
一、问题分析
1. 问题描述
给定无向连通图中一个节点的引用,要求返回该图的深拷贝 (克隆)。图中每个节点包含值val和邻居列表neighbors,需保证:
- 新图与原图结构完全一致,但所有节点都是新创建的(内存独立);
- 无向图的双向引用需正确复制(如节点 A 的邻居包含 B,则节点 B 的邻居也需包含 A 的克隆节点);
- 避免重复创建节点(防止循环引用导致死循环或重复节点)。
2. 核心难点
- 循环引用处理:无向图中节点间的双向引用(如 1↔2),直接递归 / 遍历会重复访问节点;
- 深拷贝保证:必须为每个节点创建新实例,且邻居列表指向克隆节点而非原节点;
- 连通性保证:原图是连通的,需遍历所有可达节点并完成克隆。
二、题目解析
1. 输入输出定义
- 输入:无向连通图的起始节点(值为 1);
- 输出:克隆图的起始节点(新内存地址,结构与原图一致)。
2. 示例理解
以邻接列表[[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]为例:
- 节点 1 的邻居是 2、4;
- 节点 2 的邻居是 1、3;
- 节点 3 的邻居是 2、4;
- 节点 4 的邻居是 1、3;克隆后需生成新的 4 个节点,邻居关系与原图完全一致。
三、算法分析
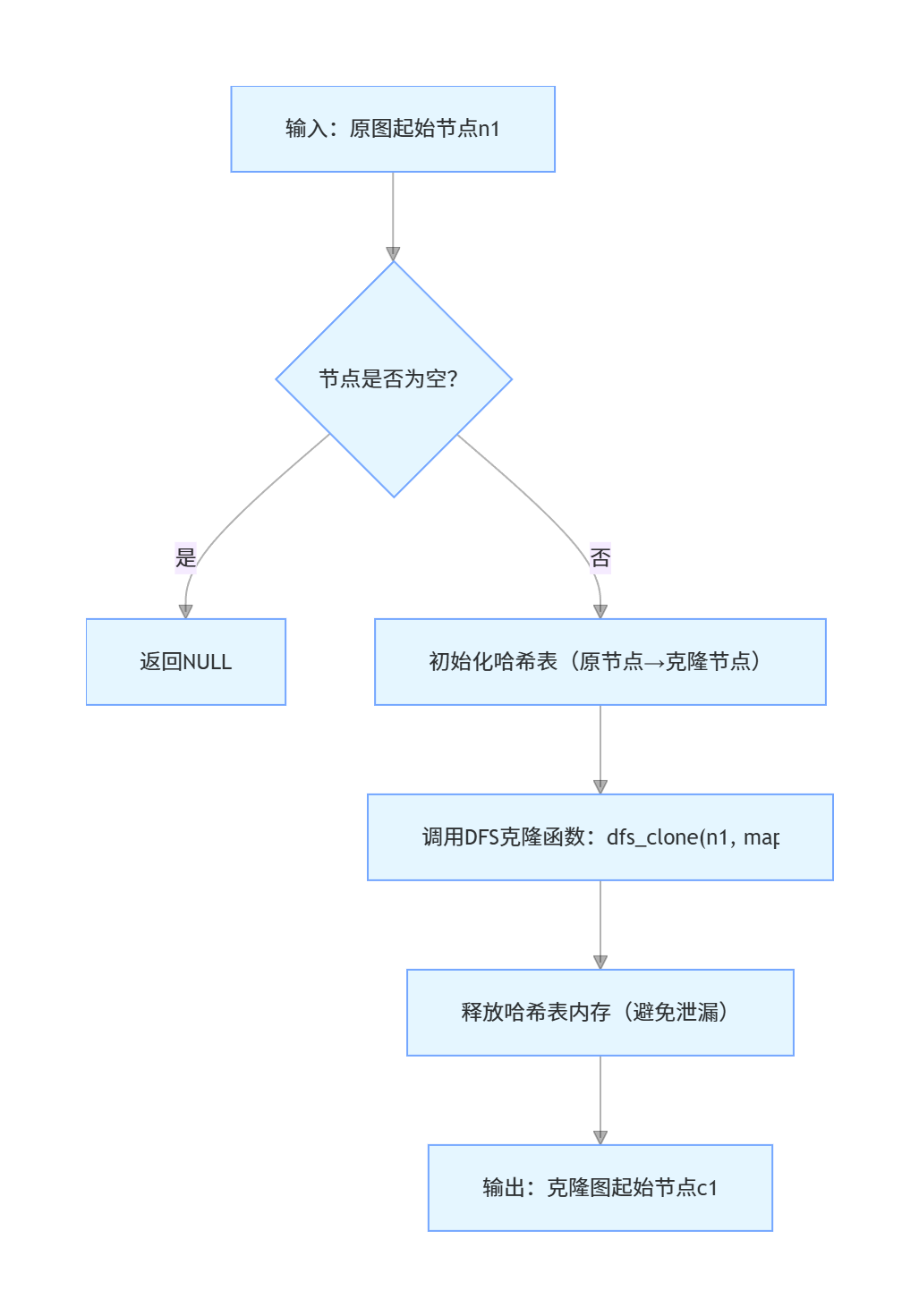
采用深度优先搜索(DFS)+ 哈希表(映射表) 实现,核心逻辑:
- 哈希表记录映射关系:键为原节点指针,值为克隆节点指针,避免重复创建;
- DFS 遍历 + 克隆 :
- 若当前节点已克隆(哈希表中存在),直接返回克隆节点;
- 若未克隆,创建新节点,存入哈希表;
- 递归克隆当前节点的所有邻居,添加到新节点的邻居列表;
- 无向图处理:递归过程中自动处理双向引用(如克隆 1 的邻居 2 时,会同步克隆 2 的邻居 1)。
objectivec
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 图节点定义
struct Node {
int val;
int numNeighbors;
struct Node** neighbors;
};
// 哈希表节点定义(用于存储原节点→克隆节点的映射)
typedef struct HashNode {
struct Node* key; // 原节点指针
struct Node* value; // 克隆节点指针
struct HashNode* next; // 链表下一个节点
} HashNode;
// 哈希表定义
#define HASH_SIZE 1009 // 哈希表大小(质数,减少冲突)
typedef struct {
HashNode* table[HASH_SIZE];
} HashMap;
// 哈希函数:将指针转换为整数,取模
static int hash_func(struct Node* key) {
return (unsigned long)key % HASH_SIZE;
}
// 初始化哈希表
HashMap* hash_map_init() {
HashMap* map = (HashMap*)malloc(sizeof(HashMap));
memset(map->table, 0, sizeof(map->table));
return map;
}
// 哈希表存入键值对
void hash_map_put(HashMap* map, struct Node* key, struct Node* value) {
int idx = hash_func(key);
HashNode* node = (HashNode*)malloc(sizeof(HashNode));
node->key = key;
node->value = value;
node->next = map->table[idx]; // 头插法
map->table[idx] = node;
}
// 哈希表查询键对应的值
struct Node* hash_map_get(HashMap* map, struct Node* key) {
int idx = hash_func(key);
HashNode* cur = map->table[idx];
while (cur) {
if (cur->key == key) {
return cur->value;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// 释放哈希表内存
void hash_map_free(HashMap* map) {
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_SIZE; i++) {
HashNode* cur = map->table[i];
while (cur) {
HashNode* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
}
}
free(map);
}
// 创建新节点(初始化值和邻居数组)
struct Node* create_node(int val) {
struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->val = val;
node->numNeighbors = 0;
node->neighbors = NULL;
return node;
}
// 递归克隆节点(核心DFS逻辑)
struct Node* dfs_clone(struct Node* node, HashMap* map) {
// 边界条件:节点为空
if (node == NULL) return NULL;
// 已克隆过,直接返回
struct Node* cloned = hash_map_get(map, node);
if (cloned != NULL) return cloned;
// 创建当前节点的克隆
cloned = create_node(node->val);
hash_map_put(map, node, cloned); // 先存入映射,避免循环引用
// 克隆所有邻居
cloned->numNeighbors = node->numNeighbors;
if (node->numNeighbors > 0) {
cloned->neighbors = (struct Node**)malloc(sizeof(struct Node*) * node->numNeighbors);
for (int i = 0; i < node->numNeighbors; i++) {
// 递归克隆邻居节点
cloned->neighbors[i] = dfs_clone(node->neighbors[i], map);
}
}
return cloned;
}
// 克隆图主函数
struct Node* cloneGraph(struct Node* node) {
// 初始化哈希表
HashMap* map = hash_map_init();
// DFS克隆
struct Node* res = dfs_clone(node, map);
// 释放哈希表(避免内存泄漏)
hash_map_free(map);
return res;
}
// 辅助函数:释放图的内存(测试用)
void free_graph(struct Node* node, HashMap* visited) {
if (node == NULL) return;
// 避免重复释放
if (hash_map_get(visited, node) != NULL) return;
hash_map_put(visited, node, node);
// 释放邻居数组
if (node->neighbors != NULL) {
for (int i = 0; i < node->numNeighbors; i++) {
free_graph(node->neighbors[i], visited);
}
free(node->neighbors);
}
free(node);
}
int main() {
// 构建原图:1→2、4;2→1、3;3→2、4;4→1、3
struct Node* n1 = create_node(1);
struct Node* n2 = create_node(2);
struct Node* n3 = create_node(3);
struct Node* n4 = create_node(4);
n1->numNeighbors = 2;
n1->neighbors = (struct Node**)malloc(sizeof(struct Node*) * 2);
n1->neighbors[0] = n2;
n1->neighbors[1] = n4;
n2->numNeighbors = 2;
n2->neighbors = (struct Node**)malloc(sizeof(struct Node*) * 2);
n2->neighbors[0] = n1;
n2->neighbors[1] = n3;
n3->numNeighbors = 2;
n3->neighbors = (struct Node**)malloc(sizeof(struct Node*) * 2);
n3->neighbors[0] = n2;
n3->neighbors[1] = n4;
n4->numNeighbors = 2;
n4->neighbors = (struct Node**)malloc(sizeof(struct Node*) * 2);
n4->neighbors[0] = n1;
n4->neighbors[1] = n3;
// 克隆图
struct Node* cloned = cloneGraph(n1);
// 验证克隆结果(输出克隆节点1的邻居值)
printf("克隆节点1的邻居值:");
for (int i = 0; i < cloned->numNeighbors; i++) {
printf("%d ", cloned->neighbors[i]->val);
}
printf("\n"); // 应输出:2 4
// 释放原图和克隆图内存
HashMap* visited1 = hash_map_init();
free_graph(n1, visited1);
hash_map_free(visited1);
HashMap* visited2 = hash_map_init();
free_graph(cloned, visited2);
hash_map_free(visited2);
return 0;
}四、复杂度分析
1. 时间复杂度:O (N + E)
- N:图中节点数量;
- E:图中边的数量;
- 每个节点仅被克隆一次(哈希表去重),每条边仅被处理两次(无向图双向引用),总操作数为 O (N + E)。
2. 空间复杂度:O (N)
- 哈希表存储 N 个节点的映射,空间 O (N);
- DFS 递归栈深度最坏为 O (N)(如链式图);
- 总空间复杂度为 O (N)。