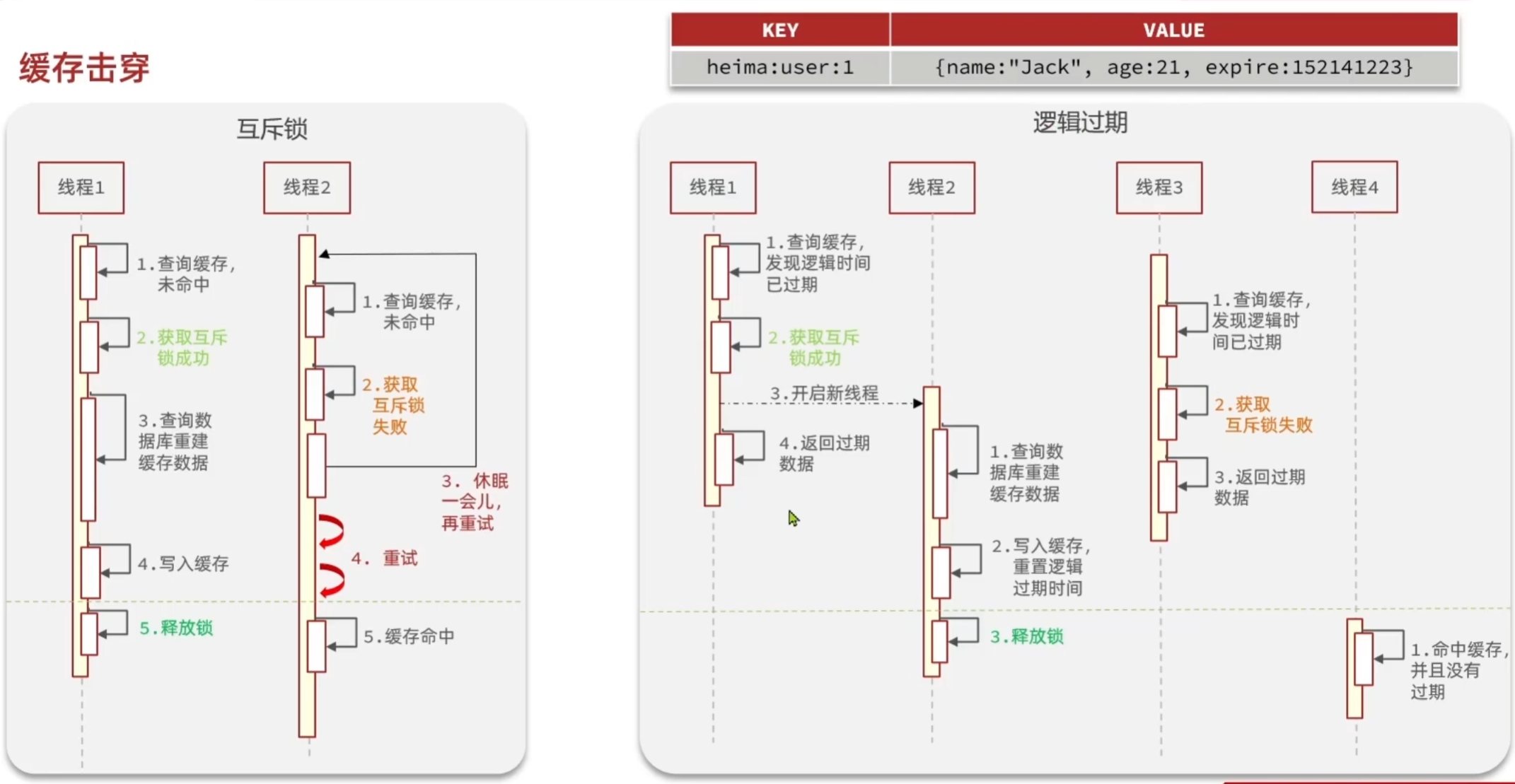
- 互斥锁:当请求查询缓存且缓存未命中时,线程获取互斥锁,只有获取锁的线程去查询数据库并将数据写入缓存,其他线程需等待,待缓存有数据后再读取。
- 逻辑过期:给缓存数据设置逻辑过期时间,当请求发现缓存数据逻辑过期时,启动一个新线程去查询数据库更新缓存,当前线程继续返回旧的缓存数据。
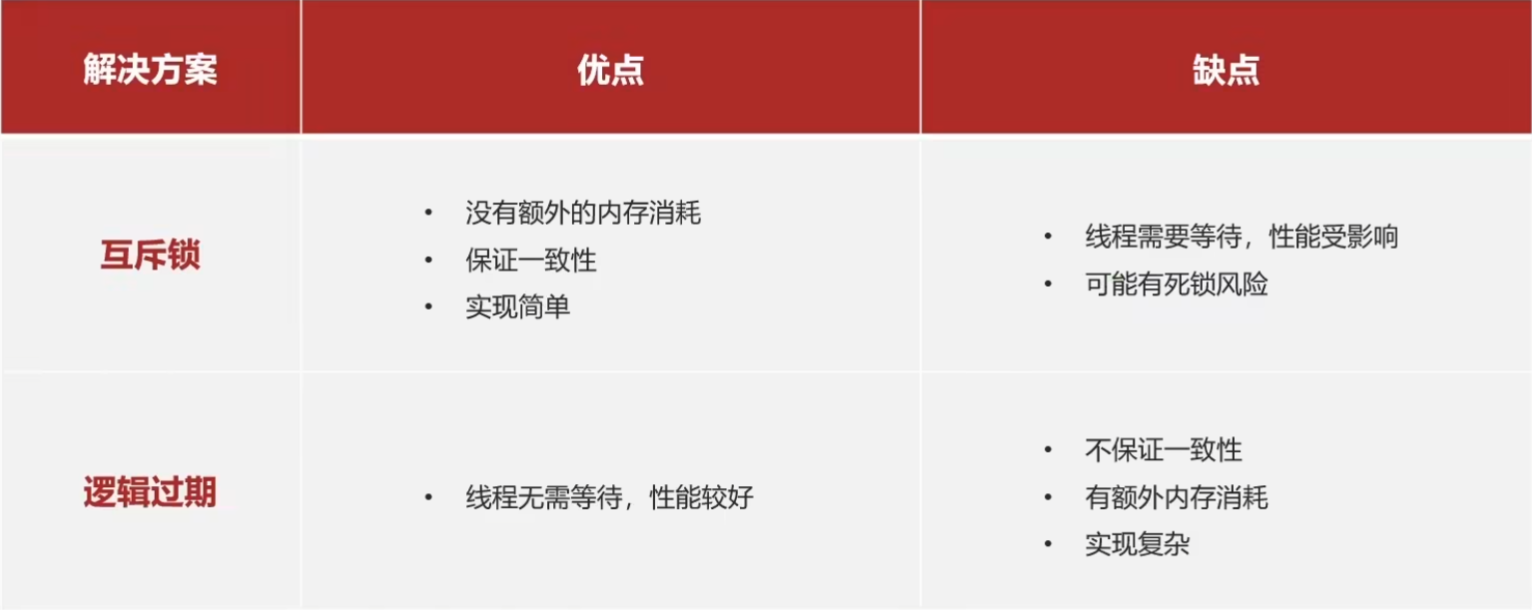
6.1 基于互斥锁方式解决缓存击穿问题
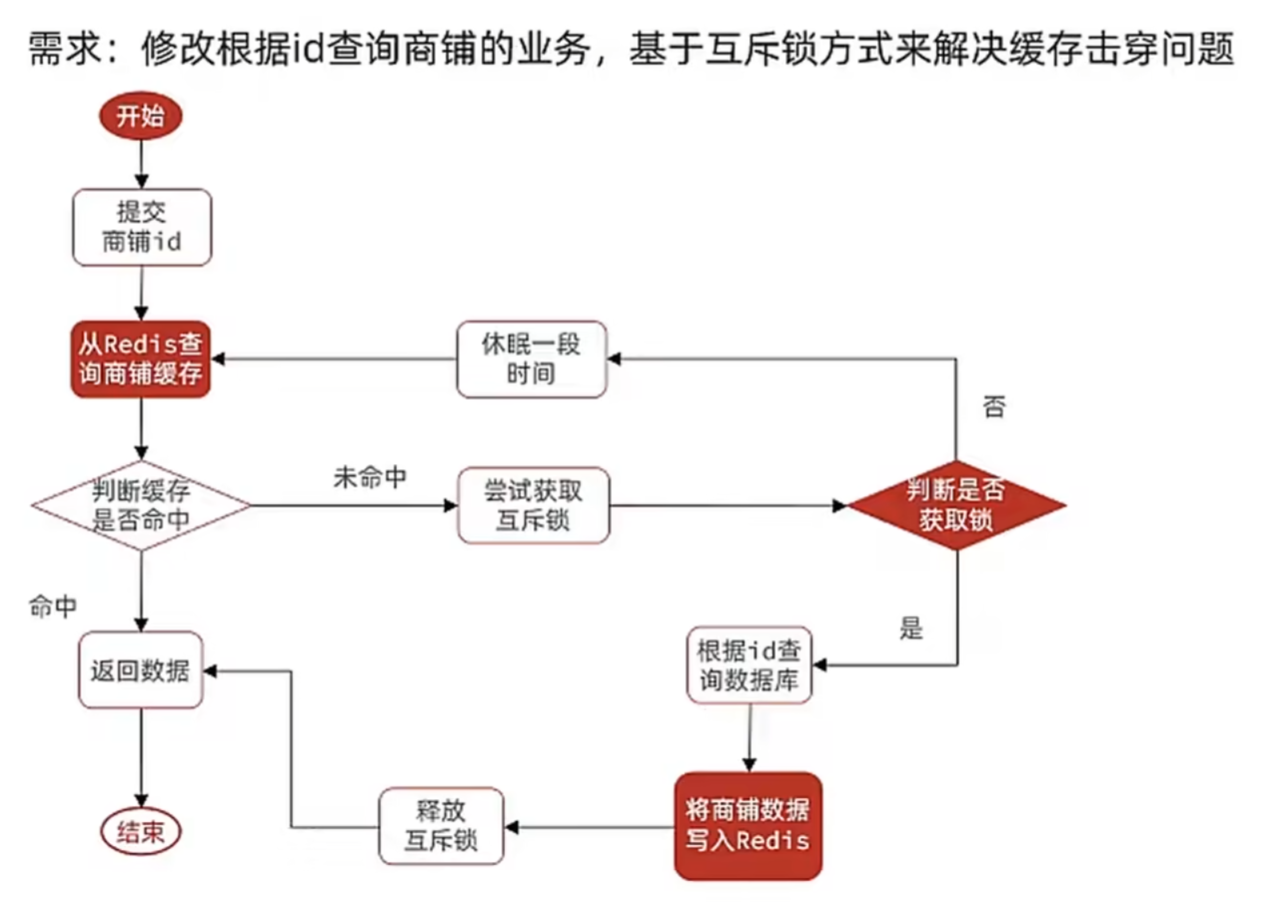
业务层关于根据id查询店铺的代码:
java
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Override
public Result queryById(Long id) {
//互斥锁解决缓存击穿
Shop shop = queryWithMutex(id);
if (shop == null) {
return Result.fail("店铺不存在");
}
// 7.返回
return Result.ok(shop);
}
public Shop queryWithMutex(Long id) {
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺缓存
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
return JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, Shop.class);
}
//判断命中的是否是空字符串""(在数据库中查询依旧不存在的id,我们存入redis的值为"")
if (shopJson != null) {
return null;
}
//redis中没有对应的缓存,则查询数据库
// 4.实现缓存重建
// 4.1.获取互斥锁
String lockKey = "lock:shop:" + id;// 锁的 key 与店铺 id 绑定(lock:shop:1),不同店铺的缓存重建互不干扰,减少锁竞争。
try{
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
// 4.2.判断是否获取成功
if (!isLock) {
// 4.3.获取失败,则休眠并重试
Thread.sleep(50);
return queryWithMutex(id);
}
// 4.4.获取锁成功,根据id查询数据库
Shop shop = getById(id);
//模拟重建的延时
Thread.sleep(200);
// 5.数据库不存在,返回错误
if (shop == null) {
//将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return null;
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(shop), RedisConstants.CACHE_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
// 7.返回
return shop;
} catch (InterruptedException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 8.释放锁
unLock(lockKey);
}
}
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}实现原理 :通过 Redis 的**setIfAbsent**命令实现分布式锁,保证同一时间只有一个线程能执行缓存重建(从数据库查询数据并写入缓存),避免大量请求同时穿透到数据库。
tryLock方法的实现依赖 Redis 的setIfAbsent命令(原子操作 ),setIfAbsent是 Redis 的原子命令,确保多个线程同时尝试获取锁时,只有一个线程能成功。
java
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
// setIfAbsent:若key不存在则设置值,返回true;若已存在则不操作,返回false
// 同时设置锁的过期时间(10秒),避免锁未释放导致死锁
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}6.2 基于逻辑过期方式解决缓存击穿问题
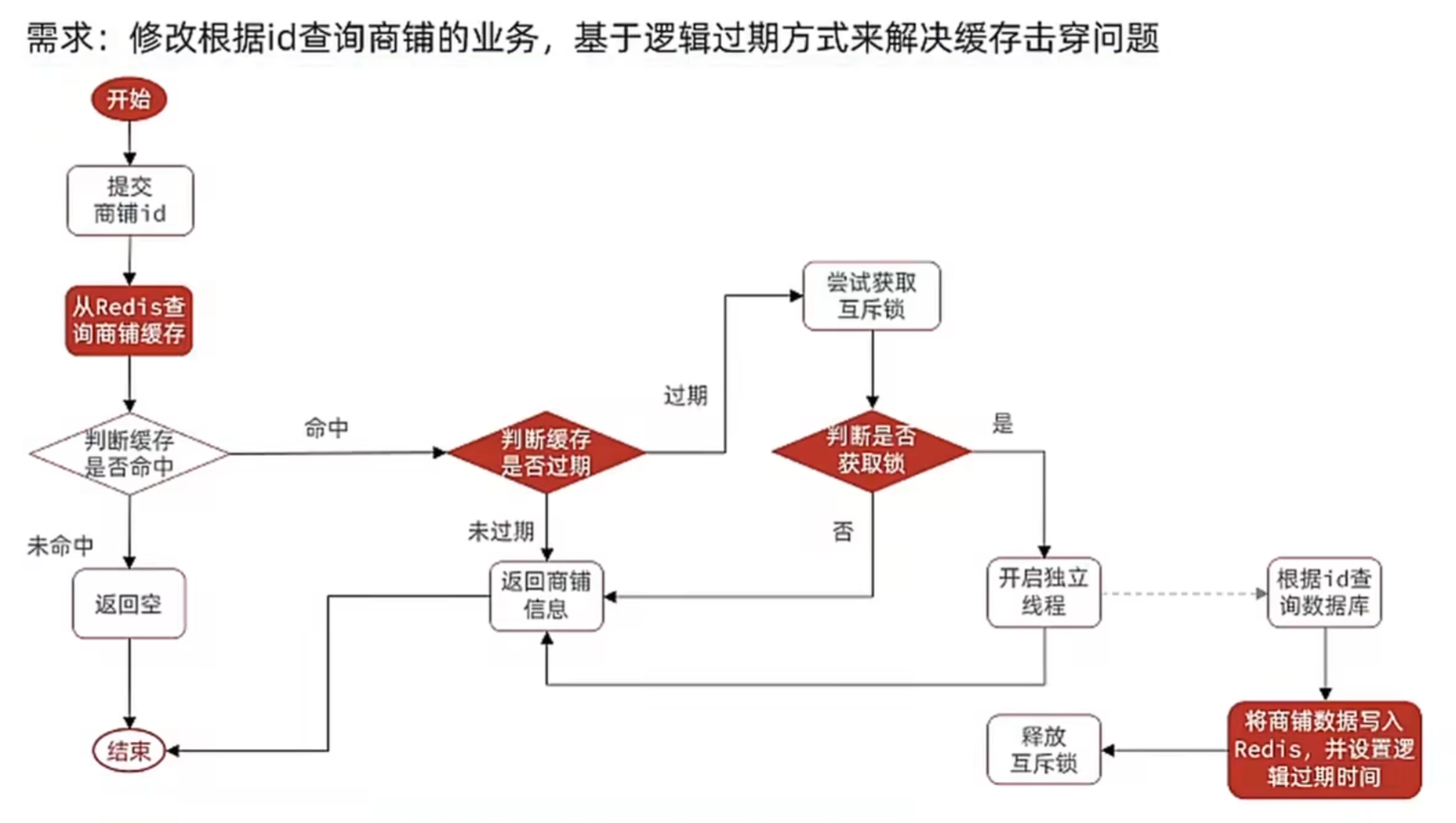
业务层具体实现:
java
@Service
public class ShopServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ShopMapper, Shop> implements IShopService {
@Resource
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Override
public Result queryById(Long id) {
//逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
Shop shop = queryWithLogicalExpire(id);
// 7.返回
return Result.ok(shop);
}
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public Shop queryWithLogicalExpire(Long id) {
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺缓存
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
// 3.不存在,直接返回null
return null;
}
//4.命中,把json反序列化为对象
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
Shop shop = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), Shop.class);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
// 5.判断是否过期
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())) {
//未过期,直接返回
return shop;
}
//已过期,需要缓存重建
//6.重建缓存
//获取互斥锁
String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
//判断获取锁是否成功
if (isLock) {
//获取锁成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {
//重建缓存
try {
this.saveShopToRedis(id, 3600L);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放锁
unLock(lockKey);
}
});
}
//返回过期的商铺信息
return shop;
}
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
private void saveShopToRedis(Long id, Long expireSeconds) throws InterruptedException {
// 1.查询店铺数据
Shop shop = getById(id);
Thread.sleep(200);
// 2.封装逻辑过期时间
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(shop);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(expireSeconds));
// 3.写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}
}RedisData:
java
@Data
public class RedisData {
private LocalDateTime expireTime;// 逻辑过期时间
private Object data;// 实际数据(Shop对象)
}**核心思路:**不依赖 Redis 的原生过期时间,而是在缓存数据中嵌入一个 "逻辑过期时间",当检测到数据过期时,先返回旧数据,同时异步重建缓存,避免大量请求阻塞或穿透到数据库。
原理:
- 缓存不删除:热点数据的缓存始终存在(Redis 不自动删除),避免了 "缓存突然消失导致大量请求穿透" 的问题。
- 过期仍可用:数据过期后,先返回旧数据保证服务可用性,用户无感知。
- 异步重建:只有一个线程(通过互斥锁控制)在后台异步重建缓存,避免数据库压力。
- 最终一致性:重建完成后,新数据会覆盖旧缓存,后续请求会获取到最新数据,保证数据最终一致。
逻辑过期适合容忍短期数据不一致的热点数据(如热门商品、高频访问的店铺信息)。其优势是响应速度快(不阻塞请求),缺点是需要额外存储过期时间,且数据存在短暂不一致窗口。
7.封装Redis缓存工具类
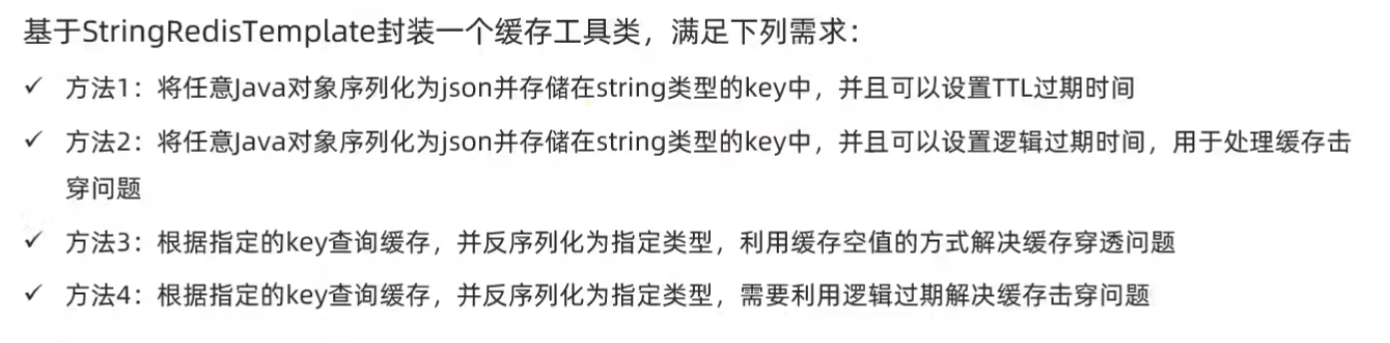
java
public class CacheClient {
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public CacheClient(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
// 写入缓存
public void set(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(value), time, unit);
}
//逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
public void setWithLogicalExpire(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit){
// 封装逻辑过期时间
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(value);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(unit.toSeconds(time)));
// 写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}
// 缓存穿透工具类
public <R, ID> R queryWithPassThrough(
String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
String key = keyPrefix + id;
// 1.从redis查询缓存
String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)) {
// 3.存在,直接返回
return JSONUtil.toBean(json, type);
}
//判断命中的是否是空字符串 ""
if (json != null) {
return null;
}
// 4.不存在,根据id查询数据库 即shopJson == null,说明redis中的缓存过期
R r = dbFallback.apply(id);
// 5.数据库不存在,返回错误
if (r == null) {
//将空值写入redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", RedisConstants.CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return null;
}
// 6.存在,写入redis
this.set(key, r, time, unit);
// 7.返回
return r;
}
//逻辑过期解决缓存击穿
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public <R,ID> R queryWithLogicalExpire(
String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
String key = keyPrefix + id;
// 1.从redis查询商铺缓存
String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
// 2.判断是否存在
if (StrUtil.isBlank(json)) {
// 3.不存在,直接返回null
return null;
}
//4.命中,把json反序列化为对象
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(json, RedisData.class);
R r = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), type);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
// 5.判断是否过期
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())) {
//未过期,直接返回
return r;
}
//已过期,需要缓存重建
//6.重建缓存
//获取互斥锁
String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
//判断获取锁是否成功
if (isLock) {
//获取锁成功,开启独立线程,实现缓存重建
CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {
//重建缓存
try {
//查询数据库
R rr = dbFallback.apply(id);
//写入redis
this.setWithLogicalExpire(key, rr, time, unit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放锁
unLock(lockKey);
}
});
}
//返回过期的商铺信息
return r;
}
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
private void unLock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}